Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 620-628.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0620
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics of climate comfort period in Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018
JIANG Zhongbao1,2( ), WANG Yukun3(
), WANG Yukun3( ), YANG Xueyan1,2, LI Shangfeng2,4,5, YU Xiujing1,2, PAN Chunxiao1, QIU Yixuan1
), YANG Xueyan1,2, LI Shangfeng2,4,5, YU Xiujing1,2, PAN Chunxiao1, QIU Yixuan1
- 1. Jilin Climate Center, Changchun 130062, China
2. Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Changbai Mountain Meteorology & Climate Change, Changchun 130062, China
3. Jilin Meteorological Information Network Center, Changchun 130062, China
4. Institute of Meteorological Sciences of Jilin Province, Changchun 130062, China
5. Laboratory of Research for Middle-High Latitude Circulation Systems and East Asian Monsoon, Changchun 130062, China
-
Received:2023-06-09Revised:2023-11-07Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-13
1961—2018年长白山气候舒适期变化特征
姜忠宝1,2( ), 王玉昆3(
), 王玉昆3( ), 杨雪艳1,2, 李尚锋2,4,5, 于秀晶1,2, 潘春晓1, 邱译萱1
), 杨雪艳1,2, 李尚锋2,4,5, 于秀晶1,2, 潘春晓1, 邱译萱1
- 1.吉林省气候中心,吉林 长春 130062
2.长白山气象与气候变化吉林省重点实验室,吉林 长春 130062
3.吉林省气象信息网络中心,吉林 长春 130062
4.吉林省气象科学研究所,吉林 长春 130062
5.中高纬度环流系统与东亚季风研究开放实验室,吉林 长春 130062
-
通讯作者:王玉昆(1972—),男,硕士,正高级工程师,主要研究气候变化与气象信息技术。E-mail:21662113@qq.com 。 -
