Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 910-922.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0910
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
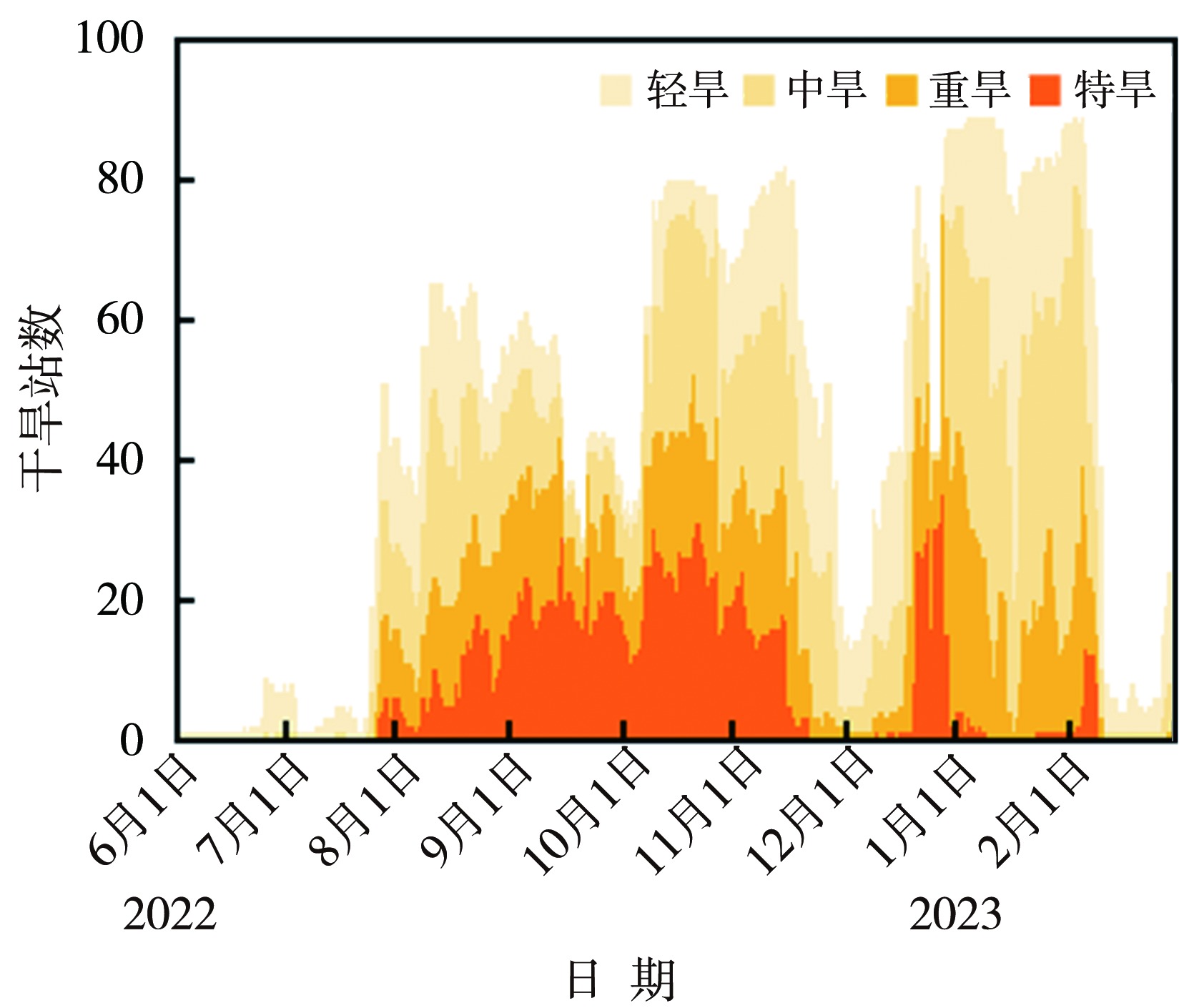
Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province
XIE Ao1,2( ), LUO Boliang1,2(
), LUO Boliang1,2( ), DENG Jianbo1,2, GAO Xiaxia1,2
), DENG Jianbo1,2, GAO Xiaxia1,2
- 1. Institute of Meteorological Science of Hunan Province, Changsha 410118, China
2. Key Laboratory of Preventing and Reducing Meteorological Disaster of Hunan Province, Changsha 410118, China
-
Received:2023-07-14Revised:2023-09-28Online:2023-12-31Published:2024-01-03
湖南2022/2023年夏秋冬季持续极端干旱事件特征及成因分析
谢傲1,2( ), 罗伯良1,2(
), 罗伯良1,2( ), 邓剑波1,2, 高霞霞1,2
), 邓剑波1,2, 高霞霞1,2
- 1.湖南省气象科学研究所,湖南 长沙 410118
2.气象防灾减灾湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410118
-
通讯作者:罗伯良(1965—),男,正高级工程师,主要从事气候诊断与预测。E-mail:luobailiang@163.com 。 -
作者简介:谢傲(1990—),女,工程师,主要从事气候诊断与预测。E-mail:xieao0209@163.com。 -
基金资助:湖南省自然科学基金重大专项(2021JC0009);湖南省自然科学基金项目(2023JJ60542)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922.
谢傲, 罗伯良, 邓剑波, 高霞霞. 湖南2022/2023年夏秋冬季持续极端干旱事件特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 910-922.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0910
