Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 884-896.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0884
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023
WANG Yun( ), WANG Lijuan(
), WANG Lijuan( ), LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping
), LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping
- Institute of Arid Meteorology, China Meteorological Administration, Gansu Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change and Reducing Disaster, Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2023-09-28Revised:2023-11-29Online:2023-12-31Published:2024-01-03
2023年上半年我国干旱的特征及其成因分析
王昀( ), 王丽娟(
), 王丽娟( ), 陆晓娟, 张金玉, 王芝兰, 沙莎, 胡蝶, 杨扬, 颜鹏程, 李忆平
), 陆晓娟, 张金玉, 王芝兰, 沙莎, 胡蝶, 杨扬, 颜鹏程, 李忆平
- 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:王丽娟(1986—),女,四川广安人,副研究员,主要从事卫星遥感研究。E-mail:wanglijuan01@126.com 。 -
作者简介:王昀(1990—),女,新疆乌鲁木齐人,助理研究员,主要从事干旱监测研究。E-mail:yunwang@vip.163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目(42105131);中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所攻关/共创基金项目(JYGG202307)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896.
王昀, 王丽娟, 陆晓娟, 张金玉, 王芝兰, 沙莎, 胡蝶, 杨扬, 颜鹏程, 李忆平. 2023年上半年我国干旱的特征及其成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 884-896.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0884
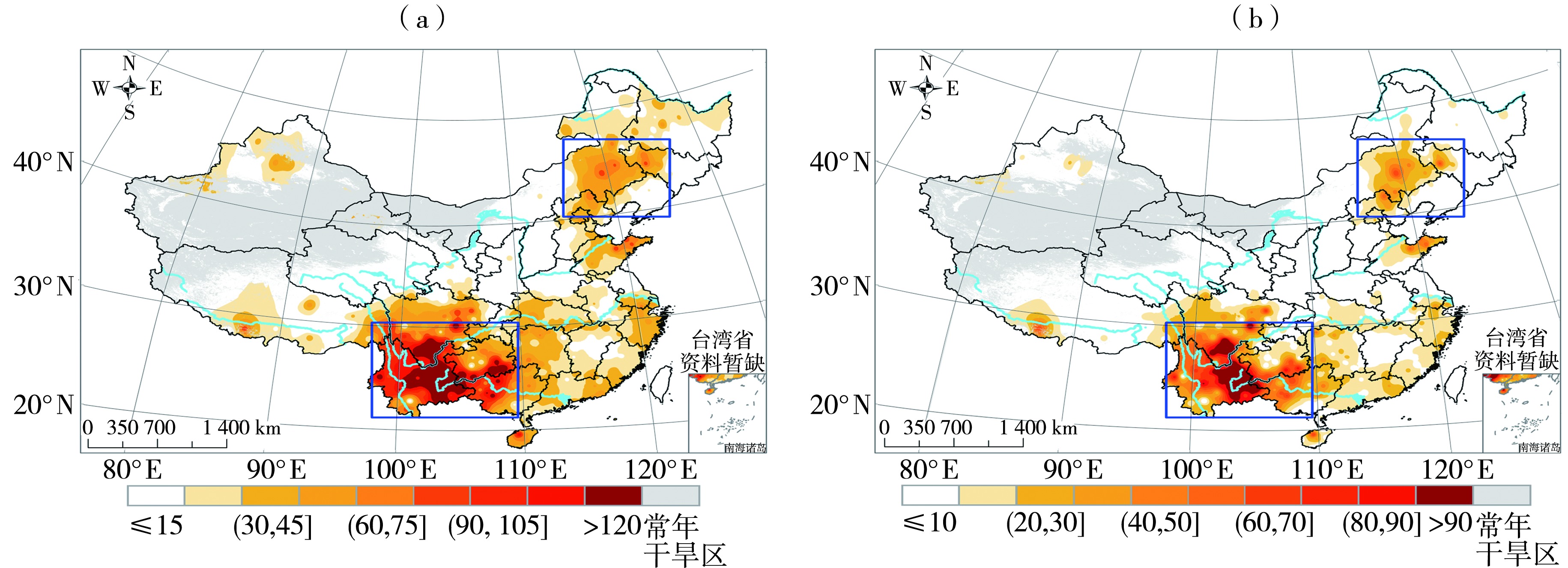
Fig.1 The spatial distribution of cumulative days of meteorological drought with moderate drought and above (a) and severe drought and above (b) in China from January to June 2023 (Unit: d) (The blue border areas represent the southwestern region of China and the eastern of Inner Mongolia)

Fig.5 Daily evolution of drought station frequency ratios at different levels in the southwest (a) and eastern Inner Mongolia (b) of the first half of 2023