作者简介:姜忠宝(1983—),男,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事气候变化与气候资源开发利用研究。E-mail: zb.jiang@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41875119);中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2022J007);吉林省科技发展计划重点研发项目(20230203135SF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIANG Zhongbao, WANG Yukun, YANG Xueyan, LI Shangfeng, YU Xiujing, PAN Chunxiao, QIU Yixuan. Characteristics of climate comfort period in Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 620-628.
姜忠宝, 王玉昆, 杨雪艳, 李尚锋, 于秀晶, 潘春晓, 邱译萱. 1961—2018年长白山气候舒适期变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 620-628.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0620
| 温湿指数(THI) | 风效指数(K) | 着衣指数(ICL) | 级别及赋值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分级值 | 感觉程度 | 分级值 | 感觉程度 | 分级值 | 适宜衣着 | 级别 | 赋值 |
| <40 | 极冷,极不舒适 | <-1 200 | 极冷 | >2.5 | 羽绒或毛皮衣 | e | 1 |
| 40~<45 | 寒冷,不舒适 | -1 200~<-1 000 | 冷 | >1.8~2.5 | 便服加坚实外套 | d | 3 |
| 45~<55 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -1 000~<-800 | 冷凉 | >1.5~1.8 | 冬季常用服装 | c | 5 |
| 55~<60 | 清凉,舒适 | -800~<-600 | 凉 | >1.3~1.5 | 春秋常用便服 | b | 7 |
| 60~<65 | 凉,非常舒适 | -600~<-300 | 舒适 | >0.7~1.3 | 衬衫和常用便服 | A | 9 |
| 65~<70 | 暖,舒适 | -300~<-200 | 暖 | >0.5~0.7 | 轻便的夏装 | B | 7 |
| 70~<75 | 偏热,较舒适 | -200~<-50 | 暖热 | >0.3~0.5 | 短袖开领衫 | C | 5 |
| 75~<80 | 闷热,不舒适 | -50~<80 | 热 | >0.1~0.3 | 热带单衣 | D | 3 |
| ≥80 | 极闷热,极不舒适 | ≥80 | 炎热 | ≤0.1 | 超短裙 | E | 1 |
Tab.1 Grade standard and their values of THI, K and ICL
| 温湿指数(THI) | 风效指数(K) | 着衣指数(ICL) | 级别及赋值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分级值 | 感觉程度 | 分级值 | 感觉程度 | 分级值 | 适宜衣着 | 级别 | 赋值 |
| <40 | 极冷,极不舒适 | <-1 200 | 极冷 | >2.5 | 羽绒或毛皮衣 | e | 1 |