| 干旱等级 | 干旱类型 | SPI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | -0.5<SPI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<SPI≤-0.5 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<SPI≤-1.0 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<SPI≤-1.5 |
| 5 | 特旱 | SPI≤-2.0 |
Tab.1 Classification of meteorological drought grade based on SPI
| 干旱等级 | 干旱类型 | SPI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | -0.5<SPI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<SPI≤-0.5 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<SPI≤-1.0 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<SPI≤-1.5 |
| 5 | 特旱 | SPI≤-2.0 |

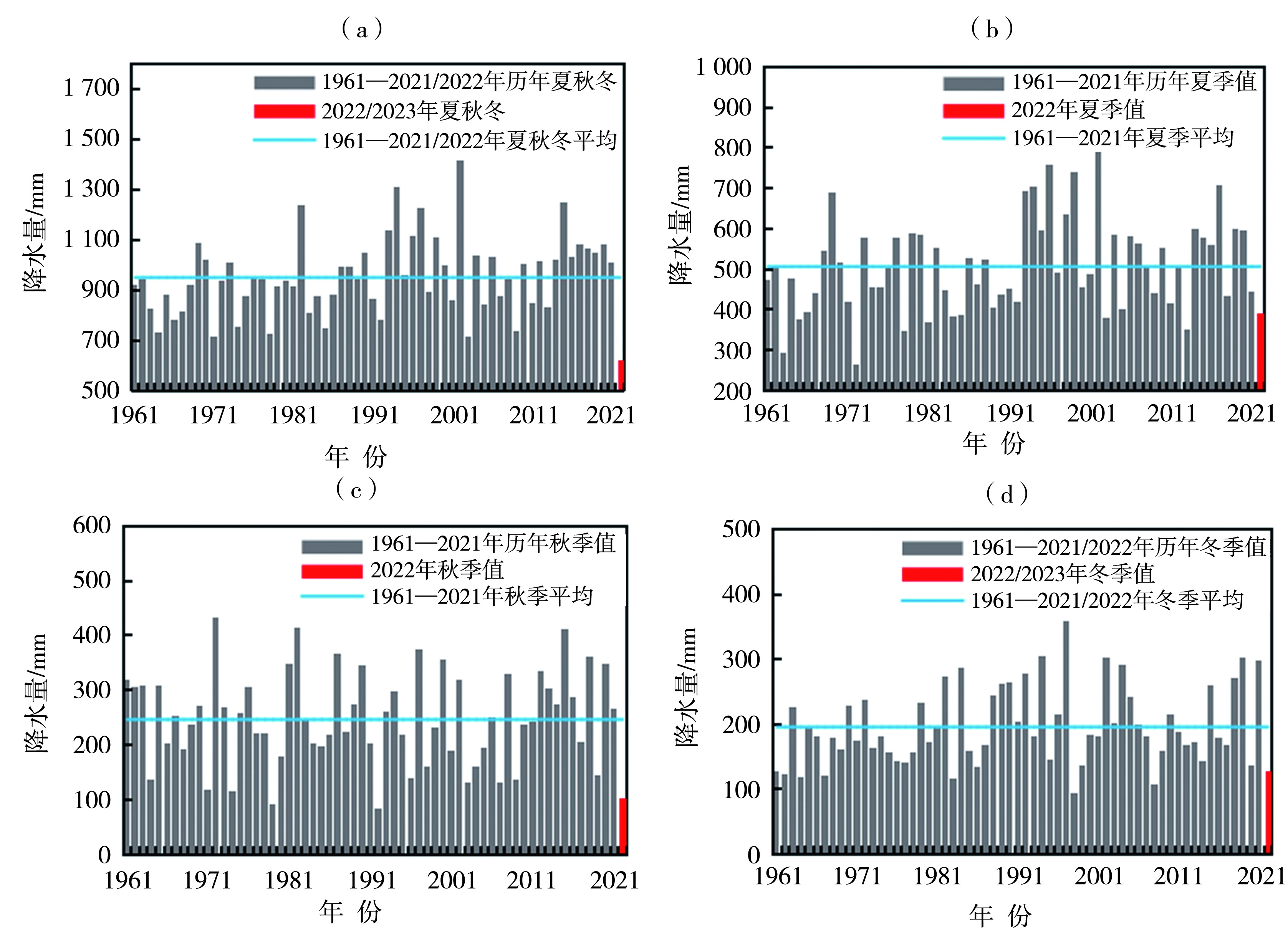
Fig.5 Time series of average air temperature (a) and regional high temperature days (b) from June to August during 1961-2022,and spatial distributions of temperature anomaly (c, Unit: ℃) and regional high temperature days anomaly (d, Unit: d) in Hunan from June to August 2022
| 月 份 | 面积指数 | 强度指数 | 脊线指数/°N | 北界指数/°N | 西伸脊点/°E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022年6月 | 2.0 | 59.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | -3.8 |
