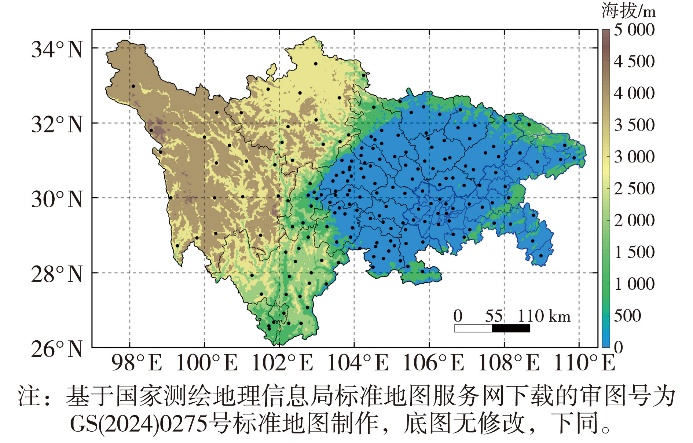
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 355-365.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0355
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis on differences of characteristics and atmospheric circulation causes of meteorological drought during summer in Sichuan-Chongqing region
HE Huigen1( ), ZHANG Chi1(
), ZHANG Chi1( ), CHENG Qingyan2, LI Yonghua1, GAN Weiwei3, JIN Yan4
), CHENG Qingyan2, LI Yonghua1, GAN Weiwei3, JIN Yan4
- 1. CMA Key Open Laboratory of Transforming Climate Resources to Economy, Chongqing Climate Center, Chongqing 401147, China
2. Chengdu Meteorological Bureau, Chengdu 611133, China
3. Sichuan Climate Center, Chengdu 610072, China
4. Yunnan Climate Center, Kunming 650034, China
-
Received:2024-07-02Revised:2024-10-14Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
