Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 163-175.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-02-0163
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Drought evolution characteristics and vegetation response in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022
SU Tianxin1( ), MENG Xianhong2,3, YANG Xianyu1(
), MENG Xianhong2,3, YANG Xianyu1( ), AN Yingying2,3, ZHAO Cailing4
), AN Yingying2,3, ZHAO Cailing4
- 1. College of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology/ Sichuan Key Laboratory of Plateau Atmosphere and Environment, Chengdu 610225, China
2. Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences / Key Laboratory of Cryosphere Science and Frozen Soil Engineering, Lanzhou 730000, China
3. Field Scientific Observatory for Climate and Environment in the Yellow River Source Region, Lanzhou 730000, China
4. Key Laboratory for Arid Climate Change and Disaster Reduction of Gansu Province, Lanzhou Institute of Arid Meteorology/ Key Laboratory for Arid Climate Change and Disaster Reduction of the China Meteorological Administration, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2024-11-28Revised:2025-01-16Online:2025-04-30Published:2025-05-13
1963—2022年西北地区中西部干旱演变特征及植被响应研究
苏天鑫1( ), 孟宪红2,3, 杨显玉1(
), 孟宪红2,3, 杨显玉1( ), 安颖颖2,3, 赵采玲4
), 安颖颖2,3, 赵采玲4
- 1.成都信息工程大学大气科学学院/高原大气与环境四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610225
2.中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院/冰冻圈科学与冻土工程重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730000
3.甘肃省黄河源区气候与环境野外科学观测研究站,甘肃 兰州 730000
4.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室/中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:杨显玉(1982—),男,内蒙古赤峰人,副教授,主要从事陆面过程与气候变化研究。E-mail:xyang@cuit.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:苏天鑫(2001—),男,湖北襄阳人,硕士研究生,主要从事区域气候变化及其影响研究。E-mail:sutianxin2001@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国科学院B类先导专项(XDB0720200);甘肃省科技领军人才项目(24RCKB009);中国科学院“西部之光-西部交叉团队”项目(xbzg-zdsys-202215);甘肃省科技计划项目(23JRRA654);干旱气象科学研究基金项目(IAM201803)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SU Tianxin, MENG Xianhong, YANG Xianyu, AN Yingying, ZHAO Cailing. Drought evolution characteristics and vegetation response in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 163-175.
苏天鑫, 孟宪红, 杨显玉, 安颖颖, 赵采玲. 1963—2022年西北地区中西部干旱演变特征及植被响应研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(2): 163-175.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-02-0163
