Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 836-843.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0836
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification and evolution characteristics of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin
YANG Xiaoling1,2( ), SUN Xuying1(
), SUN Xuying1( ), YANG Jinhu1, WU Wen2, ZHAO Huihua2, CHEN Jing2
), YANG Jinhu1, WU Wen2, ZHAO Huihua2, CHEN Jing2
- 1. Institute of Arid Meteorology, China Meteorological Administration, Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province, Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change and Reducing Disaster of CMA, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. Wuwei National Climate Observation Platform, Wuwei 733099, Gansu, China
-
Received:2024-08-13Revised:2024-09-29Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
石羊河流域复合高温干旱事件的识别及其演变特征
杨晓玲1,2( ), 孙旭映1(
), 孙旭映1( ), 杨金虎1, 吴雯2, 赵慧华2, 陈静2
), 杨金虎1, 吴雯2, 赵慧华2, 陈静2
- 1.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.武威国家气候观象台,甘肃 武威 733099
-
通讯作者:孙旭映(1973—),男,副研究员,主要从事区域气候变化研究工作。E-mail:sun_xuying@163.com。 -
作者简介:杨晓玲(1971—),女,高级工程师,主要从事天气预报及气候变化研究工作。E-mail:wwqxj6150343@163.com。 -
基金资助:干旱气象科学研究基金项目“石羊河流域复合高温干旱事件识别与演变特征研究”(IAM202408);国家自然科学基金项目(42375039);国家自然科学基金项目(42175192);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究项目(2019QZKK0105)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Xiaoling, SUN Xuying, YANG Jinhu, WU Wen, ZHAO Huihua, CHEN Jing. Identification and evolution characteristics of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 836-843.
杨晓玲, 孙旭映, 杨金虎, 吴雯, 赵慧华, 陈静. 石羊河流域复合高温干旱事件的识别及其演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 836-843.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0836

Fig.2 Spatial distribution of average frequency of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin in different decades from 1961 to 2023 (Unit: times)

Fig.3 The inter-annual variation of the occurrence frequency of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin during 1961-2023
| 时段 | 气候倾向率/[次·(10 a)-1] | 趋势系数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全流域 | 上游 | 中游 | 下游 | 全流域 | 上游 | 中游 | 下游 | |
| 1961—1996年 | -0.273 | -0.401 | -0.265 | -0.153 | -0.368** | -0.413** | -0.337* | -0.191 |
