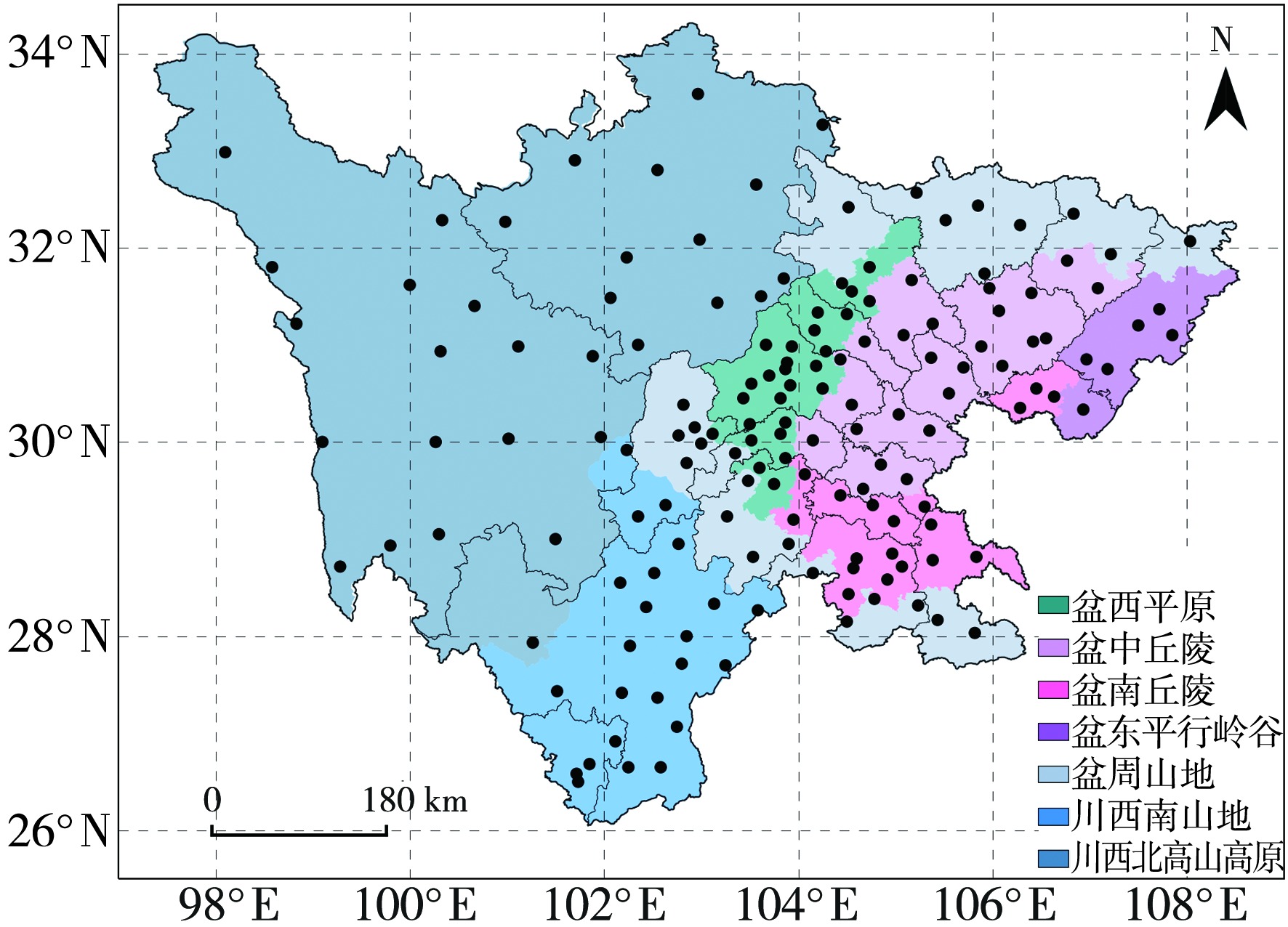
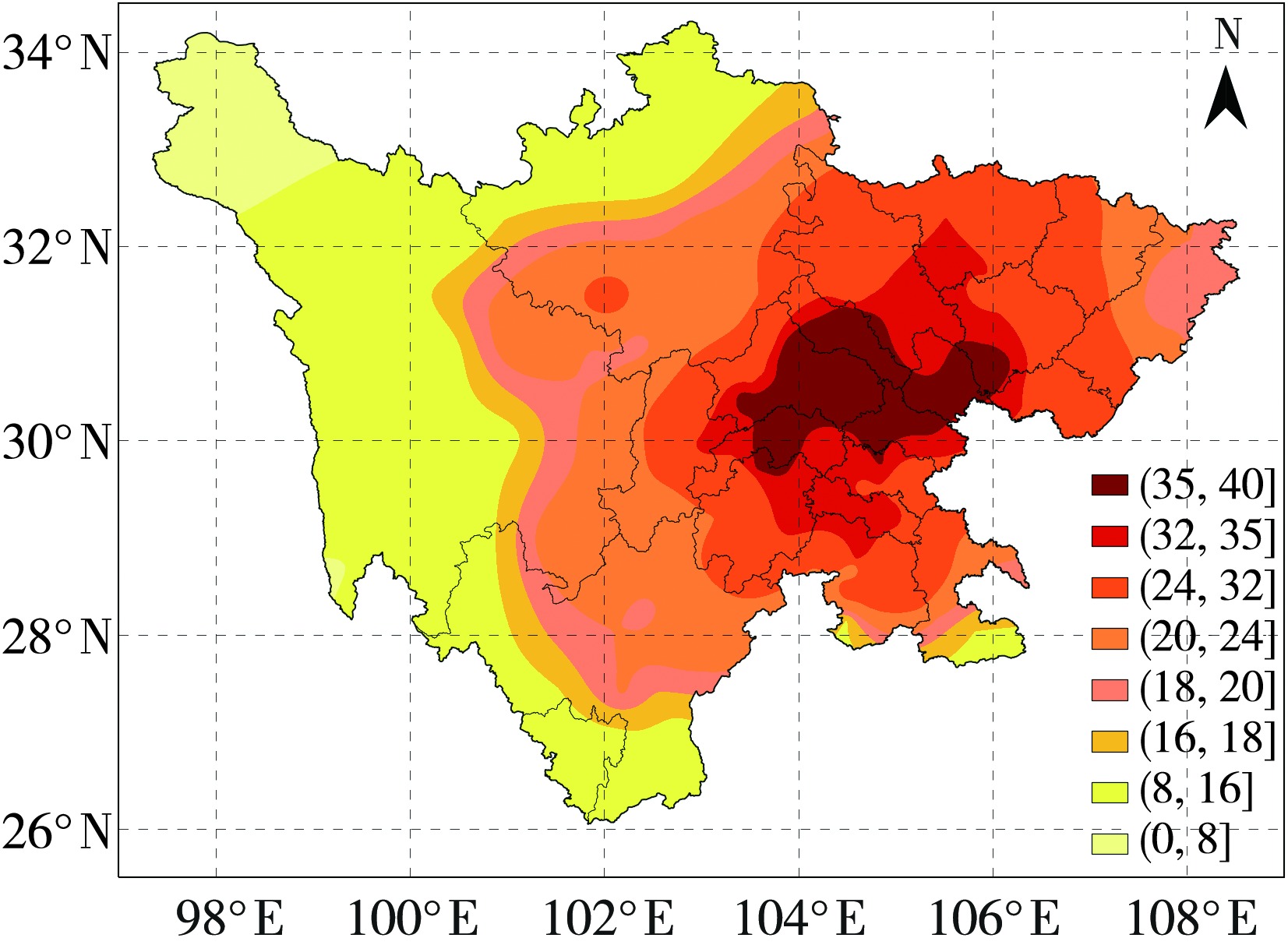
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 241-250.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0241
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021
CAI Yiheng1,2( ), LI Shuai3(
), LI Shuai3( ), ZHANG Qiang4, DENG Biao1,2, LUO Yu1,2, SUN Rui1,2
), ZHANG Qiang4, DENG Biao1,2, LUO Yu1,2, SUN Rui1,2
- 1. Institute of Plateau Meteorology, CMA/ Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateau and Basin Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
2. Sichuan Provincial Climate Centre, Chengdu 610072, China
3. Operation and Administration Center for River Basin Hydro Complex, China Three Gorges Corporation, Yichang 443133, Hubei, China
4. National Climate Centre, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2022-11-30Revised:2023-01-17Online:2023-04-30Published:2023-05-09