| 等级 | 干旱类型 | SPEI值 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | -0.5<SPEI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<SPEI≤-0.5 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<SPEI≤-1.0 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<SPEI≤-1.5 |
| 5 | 特旱 | SPEI≤-2.0 |
Tab.1 Drought classification criteria based on SPEI
| 等级 | 干旱类型 | SPEI值 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | -0.5<SPEI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<SPEI≤-0.5 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<SPEI≤-1.0 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<SPEI≤-1.5 |
| 5 | 特旱 | SPEI≤-2.0 |
| 监测结果 | 监测效果 | 评分 |
|---|---|---|
| 空检测或漏监测 | 差 | 0 |
| 程度和范围均有偏差 | 较差 | 1 |
| 程度和范围有1项符合 | 一般 | 2 |
| 程度和范围均符合 | 较好 | 3 |
Tab.2 Drought event SPEI applicability rating criteria
| 监测结果 | 监测效果 | 评分 |
|---|---|---|
| 空检测或漏监测 | 差 | 0 |
| 程度和范围均有偏差 | 较差 | 1 |
| 程度和范围有1项符合 | 一般 | 2 |
| 程度和范围均符合 | 较好 | 3 |
| 干旱类型 | 年份 | 主要旱区 | 评分 | 准确率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春旱 | 1974 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | 62.50 |
| 1977 | 新疆局部、青海大部 | 2 | ||
| 1978 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | ||
| 1981 | 甘肃大部 | 1 | ||
| 1986 | 新疆大部、甘肃河西 | 1 | ||
| 2000 | 新疆大部、甘肃大部、青海海东 | 3 | ||