| 1997—2023年 | 0.327 | 0.293 | 0.316 | 0.372 | 0.353* | 0.300 | 0.291 | 0.334* |
| 1961—2023年 | 0.272 | 0.277 | 0.252 | 0.285 | 0.505*** | 0.437** | 0.449*** | 0.501*** |
Tab.1 Climate tendency rate and trend coefficient of annual frequency of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin in different periods from 1961 to 2023
| 时段 | 气候倾向率/[次·(10 a)-1] | 趋势系数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全流域 | 上游 | 中游 | 下游 | 全流域 | 上游 | 中游 | 下游 | |
| 1961—1996年 | -0.273 | -0.401 | -0.265 | -0.153 | -0.368** | -0.413** | -0.337* | -0.191 |
| 1997—2023年 | 0.327 | 0.293 | 0.316 | 0.372 | 0.353* | 0.300 | 0.291 | 0.334* |
| 1961—2023年 | 0.272 | 0.277 | 0.252 | 0.285 | 0.505*** | 0.437** | 0.449*** | 0.501*** |
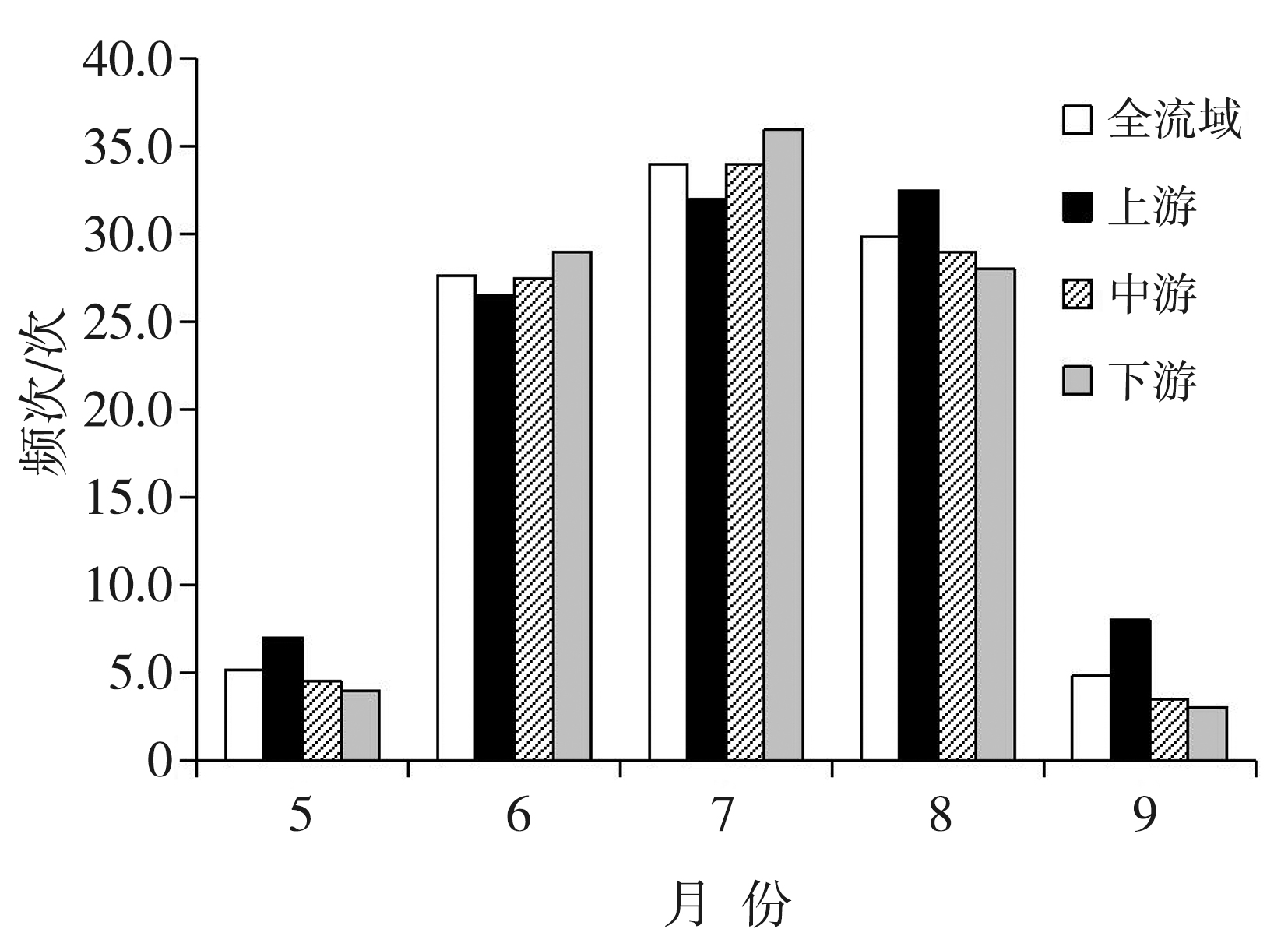
Fig.4 The monthly variation of occurrence frequency of compound high-temperature and drought events in different sub-regions of the Shiyang River Basin from May to September during 1961-2023
| 流域分区 | 轻旱 (0<X<1) | 中旱 (1≤X<3) | 重旱 (3≤X<5) | 特旱 (X≥5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全流域 | 15 | 18 | 11 | 6 |
| 上游 | 13 | 17 | 10 | 9 |
| 中游 | 15 | 19 | 11 | 4 |
| 下游 | 17 | 17 | 12 | 6 |
Tab.2 The occurrence frequency of compound high-temperature and drought events with different grades in the Shiyang River Basin during 1961-2023 单位:次
| 流域分区 | 轻旱 (0<X<1) | 中旱 (1≤X<3) | 重旱 (3≤X<5) | 特旱 (X≥5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全流域 | 15 | 18 | 11 | 6 |
| 上游 | 13 | 17 | 10 | 9 |
| 中游 | 15 | 19 | 11 | 4 |
| 下游 | 17 | 17 | 12 | 6 |
| [1] | 柏庆顺, 颜鹏程, 蔡迪花, 等, 2019. 近56 a中国西北地区不同强度干旱的年代际变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 722-728. |
| [2] | 成爱芳, 赵景波, 2012. 武威地区清代—民国时期干旱灾害特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 26(1): 98-103. |
| [3] | 邓振镛, 文小航, 黄涛, 等, 2009. 干旱与高温热浪的区别与联系[J]. 高原气象, 28(3): 702-709. |
| [4] |
丁文魁, 李兴宇, 杨晓玲, 等, 2022. 气象干旱变化特征及其对粮食产量的影响: 以甘肃武威市为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(2): 656-664.
DOI |
| [5] | 豆晓军, 吕娟, 孙洪泉, 等, 2018. 基于标准化降水指数的1959—2014年中国季节干旱时空特征分析[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 16(2): 149-155. |
| [6] |
范进进, 秦鹏程, 史瑞琴, 等, 2022. 气候变化背景下湖北省高温干旱复合灾害变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 780-790.
