Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 897-909.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0897
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Drought and disaster variation characteristics in Guizhou based on Meteorological Drought Composite Index
XU Dan( ), LONG Li(
), LONG Li( ), ZHANG Donghai, REN Manlin, CHEN Juan
), ZHANG Donghai, REN Manlin, CHEN Juan
- Guizhou Climate Center, Guiyang 550002, China
-
Received:2023-06-02Revised:2023-11-26Online:2023-12-31Published:2024-01-03
基于MCI干旱综合指数的贵州省干旱时空分布及灾情变化特征
- 贵州省气候中心,贵州 贵阳 550002
-
通讯作者:龙俐(1979—),女,高级工程师,主要从事气候监测、风险评估研究。E-mail:x77043272@qq.com 。 -
作者简介:许丹(1969—),女,高级工程师,主要从事气候监测、气候变化研究。E-mail: xudan69@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41965010);及贵州省科技支撑计划项目(黔科合支撑[2021]508)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XU Dan, LONG Li, ZHANG Donghai, REN Manlin, CHEN Juan. Drought and disaster variation characteristics in Guizhou based on Meteorological Drought Composite Index[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 897-909.
许丹, 龙俐, 张东海, 任曼琳, 陈娟. 基于MCI干旱综合指数的贵州省干旱时空分布及灾情变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 897-909.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0897
| 无旱 | 轻旱 | 中旱 | 重旱 | 特旱 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI>-0.5 | -1.0<MCl≤-0.5 | -1.5<MCl≤-1.0 | -2.0<MCI≤-1.5 | MCI≤-2.0 |
Tab.1 Classification of drought grade based on MCI
| 无旱 | 轻旱 | 中旱 | 重旱 | 特旱 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI>-0.5 | -1.0<MCl≤-0.5 | -1.5<MCl≤-1.0 | -2.0<MCI≤-1.5 | MCI≤-2.0 |
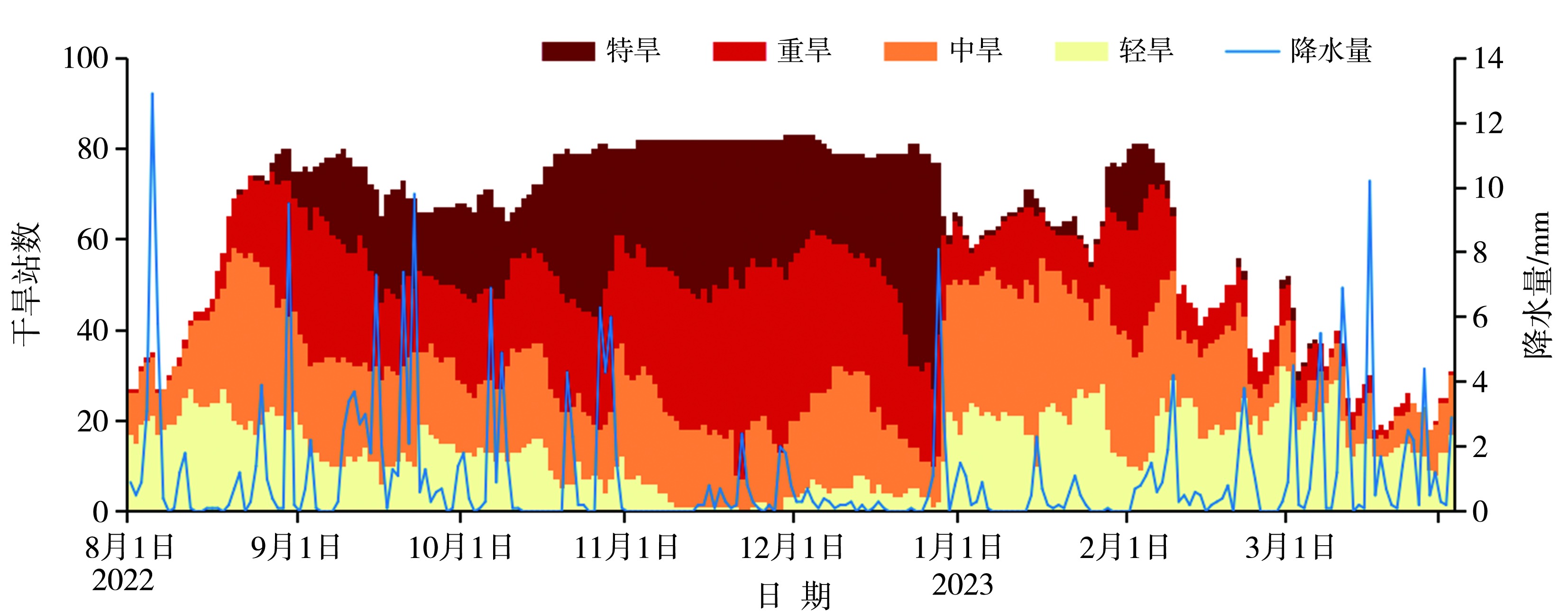
Fig.2 Evolution of daily station numbers of drought with different grades based on MCI and regional average precipitation during the continuous drought process in summer, autumn and winter of 2022/2023 in Guizhou Province
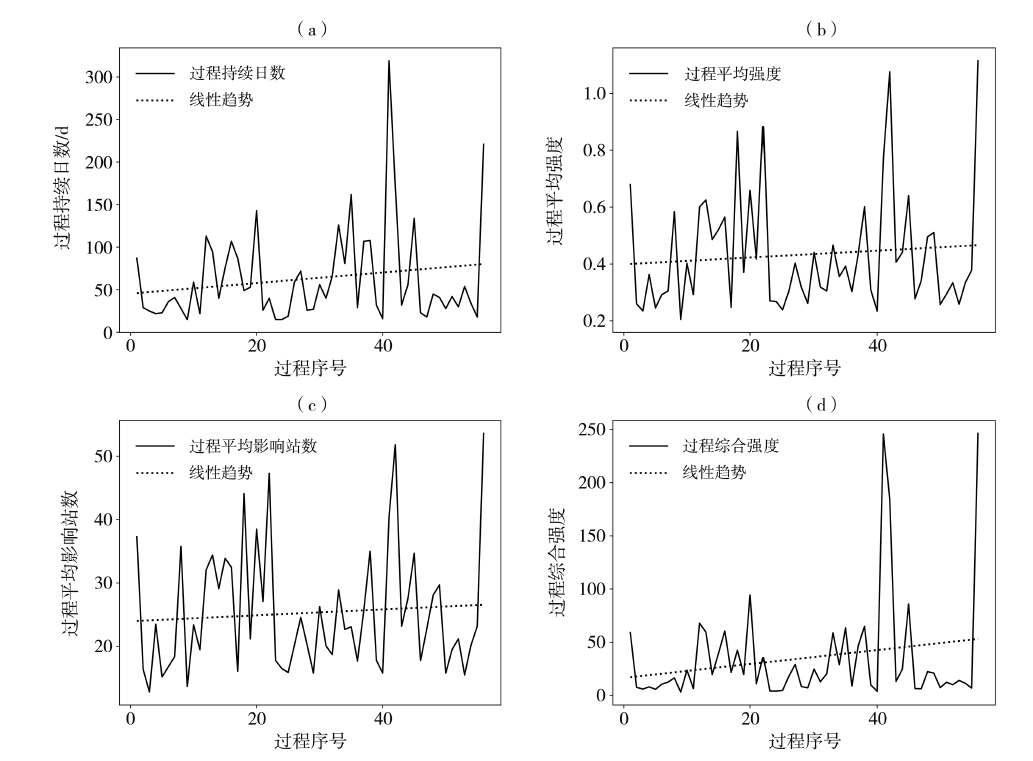
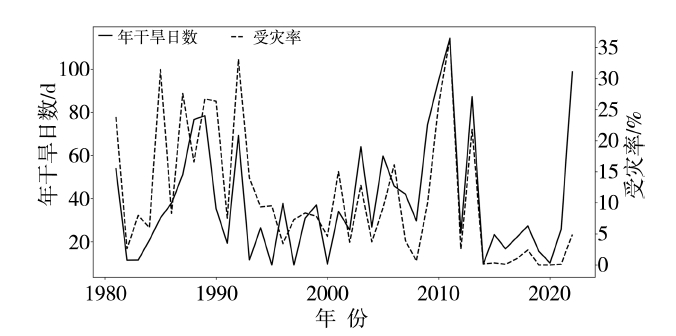
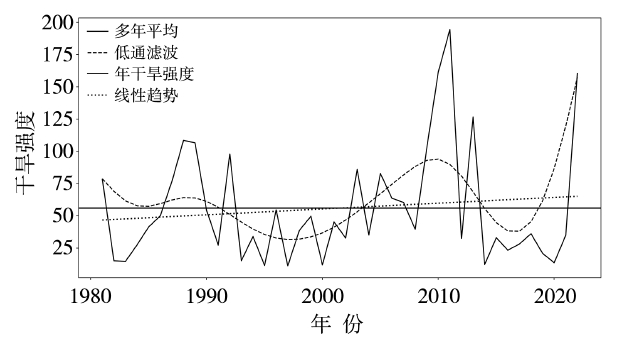