Fig.6 Spatial distribution of 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid lines), and its anomalies (color shaded) in March (a), April (b), May (c) and June (d) in 2023 (Unit: gpm) (The red solid lines represent the 5 880 gpm contour lines, the black thick solid lines represent the 5 880 gpm contour lines for the climate state from 1981 to 2010, areas exceeding a standard deviation are covered with black dots)

Fig.8 Spatial distribution of 500 hPa geopotential height anomaly (the color shaded, Unit: gpm) and T-N wave activity flux (arrow vectors, Unit: m2·s-2) in April (a), May (b) and June (c) of 2023

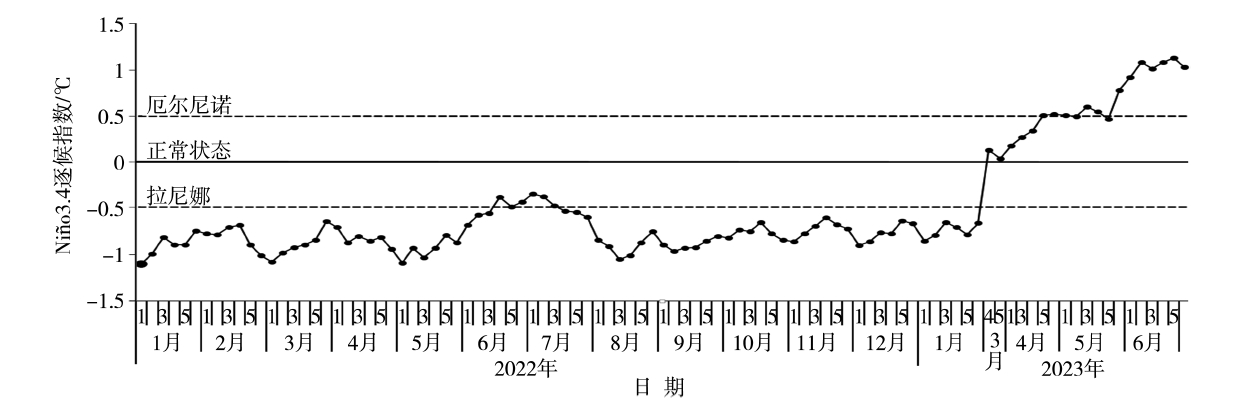
Fig.10 Global sea surface temperature-anomaly field in March (a), April (b), May (c) and June (d) in 2023 (Unit: ℃) (http://cmdp.ncc-cma.net/pred/cn_enso.php?product=cn_enso_oisstv2&pred_elem=month_ssta)。
| [1] | 陈艳, 2013. 传统Niño指数在全球海域的关联性及多指数的统一性初步研究[D]. 山东: 中国海洋大学. |
| [2] | 贺晋云, 张明军, 王鹏, 等, 2011. 近50年西南地区极端干旱气候变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 66(9): 1 179-1 190. |
| [3] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 2022. 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 721-732.
DOI |
| [4] | 李耀辉, 2013. GRAPES_SDM沙尘模式和CABLE陆面模式的发展及其应用推广. 兰州: 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所. |
| [5] | 李耀辉, 张良, 张虎强, 等, 2015. 基于CABLE陆面模式的干旱监测及其对典型干旱事件的效果检验[J]. 高原气象, 34(4): 1 005-1 018. |
| [6] | 李韵婕, 任福民, 李忆平, 等, 2014. 1960—2010年中国西南地区区域性气象干旱事件的特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 72(2): 266-276. |
| [7] |
李忆平, 王劲松, 李耀辉, 2015. 2009/2010年中国西南区域性大旱的特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 33(4): 537-545.