| 2022年7月 | 7.3 | 190.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -19.1 |
| 2022年8月 | 10.7 | 333.9 | 0.2 | 2.2 | -42.9 |
| 2022年9月 | 4.8 | 73.5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | -38.1 |
| 2022年10月 | 4.7 | 107.7 | 1.2 | 0.7 | -34.0 |
| 2022年11月 | 5.0 | 94.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 | -29.0 |
| 2022年12月 | -0.3 | -15.8 | -1.4 | -2.9 | 17.3 |
| 2023年1月 | -0.8 | -22.9 | 2.0 | -0.1 | 16.4 |
| 2023年2月 | -0.2 | -5.1 | 3.0 | -0.3 | 15.1 |
Tab.2 Monthly characteristic index anomalies of western Pacific subtropical high from June 2022 to February 2023
| 月 份 | 面积指数 | 强度指数 | 脊线指数/°N | 北界指数/°N | 西伸脊点/°E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022年6月 | 2.0 | 59.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | -3.8 |
| 2022年7月 | 7.3 | 190.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -19.1 |
| 2022年8月 | 10.7 | 333.9 | 0.2 | 2.2 | -42.9 |
| 2022年9月 | 4.8 | 73.5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | -38.1 |
| 2022年10月 | 4.7 | 107.7 | 1.2 | 0.7 | -34.0 |
| 2022年11月 | 5.0 | 94.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 | -29.0 |