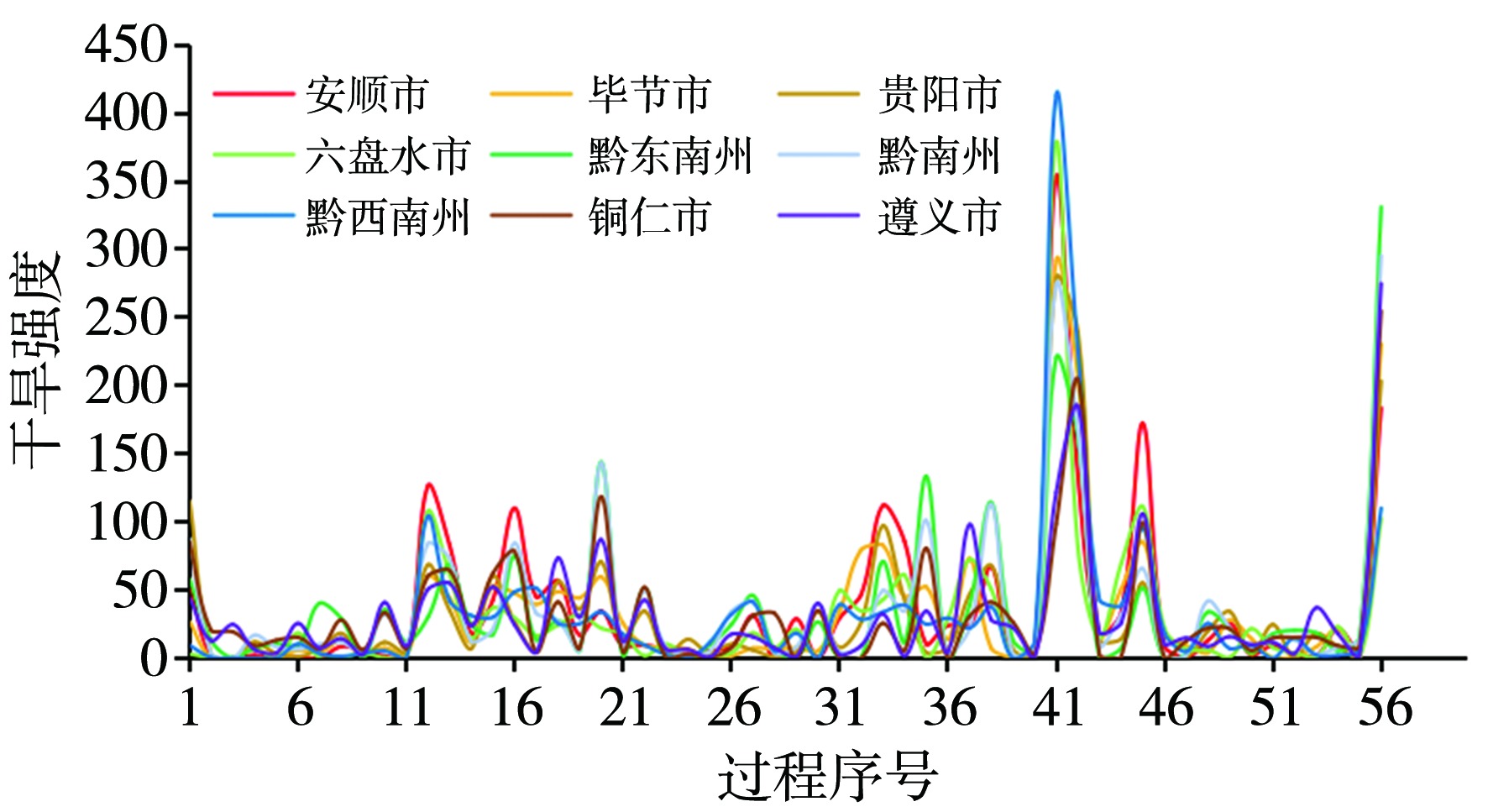
Fig.7 Variations of duration days (a),average intensity (b),average affected area (c) and comprehensive intensity index(d) of regional drought processes in Guizhou Province from 1981 to 2022
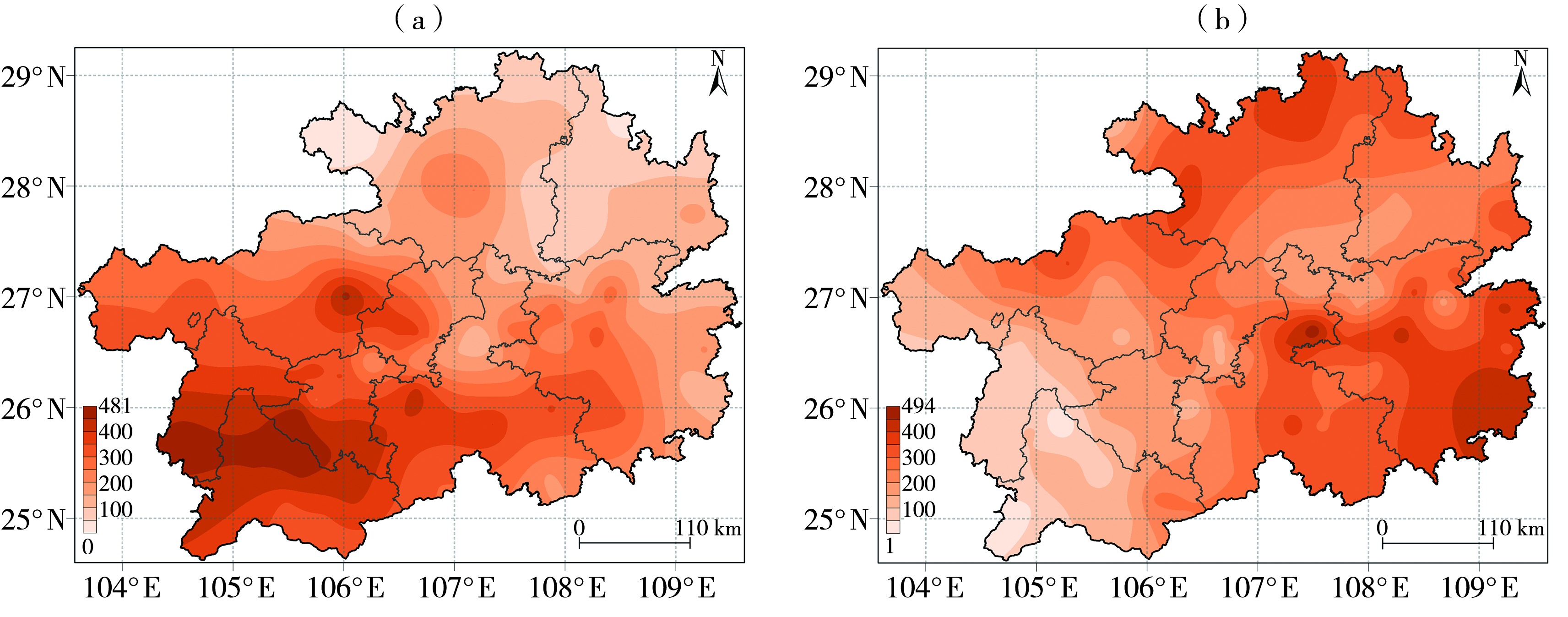
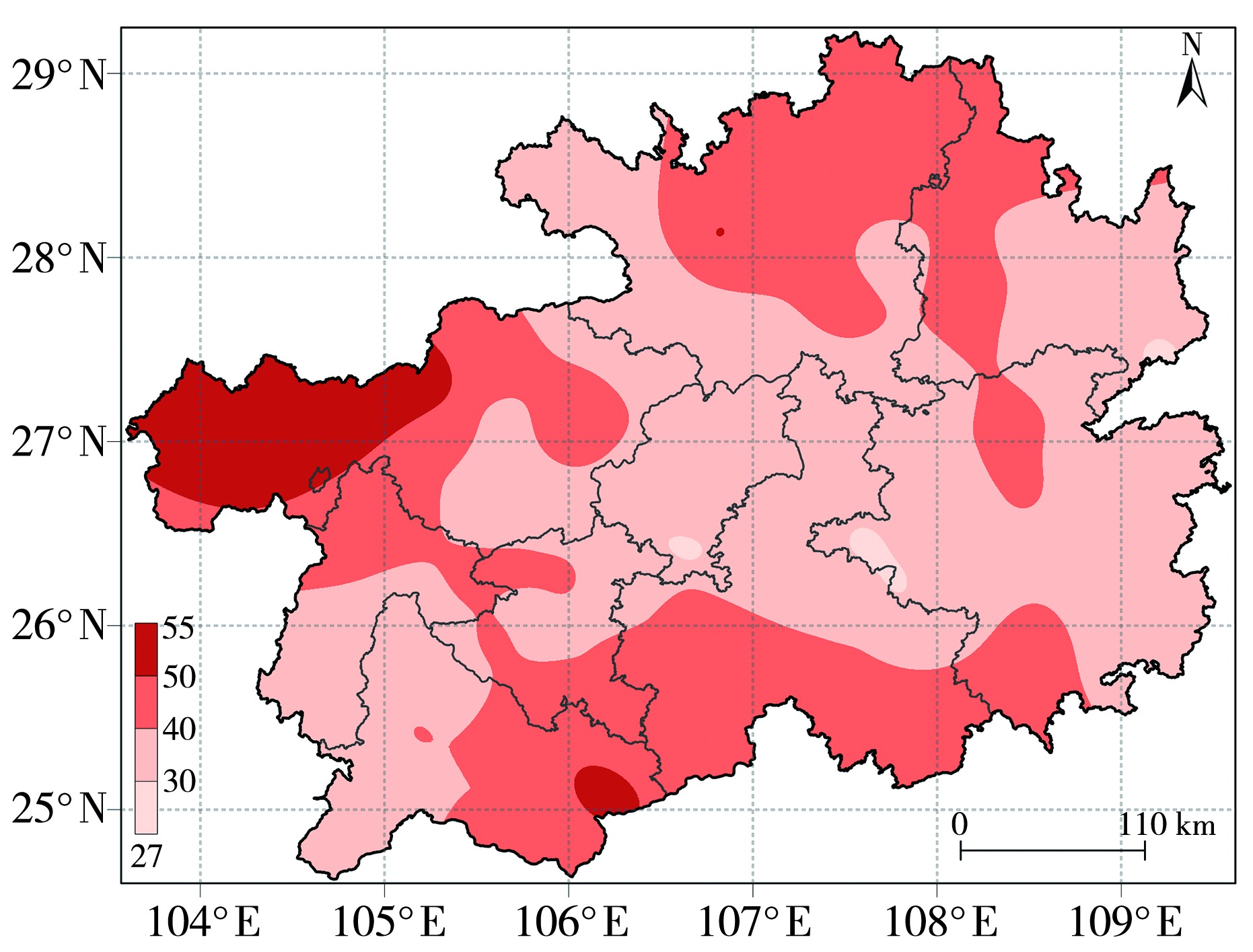
Fig.9 Spatial distribution of drought intensity during regional drought processes from 9 August 2009 to 23 June 2010 (a) and from 8 August 2022 to 16 March 2023 (b) in Guizhou Province
| 地区 | 时 段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981—2022 | 1981—1990 | 1991—2000 | 2001—2010 | 2011—2022 | |
| 全省 | 525.3 | 735.9 | 480.2 | 631.7 | 298.6 |
| 贵阳市 | 25.4 | 54.0 | 15.1 | 22.1 | 11.9 |
| 遵义市 | 99.9 | 149.6 | 94.2 | 115.1 | 46.1 |
| 铜仁市 | 55.7 | 85.6 | 38.2 | 79.7 | 22.8 |
| 黔东南州 | 42.9 | 64.4 | 26.2 | 58.6 | 24.1 |
| 黔南州 | 51.7 | 82.0 | 38.0 | 69.8 | 20.1 |
| 毕节市 | 115.2 | 167.1 | 122.3 | 143.7 | 35.6 |
| 六盘水市 | 29.3 | 31.9 | 23.1 | 45.0 | 19.2 |
| 安顺市 | 29.7 | 44.8 | 17.7 | 45.6 | 12.4 |