| 40~<45 | 寒冷,不舒适 | -1 200~<-1 000 | 冷 | >1.8~2.5 | 便服加坚实外套 | d | 3 |
| 45~<55 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -1 000~<-800 | 冷凉 | >1.5~1.8 | 冬季常用服装 | c | 5 |
| 55~<60 | 清凉,舒适 | -800~<-600 | 凉 | >1.3~1.5 | 春秋常用便服 | b | 7 |
| 60~<65 | 凉,非常舒适 | -600~<-300 | 舒适 | >0.7~1.3 | 衬衫和常用便服 | A | 9 |
| 65~<70 | 暖,舒适 | -300~<-200 | 暖 | >0.5~0.7 | 轻便的夏装 | B | 7 |
| 70~<75 | 偏热,较舒适 | -200~<-50 | 暖热 | >0.3~0.5 | 短袖开领衫 | C | 5 |
| 75~<80 | 闷热,不舒适 | -50~<80 | 热 | >0.1~0.3 | 热带单衣 | D | 3 |
| ≥80 | 极闷热,极不舒适 | ≥80 | 炎热 | ≤0.1 | 超短裙 | E | 1 |
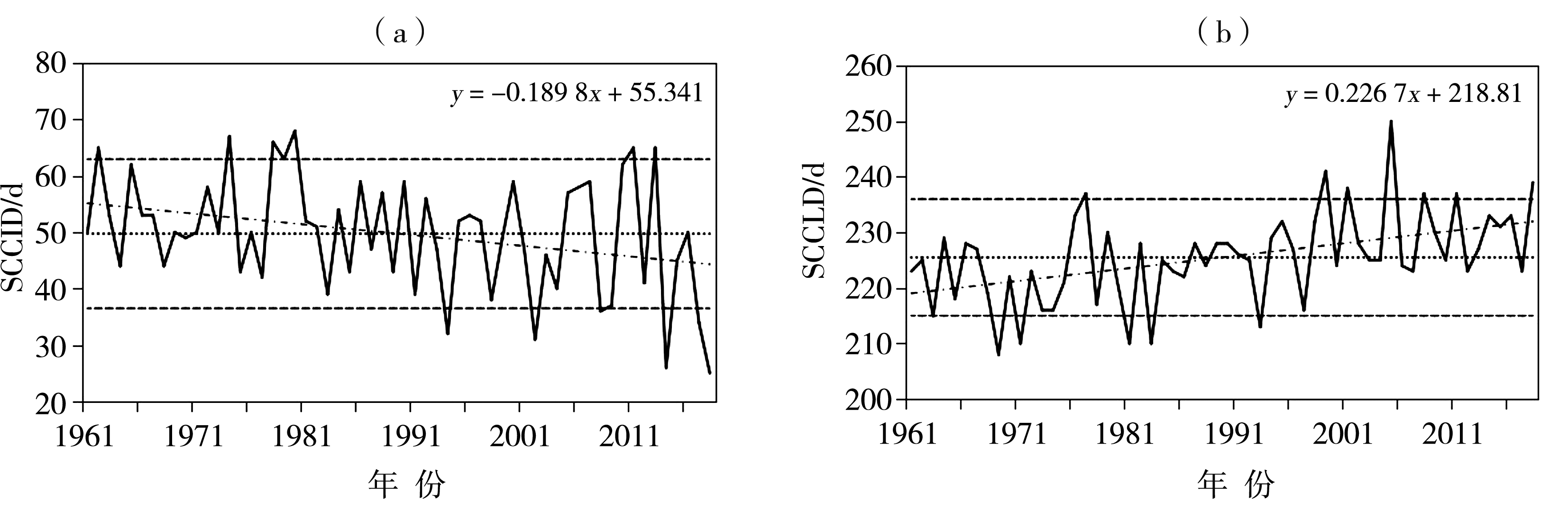
Fig.1 Annul variations of SCCID (a) and SCCLD (b) in the Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018 (The solid line is the annual change sequence, the dotted line is the average value, the dot-dash line is the linear trend, and the black dashed lines are ±1.28σ)
| 时段 | SCCID | SCCLD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日期 | 距平/d | 日期 | 距平/d | ||
| 1961—1970 | 4月21日 | +2 | 10月7日 | -5 | |
| 1971—1980 | 4月25日 | +6 | 10月8日 | -4 | |
| 1981—1990 | 4月19日 | 0 | 10月9日 | -3 | |
| 1991—2000 | 4月17日 | -2 | 10月13日 | +2 | |
| 2001—2010 | 4月16日 | -3 | 10月17日 | +6 | |
| 2011—2018 | 4月13日 | -6 | 10月17日 | +6 | |
| 1961—2018 | 4月19日 | 10月11日 | |||
Tab.2 Decadal average date and anomaly of SCCID and SCCLD in the Changbai Mountain region
| 时段 | SCCID | SCCLD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日期 | 距平/d | 日期 | 距平/d | ||
| 1961—1970 | 4月21日 | +2 | 10月7日 | -5 | |
| 1971—1980 | 4月25日 | +6 | 10月8日 | -4 | |