川渝地区夏季气象干旱差异及大气环流成因分析
何慧根1( ), 张驰1(
), 张驰1( ), 成青燕2, 李永华1, 甘薇薇3, 金燕4
), 成青燕2, 李永华1, 甘薇薇3, 金燕4
- 1.中国气象局气候资源经济转化重点开放实验室,重庆市气候中心,重庆 401147
2.成都市气象局,四川 成都 611133
3.四川省气候中心,四川 成都 610072
4.云南省气候中心,云南 昆明 650034
-
通讯作者:张驰 -
作者简介:何慧根(1979—),男,云南大理人,正高级工程师,主要从事气候预测和气候诊断研究。E-mail: hhg0258@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2022J031);中国气象局复盘总结专项(FPZJ2024-110);中国气象局气象能力提升联合研究专项(22NLTSZ005);及高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室科技发展基金项目(2018-青年-07)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HE Huigen, ZHANG Chi, CHENG Qingyan, LI Yonghua, GAN Weiwei, JIN Yan. Analysis on differences of characteristics and atmospheric circulation causes of meteorological drought during summer in Sichuan-Chongqing region[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 355-365.
何慧根, 张驰, 成青燕, 李永华, 甘薇薇, 金燕. 川渝地区夏季气象干旱差异及大气环流成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 355-365.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0355
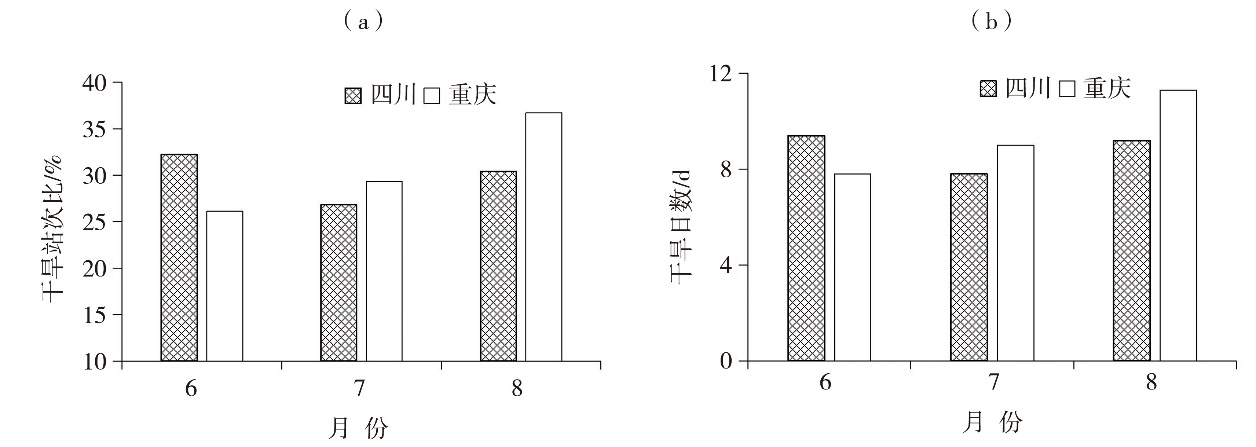
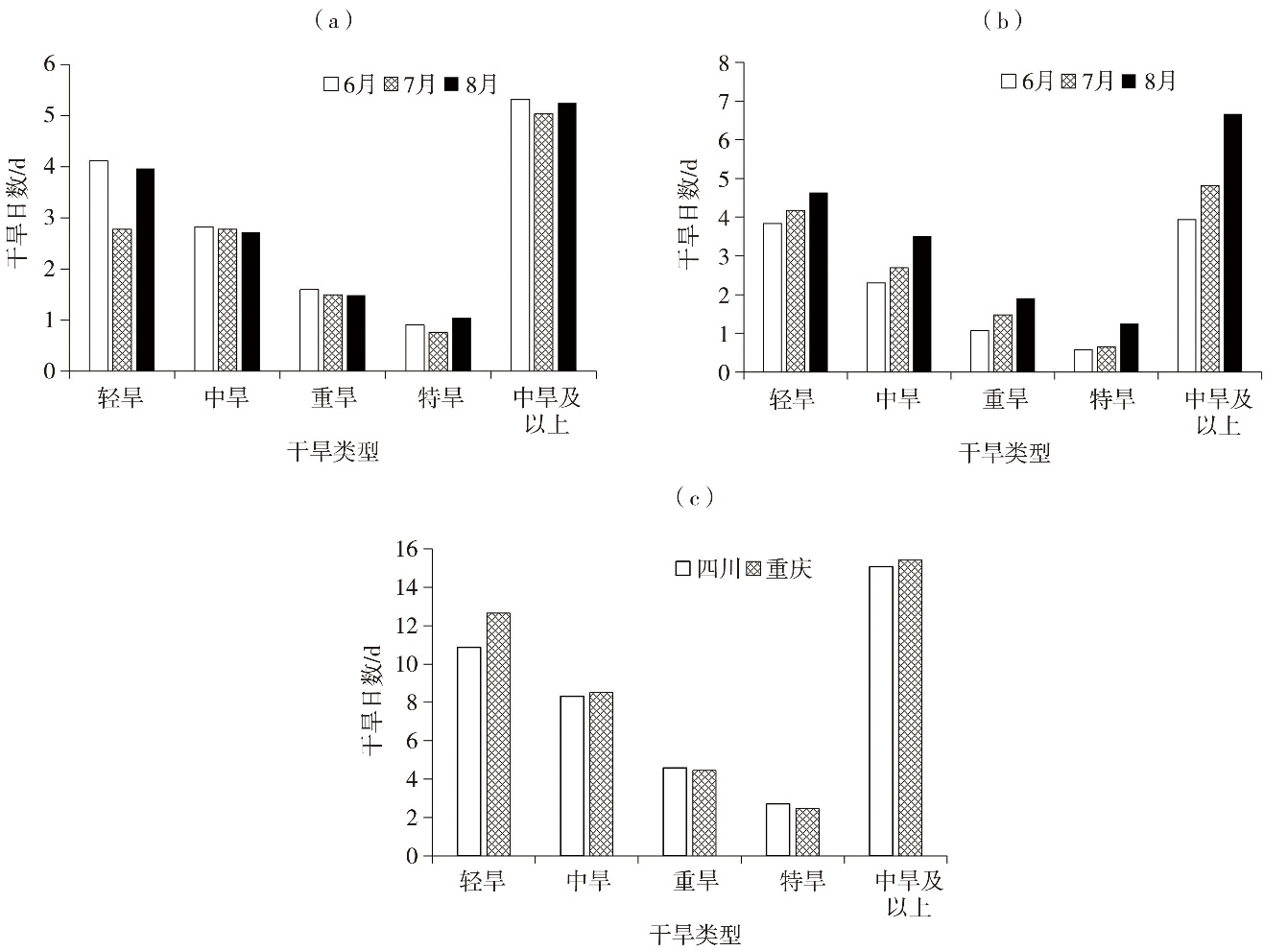
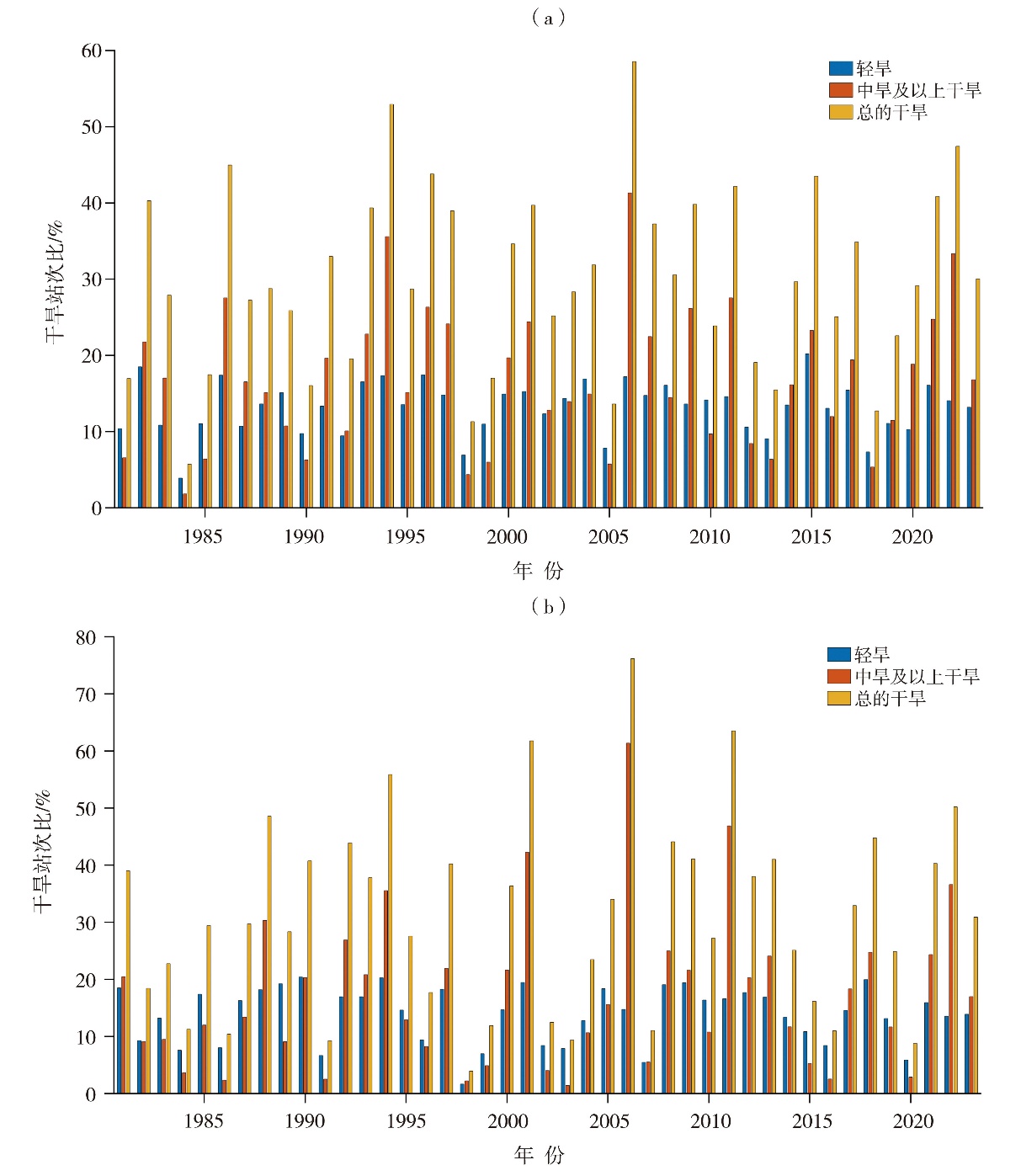
Fig.2 The multi-year monthly average of percentage of stations with drought (a) and drought days (b) in summer in Sichuan and Chongqing during 1981-2023
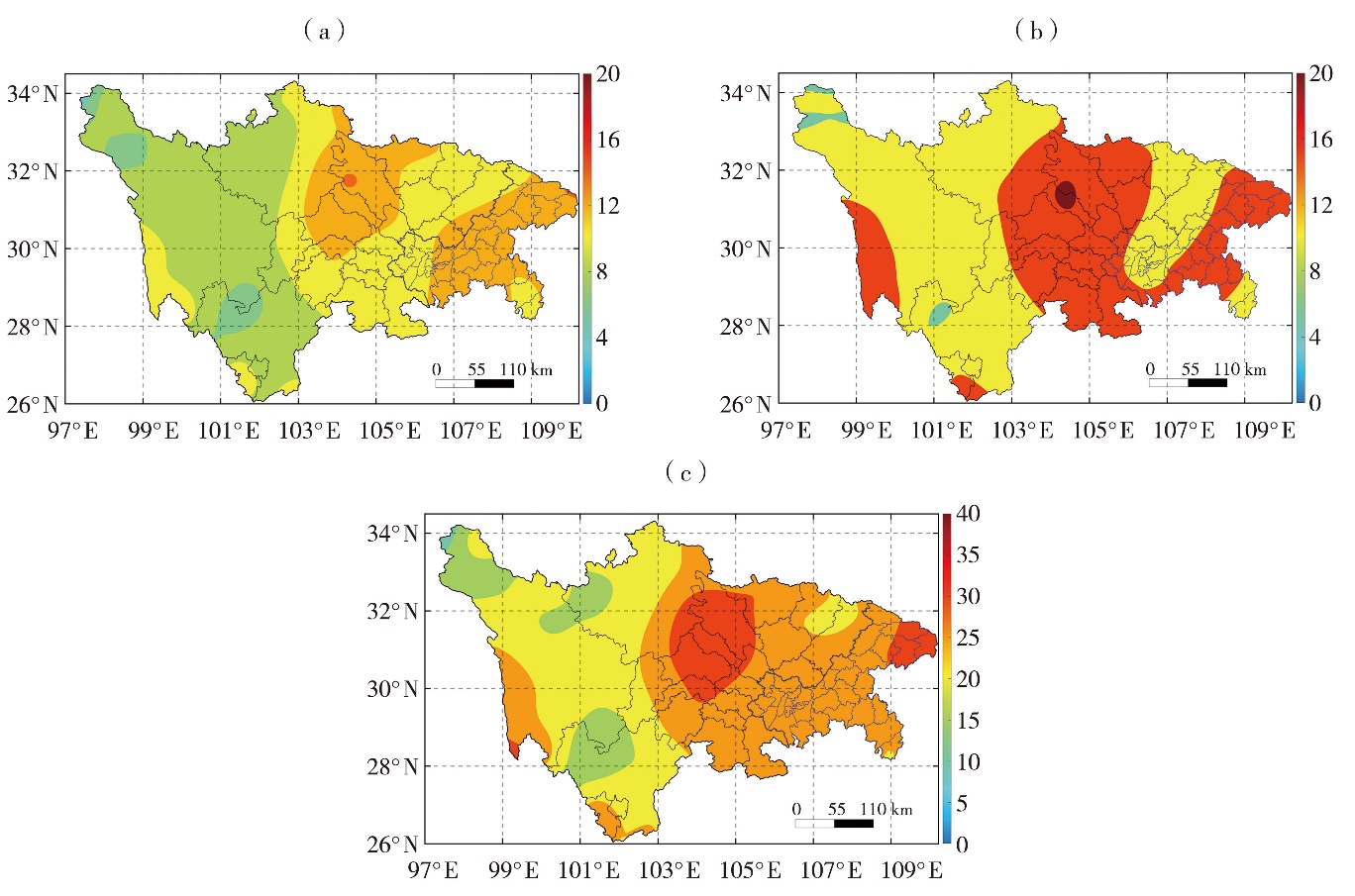
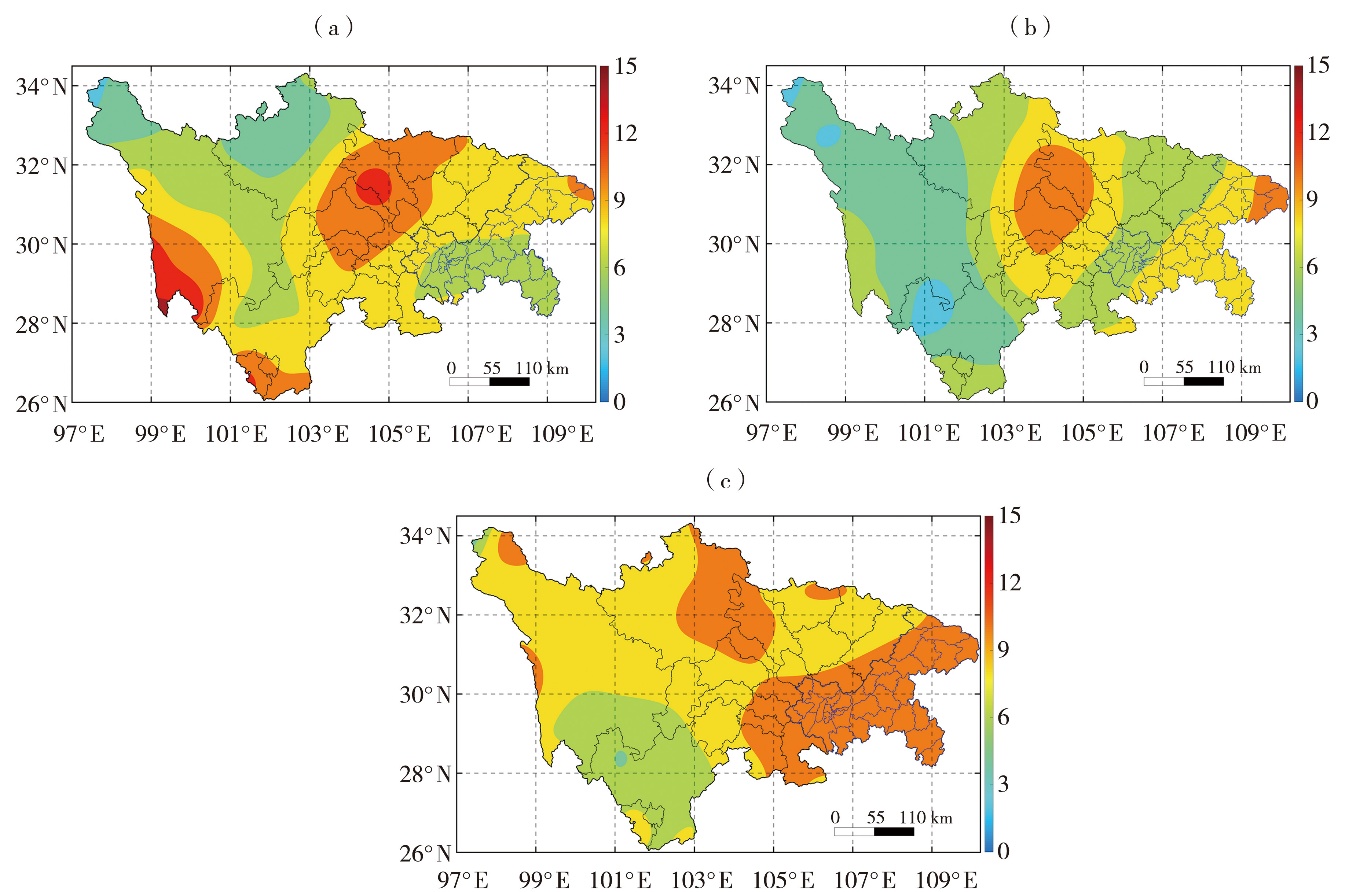
Fig.5 The spatial distribution of average days of light drought (a), moderate drought and above (b), and total drought days (c) during summer in Sichuan and Chongqing (Unit: d)
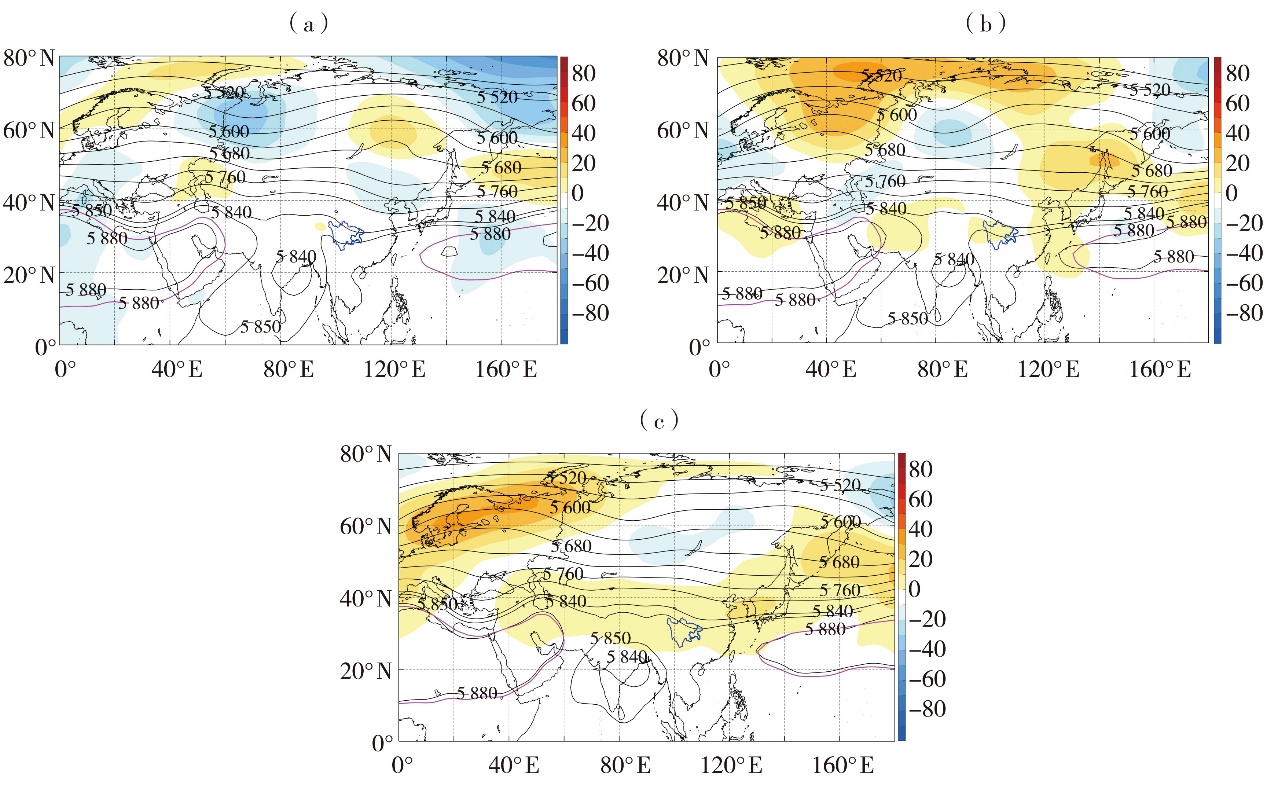