1997—2021年四川省干旱时空变化特征分析
蔡怡亨1,2( ), 李帅3(
), 李帅3( ), 张强4, 邓彪1,2, 罗玉1,2, 孙蕊1,2
), 张强4, 邓彪1,2, 罗玉1,2, 孙蕊1,2
- 1.中国气象局成都高原气象研究所/高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
2.四川省气候中心,四川 成都 610072
3.中国长江三峡集团有限公司流域枢纽运行管理中心 湖北 宜昌 443133
4.国家气候中心,北京 100081
-
通讯作者:李帅(1987—),男,高级工程师,主要从事水文水资源管理和研究。E-mail:li_shuai@ctg.com.cn。 -
作者简介:蔡怡亨(1995—),男,助理工程师,主要从事气候与气候变化研究。E-mail:1952943140@qq.com。 -
基金资助:中国长江三峡集团有限公司项目(0704182);国家自然科学基金项目(52109024);国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFC1502402);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(20JR10RA447)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CAI Yiheng, LI Shuai, ZHANG Qiang, DENG Biao, LUO Yu, SUN Rui. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 241-250.
蔡怡亨, 李帅, 张强, 邓彪, 罗玉, 孙蕊. 1997—2021年四川省干旱时空变化特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 241-250.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0241
| 起止年 | 相邻站点数阈值 | 第p个百分位 |
|---|---|---|
| 1997—2008 | 15 | 15 |
| 2009—2015 | 25 | 15 |
| 2016—2021 | 35 | 14 |
Tab.1 The threshold of the number of neighbor stations and percentile of meteorological drought threshold of regional drought processes in Sichuan Province
| 起止年 | 相邻站点数阈值 | 第p个百分位 |
|---|---|---|
| 1997—2008 | 15 | 15 |
| 2009—2015 | 25 | 15 |
| 2016—2021 | 35 | 14 |
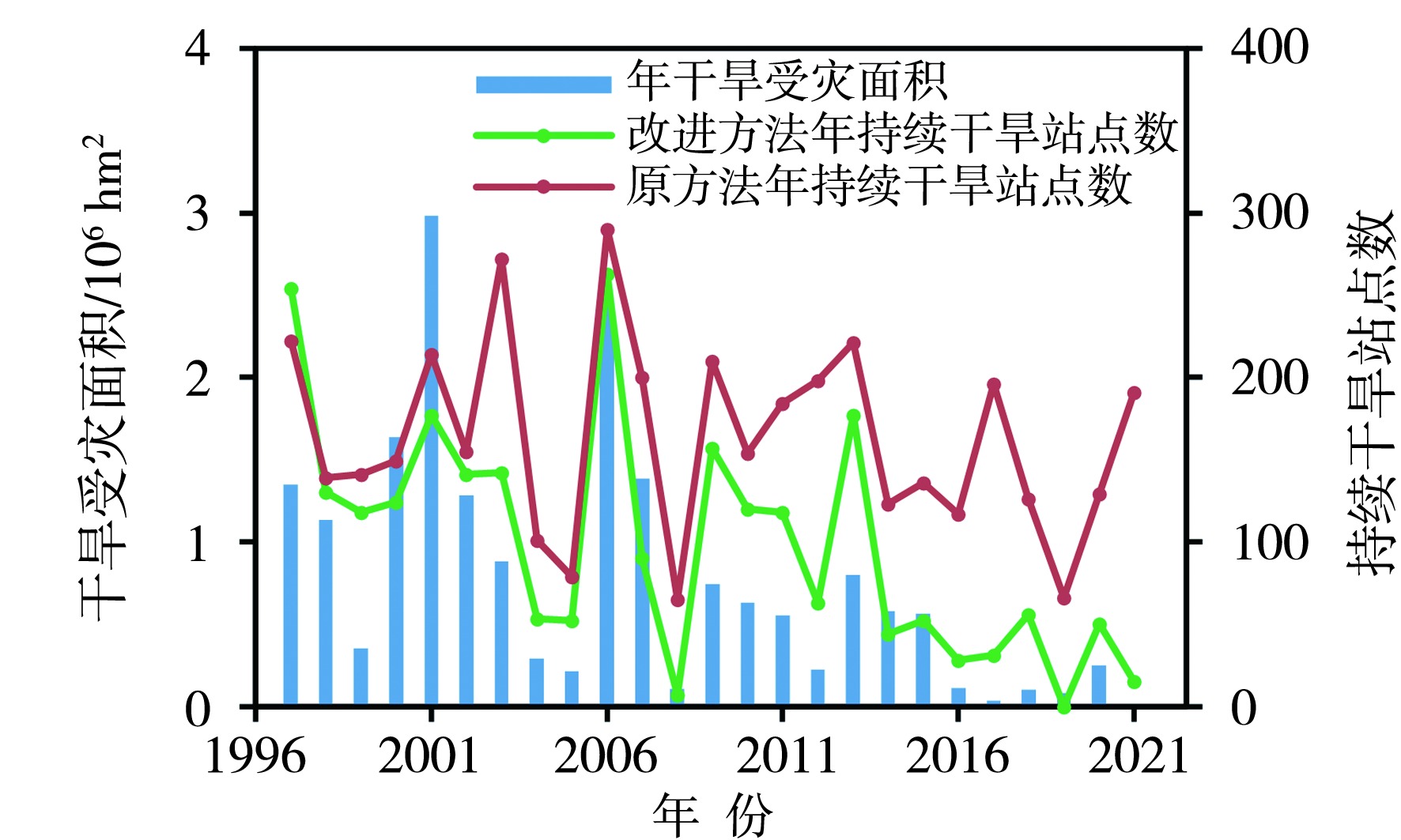
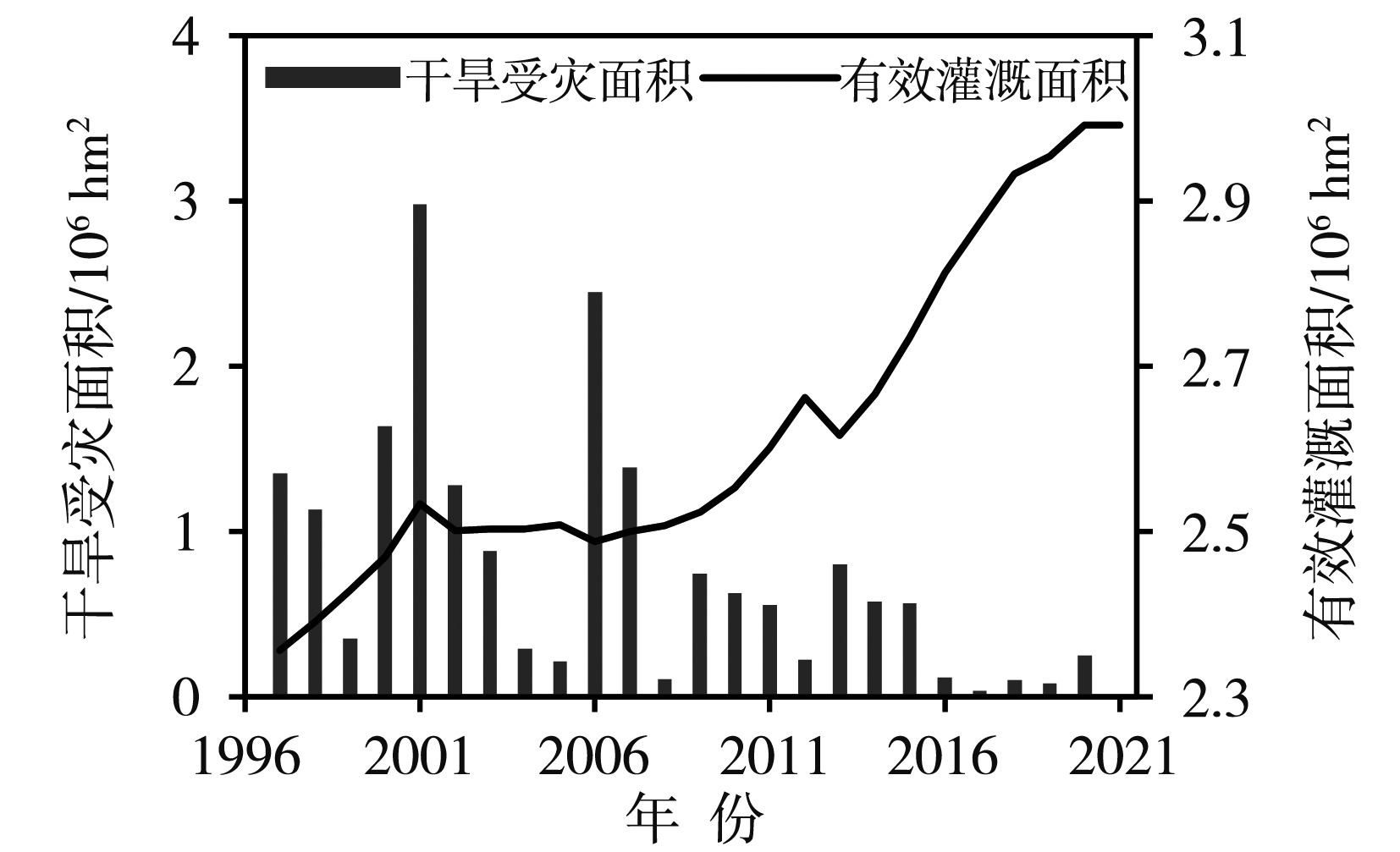
Fig.3 Variations of annual accumulated number of stations with persistent drought and annual drought disaster area in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021
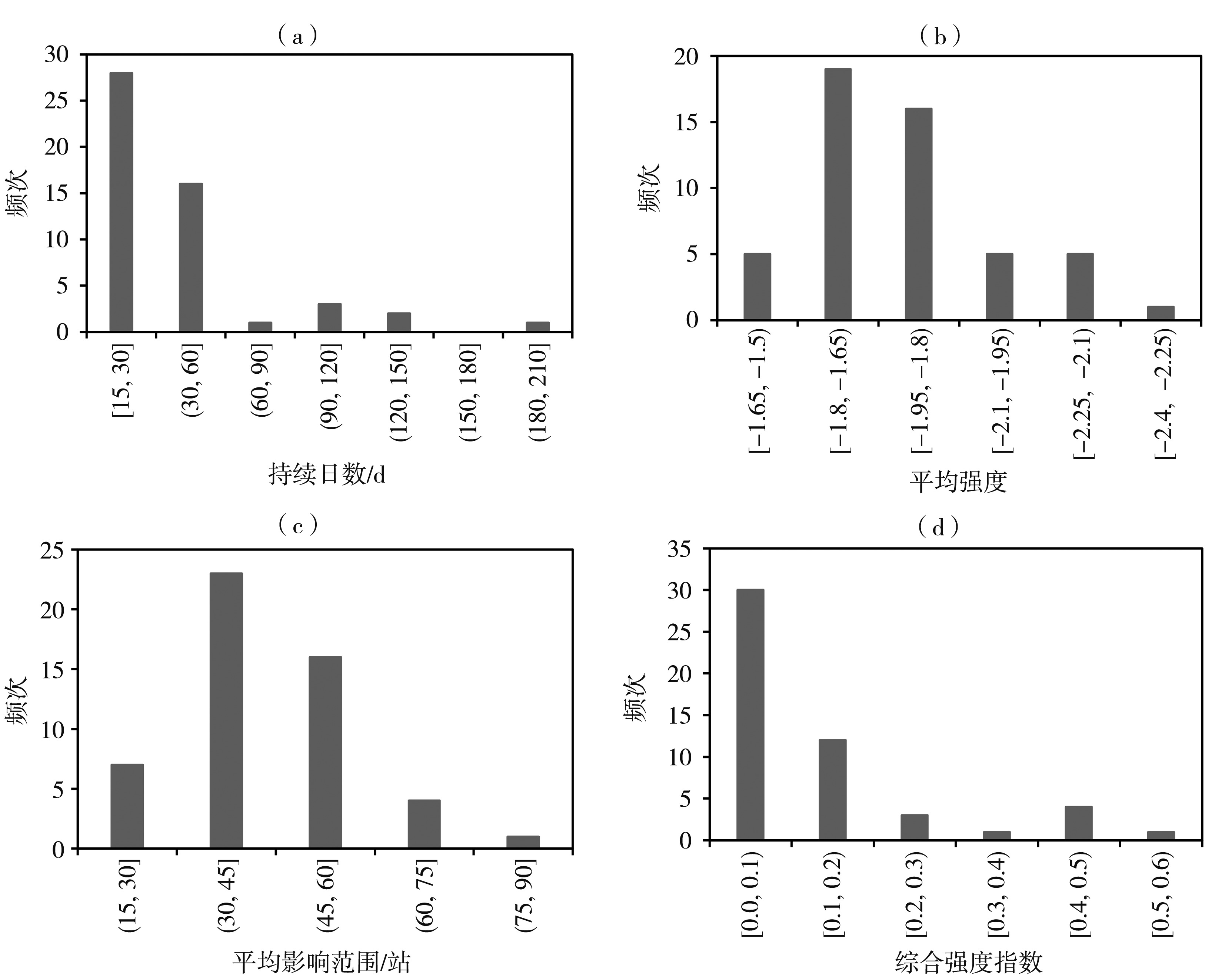
Fig.4 The frequency distribution of regional drought process characteristic variables in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 (a) durative day,(b) average intensity,(c) average influential area,(d) comprehensive intensity index