| 1981—1990 | 4月19日 | 0 | 10月9日 | -3 | |
| 1991—2000 | 4月17日 | -2 | 10月13日 | +2 | |
| 2001—2010 | 4月16日 | -3 | 10月17日 | +6 | |
| 2011—2018 | 4月13日 | -6 | 10月17日 | +6 | |
| 1961—2018 | 4月19日 | 10月11日 | |||
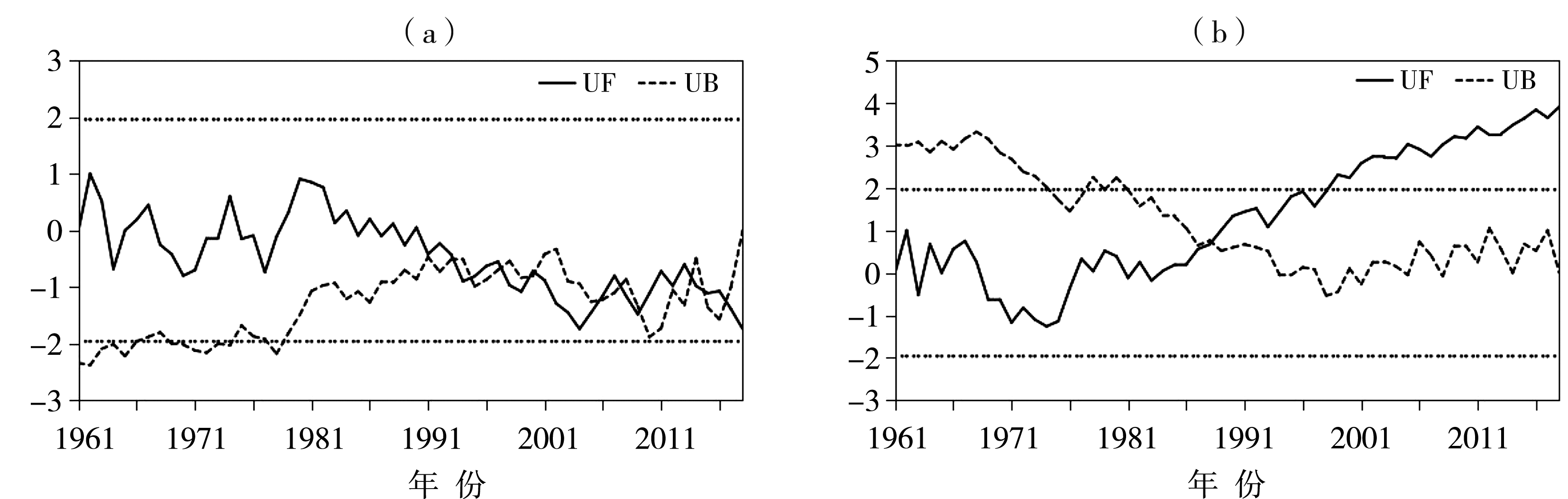
Fig.2 Mann-Kendall test curves of SCCID (a) and SCCLD (b) in the Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018 (The dashed line is the critical value of the significance level of α=0.05)
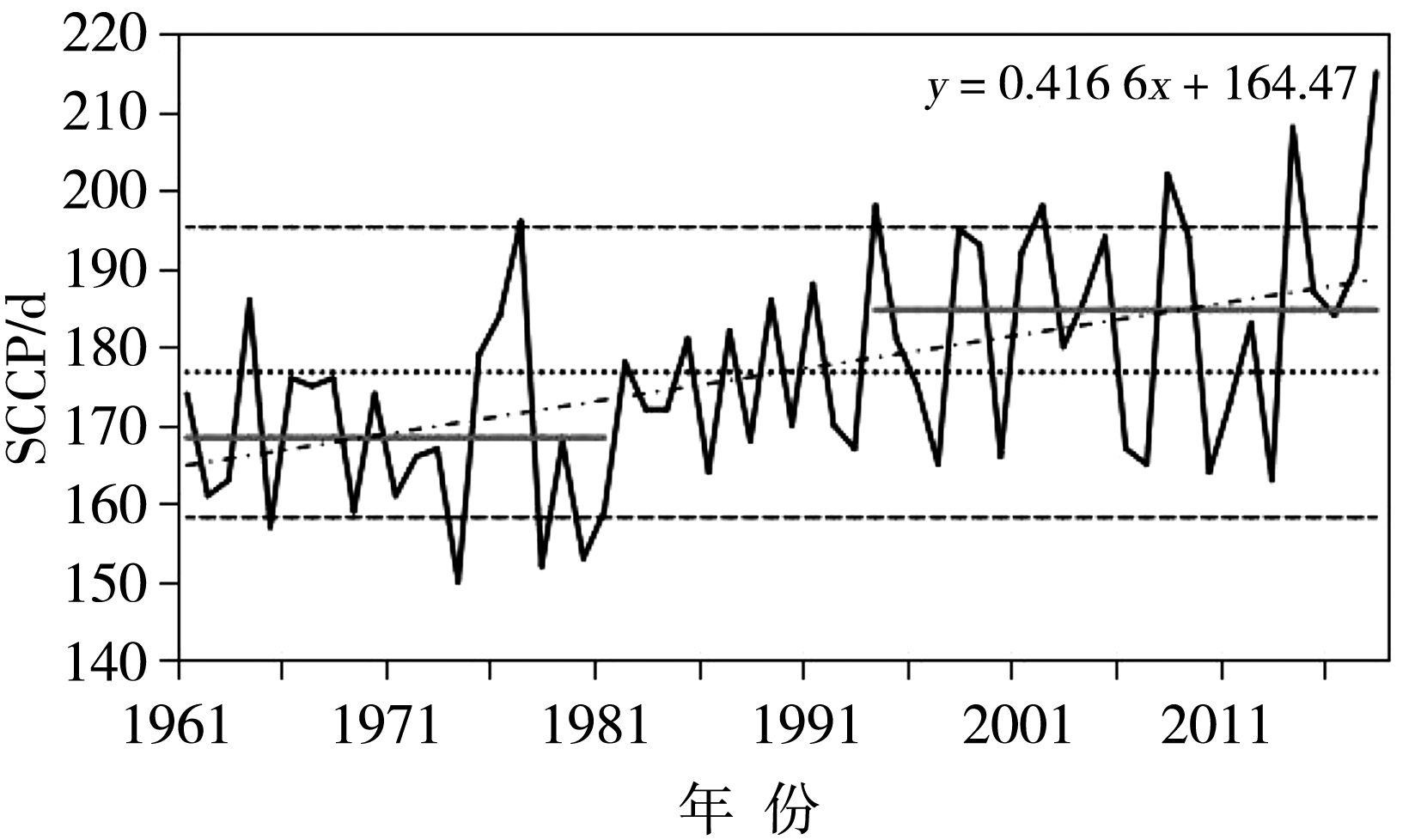
Fig.3 Variation of annual SCCP in the Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018 (The solid line is the annual change sequence, the dotted line is the average, the dot-dash line is the linear trend, and the dashed lines are ±1.28σ)
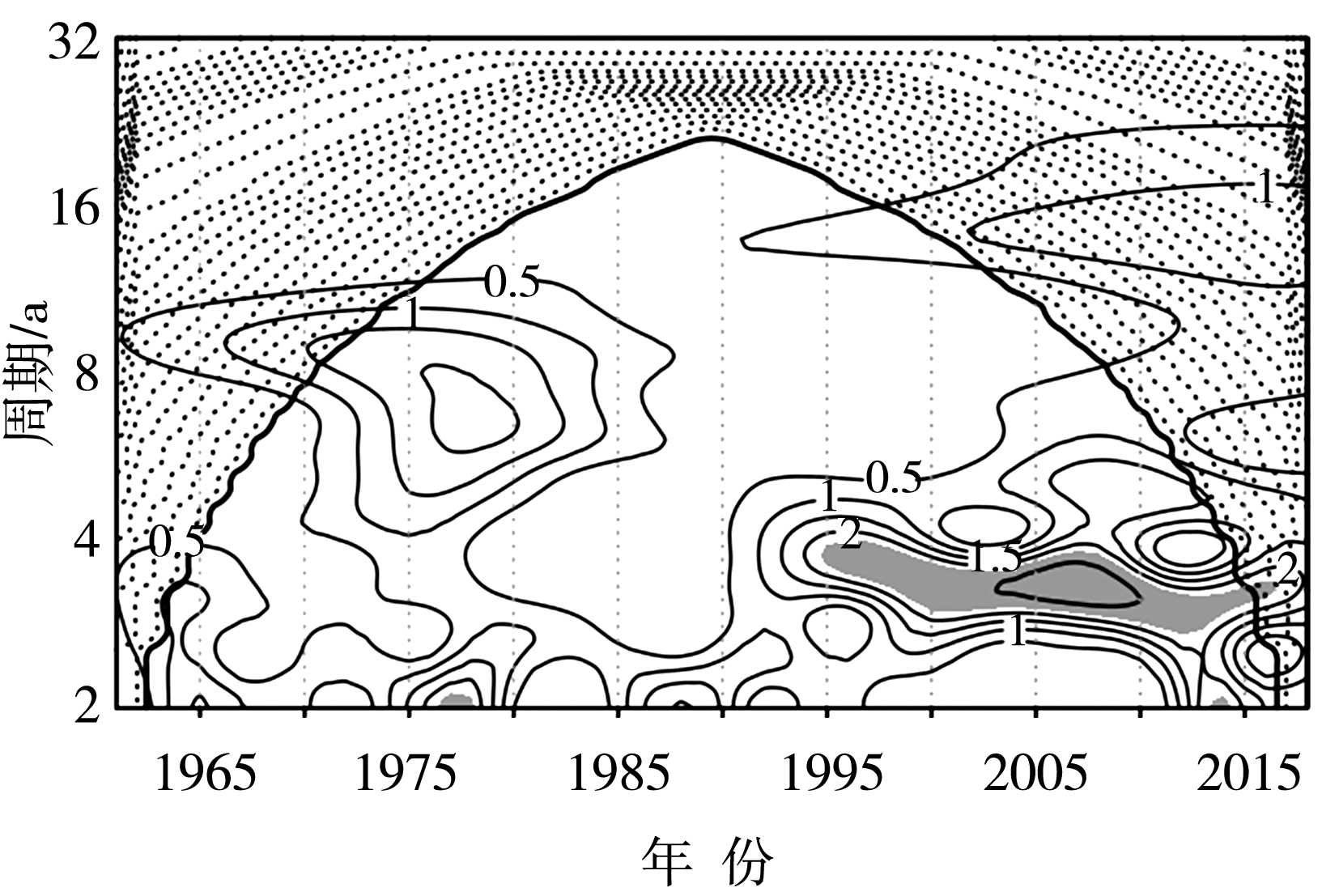
Fig.4 Morlet wavelet transform power spectrum of SCCP in the Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018 (The shaded means passing the significance test at 90% confidence level, the dotted means the area affected by the boundary)
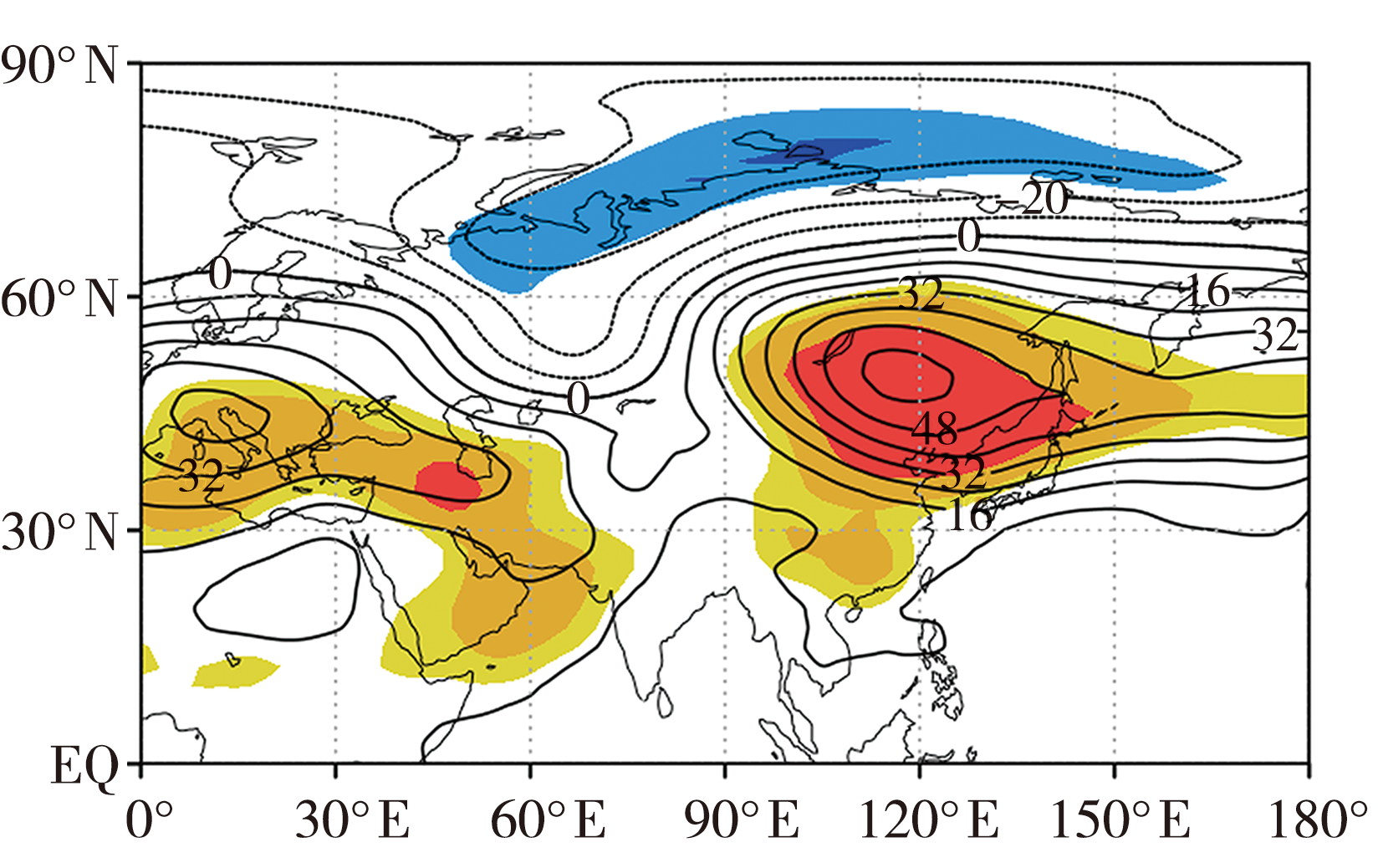
Fig.5 Distribution of difference of 500 hPa height field in spring between the abnormally early years and abnormally late years of SCCID (Unit: m) (The yellow or light blue, orange or dark blue, red shaded areas mean passing the significance test at the confidence levels of 90%, 95% and 99%, respectively)

Fig.6 The distribution of 500 hPa height anomaly field composition in spring in the abnormally early years (a) and abnormally late years (b) of SCCID (Unit: m)