DOI |
| [7] | 吉春容, 白书军, 胡启瑞, 等, 2019. 棉田干旱指标研究进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(1): 136-143. |
| [8] | 李柏贞, 周广胜, 2014. 干旱指标研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 34(5): 1 043-1 052 |
| [9] | 李庆祥, 黄嘉佑, 2011. 对我国极端高温事件阈值的探讨[J]. 应用气象学报, 22(2): 138-144. |
| [10] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 748-763.
DOI |
| [11] | 刘晓冉, 程炳岩, 杨茜, 等, 2009. 川渝地区夏季高温干旱变化特征及其异常年环流形势分析[J]. 高原气象, 28(2): 306-313. |
| [12] | 柳崇健, 1998. 天气预报技术的若干进展[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:211-212. |
| [13] |
卢冬燕, 朱秀芳, 唐明秀, 等, 2024. 不同温升情景下中国旱灾风险变化评估[J]. 干旱区地理, 47(3): 369-379.
DOI |
| [14] |
罗晓玲, 胡丽莉, 杨梅, 2015. 近30年石羊河流域气象灾害特征及风险评估技术研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 31(32): 205-210.
DOI |
| [15] | 马柱国, 符淙斌, 2005. 中国干旱和半干旱带的10年际演变特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(3): 519-525. |
| [16] | 全国气候与气候变化标准化技术委员会, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [17] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 764-770.
DOI |
| [18] | 孙蕊, 邓彪, 王顺久, 等, 2023. 2022年夏季四川省区域性高温和干旱过程监测评估[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(2): 72-80. |
| [19] | 王劲松, 李耀辉, 王润元, 等, 2012. 我国气象干旱研究进展评述[J]. 干旱气象, 30(4): 497-508. |
| [20] |
王胜, 田红, 吴蓉, 等, 2022. 2022年安徽省区域性高温和干旱过程综合评估[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 771-779.
DOI |
| [21] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [22] | 王志伟, 翟盘茂, 2003. 中国北方近50年干旱变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 58(增刊1): 61-68. |
| [23] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社, 37-41. |
| [24] | 武新英, 郝增超, 张璇, 等, 2021. 中国夏季复合高温干旱分布及变异趋势[J]. 水利水电技术: 中英文, 52(12): 90-98. |
| [25] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [26] | 严志明, 李茹冰, 李岩瑛, 等, 2024. 2023年河西走廊东部特重干旱特征及成因[J]. 中南农业科技, 45(5): 92-94. |
| [27] | 严中伟, 杨赤, 2000. 近几十年中国极端气候变化格局[J]. 气候与环境研究, 5(3): 267-272. |
| [28] | 杨晓玲, 丁文魁, 孙占峰, 等, 2022. 近60年河西走廊东部气象干旱演变特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(1): 242-248. |
| [29] | 杨晓玲, 李兴宇, 郭丽梅, 等, 2023. 石羊河流域干旱特征及其灾度和危险度分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(1): 46-52. |
| [30] |
杨英杰, 曹倩, 税玥, 2024. 中亚复合高温干旱事件识别与特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(1): 19-26.
DOI |
| [31] | 翟盘茂, 刘静, 2012. 气候变暖背景下的极端天气气候事件与防灾减灾[J]. 中国工程科学, 14(9): 55-63. |
| [32] |
张强, 韩兰英, 张立阳, 等, 2014. 论气候变暖背景下干旱和干旱灾害风险特征与管理策略[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(1): 80-91.
DOI |
| [33] | 张强, 李栋梁, 姚玉璧, 等, 2024. 干旱形成机制与预测理论方法及其灾害风险特征研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 1-21. |
| [34] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [35] | 张强, 朱飙, 杨金虎, 等, 2021. 西北地区气候湿化趋势的新特征[J]. 科学通报, 66(增刊2): 3 757-3 771 |
| [36] |
张强, 2022. 科学解读“2022年长江流域重大干旱”[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 545-548.