| 排位 | D/d(过程) | Aa/站(过程) | Ia(过程) | Z(过程) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 201 (1997-07-18至1998-02-03) | 83.62 (2012-12-21至2013-04-04) | -2.30 (1997-01-01至1997-01-22) | 0.60 (2012-12-21至2013-04-04) |
| 2 | 136 (2000-12-19至2001-05-03) | 70.60 (2009-02-04至2009-02-28) | -2.23 (2009-11-01至2009-12-12) | 0.48 (1997-07-18至1998-02-03) |
| 3 | 130 (2011-08-09至2011-12-16) | 70.02 (2002-08-29至2002-10-18) | -2.20 (2010-01-02至2010-02-17) | 0.43 (2006-06-10至2006-10-04) |
| 4 | 117 (2006-06-10至2006-10-04) | 65.45 (2010-01-02至2010-02-17) | -2.15 (2011-08-09至2011-12-16) | 0.43 (2011-08-09至2011-12-16) |
| 5 | 105 (2012-12-21至2013-4-4) | 60.81 (1997-07-18至1998-02-03) | -2.15 (1998-11-01至1998-12-09) | 0.41 (1999-01-11至1999-04-24) |
Tab.2 Regional drought processes with the top 5 characteristic variable and comprehensive intensity index (Z) in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021