| 2022年12月 | -0.3 | -15.8 | -1.4 | -2.9 | 17.3 |
| 2023年1月 | -0.8 | -22.9 | 2.0 | -0.1 | 16.4 |
| 2023年2月 | -0.2 | -5.1 | 3.0 | -0.3 | 15.1 |
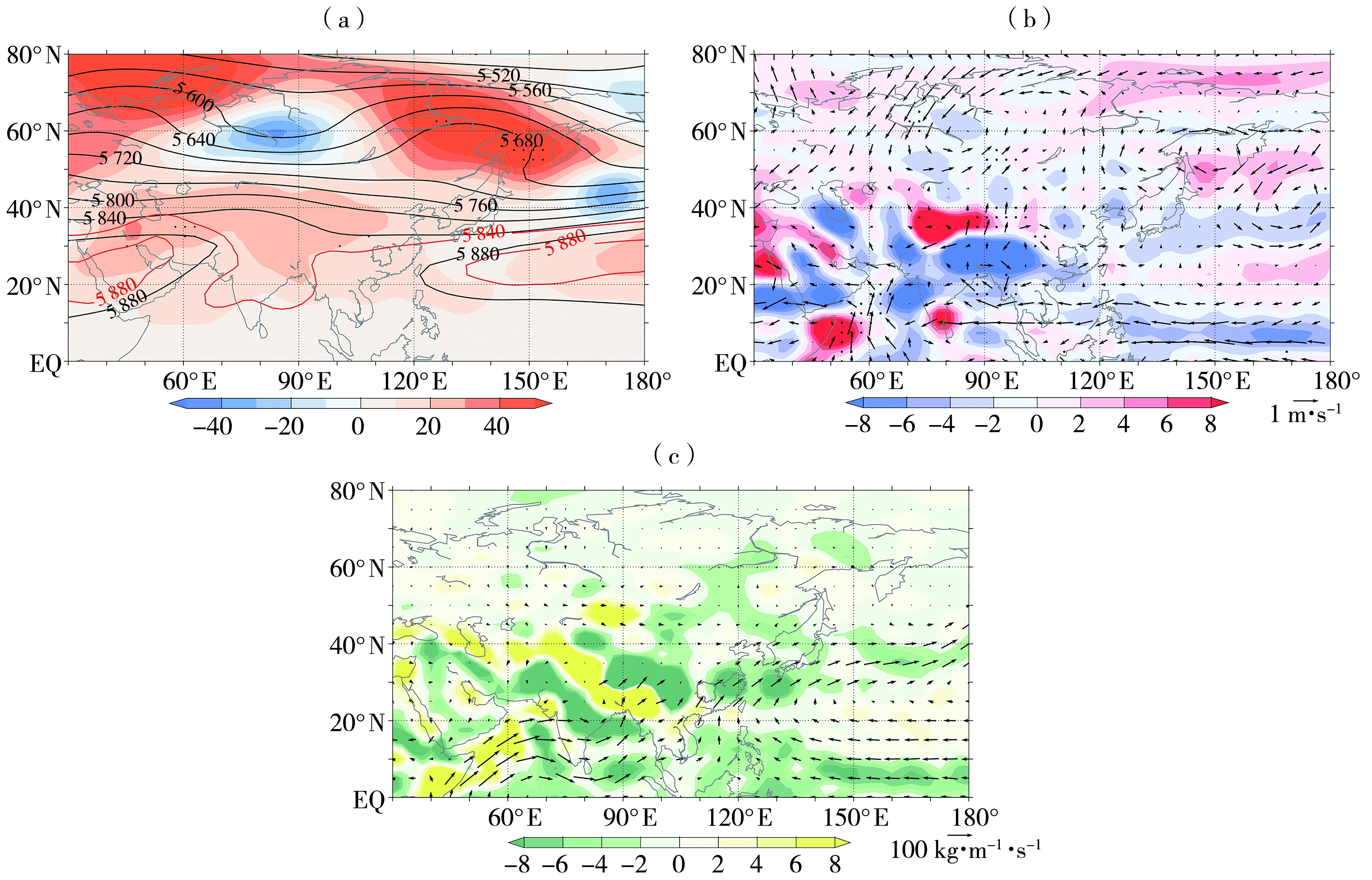
Fig.6 The 500 hPa geopotential height (black contours) and anomaly (color shaded, Unit: gpm) (a), the anomaly of 850 hPa horizontal wind (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and vertical wind speed (color shaded, Unit: 10-2 Pa·s-1) (b), and vertically integrated water vapor flux (vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence anomaly (color shaded, Unit: 10-7 kg·m-2·s-1) (c) from June to July 2022 (The red contours are climate state, the dotted area indicates that the anomaly exceeded the extreme value since 1981. the same as below)

Fig.7 The 500 hPa geopotential height (black contours) and anomaly (color shaded, Unit: gpm) (a), the anomaly of 850 hPa wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and vertical wind speed (color shaded, Unit: 10-2 Pa·s-1 ) (b), and vertically integrated water vapor flux (vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence anomaly (color shaded, Unit: 10-7 kg·m-2·s-1) (c) from August to November 2022

