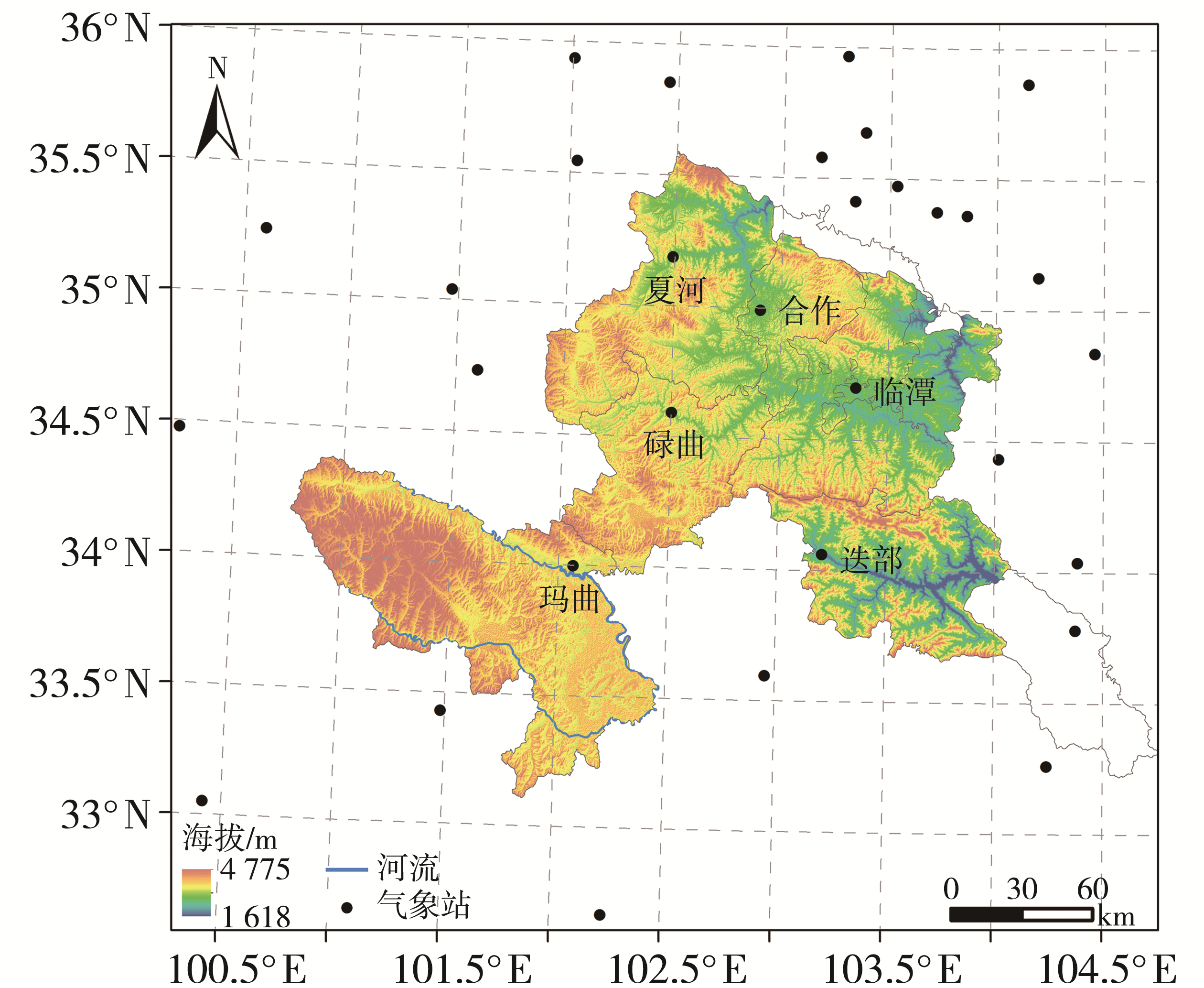
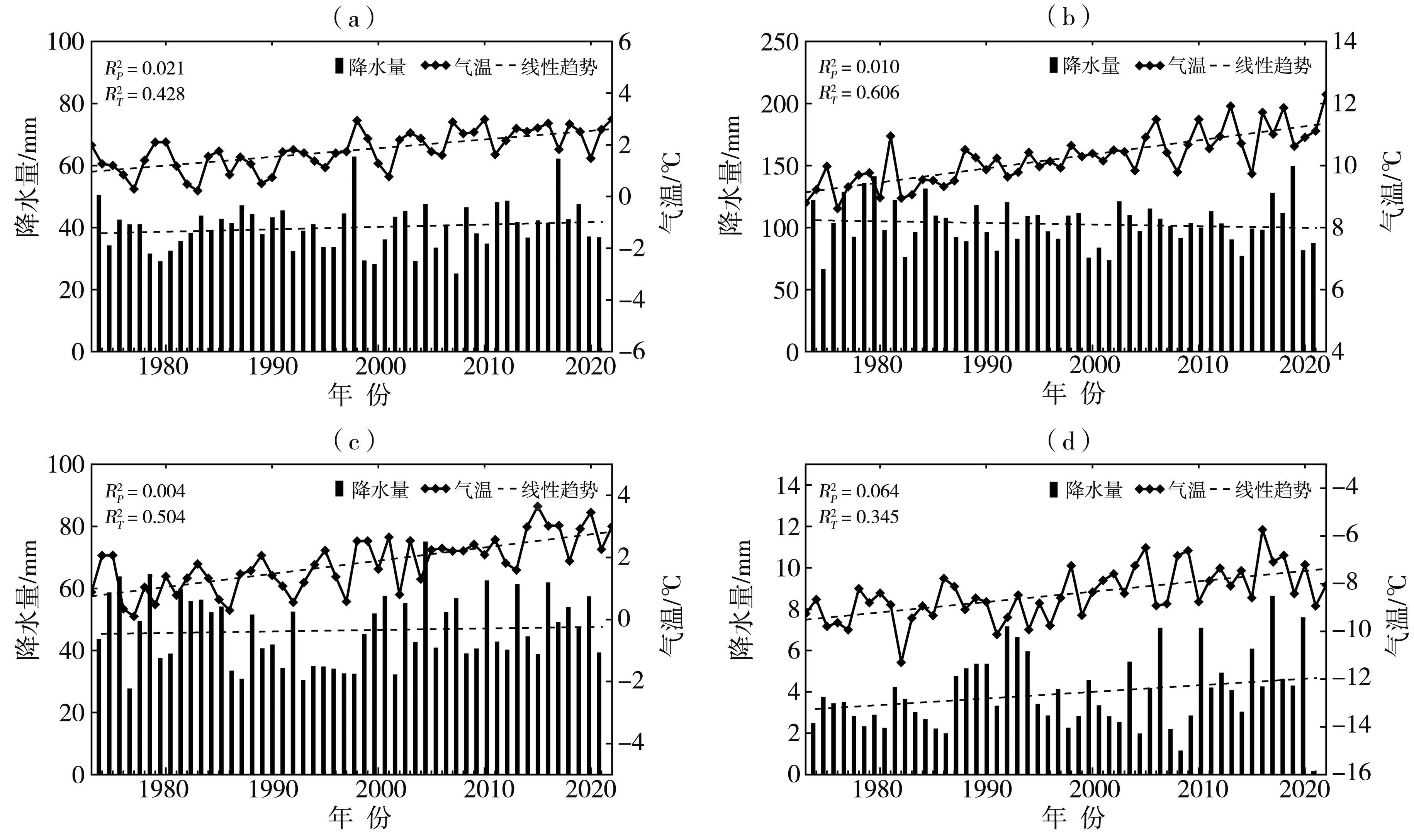
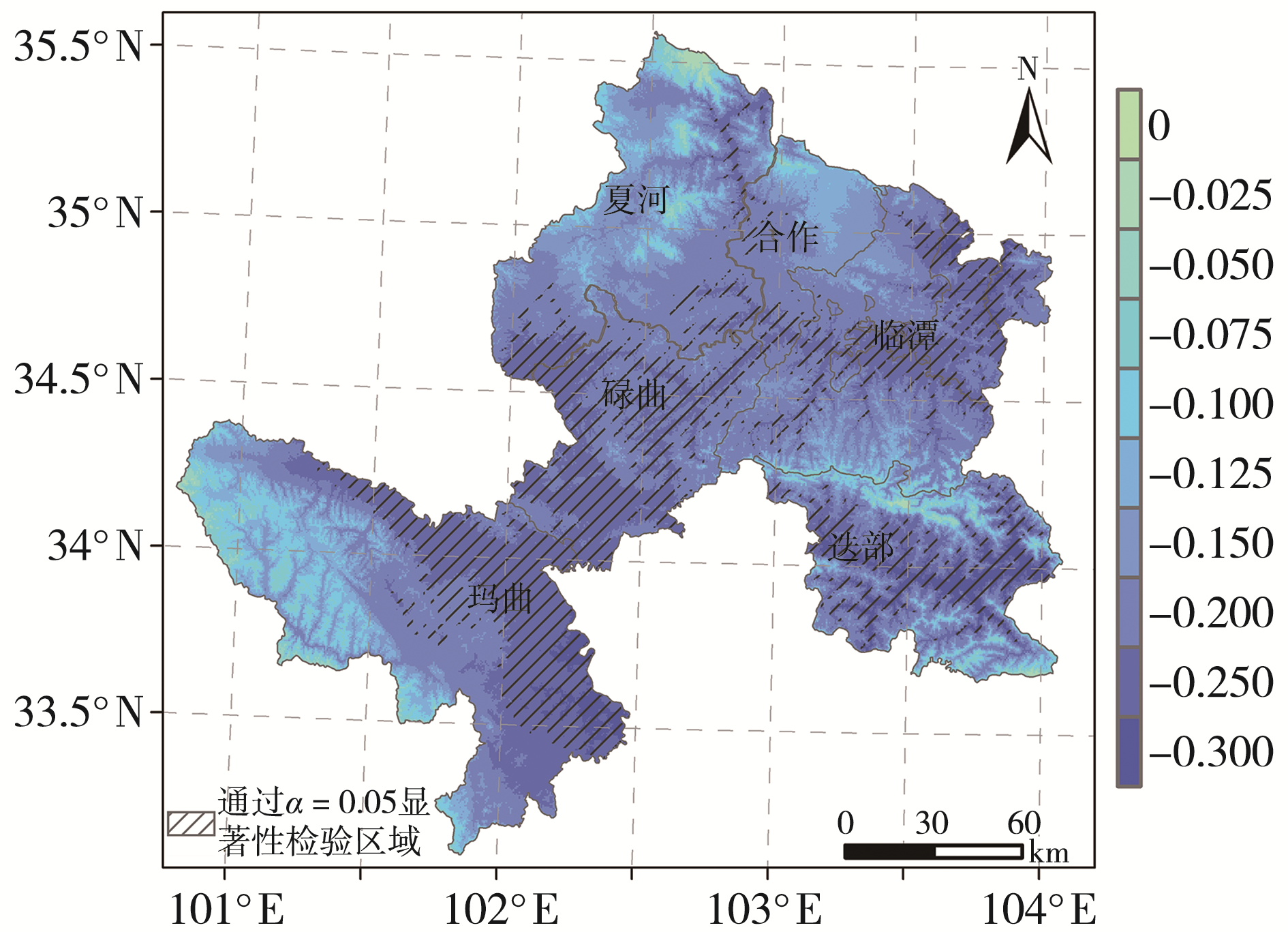
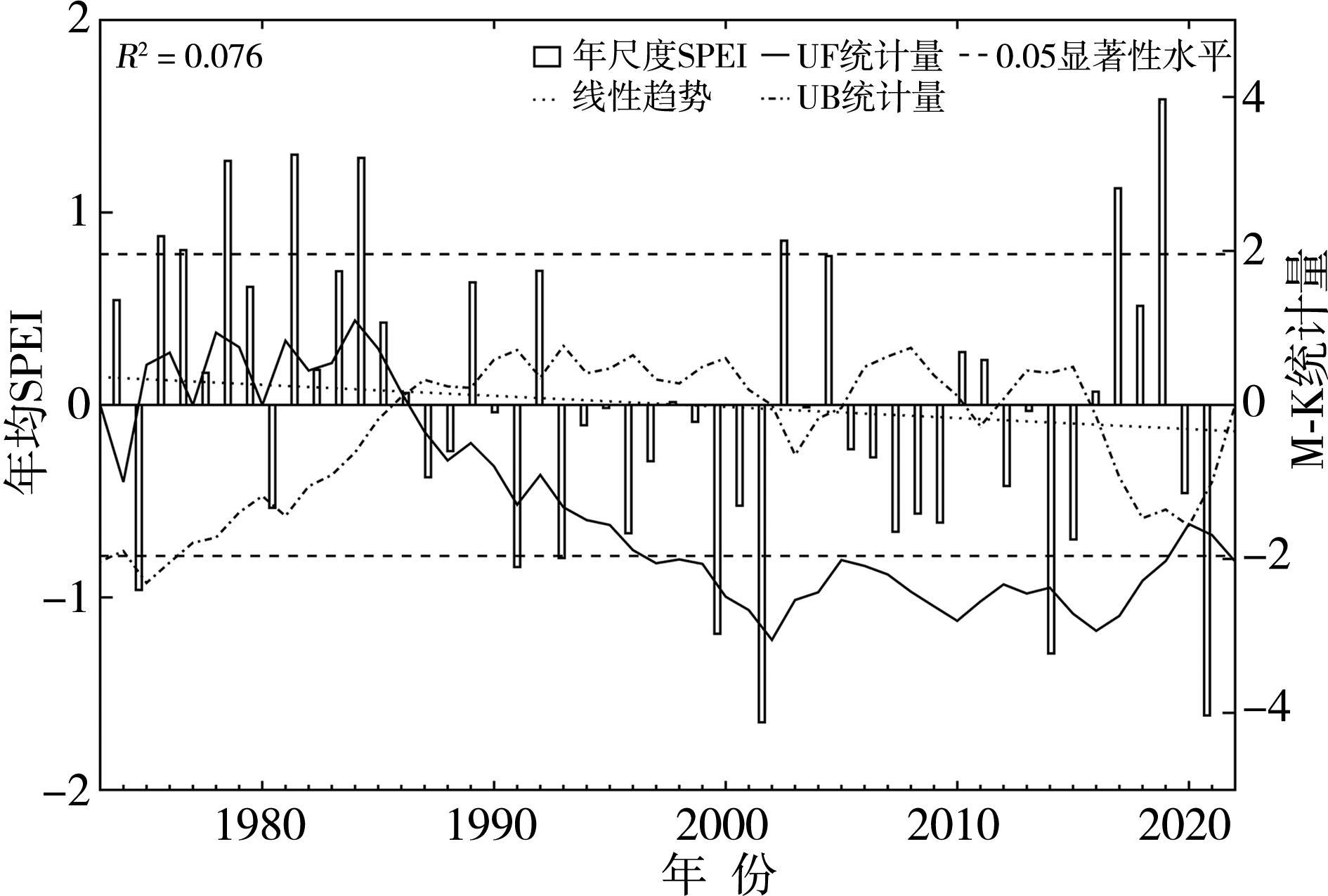
| [1] |
柏庆顺, 颜鹏程, 蔡迪花, 等, 2019. 近56 a中国西北地区不同强度干旱的年代际变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 722-728.
|
| [2] |
陈发虎, 谢亭亭, 杨钰杰, 等, 2023. 我国西北干旱区“暖湿化”问题及其未来趋势讨论[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 53(6): 1 246-1 262.
|
| [3] |
陈燕丽, 唐梅蓉, 张会, 等, 2022. 广西喀斯特地区植被覆盖度和净初级生产力对SPEI干旱指数的响应差异[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 042-1 050.
|
| [4] |
董安祥, 王鹏祥, 林彬, 2005. 中国气象灾害大典∙甘肃卷[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [5] |
范进进, 秦鹏程, 史瑞琴, 等, 2022. 气候变化背景下湖北省高温干旱复合灾害变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 780-790.
DOI
|
| [6] |
高秉丽, 巩杰, 李焱, 等, 2022. 基于SPEI的黄河流域多尺度干湿特征分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(3): 723-733.
|
| [7] |
国家气候中心,中国气象局预报与网络司, 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 2017. 气象干旱等级: GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
| [8] |
黄浩, 张勃, 马尚谦, 等, 2020. 甘肃河东地区气象干旱时空变化及干旱危险性分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 41(7): 459-469.
|
| [9] |
江笑薇, 白建军, 刘宪峰, 2019. 基于多源信息的综合干旱监测研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(3): 275-287.