| 黔西南州 | 41.6 | 54.5 | 43.3 | 46.8 | 23.5 |
Tab.2
| 地区 | 时 段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981—2022 | 1981—1990 | 1991—2000 | 2001—2010 | 2011—2022 | |
| 全省 | 525.3 | 735.9 | 480.2 | 631.7 | 298.6 |
| 贵阳市 | 25.4 | 54.0 | 15.1 | 22.1 | 11.9 |
| 遵义市 | 99.9 | 149.6 | 94.2 | 115.1 | 46.1 |
| 铜仁市 | 55.7 | 85.6 | 38.2 | 79.7 | 22.8 |
| 黔东南州 | 42.9 | 64.4 | 26.2 | 58.6 | 24.1 |
| 黔南州 | 51.7 | 82.0 | 38.0 | 69.8 | 20.1 |
| 毕节市 | 115.2 | 167.1 | 122.3 | 143.7 | 35.6 |
| 六盘水市 | 29.3 | 31.9 | 23.1 | 45.0 | 19.2 |
| 安顺市 | 29.7 | 44.8 | 17.7 | 45.6 | 12.4 |
| 黔西南州 | 41.6 | 54.5 | 43.3 | 46.8 | 23.5 |

Fig.10 The spatial distribution of correlation coefficients between summer drought intensity in Guizhou Province and global sea surface temperature anomaly in previous spring (the dotted passing the significance test at α=0.05)
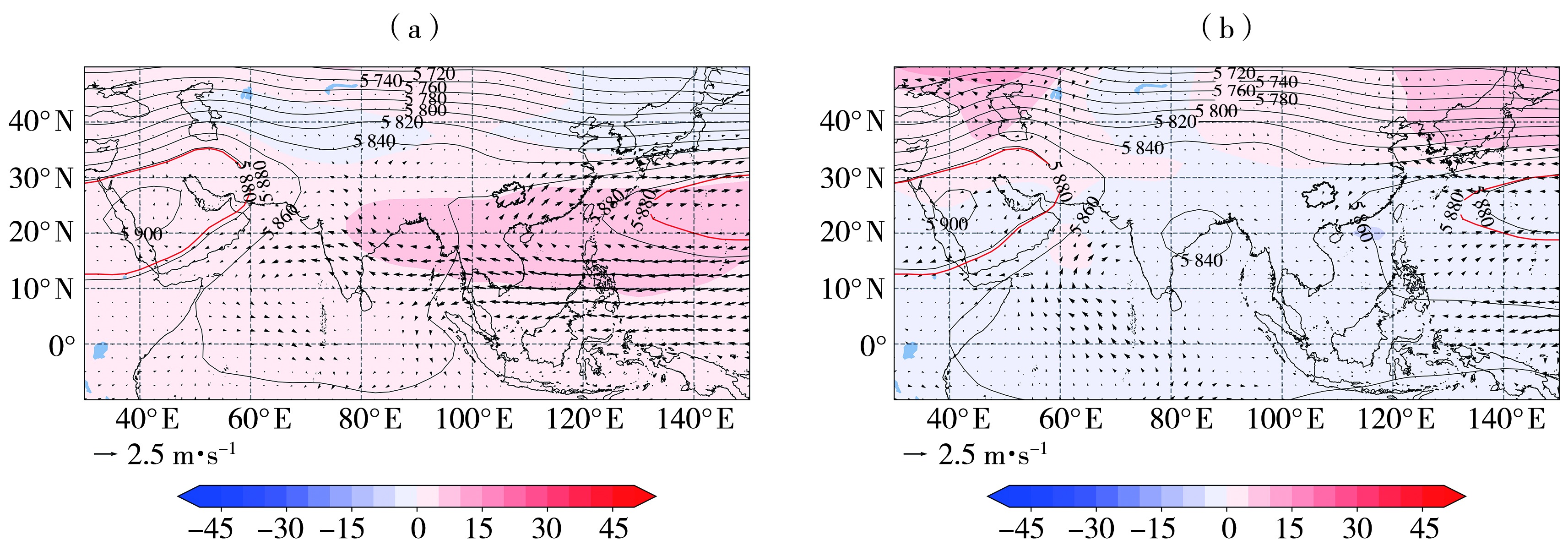