Fig.8 The 500 hPa geopotential height (black contours) and anomaly (color shaded, Unit: gpm) (a), the anomaly of 850 hPa wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and vertical velocity (color shaded, Unit: 10-2 Pa·s-1 ) (b), and vertically integrated water vapor flux (vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence anomaly (color shaded, Unit: 10-7 kg·m-2·s-1) (c) from December 2022 to the first ten-day period of February 2023
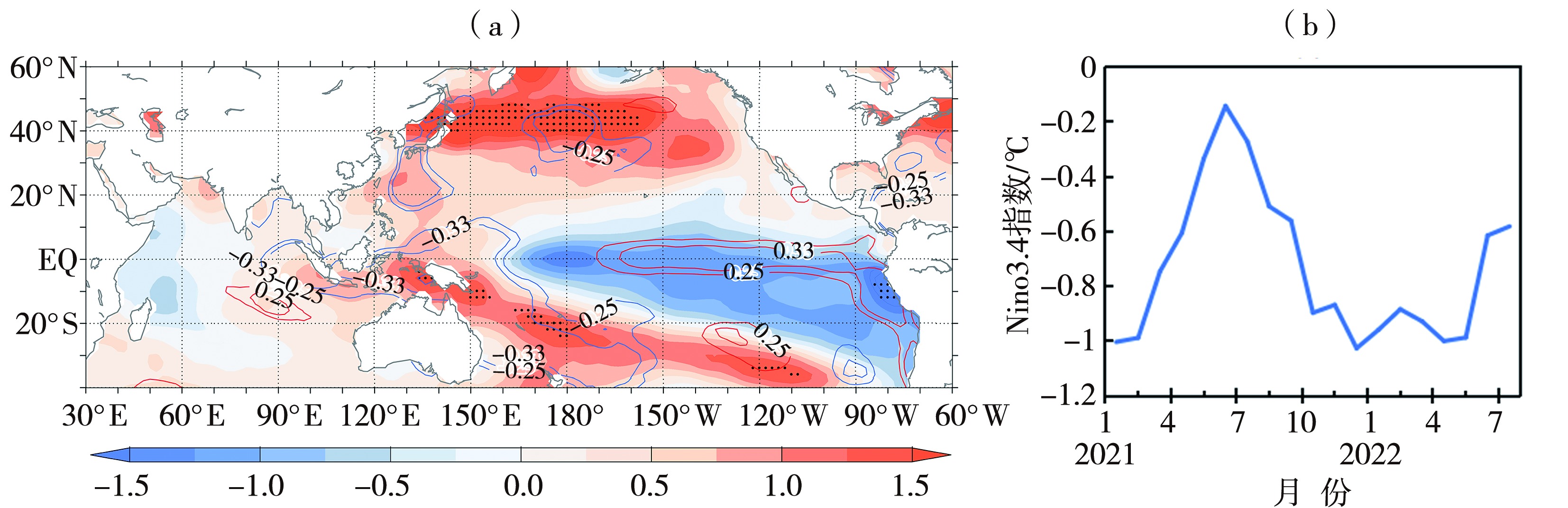
Fig.9 Correlation coefficient between the total precipitation in summer,autumn and winter in Hunan and SST in the Northern Hemisphere in early spring from 1981 to 2021/2022 (contours, only displaying contour lines that pass the significance test at α=0.10) and SSTA in spring of 2022 (color shaded, Unit: ℃) (a), and temporal evolution of Niño3.4 index from January 2021 to July 2022 (b)
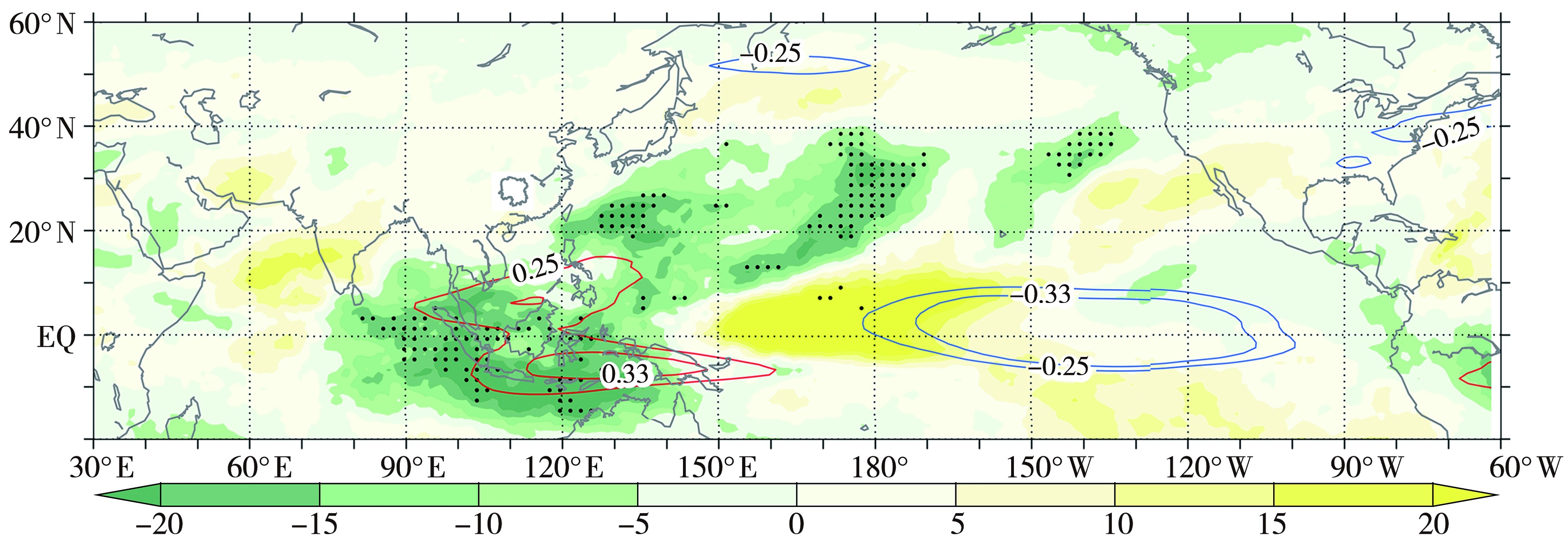
Fig.10 The distribution of correlation coefficient between the total precipitation in summer, autumn and winter in Hunan and the OLR at the same period from 1981 to 2021/2022 (contours, only displaying contour lines that pass significance test at α=0.10) and anomaly of the OLR from August 2022 to February 2023 (color shaded, Unit: W·m-2)

Fig.11 The longitude-height profiles of ω (Unit: Pa·s-1) and the wind field anomaly composition of u and ω (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) over the equatorial region (a, c, e) and the area between 24.5°N and 30.5°N (b, d, f) from June to July 2022 (a, b), from August to November 2022 (c, d) and from December 2022 to the first ten-day period of February 2023 (e, f)

Fig.12 The schematic diagram of the impact of SST and atmospheric circulation anomaly on persistent drought event in summer antumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan (The color shaded on the bottom map shows the SSTA from March to May in 2022, and the upper contours are 500 hPa potential height field from August to November 2022)
| [1] | 白超海, 2010. 湖南省干旱成因分析及对策研究[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 20(6): 20-22. |
| [2] | 国家气候中心, 中国气象局预报与网络司, 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 2017. 气象干旱等级: GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [3] |
韩兰英, 张强, 贾建英, 等, 2019. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱强度、频次和持续时间及其南北差异性[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(5): 1-10.