Fig.7 The composited 500 hPa geopotential height field (black contour lines) and its anomaly field (color shaded) in summer in years with severe drought in Sichuan (a), years with severe drought in Chongqing (b), and years with severe drought both in Sichuan and Chongqing (c) (Unit: gpm) (The area enclosed by the blue line represents Sichuan and Chongqing, the same as below; the pink lines represent the climate average 5 880 gpm line)
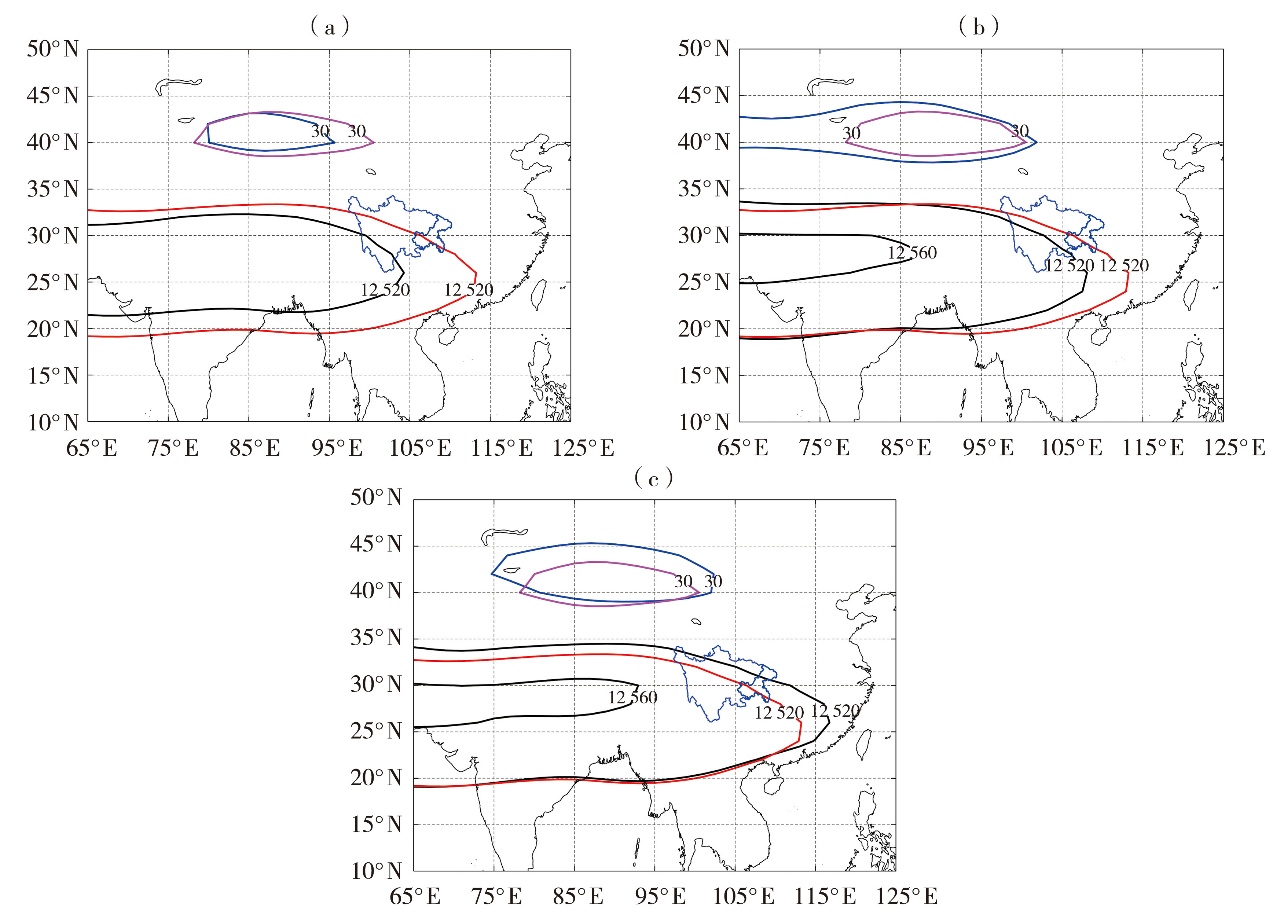
Fig.8 The composited 200 hPa geopotential height contours greater than 12 520 gpm (black lines) and the climatological mean of 12 520 gpm (red line) (Unit: gpm), zonal wind speed exceeding 30 m·s-1 (blue thick line) and the climatological mean of zonal wind speed at 30 m·s-1 (pink line) (Unit: m·s-1) at 200 hPa in summer in years with severe drought in Sichuan (a), years with severe drought in Chongqing (b), and years with severe drought both in Sichuan and Chongqing (c)