| 2004 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | ||
| 2015 | 新疆大部、甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 夏旱 | 1972 | 甘肃河东、青海海东 | 2 | 79.17 |
| 1978 | 新疆大部、甘肃河西 | 2 | ||
| 1990 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | ||
| 1991 | 西北大部 | 3 | ||
| 1995 | 甘肃河东、青海大部 | 3 | ||
| 1997 | 甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 2006 | 西北大部 | 3 | ||
| 2017 | 甘肃大部、青海东部 | 2 | ||
| 秋旱 | 1986 | 新疆大部 | 2 | 83.33 |
| 1991 | 新疆北部、甘肃河东 | 3 | ||
| 1998 | 甘肃河东 | 3 | ||
| 1999 | 甘肃中东部 | 2 | ||
| 春夏秋连旱 | 1978 | 新疆大部 | 2 | 75.00 |
| 1997 | 甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 2008 | 新疆大部 | 3 | ||
| 2022 | 甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 整体 | 53 | 73.61 | ||
Tab.3 Drought events in study area、monitoring effectiveness rating and accuracy
| 干旱类型 | 年份 | 主要旱区 | 评分 | 准确率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春旱 | 1974 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | 62.50 |
| 1977 | 新疆局部、青海大部 | 2 | ||
| 1978 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | ||
| 1981 | 甘肃大部 | 1 | ||
| 1986 | 新疆大部、甘肃河西 | 1 | ||
| 2000 | 新疆大部、甘肃大部、青海海东 | 3 | ||
| 2004 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | ||
| 2015 | 新疆大部、甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 夏旱 | 1972 | 甘肃河东、青海海东 | 2 | 79.17 |