DOI |
| [4] | 冷春香, 2003. 西太平洋副高在1998年和2001年梅汛期长江大涝大旱中的作用[J]. 气象, 29(6): 7-11. |
| [5] | 李崇银, 穆明权, 2001. 赤道印度洋海温偶极子型振荡及其气候影响[J]. 大气科学, 25(4): 433-443. |
| [6] |
李忆平, 张金玉, 岳平, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季长江流域重大干旱特征及其成因研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 733-747.
DOI |
| [7] | 刘宣飞, 袁慧珍, 管兆勇, 2008. ENSO对IOD与中国夏季降水关系的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 24(5): 502-506. |
| [8] | 罗伯良, 彭莉莉, 张超, 2010. 2009年盛夏湖南持续高温干旱及同期大气环流异常分析[J]. 干旱气象, 28(1): 20-25. |
| [9] |
罗伯良, 李易芝, 2014. 2013年夏季湖南严重高温干旱及其大气环流异常[J]. 干旱气象, 32(4): 593-598.
DOI |
| [10] | 吕星玥, 荣艳淑, 石丹丹, 2019. 长江中下游地区2010/2011年秋冬春连旱成因再分析[J]. 干旱气象, 37(2): 198-208. |
| [11] | 马柱国, 2007. 华北干旱化趋势及转折性变化与太平洋年代际振荡的关系[J]. 科学通报, 52(10): 1 199-1 206. |
| [12] |
马鹏里, 韩兰英, 张旭东, 等, 2019. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱变化的区域特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(6): 209-215.
DOI |
| [13] | 裴文涛, 陈栋栋, 薛文辉, 等, 2019. 近55年来河西地区干旱时空演变特征及其与ENSO事件的关系[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 37(1): 250-258. |
| [14] |
彭莉莉, 戴泽军, 罗伯良, 等, 2015. 2013年夏季西太平洋副高异常特征及其对湖南高温干旱的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 33(2): 195-201.
DOI |
| [15] | 外力·吾甫尔, 严佩文, 黄丹青, 2020. 华南地区秋季无降水日的变化特征及其与海温的联系[J]. 热带气象学报, 36(1): 108-114. |
| [16] | 王婷, 章新平, 黎祖贤, 等, 2016. 近52年来洞庭湖流域气象干旱的时空分布特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 25(3): 514-522. |
| [17] | 汪文萍, 2003. 湖南旱灾的成因及对策[J]. 湖南农业科学, 32(6): 3-5. |
| [18] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [19] | 谢傲, 罗伯良, 2020. 湖南夏季降水与前期北太平洋海温异常的关系[J]. 气象与环境科学, 43(4) : 49-57. |
| [20] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [21] | 杨诗君, 易知之, 2023. 2022年湖南省干旱状况及应对措施分析[J]. 水利水电快报, 44(4): 19-23. |
| [22] | 殷田园, 殷淑燕, 李富民, 2019. 秦岭南北区域夏季极端降水与西太平洋副热带高压的关系[J]. 干旱区研究, 36(6): 1 379-1 390. |
| [23] | 张超, 罗伯良, 2021. 湖南夏秋季持续性区域气象干旱的时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 193-202. |
| [24] | 章大全, 袁媛, 韩荣青, 2023. 2022年夏季我国气候异常特征及成因分析[J]. 气象, 49(1): 110-121. |
| [25] | 张剑明, 居晶琳, 黎祖贤, 等, 2011. 湖南省农业旱灾的年际变化及重灾年份预测[J]. 自然灾害学报, 20(5): 105-110. |
| [26] | 张剑明, 廖玉芳, 彭嘉栋, 等, 2013. 湖南气象干旱日数的时空变化特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 34(6): 621-628. |
| [27] |
张剑明, 廖玉芳, 吴浩, 等, 2018. 湖南夏秋干旱及环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(3): 353-364.