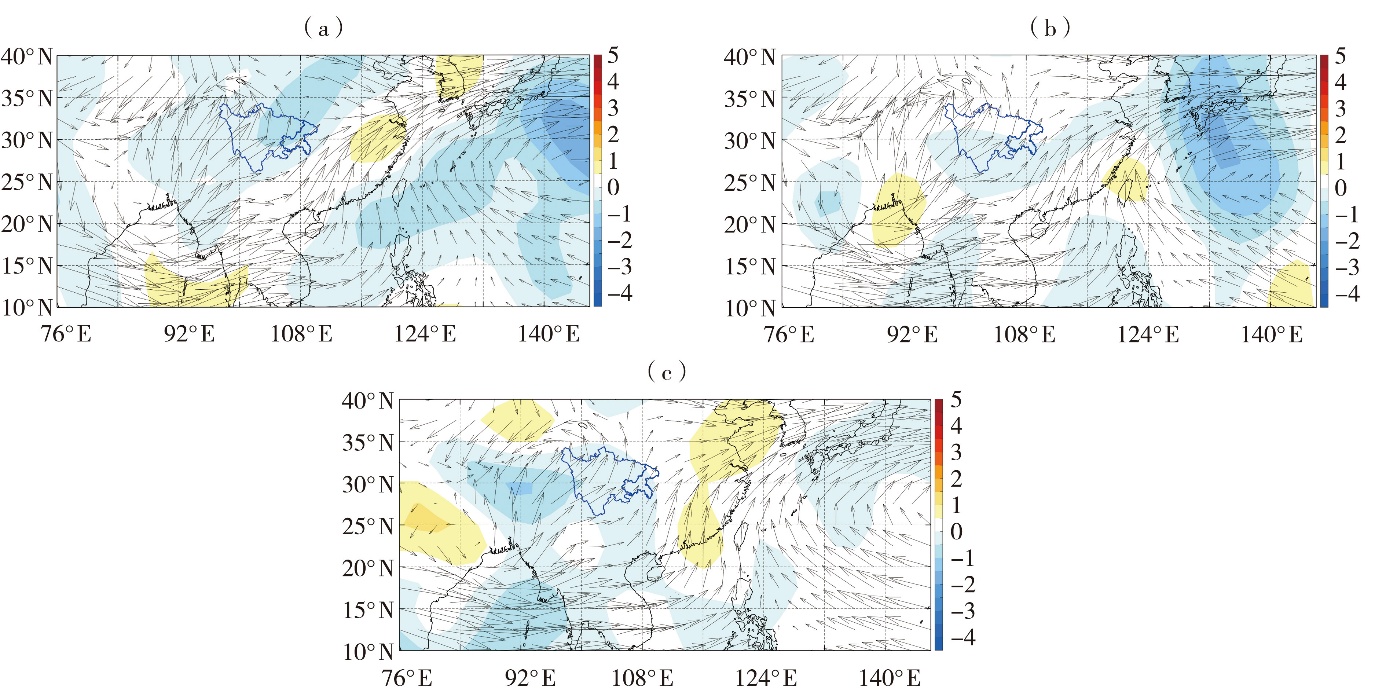
Fig.9 The composited 700 hPa wind filed (arrow vetcors) and meridional wind anomaly field (color shaded) in summer for years with severe drought in Sichuan (a), years with severe drought in Chongqing (b), and years with severe drought both in Sichuan and Chongqing (c) (Unit: m·s-1)
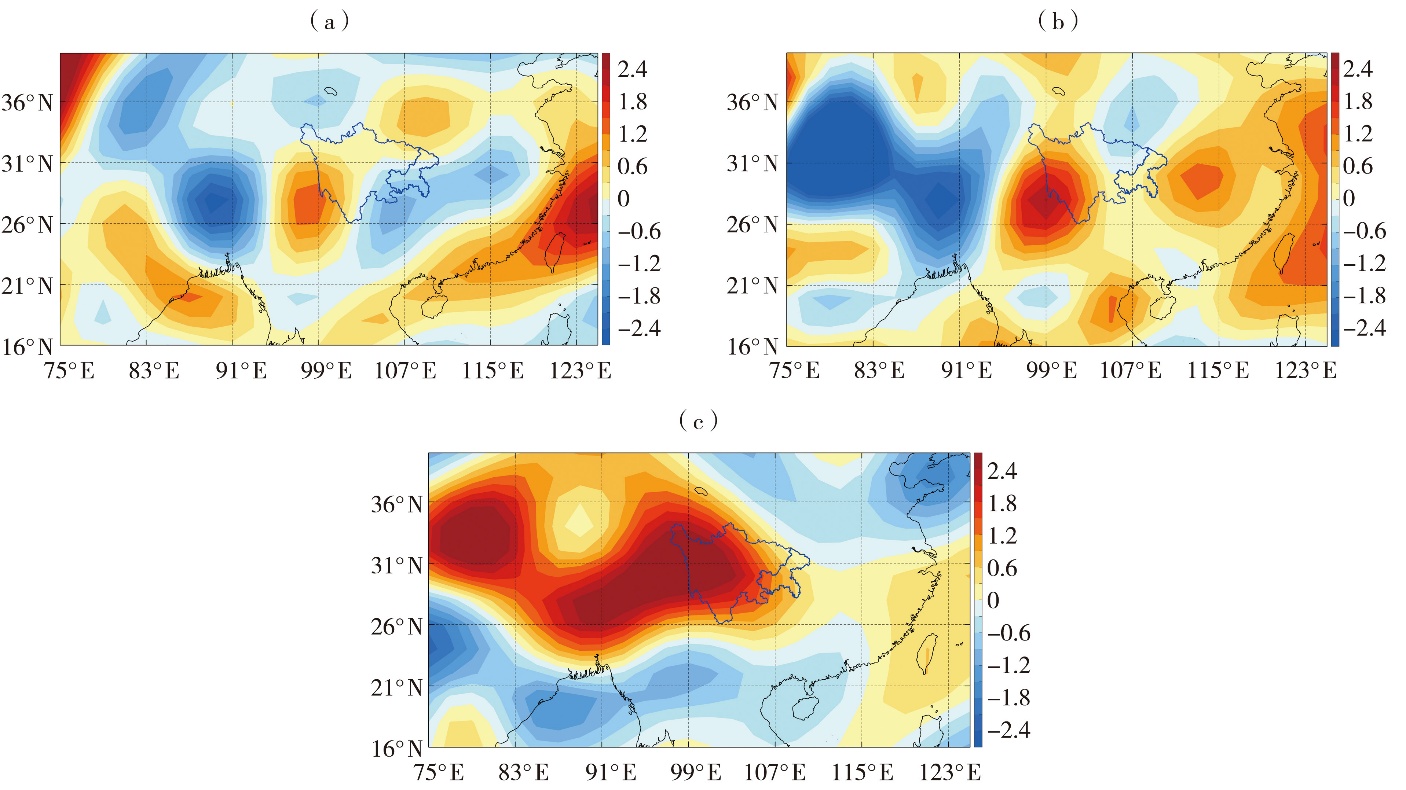
Fig.10 The composited 700 hPa vertical velocity field in summer in years with severe drought in Sichuan (a), years with severe drought in Chongqing (b), years with severe drought both in Sichuan and Chongqing (c) (Unit: 10-2 Pa·s-1)
| [1] | 邓彪, 孙蕊, 邢开瑜, 等, 2024. 1961—2022年四川省区域性干旱过程识别及时空演变特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(1):85-93. |
| [2] | 高洁, 肖红茹, 郭善云, 2023. 2022年夏季四川持续高温干旱特征及初步分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(5):118-126. |