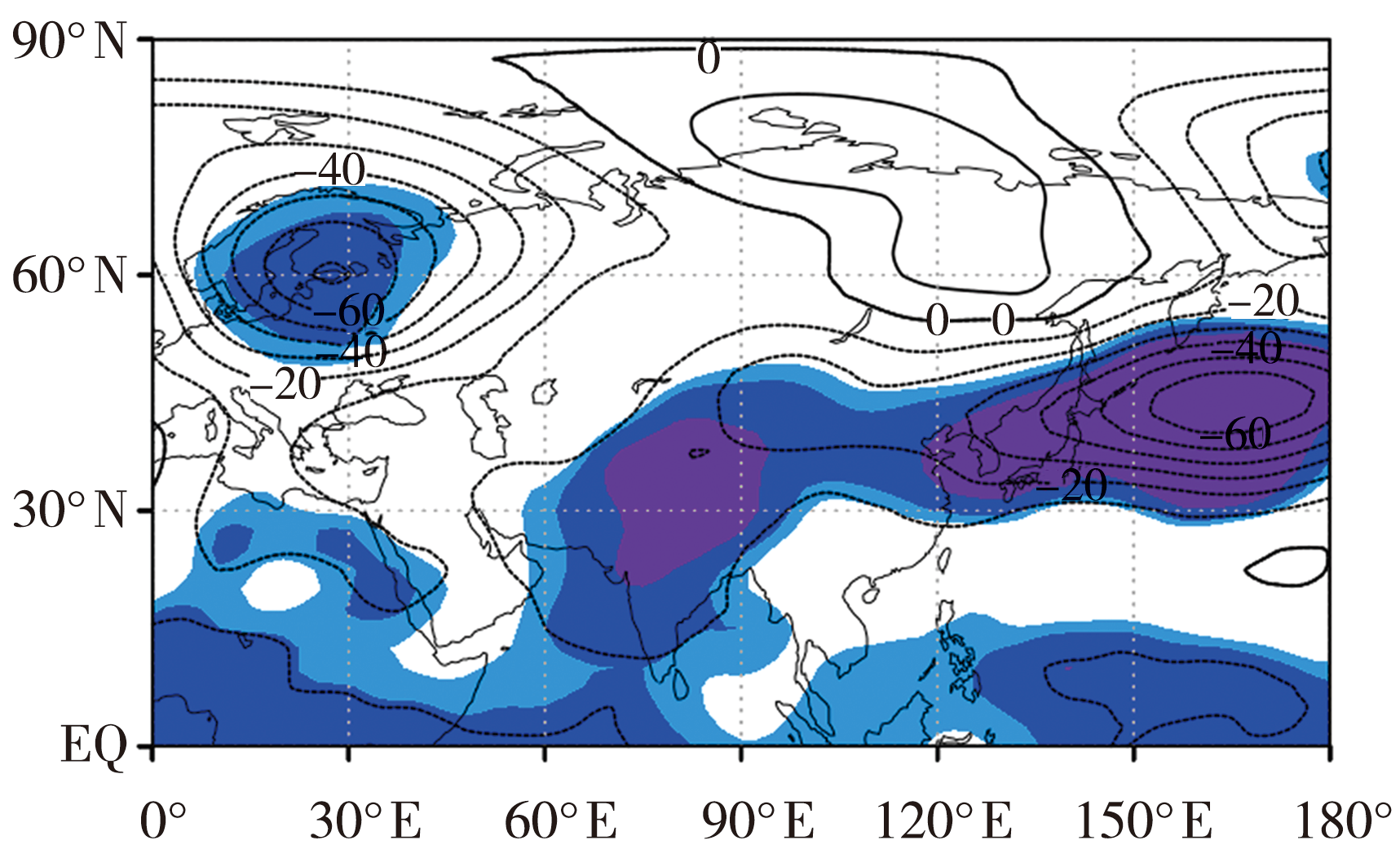
Fig.7 Distribution of difference of 500 hPa height field in autumn between the abnormally early years and abnormally late years of SCCLD (Unit: m) (The light blue, dark blue and purple shaded areas show the confidence levels are 90%, 95% and 99%, respectively)
| 月份 | THI | 感觉 | K | 感觉 | ICL | 适宜着衣 | CCI | 评价结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1月 | 10.0 | 极冷极不舒适 | -1 127.5 | 冷 | 3.71 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 2.2 | 不舒适 |
| 2月 | 17.0 | 极冷极不舒适 | -1 053.8 | 冷 | 3.41 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 2.2 | 不舒适 |
| 3月 | 31.1 | 极冷极不舒适 | -878.6 | 冷凉 | 2.74 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 3.4 | 较不舒适 |
| 4月 | 45.1 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -644.6 | 凉 | 2.03 | 便服加坚实外套 | 6.0 | 较舒适 |
| 5月 | 54.5 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -453.1 | 舒适 | 1.53 | 传统冬季常用服 | 7.4 | 舒适 |
| 6月 | 61.3 | 凉,非常舒适 | -311.8 | 舒适 | 1.18 | 衬衫和常用服 | 9.0 | 舒适 |
| 7月 | 67.2 | 暖,舒适 | -228.5 | 暖 | 0.92 | 衬衫和常用服 | 7.2 | 舒适 |
| 8月 | 65.5 | 暖,舒适 | -245.3 | 暖 | 1.00 | 衬衫和常用服 | 7.2 | 舒适 |
| 9月 | 54.3 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -400.0 | 舒适 | 1.51 | 传统冬季常用服 | 7.4 | 舒适 |
| 10月 | 43.3 | 寒冷,较不舒适 | -617.1 | 凉 | 2.08 | 便服加坚实外套 | 5.4 | 较舒适 |
| 11月 | 29.1 | 极冷极不舒适 | -870.1 | 冷凉 | 2.77 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 3.4 | 较不舒适 |
| 12月 | 15.0 | 极冷极不舒适 | -1072.4 | 冷 | 3.45 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 2.2 | 不舒适 |