| 排位 | D/d(过程) | Aa/站(过程) | Ia(过程) | Z(过程) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 201 (1997-07-18至1998-02-03) | 83.62 (2012-12-21至2013-04-04) | -2.30 (1997-01-01至1997-01-22) | 0.60 (2012-12-21至2013-04-04) |
| 2 | 136 (2000-12-19至2001-05-03) | 70.60 (2009-02-04至2009-02-28) | -2.23 (2009-11-01至2009-12-12) | 0.48 (1997-07-18至1998-02-03) |
| 3 | 130 (2011-08-09至2011-12-16) | 70.02 (2002-08-29至2002-10-18) | -2.20 (2010-01-02至2010-02-17) | 0.43 (2006-06-10至2006-10-04) |
| 4 | 117 (2006-06-10至2006-10-04) | 65.45 (2010-01-02至2010-02-17) | -2.15 (2011-08-09至2011-12-16) | 0.43 (2011-08-09至2011-12-16) |
| 5 | 105 (2012-12-21至2013-4-4) | 60.81 (1997-07-18至1998-02-03) | -2.15 (1998-11-01至1998-12-09) | 0.41 (1999-01-11至1999-04-24) |
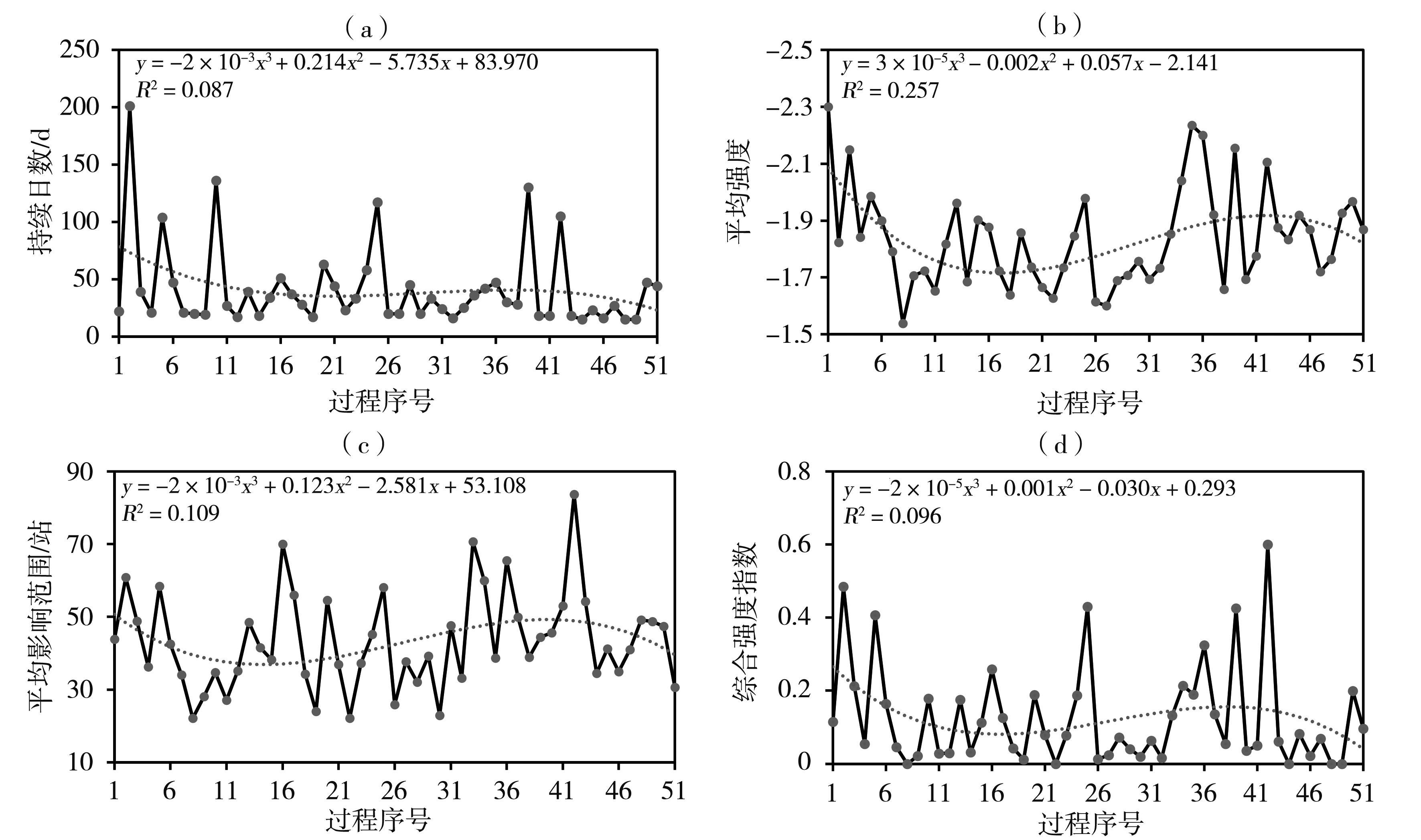