DOI
|
| [10] |
赖力, 2020. 甘肃省气象-农业干旱时空变化特征及响应关系[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
| [11] |
蓝浩宸, 刘琰琰, 张玉芳, 等, 2023. 基于标准化降水蒸散指数的川西高原干旱时空变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 34(6): 1 533-1 540.
|
| [12] |
刘兴元, 陈全功, 王永宁, 2006. 甘南草地退化对生态安全与经济发展的影响[J]. 草业科学, 23(12): 39-42.
|
| [13] |
马悦, 何洪鸣, 赵宏飞, 2023. 基于GIS和RUSLE的甘南州土壤侵蚀时空演变[J]. 水土保持研究, 30(3): 37-46.
|
| [14] |
师玉锋, 梁思琦, 彭守璋, 2020. 1901—2017年黄土高原地区气候干旱的时空变化[J]. 水土保持通报, 40(1): 283-289.
|
| [15] |
谭剑波, 李爱农, 雷光斌, 2016. 青藏高原东南缘气象要素Anusplin和Cokriging空间插值对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 35(4): 875-886.
DOI
|
| [16] |
王晨鹏, 2021. 中国区域性干旱变化特征分析[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院.
|
| [17] |
王劲松, 姚玉璧, 王莺, 等, 2022. 青藏高原地区气象干旱研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 37(5): 441-461.
DOI
|
| [18] |
王玲玲, 何巍, 罗米娜, 等, 2021. 基于归一化旱情综合指数的川西高原草地伏旱监测分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6): 884-893.
|
| [19] |
王伟军, 赵雪雁, 万文玉, 等, 2016. 2000—2014年甘南高原植被覆盖度变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(9): 2 494-2 504.
|
| [20] |
汪生珍, 2022. 基于综合干旱指数的青藏高原干旱动态变化及植被响应[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学.
|
| [21] |
武荣盛, 侯琼, 杨玉辉, 等, 2021. 多时间尺度气象干旱指数在内蒙古典型草原的适应性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 177-184.
|
| [22] |
姚旭阳, 张明军, 张宇, 等, 2022. 中国西北地区气候转型的新认识[J]. 干旱区地理, 45(3): 671-683.
|
| [23] |
张强, 2022. 科学解读“2022年长江流域重大干旱”[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 545-548.
DOI
|
| [24] |
张月晴, 肖国杰, 陈孟佳, 2021. 近60年银川气温变化特征分析[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 36(6): 680-686.
|
| [25] |
郑健, 鲍婷婷, 王春霞, 等, 2023. 考虑气候分区的甘肃省干旱时空分布特征分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 54(2): 311-320.
|
| [26] |
周俊菊, 冯炜, 向鹃, 等, 2022. 基于SPEI指数的近58 a甘肃省干旱特征分析[J]. 气象科学, 42(1): 99-107.
|
| [27] |
庄少伟, 2013. 基于标准化降水蒸发指数的中国区域干旱化特征分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学.
|
| [28] |
BRYANT E, 1991. Natural hazards[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge Universisty Press.
|
| [29] |
HUTCHINSON M F, XU T, 2013. Anusplin Version 4.4 User Guide[M]. Canberra: Fenner School of Environment and Society, The Australian National University.
|
| [30] |
MANN H B, 1945. Non-parametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica, 13: 245-259.
DOI
URL
|
| [31] |
MCKEE T B, DOESKEN N J, KLEIST J, 1993. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales[C]// In proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, California, American Meteor Society: 179-184.
|
| [32] |
MISHRA A K, SINGH V P, 2010. A review of drought concepts[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 391(1/2): 202-216.
DOI
URL
|
| [33] |
PALMER W C, 1965. Meteorological drought[M]. Washington D C: U.S. Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau.
|
| [34] |
SEN P K, 1968. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's tau[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 63(324): 1 379-1 389.
|
| [35] |
IPCC, 2007. Climate change 2007: The physical science basis//Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
|
| [36] |
THORNTHWAITE C W, 1948. An approach toward a rational classification of climate[J]. Geographical Review, 38(1): 55-94.
DOI
URL
|
| [37] |
VICENTE-SERRANO S M, BEGUERÍA S, LÓPEZ-MORENO J I, 2010. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(7): 1 696-1 718.
|
 ), HE Tao2, GUO Ruixia3,4, WANG Chengfu2, ZHANG Yanrong2, LI Qi1(
), HE Tao2, GUO Ruixia3,4, WANG Chengfu2, ZHANG Yanrong2, LI Qi1( )
)
 ), 何涛2, 郭瑞霞3,4, 王成福2, 张艳荣2, 李琪1(
), 何涛2, 郭瑞霞3,4, 王成福2, 张艳荣2, 李琪1( )
)