| [3] | 龚道溢, 朱锦红, 王绍武, 2002. 长江流域夏季降水与前期北极涛动的显著相关[J]. 科学通报, 47(7):546-549. |
| [4] | 何慧根, 张驰, 吴遥, 等, 2023. 重庆夏季高温干旱特征及其对拉尼娜事件的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6):873-883. |
| [5] | 黄小梅, 赵旋, 肖丁木, 2019. 1961—2016年四川盆地夏季高温热浪变化特征分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 39(2):14-22. |
| [6] | 李新周, 马柱国, 刘晓东, 2006. 中国北方干旱化年代际特征与大气环流的关系[J]. 大气科学, 30(2):277-284. |
| [7] |
李忆平, 李耀辉, 2017. 气象干旱指数在中国的适应性研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5):709-723.
DOI |
| [8] | 李永华, 徐海明, 刘德, 2009. 2006年夏季西南地区东部特大干旱及其大气环流异常[J]. 气象学报, 67(1):122-132. |
| [9] | 李韵婕, 任福民, 李忆平, 等, 2014. 1960—2010年中国西南地区区域性气象干旱事件的特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 72(2):266-276. |
| [10] | 廖要明, 张存杰, 2017. 基于MCI的中国干旱时空分布及灾情变化特征[J]. 气象, 43(11):1402-1 409. |
| [11] | 刘晓冉, 程炳岩, 杨茜, 等, 2009. 川渝地区夏季高温干旱变化特征及其异常年环流形势分析[J]. 高原气象, 28(2):306-313. |
| [12] | 彭京备, 刘舸, 孙淑清, 2016. 2013年我国南方持续性高温天气及副热带高压异常维持的成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 40(5):897-906. |
| [13] | 彭京备, 张庆云, 布和朝鲁, 2007. 2006年川渝地区高温干旱特征及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(3):464-474. |
| [14] |
齐冬梅, 李跃清, 王莺, 等, 2017. 基于Z指数的四川干旱时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5):734-744.
DOI |
| [15] | 祁海霞, 智协飞, 白永清, 2011. 中国干旱发生频率的年代际变化特征及趋势分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 34(4):447-455. |
| [16] | 全国气候与气候变化标准化技术委员会, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [17] | 邵小路, 姚凤梅, 张佳华, 等, 2014. 华北地区夏季旱涝的大气环流特征诊断[J]. 干旱区研究, 31(1):131-137. |
| [18] |
苏秀程, 王磊, 李奇临, 等, 2014. 近50 a中国西南地区地表干湿状况研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 29(1):104-116.