Fig.11 The composited 850 hPa wind field anomalies (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and 500 hPa geopotential height field (black contours) and its anomalies (the color shaded) (Unit: gpm) in summer of El Niño (a) and La Niña (b) decaying years (the red contours for the climate state during 1981-2022)

Fig.12 Composite vertically integrated water vapor flux (vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence (the color shaded, Unit: 10-5 kg·m-2·s-1) anomalies in summer of El Niño (a) and La Niña (b) decaying years
| [1] | 白慧, 吴战平, 龙俐, 等, 2013. 基于标准化前期降水指数的气象干旱指标在贵州的适用性分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 35(5): 661-668. |
| [2] |
蔡怡亨, 李帅, 张强, 等, 2023. 1997—2021年四川省干旱时空变化特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 241-250.
DOI |
| [3] | 陈文, 2002. El Niño和 La Niña事件对东亚冬、夏季风循环的影响[J]. 大气科学, 26(5): 595-610. |
| [4] | 陈燕丽, 唐梅蓉, 张会, 等, 2022. 广西喀斯特地区植被覆盖度和净初级生产力对SPEI干旱指数的响应差异[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 042-1 050. |
| [5] | 成青燕, 高晓清, 林纾, 等, 2017. 基于MCI指标的甘肃省近50年干旱特征分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 35(1): 211-218. |
| [6] | 池再香, 杜正静, 陈忠明, 等, 2012. 2009-2010年贵州秋、冬、春季干旱气象要素与环流特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 31(1): 176-184. |
| [7] | 樊高峰, 苗长明, 毛裕定, 等, 2006. 干旱指标及其在浙江省干旱监测分析中的应用[J]. 气象, 32(2): 70-74. |
| [8] | 符淙斌, 腾星林, 1988. 我国夏季的气候异常与埃尔尼诺/南方涛动现象的关系[J]. 大气科学, 12(特刊): 133-141. |
| [9] | 高睿娜, 王素艳, 高娜, 等, 2021. CI和MCI干旱指数在宁夏的适应性对比[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 185-192. |
| [10] | 国家气候中心, 云南省气象局, 2021. 区域性干旱过程监测评估方法:QX/T597—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [11] | 国家气候中心, 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 中国气象局预报与网络司, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [12] | 韩海涛, 胡文超, 陈学君, 等, 2009. 三种气象干旱指标的应用比较研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 27(1): 237-247. |
| [13] |
韩兰英, 张强, 贾建英, 等, 2019. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱强度、频次和持续时间及其南北差异性[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(5): 1-10.