DOI |
| [8] |
李忆平, 李耀辉, 2017. 气象干旱指数在中国的适应性研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5): 709-723.
DOI |
| [9] |
李忆平, 张金玉, 岳平, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季长江流域重大干旱特征及其成因研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 733-747.
DOI |
| [10] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽, 冯晓晶, 2021. 内蒙古地区夏季旱涝急转环流异常特征及其预测[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 203-214. |
| [11] | 吕纯月, 管兆勇, 黄垭, 2021. 1961—2018年西南地区夏季干旱变化特征及其与环流异常的联系[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(4): 573-584. |
| [12] | 孙博, 王会军, 黄艳艳, 等, 2023. 2022年夏季中国高温干旱气候特征及成因探讨[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(1): 1-8. |
| [13] | 施春华, 金鑫, 刘仁强, 2017. 大气动力学中三种Rossby波作用通量的特征差异和适用性比较[J]. 大气科学学报, 40(6): 850-855. |
| [14] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 764-770.
DOI |
| [15] |
唐懿, 蔡雯悦, 翟建青, 等, 2022. 2021年夏季中国气候异常特征及主要气象灾害[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 179-186.
DOI |
| [16] | 陶诗言, 1963. 中国夏季副热带天气系统若干问题的研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| [17] | 王劲松, 郭江勇, 周跃武, 等, 2007a. 干旱指标研究的进展与展望[J]. 干旱区地理, 30(1): 60-65. |
| [18] | 王劲松, 郭江勇, 倾继祖, 2007b. 一种K干旱指数在西北地区春旱分析中的应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 22(5): 709-717. |
| [19] | 王劲松, 任余龙, 宋秀玲, 2008. K干旱指数在甘肃省干旱监测业务中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 26(4): 75-79. |
| [20] | 王劲松, 李耀辉, 王润元, 等, 2012. 我国气象干旱研究进展评述[J]. 干旱气象, 30(4): 497-508. |
| [21] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [22] | 吴秋洁, 2019. 近55年西南地区干旱气候特征及成因分析[D]. 成都: 成都信息工程大学. |
| [23] |
赵鸿, 蔡迪花, 王鹤龄, 等, 2023. 干旱灾害对粮食安全的影响及其应对技术研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 187-206.
DOI |
| [24] | 张良, 2016. 基于陆面模式的干旱监测技术及其在我国的应用效果研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [25] | 张良, ZHANG H Q, 张强, 等, 2016. 应用陆面模式进行干旱监测的过程和实现[J]. 干旱区研究, 33(3): 584-592. |
| [26] | 张强, 张存杰, 白虎志, 等, 2010. 西北地区气候变化新动态及对干旱环境的影响——总体暖干化,局部出现暖湿迹象[J]. 干旱气象, 28(1): 1-7. |
| [27] |
张强, 韩兰英, 张立阳, 等, 2014. 论气候变暖背景下干旱和干旱灾害风险特征与管理策略[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(1): 80-91.