DOI |
| [28] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(1): 758-773. |
| [29] |
张强, 2022. 科学解读“2022年长江流域重大干旱”[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 545-548.
DOI |
| [30] | 中国气象局, 2014. 中国气象灾害年鉴(2014)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 197. |
| [31] | ABRAMOWITZ M, STEGUN I A, 1964. Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables[M]. Washington D C: U.S. Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau of Standards. |
| [32] | DAI A, 2013. Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models[J]. Nature Climate Change, 3(1): 52-58. |
| [33] | HUANG B Y, THORNE P W, BANZON V F, et al, 2017. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature, version 5 (ERSSTv5): upgrades, validations, and intercomparisons[J]. Journal of Climate, 30(20): 8 179-8 205. |
| [34] | KALNAY E, KANAMITSU M, KISTLER R, et al, 1996. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 77(3): 437-471. |
| [35] | MA F, YUAN X, 2023. When will the unprecedented 2022 summer heat waves in Yangtze River Basin become normal in a warming climate?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 50(4), e2022GL101946, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2022GL101946. |
| [36] | MCKEE T B, DOESKEN N J, KLEIST J, 1993. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales[C]// In proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, California, American Meteorological Society: 179-184. |
| [37] | REYNOLDS R W, RAYNER N A, SMITH T M, et al, 2002. An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(13): 1 609-1 625. |
| [38] | WELLS N S, GODDARD , M J HAYES, 2004. A self-calibrating Palmer Drought Severity Index[J]. Journal of Climate, 17(12): 2 335-2 351. |
| [1] | WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [2] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [3] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia. Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [4] | XU Weiping, MENG Xiangxin, GU Weizong, BO Zhongkai. Relationship between extremely low temperature in spring in Shandong Province and North Atlantic SST in preceding winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 202-211. |
| [5] | LIU Shuyan, RONG Yanshu, LYU Xingyue, YIN Yuting. Comparative Analysis of Drought in China and the United States in 2012 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 717-726. |
| [6] | ZHANG Chao, LUO Boliang. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Persistent Regional Meteorological Drought in Summer and Autumn in Hunan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 193-202. |
| [7] | WANG Jianjiang, MA Hao, YU Liping, GONG Liqing, WANG Chen. Analysis of Atmospheric Circulation Characteristics Associated with Autumn Drought over Zhejiang Province in 2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 1-7. |
| [8] | MA Youxuan, LI Wanzhi, WANG Lixia, BAI Wenrong, WANG Ziwen. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Atmospheric Circulation Diagnosis of Spring Drought Based on SPI in Qinghai Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 362-370. |
| [9] | LIU Xiaoran, HU Zuheng, LI Yonghua, TANG Hongyu. Variation Characteristics and Formation Cause of Cold and Warm Winter in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 404-410. |
| [10] | LUO Liansheng, XU Min, HE Dongyan. Interdecadal Characteristics of Summer Precipitation over Huaihe River Basinand the Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies Since 2000 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 540-549. |
| [11] | Lü Xingyue, RONG Yanshu, SHI Dandan. Reanalysis on the Causes of Continuous Drought from Autumn 2010 to Spring 2011 in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 198-208. |
| [12] | CAI Xinling, LI Yu, LI Qian, HU Shulan. Climatic Characteristics of Autumn Rain in Shaanxi and Their Relationship with Atmospheric Circulation and SST During 1961-2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 226-232. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jianming, LIAO Yufang, WU Hao, ZHANG Jianjun, ZHAO Hui. Characteristics of Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies and Drought in Summer and Autumn in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 353-. |
| [14] | HU Chunli1, LI Rongping1, WANG Ting1, LI Fei2, LI Linlin1. Forecast Model of Rice Harvest in Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 501-. |
| [15] | QUE Zhiping, WU Fan, ZHOU Junhui. Rainfall Anomaly and Its Causes in Jiangxi Province in November 2015 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(2): 263-271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||