Tab.3 Evaluation results of THI, K and ICL and CCI
| 月份 | THI | 感觉 | K | 感觉 | ICL | 适宜着衣 | CCI | 评价结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1月 | 10.0 | 极冷极不舒适 | -1 127.5 | 冷 | 3.71 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 2.2 | 不舒适 |
| 2月 | 17.0 | 极冷极不舒适 | -1 053.8 | 冷 | 3.41 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 2.2 | 不舒适 |
| 3月 | 31.1 | 极冷极不舒适 | -878.6 | 冷凉 | 2.74 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 3.4 | 较不舒适 |
| 4月 | 45.1 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -644.6 | 凉 | 2.03 | 便服加坚实外套 | 6.0 | 较舒适 |
| 5月 | 54.5 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -453.1 | 舒适 | 1.53 | 传统冬季常用服 | 7.4 | 舒适 |
| 6月 | 61.3 | 凉,非常舒适 | -311.8 | 舒适 | 1.18 | 衬衫和常用服 | 9.0 | 舒适 |
| 7月 | 67.2 | 暖,舒适 | -228.5 | 暖 | 0.92 | 衬衫和常用服 | 7.2 | 舒适 |
| 8月 | 65.5 | 暖,舒适 | -245.3 | 暖 | 1.00 | 衬衫和常用服 | 7.2 | 舒适 |
| 9月 | 54.3 | 偏冷,较不舒适 | -400.0 | 舒适 | 1.51 | 传统冬季常用服 | 7.4 | 舒适 |
| 10月 | 43.3 | 寒冷,较不舒适 | -617.1 | 凉 | 2.08 | 便服加坚实外套 | 5.4 | 较舒适 |
| 11月 | 29.1 | 极冷极不舒适 | -870.1 | 冷凉 | 2.77 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 3.4 | 较不舒适 |
| 12月 | 15.0 | 极冷极不舒适 | -1072.4 | 冷 | 3.45 | 羽绒服或者毛衣 | 2.2 | 不舒适 |
| [1] | 曹伟宏, 何元庆, 李宗省, 等, 2012. 云南丽江旅游气候舒适度分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 34(1): 201-206. |
| [2] | 曹云, 孙应龙, 吴门新, 2019. 近50年京津冀气候舒适度的区域时空特征分析[J]. 生态学报, 39(20): 7 567-7 582. |
| [3] | 陈乾金, 张永山, 1995. 华北异常初终霜冻气候特征的研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 4(2): 33-39. |
| [4] | 范业正, 郭来喜, 1998. 中国海滨旅游地适宜性评价[J]. 自然资源学报, 13(4): 304-311. |