| 1978 | 新疆大部、甘肃河西 | 2 | ||
| 1990 | 新疆大部、甘肃河东 | 2 | ||
| 1991 | 西北大部 | 3 | ||
| 1995 | 甘肃河东、青海大部 | 3 | ||
| 1997 | 甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 2006 | 西北大部 | 3 | ||
| 2017 | 甘肃大部、青海东部 | 2 | ||
| 秋旱 | 1986 | 新疆大部 | 2 | 83.33 |
| 1991 | 新疆北部、甘肃河东 | 3 | ||
| 1998 | 甘肃河东 | 3 | ||
| 1999 | 甘肃中东部 | 2 | ||
| 春夏秋连旱 | 1978 | 新疆大部 | 2 | 75.00 |
| 1997 | 甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 2008 | 新疆大部 | 3 | ||
| 2022 | 甘肃大部 | 2 | ||
| 整体 | 53 | 73.61 | ||
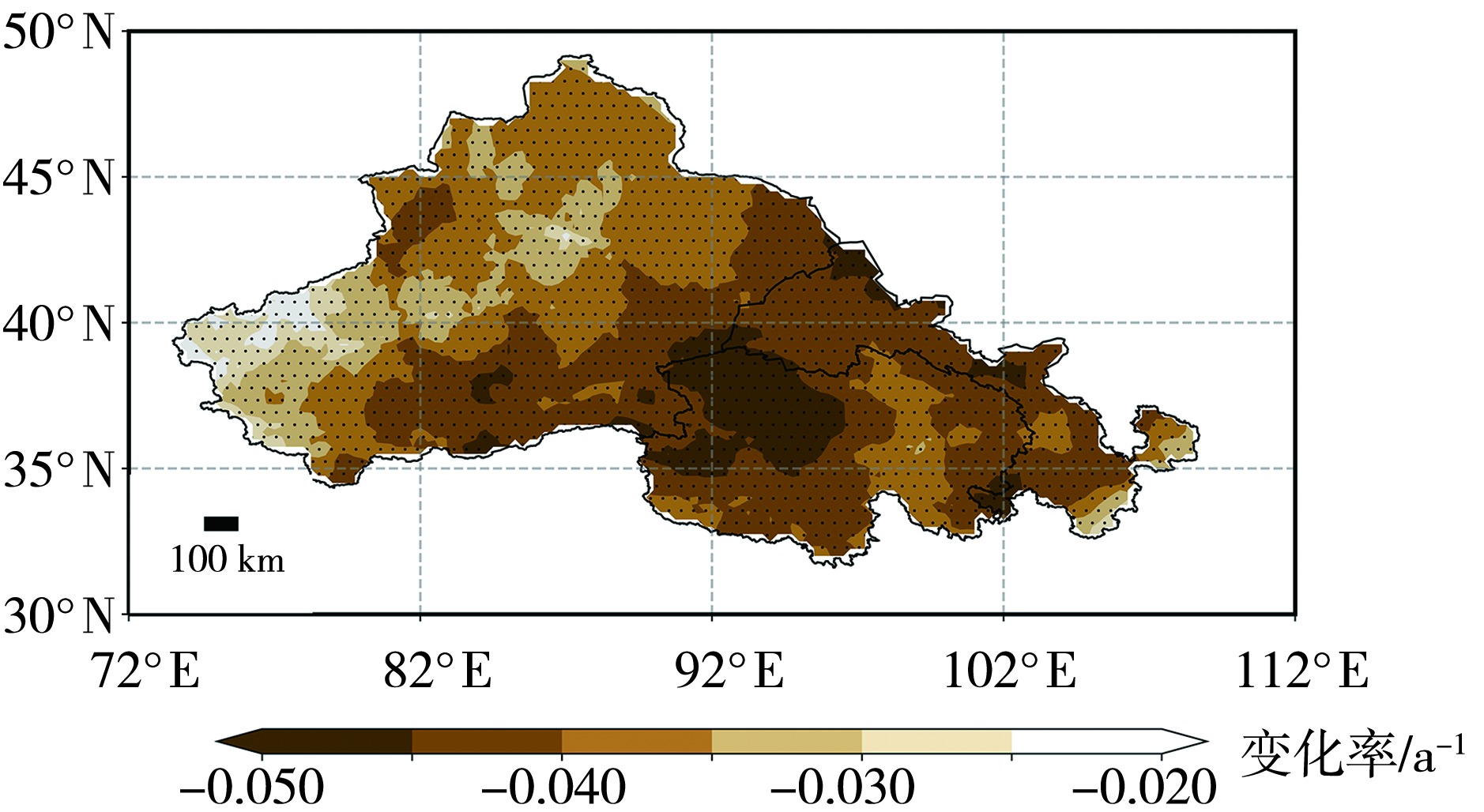
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of the SPEI change rate in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022 (The dotted areas indicate significance at the 95% confidence level)

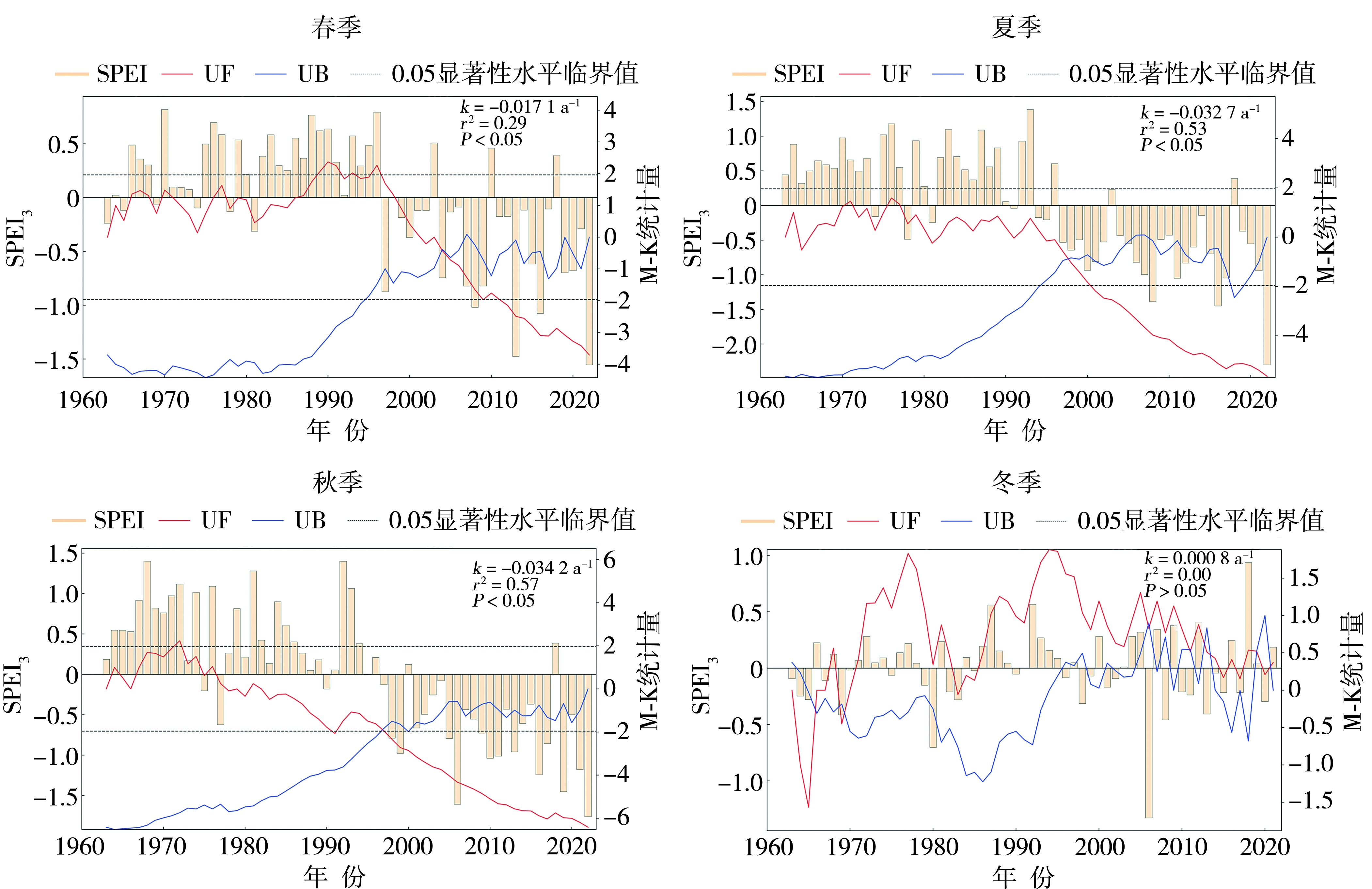
Fig.6 Wavelet analysis of drought cycles based on SPEI (a) and corresponding wavelet coefficient variance (b) in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022
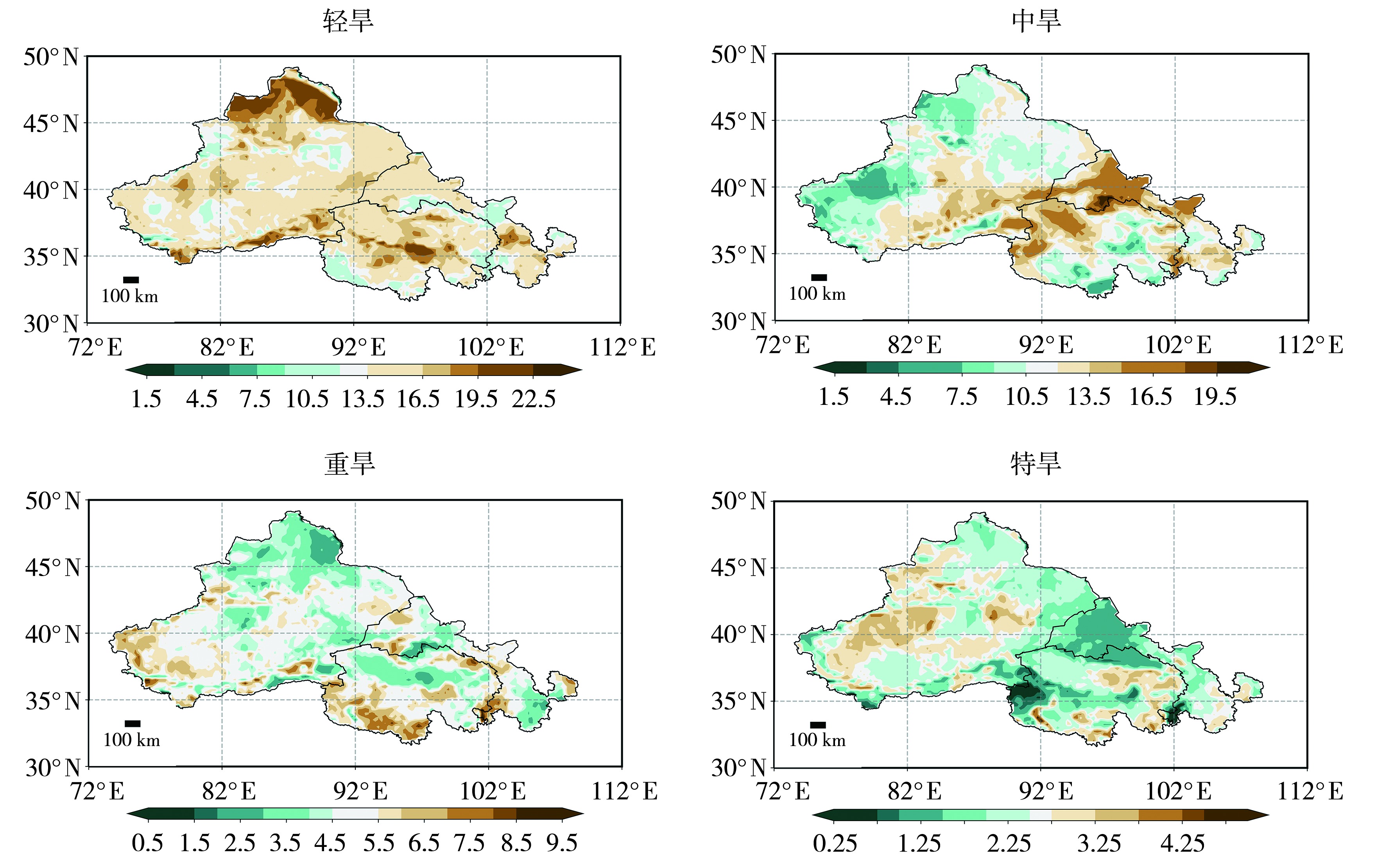
Fig.7 Spatial distribution of drought occurrence frequency (Unit: %) at different severity levels in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022