DOI |
| [14] | 胡实, 莫兴国, 林忠辉, 2015. 未来气候情景下我国北方地区干旱时空变化趋势[J]. 干旱区地理, 38(2): 239-248. |
| [15] | 黄健, 李谢辉, 王磊, 等, 2020. 基于SPEI指数的西南地区近42 a干旱时空变化分析[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 35(3): 359-366. |
| [16] | 金祖辉, 陶诗言, 1999. ENSO循环与中国东部地区夏季和冬季降水关系的研究[J]. 大气科学, 23(6): 663-672. |
| [17] | 李红梅, 王钊, 高茂盛, 等, 2015. CI指数的改进及其在陕西省的适用性分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 33(3): 260-266. |
| [18] |
李忆平, 李耀辉, 2017. 气象干旱指数在中国的适应性研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5): 709-723.
DOI |
| [19] | 廖留峰, 杨富燕, 张东海, 等, 2019. 气候变化背景下贵州夏旱变化特征分析[J]. 中低纬山地气象, 43(2): 29-33. |
| [20] | 廖要明, 张存杰, 2017. 基于MCI的中国干旱时空分布及灾情变化特征[J]. 气象, 43(11): 1 402-1 409. |
| [21] | 罗宁, 2006. 中国气象灾害大典(贵州卷)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [22] | 毛春艳, 戴丽, 杨广斌, 等, 2021. 1960-2016年贵州喀斯特山区干旱时空动态分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 32(3): 64-72. |
| [23] | 茅海祥, 聂云, 杨群, 等, 2020. 1980—2018年贵州省PDSI干旱指数与降水Z指数对比分析[J]. 现代农业科技,(7): 202-208. |
| [24] | 潘杉, 贺中华, 陈莉会, 等, 2023. 基于不同时间尺度的贵州省近50年气象干旱时空演化特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 30(3): 279-288. |
| [25] | 乔丽, 杜继稳, 薛春芳, 等, 2010. 干旱指标在陕西省适用性研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 28(2): 1-6. |
| [26] | 苏跃, 廖婧琳, 冯泽蔚, 等, 2008. 54年来贵州旱灾及其对粮食生产的影响[J]. 贵州农业科学, 36(1): 51-53. |
| [27] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 764-770
DOI |
| [28] | 王劲松, 郭江勇, 周跃武, 等, 2007. 干旱指标研究的进展与展望[J]. 干旱区地理, 30(1): 60-65. |
| [29] |
王敏, 尹义星, 陈晓旸, 等, 2022. 基于SPEI的近百年天津地区气象干旱时空演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1): 11-21.
DOI |
| [30] |
王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2020. 多种干旱指数在中国北方的适用性及其差异原因初探[J]. 高原气象, 39(3): 628-640.
DOI |
| [31] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [32] | 王越, 江志红, 张强, 等, 2007. 基于Palmer湿润指数的旱涝指标研究[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 30(3): 383-389. |
| [33] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术(2版)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 37-38, 51-53. |
| [34] | 吴秀兰, 段春锋, 玛依拉·买买提艾力, 等, 2022. 基于MCI的新疆近60 a干旱时空特征分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(1): 75-83. |
| [35] | 吴哲红, 詹沛刚, 陈贞宏, 等, 2012. 3种干旱指数对贵州省安顺市历史罕见干旱的评估分析[J]. 干旱气象, 30(3): 355-322. |
| [36] | 武荣盛, 侯琼, 杨玉辉, 等, 2021. 多时间尺度气象干旱指数在内蒙古典型草原的适应性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 177-184. |
| [37] | 夏阳, 严小冬, 龙园, 等, 2013. GEV指数表征的贵州夏旱分布特征及干旱事件的异常环流特征[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 9(2): 252-264. |
| [38] | 谢清霞, 李刚, 袁晨, 等, 2016. 基于CI指数的西南地区1961—2012年春季干旱分布特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 10(4): 53-58. |
| [39] | 谢五三, 张强, 李威, 等, 2021. 干旱指数在中国东北、西南和长江中下游地区适用性分析[J]. 高原气象, 40(5): 1 136-1 146. |
| [40] | 许炳南, 张弼洲, 黄继用, 等, 1997. 贵州春旱、夏旱、倒春寒、秋风的规律、成因及长期预报研究[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 7-137. |
| [41] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [42] | 严小冬, 宋燕, 吴战平, 等, 2016. 基于GEV干旱指数的贵州春旱时空变化及预测模型探析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 38(2): 256-266. |
| [43] | 杨帆, 陈波, 张超, 等, 2015. 新气象干旱综合监测指数(MCI)在黔东南本地化应用[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 35(3): 56-61. |
| [44] | 杨歆雨, 张容焱, 潘航, 等, 2022. 福建省多维度气象干旱特征时空分布分析[J]. 气象, 48(12): 1 565-1 576. |
| [45] | 姚玉璧, 张存杰, 邓振镛, 等, 2007. 气象、农业干旱指标综述[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 25(1): 191-195. |
| [46] |
尹晗, 李耀辉, 2013. 我国西南干旱研究最新进展综述[J]. 干旱气象, 31(1): 182-193.