DOI |
| [37] | 张庆云, 陶诗言, 彭京备, 2008. 我国灾害性天气气候事件成因机理的研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 32(4): 815-825. |
| [38] | 赵佳琪, 张强, 朱秀迪, 等, 2021. 中国旱灾风险定量评估[J]. 生态学报, 41(3): 1 021-1 031 |
| [39] | 中国水旱灾害防御公报编写组, 2021. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2020概要[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 31(11): 26-32. |
| [40] | DAI A G, 2013. Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models[J]. Nature Climate Change, 3: 52-58. |
| [41] | DAI A G, TRENBERTH K E, QIAN T T, 2004. A global dataset of palmer drought severity index for 1870-2002: Relationship with soil moisture and effects of surface warming[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 5(6): 1 117-1 130 |
| [42] | DAI A G, ZHAO T B, 2017. Uncertainties in historical changes and future projections of drought. Part I: Estimates of historical drought changes[J]. Climatic Change, 144(3): 519-533. |
| [43] | HEIM R R, 2002. A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 83(8): 1 149-1 165 |
| [44] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change 2021:The physical science basis. Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R/OL].(2021-08-09)[2024-11-20]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/. |
| [45] | IPCC, 2023. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis[M]. Cam-bridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [46] | LI W L, SUN B, WANG H J, et al, 2023. Anthropogenic impact on the severity of compound extreme high temperature and drought/rain events in China[J]. NPJ Climate and Atmospheric Science, 6: 79. DOI: 10.1038/s41612-023-00413-3. |
| [47] | LIVEZEY R E, CHEN W Y, 1983. Statistical field significance and its determination by Monte Carlo techniques[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 111(1): 46-59. |
| [48] | LOBELL D B, ROBERTS M J, SCHLENKER W, et al, 2014. Greater sensitivity to drought accompanies maize yield increase in the U. S. Midwest[J]. Science, 344(6183): 516-519. |
| [49] | SU B D, HUANG J L, FISCHER T, et al, 2018. Drought losses in China might double between the 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(42): 10 600-10 605 |
| [50] | YOU Q L, JIANG Z H, KONG L, et al, 2017. A comparison of heat wave climatologies and trends in China based on multiple definitions[J]. Climate Dynamics, 48(11/12): 3 975-3 989 |
| [1] | ZHANG Jindan, LIU Mingchun, LI Xingyu, DING Wenkui, YANG Hua, JIANG Jufang. Characteristics of dry-wet climate change and its influence on NDVI in Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 697-704. |
| [2] | GUO Yang, SHI Chunxiang, XU Bin, SI Peng, XU Mei, WANG Min, SUN Meiling. Accuracy analysis of fog and haze identification based on CLDAS land surface fusion data in Tianjin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 657-665. |
| [3] | CAI Yiheng, LI Shuai, ZHANG Qiang, DENG Biao, LUO Yu, SUN Rui. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 241-250. |
| [4] | LIU Shuyan, RONG Yanshu, LYU Xingyue, YIN Yuting. Comparative Analysis of Drought in China and the United States in 2012 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 717-726. |
| [5] | WU Rongsheng, HOU Qiong, YANG Yuhui, FENG Xuyu, LI Bin, ZHENG Fengjie. Applicability Evaluation of Multi-time-scales Meteorological Drought Indexes in Typical Steppe of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 177-184. |
| [6] | GAO Ruina, WANG Suyan, GAO Na, ZUO Hejiang. Application Comparison of CI and MCI Drought Indexes in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 185-192. |
| [7] | ZHANG Chao, LUO Boliang. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Persistent Regional Meteorological Drought in Summer and Autumn in Hunan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 193-202. |
| [8] | SUN Li, ZHANG Jinguang, YANG Lei, ZHAO Shuhui. Micro- and Macro-Features of Cloud in Liaoning Province and Its Correlation with Precipitation Based on Aqua/CERES Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 612-618. |
| [9] | YANG Luying1, LIU Chang2, YANG Chengfang2, HAN Yongqing2. Variation Characteristics of GPS Precipitable Water Vapor During Typical Heavy Rainfall Processes Under Different Synoptic Systems [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 475-. |
| [10] | ZHOU Jiewen, LU Chuhan, SUN Yan. Review of Extratropical Cyclone Activities over East Asia and Its Climatic Effects Research Based on Objective Identification [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 907-917. |
| [11] | SUN Li1, ZHAO Shuhui1, ZHANG Jinguang1, YUAN Jian1, JIN Bo2,SONG Huaiyu2, QIN Xin1, LIU Yang1, FANG Bin1. Characteristics of Cloud Vertical Structure Based on Threshold Method of Relative Humidity in Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 619-625. |
| [12] | DUAN Yunxia, LI Deqin, LI Dawei, LIANG Hong, CHAI Xiaoling, ZHANG Shuai. Analysis on Precipitation Phase Characteristics and Its Forecast Methods of Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 51-57. |
| [13] | LI Yiping, WANG Jinsong, Li Yaohui. Characteristics of a Regional Meteorological Drought Event in Southwestern China During 2009-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 537-545. |
| [14] | NI Jiangbo,LI Wencai,SHANG Kezheng,WANG Shigong, LI Deshuai. Automatic Identificationand Prediction of Low Visibility Weather in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(1): 174-179. |
| [15] | WANG Suyan,ZHENG Guangfen,LI Xin,LI Zhenglin,YANG Jianling,FENG Jianmin. Modification of CI Comprehensive Meteorological Drought Index and Its Application in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(3): 561-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