Fig.5 The distribution of each characteristic variable of 51 regional drought processes in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 (a) durative day,(b) average intensity,(c) average influential area,(d) comprehensive intensity index
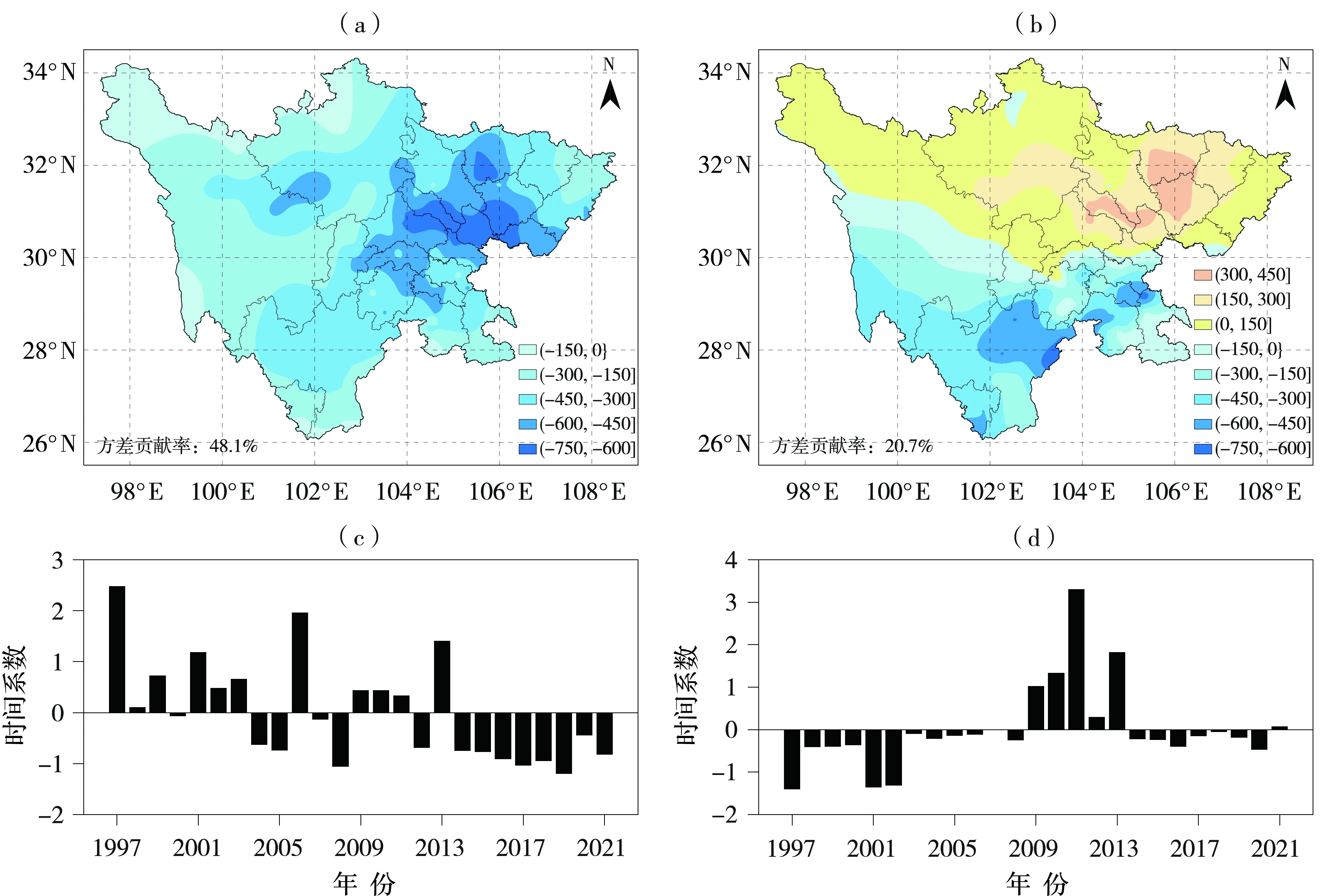
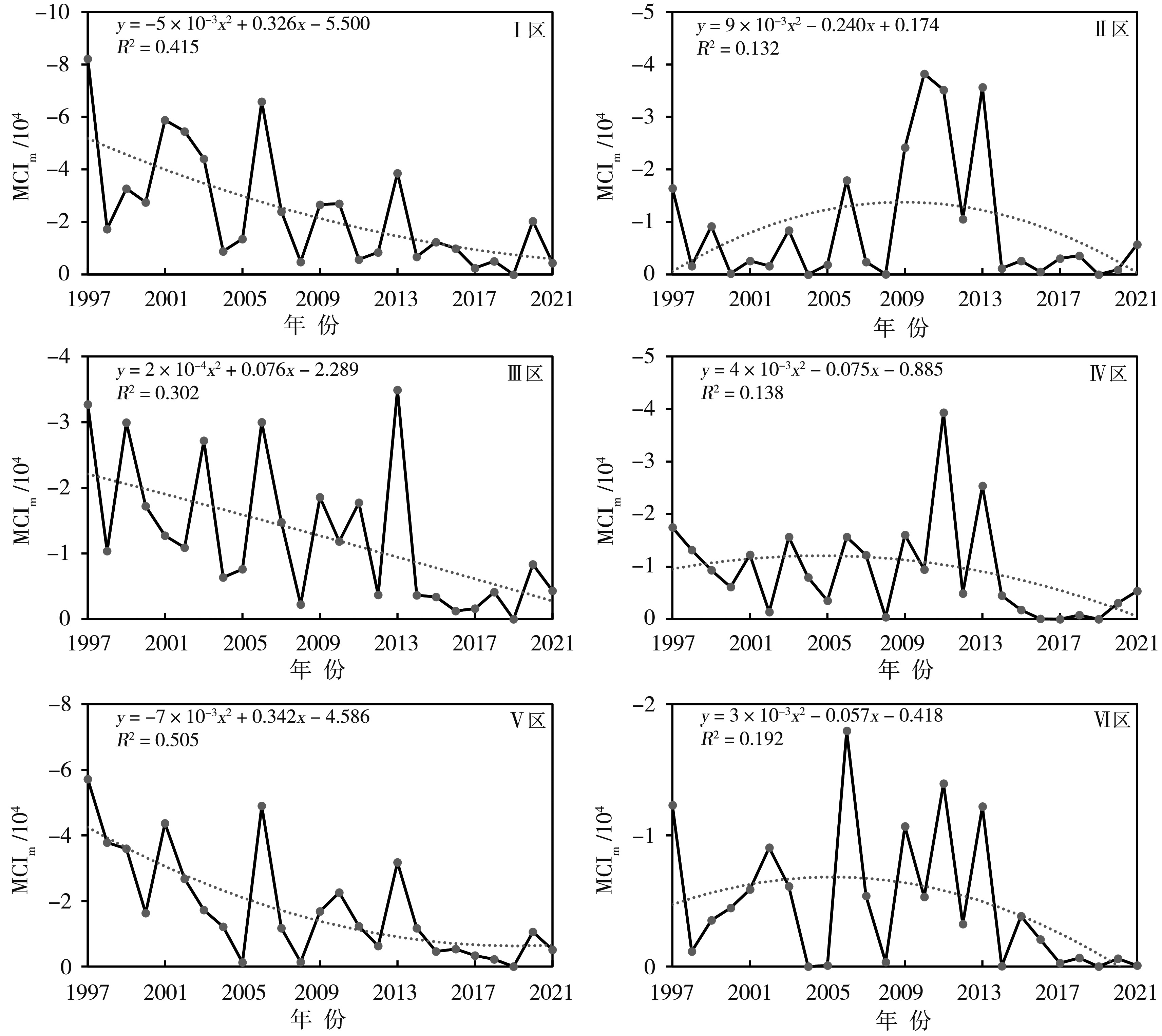
Fig.7 The spatial patterns (a, b) and time coefficients (c, d) of the first (a, c) and second (b, d) modes of annual accumulated MCIm anomaly decomposed by EOF in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021

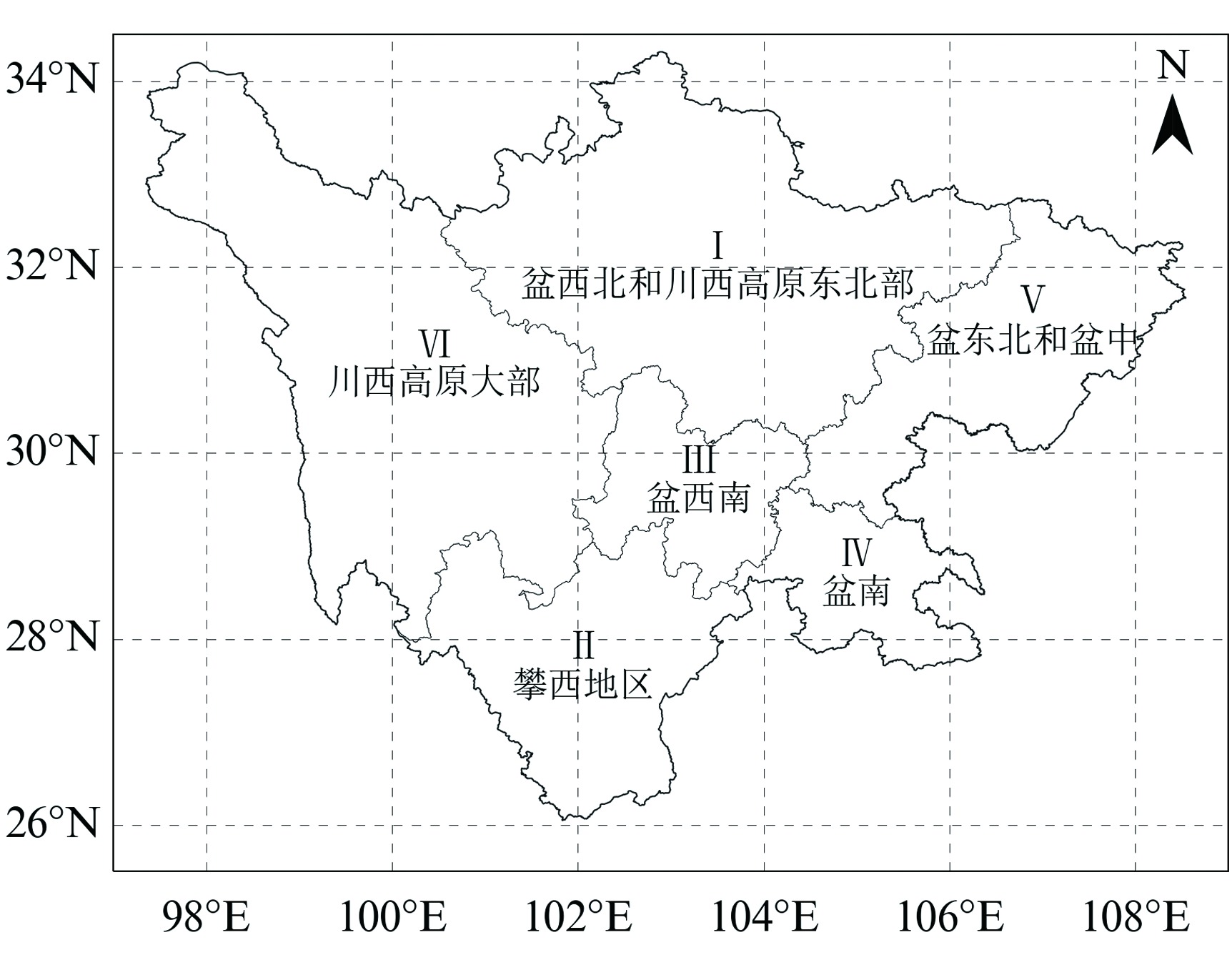
Fig.10 The real part of the wavelet coefficients of annual accumulated MCIm in six drought climatic areas in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 (The thick black contour designates critical value at the 0.050 significance level, and the cone of influence (COI) where edge effects might distort the picture is shown as a light contour)
| [1] | 安莉娟, 任福民, 李韵婕, 等, 2014. 近50年华北区域性气象干旱事件的特征分析[J]. 气象, 40(9): 1 097-1 105. |
| [2] | 樊东卫, 何勃亮, 李长华, 等, 2019. 球面距离计算方法及精度比较[J]. 天文研究与技术, 16(1): 69-76. |
| [3] | 甘书龙, 1986. 四川省农业资源与区划[M]. 成都: 四川省社会科学院出版社. |
| [4] | 郭冬, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 吴秀兰, 等, 2022. 四种气象干旱指数在新疆区域适用性研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(3): 90-101. |
| [5] |
韩兰英, 张强, 贾建英, 等, 2019. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱强度、频次和持续时间及其南北差异性[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(5): 1-10.
DOI |
| [6] | 姜大膀, 王晓欣, 2021. 对IPCC第六次评估报告中有关干旱变化的解读[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(5): 650-653. |
| [7] | 金燕, 况雪源, 晏红明, 等, 2018. 近55年来云南区域性干旱事件的分布特征和变化趋势研究[J]. 气象, 44(9): 1 169-1 178. |
| [8] | 李万志, 张调风, 马有绚, 等, 2021. 基于灾害风险因子的青海省干旱灾害风险区划[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 480-485. |
| [9] |
李忆平, 王劲松, 李耀辉, 2015. 2009/2010年中国西南区域性大旱的特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 33(4): 537-545.