DOI |
| [47] | 游漫, 贺中华, 张浪, 等, 2022. 基于相对湿润指数的贵州省气象干旱时空变化特征研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(4): 256-269. |
| [48] | 袁文平, 周广胜. 2004. 标准化降水指标与Z指数在我国应用的对比分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 28(3): 523-529. |
| [49] | 袁媛, 杨辉, 李崇银. 2012. 不同分布型厄尔尼诺事件及对中国次年夏季降水的可能影响[J]. 气象学报, 70(3): 467-478. |
| [50] | 张皓, 毛文书, 师春香, 等, 2022. 基于MCI指数的西南地区近60年夏季干旱特征[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 37(4): 442-448. |
| [51] | 朱业玉, 王记芳, 武鹏, 等, 2006. 降水Z指数在河南旱涝监测中的应用[J]. 气象与环境科学, 29(4): 20-22. |
| [52] | DAI A, ZHAO T, 2017. Uncertainties in historical changes and future projections of drought. Part I: estimates of historical, drought changes[J]. Climatic Change, 144(3): 519-533. |
| [53] | TSEGAI D, MEDAL M, AUGENSTEIN P, et al, 2022. Drought in numbers 2022-restoration for readiness and resilience[R]. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification, 1-51. |
| [54] | WANG B, WU R, FU X, 2000. Pacific-East Asian tele-connection: how does ENSO affect East Asian climate?[J]. Journal of Climate, 13: 1 517-1 536. |
| [55] | ZHANG R, SUMI A, KIMOTO M, 1996. Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: a diagnostic study of the '86/87 and '91/92 events[J]. Journal of Meteorological Soc Japan,74: 49-62. |
| [56] | ZHANG R, SUMI A, KIMOTO M, 1999. A diagnostic study of the impact of El Niño on the precipitation in China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,16: 229-241. |
| [1] | YANG Jing, ZHANG Yajie, CHEN Jinwei, ZHU Jingjing, ZHANG Mingjie, Lin Shaowu. Research on the applicability of three vegetation indices based on MODIS data in vegetation monitoring of Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 274-282. |
| [2] | ZHU Li, LYU Xiaoyu, GUO Hao, MENG Xiangchen, TIAN Yunfei. Suitability study of ERA5-Land precipitation product for drought monitoring in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 677-687. |
| [3] | DONG Zhulei, ZHAO Yanli, FENG Xiaojing, LIU Shimeng. Applicability assessment of CLDAS temperature and precipitation products in Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 811-819. |
| [4] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [5] | GAO Ruina, WANG Suyan, GAO Na, ZUO Hejiang. Application Comparison of CI and MCI Drought Indexes in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 185-192. |
| [6] | PENG Shuangzi, LIU Xinmiao, CHEN Tao, YANG Min, XU Di, KUANG Yufei, XIAO Meiying. Discussion on drought monitoring and evaluation technology in the Heng-Shao drought corridor [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 894-899. |
| [7] | NIE Yun, ZHOU Jixian, LI Xijin, RAN Yang, CHEN Chao. Environmental Condition and Structure Feature of a Warm-sector Squall Line Process in Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 782-793. |
| [8] | LIU Hao, SONG Haiqing, LI Yunpeng. Applicability Evaluation of Snow Depth Reanalysis Data in Inner Mongolia#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 639-646. |
| [9] | LUO Junjie, HE Wenbin, WANG Zhaoguo. Design and Implementation of Information Collection System for Weather Modification Operation Based on Sensor Technology#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 692-700. |
| [10] | YAO Zhenhai, YAO Yeqing, WANG Chuanhui, FAN Fan, SHI Guoping. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Somatosensory Temperature in Summer Holiday in Anhui Province During 1987-2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 454-. |
| [11] | SHI Mengyu1,2, WANG Shengjie1,2,3, YAO Junqiang1,WANG Gaofei4, ZHANG Mingjun2. Variation of Stable Isotope in Water Vapor over Urumqi and Its Relationship with ENSO Based on Isotope-enabled GCMs [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 895-. |
| [12] | GAN Wenqiang, LI Gang, WAN Xueli. Variation Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation During May-September in Guizhou Province in Recent 57 Years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(4): 617-623. |
| [13] | GE Lijuan, WANG Xiaoping, WANG Qingtao, DANG Hong, ZHAO Chuanyan. Applicability of PROSAIL Model to Spring Wheat in Semi-arid Region of the Loess Plateau Under Different Drought Stress [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 926-933. |
| [14] | QI Dongmei1, LI Yueqing1, WANG Ying2, DENG Mengyu1, REN Qian1. Temporal-spatial Abnormity Characteristics of Drought in Sichuan Province Based on Z Index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(5): 734-744. |
| [15] | LIU Xiaoyan, SUO Yong, WANG Jin. Study on Identification Index of Hail Cloud Based on CPAS System in Anshun of Guizhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 688-693. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||