| [5] | 冯新灵, 罗隆诚, 张群芳, 等, 2006. 中国西部著名风景名胜区旅游舒适气候研究与评价[J]. 干旱区地理, 29(4): 598-608. |
| [6] | 胡桂萍, 李正泉, 邓霞君, 2015. 丽水市旅游气候舒适度分析[J]. 气象科技, 43(4): 769-774. |
| [7] | 孔钦钦, 葛全胜, 席建超, 等, 2015. 中国重点旅游城市气候舒适度及其变化趋势[J]. 地理研究, 34(12): 2 238-2 246. |
| [8] | 孔钦钦, 郑景云, 王新歌, 2016. 1979—2014年中国气候舒适度空间格局及时空变化[J]. 资源科学, 38(6): 1 129-1 139. |
| [9] | 刘清春, 王铮, 许世远, 2007. 中国城市旅游气候舒适性分析[J]. 资源科学, 29(1): 133-140. |
| [10] |
卢珊, 王百朋, 张宏芳, 2015. 1971—2010年陕西省气候舒适度变化特征及区划[J]. 干旱气象, 33(6): 987-993.
DOI |
| [11] |
马蕾, 赵蔚, 杨柳, 等, 2023. 宁夏“星空旅游”气候资源适宜度评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 309-317.
DOI |
| [12] | 马丽君, 孙根年, 李玲芬, 等, 2008. 海口旅游气候舒适度与客流量年内变化相关分析[J]. 资源科学, 30(11): 1 754-1 759. |
| [13] | 马丽君, 孙根年, 马彦如, 等, 2011a. 30年来西安市气候舒适度变化对旅游客流量的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 25(9): 191-196. |
| [14] | 马丽君, 孙根年, 马彦如, 等, 2011b. 50年来北京旅游气候舒适度变化分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 25(10): 161-166. |
| [15] | 聂云, 周继先, 杨群, 等, 2021. 贵州梵净山旅游气候舒适度分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(4): 585-592. |
| [16] | 任健美, 牛俊杰, 胡彩虹, 等, 2004. 五台山旅游气候及其舒适度评价[J]. 地理研究, 23(6): 856-861. |
| [17] |
孙滢悦, 杨青山, 陈鹏, 2019. 长白山景区旅游安全风险动态评价研究[J]. 地理科学, 39(5): 770-778.
DOI |
| [18] | 王洪桥, 孟祥君, 吴正方, 2012. 吉林省旅游气候舒适度时空差异分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 26(1): 141-148. |
| [19] | 王金亮, 王平, 1999. 香格里拉旅游气候的适宜度[J]. 热带地理, 19(3): 235-239. |
| [20] |
王胜, 田红, 谢五三, 等, 2012. 近50年安徽省气候舒适度变化特征及区划研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 31(1): 40-45.