DOI |
| [19] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):764-770.
DOI |
| [20] |
王劲松, 姚玉璧, 王莺, 等, 2022. 青藏高原地区气象干旱研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 37(5):441-461.
DOI |
| [21] | 王明田, 王翔, 黄晚华, 等, 2012. 基于相对湿润度指数的西南地区季节性干旱时空分布特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 28(19):85-92. |
| [22] | 王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2015. 几种干旱指标对西南和华南区域月尺度干旱监测的适用性评价[J]. 高原气象, 34(6):1616-1 624. |
| [23] | 巫娜, 罗凝谊, 许勇, 2014. 四川盆地干旱灾害统计特征[J]. 气象科技, 42(2):309-313. |
| [24] | 吴遥, 唐红玉, 董新宁, 等, 2024. 2022年夏季重庆极端高温天气特征及其成因分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 43(1):110-120. |
| [25] | 武新英, 郝增超, 张璇, 等, 2021. 中国夏季复合高温干旱分布及变异趋势[J]. 水利水电技术:中英文(12):90-98. |
| [26] | 谢五三, 张强, 李威, 等, 2021. 干旱指数在中国东北、西南和长江中下游地区适用性分析[J]. 高原气象, 40(5):1136-1 146. |
| [27] | 姚玉璧, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2015. 气候变暖背景下中国西南干旱时空分异特征[J]. 资源科学, 37(9):1774-1 784. |
| [28] | 张驰, 唐红玉, 吴遥, 等, 2019. 两种干旱指数在重庆极端干旱事件中的应用[J]. 西南大学学报:自然科学版, 41(11):92-103. |
| [29] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等, 2015a. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 73(6):1092-1 103. |
| [30] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2015b. 中国西北地区干旱气象灾害监测预警与减灾技术研究进展及其展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 30(2):196-213. |
| [31] | 张庆云, 陶诗言, 彭京备, 2008. 我国灾害性天气气候事件成因机理的研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 32(4):815-825. |
| [32] | 张琼, 刘平, 吴国雄, 2003. 印度洋和南海海温与长江中下游旱涝[J]. 大气科学, 27(6):992-1 006. |
| [33] |
周斌, 王春学, 张顺谦, 2021. 1961—2018年四川盆地极端伏旱日数准2 a周期变化特征及其可能成因[J]. 干旱气象, 39(5):727-733.
DOI |
| [34] | 朱伟军, 王燕娜, 周兵, 等, 2016. 西北东部夏季极端干旱事件机理分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 39(4):468-479. |
| [35] | SU B D, HUANG J L, FISCHER T, et al, 2018. Drought losses in China might double between the 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(42): 10 600-10 605. |
| [36] | REN Y L, YUE P, ZHANG Q, et al, 2021. Influence of land surface aridification on regional monsoon precipitation in East Asian summer monsoon transition zone[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 144(1): 93-102. |
| [1] | YANG Xiaoling, SUN Xuying, YANG Jinhu, WU Wen, ZHAO Huihua, CHEN Jing. Identification and evolution characteristics of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 836-843. |
| [2] | WANG Yuetong, HE Dongpo, LI Zhongyan, WANG Shuo, CHEN Zaoyang. Analysis of two meteorological drought events in Guizhou Province and establishment of drought prediction model based on machine learning [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 671-682. |
| [3] | LI Chunhua, ZHU Biao, YANG Jinhu, HUANG Pengcheng. Analysis of climatic characteristics of meteorological drought in arid and semi-arid regions of China in recent 60 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 519-526. |
| [4] | CHEN Xiaoxiao, HUANG Zhiyong, QIN Pengcheng, XIA Zhihong, YAO Yao, TANG Xingzhi, WANG Yingqiong. Atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature characteristics of summer high temperature anomaly in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 553-562. |
| [5] | JIANG Zhongbao, WANG Yukun, YANG Xueyan, LI Shangfeng, YU Xiujing, PAN Chunxiao, QIU Yixuan. Characteristics of climate comfort period in Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 620-628. |
| [6] | LIU Wei, ZHAO Yanli, GAO Jing, LI Linhui, WANG Huimin. Cause analysis of flood-drought alternation event in July 2022 in arid and semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 11-18. |
| [7] | LUO Xiaoling, YANG Mei, ZHAO Huihua, LI Yanying, JIANG Jufang, FU Fenqi. Influence analysis of El Niño event on temperature, precipitation and meteorological drought in Wuwei, Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 849-859. |
| [8] | MA Siyuan, JIN Yan, ZHANG Si, WANG Chuqin, MA Zhimin. Different impacts of El Niño/Southern Oscillation events on autumn meteorological drought in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 860-872. |
| [9] | WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [10] | XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922. |
| [11] | ZHAO Huizhen, HE Tao, GUO Ruixia, WANG Chengfu, ZHANG Yanrong, LI Qi. Meteorological drought variation characteristics in the Gannan Plateau based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 688-696. |
| [12] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [13] | CAI Yiheng, LI Shuai, ZHANG Qiang, DENG Biao, LUO Yu, SUN Rui. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 241-250. |
| [14] | JIANG Shujie, CHENG Ying, FANG Nan, ZHOU Yuquan, SHAN Zhonghua, ZHANG Lei. Construction of artificial precipitation demand level index of the reservoir based on drought and water level characteristics [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 341-349. |
| [15] | XUE Liang, YUAN Shujie, WANG Jinsong. Progress and prospects of research on causes of meteorological drought in different regions in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 1-13. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||