DOI |
| [10] | 李韵婕, 任福民, 李忆平, 等, 2014. 1960—2010年中国西南地区区域性气象干旱事件的特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 72(2): 266-276. |
| [11] | 廖要明, 张存杰, 邹旭恺, 2021. 区域性干旱过程监测评估方法:QX/T597—2021[S]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [12] | 廖要明, 张存杰, 2017. 基于MCI的中国干旱时空分布及灾情变化特征[J]. 气象, 43(11): 1 402-1 409. |
| [13] | 刘振宏, 李娇, 孙艳云, 等, 2020. 辽宁西部农作物生长季干旱风险及降水满足度研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(4):124-130. |
| [14] |
马鹏里, 韩兰英, 张旭东, 等, 2019. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱变化的区域特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(6): 209-215.
DOI |
| [15] | 任福民, 2015. 中国干旱、强降水、高温和低温区域性极端事件[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [16] | 王朝勇, 孙文樵, 王智育, 等, 1999. 四川省(暨重庆市)农田水分盈亏与农业干旱评估研究[R]. 四川省水利电力研究所. |
| [17] |
王春学, 张顺谦, 陈文秀, 等, 2019. 气象干旱综合指数MCI在四川省的适用性分析及修订[J]. 中国农学通报, 35(9): 115-121.
DOI |
| [18] |
王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2020. 多种干旱指数在中国北方的适用性及其差异原因初探[J]. 高原气象, 39(3): 628-640.
DOI |
| [19] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:105-121. |
| [20] | 谢五三, 张强, 李威, 等, 2021. 干旱指数在中国东北、西南和长江中下游地区适用性分析[J]. 高原气象, 40(5): 1 136-1 146. |
| [21] | 熊志强, 1999. 四川农业灾害与减灾对策[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社. |
| [22] | 余兴湛, 蒲义良, 康伯乾, 2022. 基于SPEI的广东省近50 a干旱时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 051-1 058. |
| [23] | 张超, 罗伯良, 2021. 湖南夏秋季持续性区域气象干旱的时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 193-202. |
| [24] | 国家气候中心, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [25] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等, 2015. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 73(6): 1 092-1 103. |
| [26] | 张强, 潘学标, 马柱国, 等, 2009. 干旱[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [27] | 张强, 谢五三, 陈鲜艳, 等, 2021. 1961—2019年长江中下游区域性干旱过程及其变化[J]. 气象学报, 79(4): 570-581. |
| [28] | 赵海燕, 张文千, 邹旭恺, 等, 2021. 气候变化背景下中国农业干旱时空变化特征分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 42(1): 69-79. |
| [29] | 邹旭恺, 赵琳, 陈鲜艳, 等, 2022. 中国重大干旱事件分析(1961—2020年)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社,12. |
| [30] |
CAI X, ZHANG W, FANG X, et al, 2021. Identification of regional drought processes in North China using MCI analysis[J]. Land, 10(12): 1 390.DOI:10.2166/ws.2022.313.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
CHEN H, SUN J, 2016. Anthropogenic warming has caused hot droughts more frequently in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 544: 306-318.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
NORTH G R, BELL T L, CAHALAN R F, et al, 1982. Sampling error in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 110(7): 699-706.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
REN F, CUI D, GONG Z, et al, 2012. An objective identification technique for regional extreme events[J]. Journal of Climate, 25: 7 015-7 027.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
TORRENCE C, COMPO G, 1997. A practical guide to Wavelet analysis[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 79: 61-78.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YU M, LI Q, HAYES M J, et al, 2014. Are droughts becoming more frequent or severe in China based on the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index: 1951-2010?[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 34(3): 545-558.
DOI URL |
| [1] | FAN Jinjin, QIN Pengcheng, SHI Ruiqin, LI Mengrong, DU Liangmin. Characteristics of compound hot and drought disasters in Hubei under the background of climate change [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 780-790. |
| [2] | ZHANG Chao, LUO Boliang. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Persistent Regional Meteorological Drought in Summer and Autumn in Hunan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 193-202. |
| [3] | PENG Shuangzi, LIU Xinmiao, CHEN Tao, YANG Min, XU Di, KUANG Yufei, XIAO Meiying. Discussion on drought monitoring and evaluation technology in the Heng-Shao drought corridor [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 894-899. |
| [4] | SUN Li, ZHANG Jinguang, YANG Lei, ZHAO Shuhui. Micro- and Macro-Features of Cloud in Liaoning Province and Its Correlation with Precipitation Based on Aqua/CERES Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 612-618. |
| [5] | ZHOU Jiewen, LU Chuhan, SUN Yan. Review of Extratropical Cyclone Activities over East Asia and Its Climatic Effects Research Based on Objective Identification [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 907-917. |
| [6] | SUN Li1, ZHAO Shuhui1, ZHANG Jinguang1, YUAN Jian1, JIN Bo2,SONG Huaiyu2, QIN Xin1, LIU Yang1, FANG Bin1. Characteristics of Cloud Vertical Structure Based on Threshold Method of Relative Humidity in Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 619-625. |
| [7] | YUAN Shujie, LI Yuchun, XIANG Le, ZHANG Yiwei. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Direct Solar Radiation over Rugged Terrains in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 20-25. |
| [8] | DUAN Yunxia, LI Deqin, LI Dawei, LIANG Hong, CHAI Xiaoling, ZHANG Shuai. Analysis on Precipitation Phase Characteristics and Its Forecast Methods of Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 51-57. |
| [9] | LI Yiping, WANG Jinsong, Li Yaohui. Characteristics of a Regional Meteorological Drought Event in Southwestern China During 2009-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 537-545. |
| [10] | NI Jiangbo,LI Wencai,SHANG Kezheng,WANG Shigong, LI Deshuai. Automatic Identificationand Prediction of Low Visibility Weather in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(1): 174-179. |
| [11] | . Assessment of the Rare Drought Event Occurred in Anshun of Guizhou Province by Three Drought Indexes [J]. J4, 2012, 30(3): 315-322. |
| [12] | TUN Jian-Kun, SHU Xiao-Ding. Review of Detection and Warning Methods for Sever Hail Events by Doppler Weather Radars [J]. J4, 2009, 27(3): 197-206. |
| [13] | GUO Ni, LIANG Yun. A Study on Quantitative Identification of Sand and Dust Storm Using MODIS Data [J]. J4, 2006, 24(1): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||