DOI |
| [21] | 王树廷, 1982. 关于日平均气温稳定通过各级界限温度初终日期的统计方法[J]. 气象, 8(6): 29-30. |
| [22] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 69-72. |
| [23] | 吴昊旻, 周国华, 姜燕敏, 等, 2020. 浙江丽水市度假气候适宜度评价[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 66-72. |
| [24] | 吴普, 席建超, 葛全胜, 2010. 中国旅游气候学研究综述[J]. 地理科学进展, 29(2): 131-137. |
| [25] | 许善洋, 石培宏, 薛治国, 等, 2018. 甘肃省气候舒适度时空分异特征研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 12(2): 57-62. |
| [26] | 张曦月, 姜超, 孙建新, 等, 2018. 气候舒适度在不同海拔的时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(9): 2 808-2 818. |
| [27] | 张莹, 马敏劲, 王式功, 等, 2013. 中国大陆九大名山风景区旅游气候舒适度评价[J]. 气象, 39(9): 1 221-1 226. |
| [28] | 赵小艳, 申双和, 孙虎声, 2008. 南京旅游气候舒适度的探讨[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 31(2): 250-256. |
| [29] | HOUGHTON D D, 1985. Handbook of Applied Meteorology[M]. New York: John Wiley &Son’s.Inc.:778-811. |
| [30] | De FREITAS C R, 1979. Human climates of Northern China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 13(1): 71-77. |
| [31] | JARQUE C M, BERA A K, 1980. Efficient tests for normality, homoscedasticity and serial independence. Economics Letters, 6(3): 255-259. |
| [32] | OLIVER J E, 1973. Climate and Man’s Environment: An Introduction to Applied Climatology[M]. New York: John Wiley &son’s Inc.: 195-206. |
| [33] | KALNAY E, KANAMITSU M, KISTLER R, et al, 1996. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 77 (3): 437-472. |
| [34] | GREGORCZUK M, CENA K, 1967. Distribution of effective temperature over the surface of the earth[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 11(2): 145-149. |
| [35] | THOM E C, 1957. A new concept of cooling degree days[J]. Air Condition: Heat Ventil, 54(6): 73-80. |
| [36] | THOM E C, 1958. Cooling degree days[J]. Air Condition: Heat &Ventilation, 55: 65-72. |
| [37] | TERJUNG W H, 1966. Physiologic climates of the conterminous United States: A bioclimatic classification based on Man[J]. Physiological Climates, 5(1): 141-179. |
| [38] | YAGLOU C P, MINARD D, 1957. Control of heat casualties at military training centers[J]. AMA Archives of Industrial Health, 16(4): 302-316. |
| [1] |
WANG Yuetong , HE Dongpo , LI Zhongyan , WANG Shuo , CHEN Zaoyang.
Analysis of two meteorological drought events in Guizhou Province and establishment of drought prediction model based on machine learning
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 671-682.
|
| [2] | CHEN Xiaoxiao, HUANG Zhiyong, QIN Pengcheng, XIA Zhihong, YAO Yao, TANG Xingzhi, WANG Yingqiong. Atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature characteristics of summer high temperature anomaly in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 553-562. |
| [3] | WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [4] | XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922. |
| [5] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [6] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia. Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [7] | XU Weiping, MENG Xiangxin, GU Weizong, BO Zhongkai. Relationship between extremely low temperature in spring in Shandong Province and North Atlantic SST in preceding winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 202-211. |
| [8] | LU Shan, GUO Yong, ZHENG Jiangping, WANG Shigong. Study on Climate Comfort Degree and Its Health Care Effect in Three Tourist Cities of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 317-325. |
| [9] | WANG Jianjiang, MA Hao, YU Liping, GONG Liqing, WANG Chen. Analysis of Atmospheric Circulation Characteristics Associated with Autumn Drought over Zhejiang Province in 2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 1-7. |
| [10] | MA Youxuan, LI Wanzhi, WANG Lixia, BAI Wenrong, WANG Ziwen. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Atmospheric Circulation Diagnosis of Spring Drought Based on SPI in Qinghai Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 362-370. |
| [11] | LIU Xiaoran, HU Zuheng, LI Yonghua, TANG Hongyu. Variation Characteristics and Formation Cause of Cold and Warm Winter in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 404-410. |
| [12] | LUO Liansheng, XU Min, HE Dongyan. Interdecadal Characteristics of Summer Precipitation over Huaihe River Basinand the Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies Since 2000 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 540-549. |
| [13] | Lü Xingyue, RONG Yanshu, SHI Dandan. Reanalysis on the Causes of Continuous Drought from Autumn 2010 to Spring 2011 in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 198-208. |
| [14] | CAI Xinling, LI Yu, LI Qian, HU Shulan. Climatic Characteristics of Autumn Rain in Shaanxi and Their Relationship with Atmospheric Circulation and SST During 1961-2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 226-232. |
| [15] | HU Chunli1, LI Rongping1, WANG Ting1, LI Fei2, LI Linlin1. Forecast Model of Rice Harvest in Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 501-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