DOI |
| [28] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等, 2015. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 73(6): 1 092-1 103. |
| [29] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 王莺, 等, 2017. 中国南方干旱灾害风险特征及其防控对策[J]. 生态学报, 37(21): 7 206-7 218. |
| [30] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [31] | 郑建萌, 张万诚, 陈艳, 等, 2015. 2009—2010年云南特大干旱的气候特征及成因[J]. 气象科学, 35(4): 488-496. |
| [32] | 周扬, 李宁, 吴吉东, 2013. 内蒙古地区近30年干旱特征及其成灾原因[J]. 灾害学, 28(4): 67-73. |
| [33] | 朱乾根, 2007. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [34] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [35] | GUAN W N, HU H B, REN X J, et al, 2019. Subseasonal zonal variability of the western Pacific subtropical high in summer: climate impacts and underlying mechanisms[J]. Climate Dynamics, 53(5/6): 3 325-3 344. |
| [36] | HUANG Y Y, WANG H J, FAN K, et al, 2015. The western Pacific subtropical high after the 1970s: westward or eastward shift?[J]. Climate Dynamics, 44(7/8): 2 035-2 047. |
| [37] | HUANG Y Y, WANG B, LI X F, et al, 2018. Changes in the influence of the western Pacific subtropical high on Asian summer monsoon rainfall in the late 1990s[J]. Climate Dynamics, 51(1): 443-445. |
| [38] | KOWALCZYK E, WANG Y P, LAW R, et al, 2006. The CSIRO Atmosphere Biosphere Land Exchange (CABLE) model for use in climate models and as an offline model[M/OL]. CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric technical report, CISRO, Clayton South, Australia[2023-12-28]. https://www.cmar.csiro.au/e-print/open/kowalczykea_2006a.pdf. |
| [39] | LU R Y, LIN Z D, 2009. Role of subtropical precipitation anomalies in maintaining the summertime meridional teleconnection over the western North Pacific and East Asia[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(8): 2 058-2 072. |
| [40] | TAKAYA K, NAKAMURA H, 2001. A formulation of a phase independent wave-activity flux for stationary and migratory quasigeostrophic eddies on a zonally varying basic flow[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 58(6): 608-627. |
| [1] | LU Xiaojuan, WANG Zhilan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, HU Die, SHA Sha, WANG Suping, LI Yiping. The synergistic effect of sea temperature and MJO on spring drought in southwestern China in 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 166-179. |
| [2] | HUANG Yao, YUAN Meng, GUO Jie, SONG Wenwen, LIU Xinchao. Synoptic circulation patterns clustering analysis and physical diagnosis of high temperature weather in the lower reaches of the Jinsha River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 217-227. |
| [3] | LIU Wei, ZHAO Yanli, GAO Jing, LI Linhui, WANG Huimin. Cause analysis of flood-drought alternation event in July 2022 in arid and semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 11-18. |
| [4] | XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922. |
| [5] | ZHAO Huizhen, HE Tao, GUO Ruixia, WANG Chengfu, ZHANG Yanrong, LI Qi. Meteorological drought variation characteristics in the Gannan Plateau based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 688-696. |
| [6] | REN Manlin, LI Zhongyan, WANG Boqing, TAN Yaheng, WANG Shuo. Analysis on the causes of freezing stage characteristics in Guizhou in winter of 2021/2022 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 744-752. |
| [7] | HAO Lisheng, MA Ning, HE Liye. Circulation anomalies characteritics of the abnormal drought and high temperature event in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in summer of 2022 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 721-732. |
| [8] | LI Yiping, ZHANG Jinyu, YUE Ping, WANG Suping, ZHA Pengfei, WANG Lijuan, SHA Sha, ZHANG Liang, ZENG Dingwen, REN Yulong, HU Die. Study on characteristics of severe drought event over Yangtze River Basin in summer of 2022 and its causes [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 733-747. |
| [9] | LIN Shu, LI Hongying, HUANG Pengcheng, DUAN Xinyu. Characteristics of high temperature, drought and circulation situation in summer 2022 in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 748-763. |
| [10] | YANG Xia, XU Tingting, ZHANG Linmei, HUA Ye, ZHOU Hongkui. Characteristics and differences of rainstorm in the southern Xinjiang during warm season under different climatic backgrounds [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 222-233. |
| [11] | XING Caiying, WU Shengan, HU Deqiang, ZHU Jingjing. Analysis of cause of abnormally high temperature in Hainan Island in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 911-920. |
| [12] | ZHANG Chao, LUO Boliang. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Persistent Regional Meteorological Drought in Summer and Autumn in Hunan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 193-202. |
| [13] | MA Youxuan, LI Wanzhi, WANG Lixia, BAI Wenrong, WANG Ziwen. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Atmospheric Circulation Diagnosis of Spring Drought Based on SPI in Qinghai Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 362-370. |
| [14] | LIU Xiaoran, HU Zuheng, LI Yonghua, TANG Hongyu. Variation Characteristics and Formation Cause of Cold and Warm Winter in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 404-410. |
| [15] | ZHENG Fengqin, ZHONG Lihua, LUO Xiaoli, WEI Jingjing, SHI Caixia. Prediction of Extended-range Heavy Rainfall Processes in June in Xijiang River Basin Based on Similarity Method of Synoptic Key Areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 490-496. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||