Fig.8 Spatial distribution of seasonal SPEI trends in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022 (Unit: a-1) (The dotted areas indicate significance at the 95% confidence level)
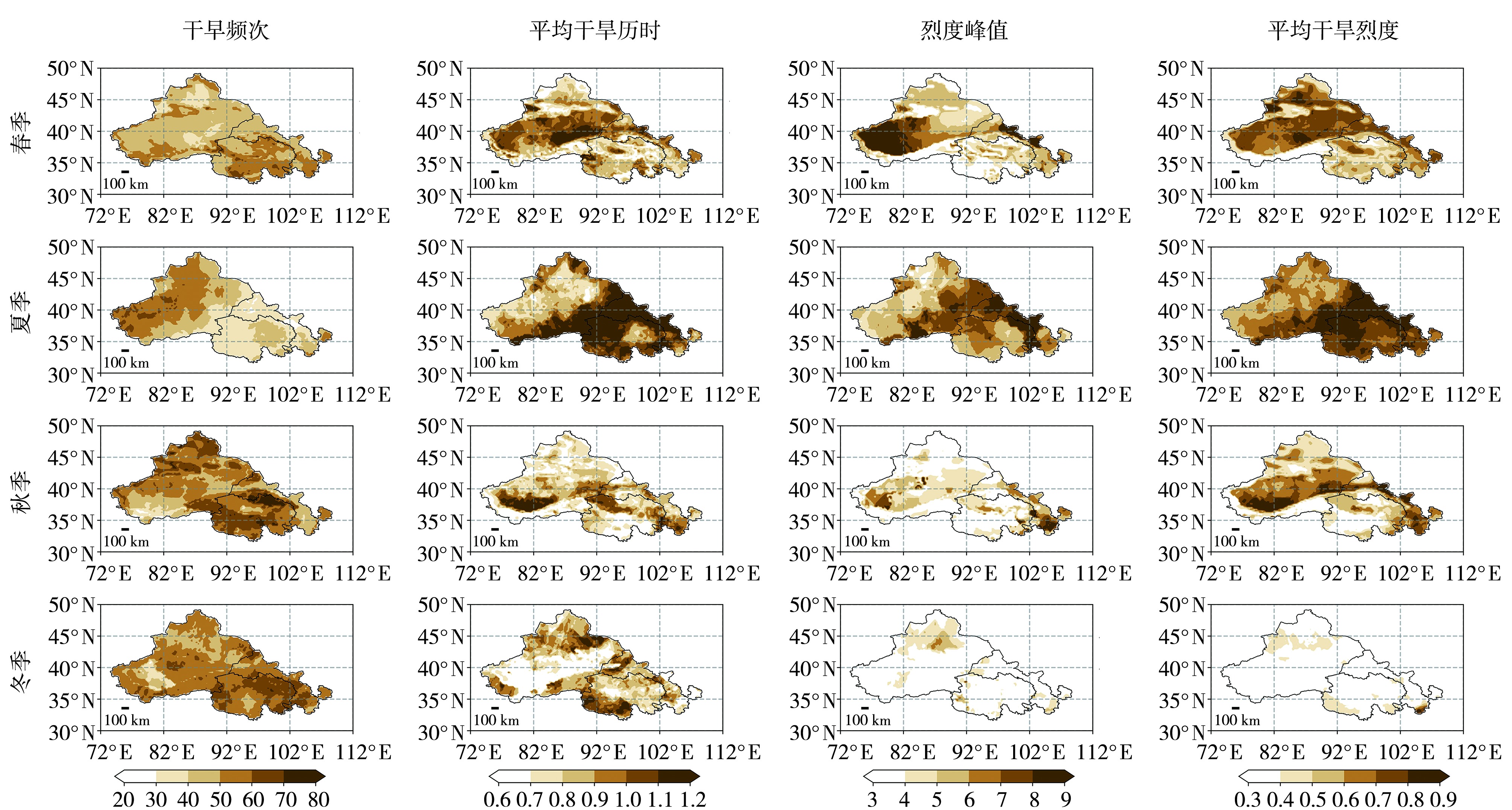
Fig.9 Spatial distribution of seasonal drought frequency, mean duration, peak intensity, and mean intensity in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022

Fig.11 Spatial distribution of annual mean NDVI and its trend changes in different periods in the midwestern region of northwest China from 2003 to 2022
| NDVI均值 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% |
|---|---|---|
| <0.1 | 18 928 780 | 41.06 |
| ~0.1<0.2 | 9 231 039 | 20.02 |
| ~0.2<0.3 | 3 847 051 | 8.35 |
| ~0.3<0.4 | 2 606 813 | 5.65 |
| ~0.4<0.95 | 11 484 042 | 24.92 |
Tab.4 Annual average statistics of NDVI in the midwestern region of northwest China from 2003 to 2022
| NDVI均值 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% |
|---|---|---|
| <0.1 | 18 928 780 | 41.06 |
| ~0.1<0.2 | 9 231 039 | 20.02 |
| ~0.2<0.3 | 3 847 051 | 8.35 |
| ~0.3<0.4 | 2 606 813 | 5.65 |
| ~0.4<0.95 | 11 484 042 | 24.92 |
| NDVI趋势 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.000 5 | ≤1.96 | 轻微退化 | 2 926 009 | 6.48 |
| <-0.000 5 | >1.96 | 显著退化 | 716 410 | 1.59 |
| -0.000 5~0.000 5 | 稳定不变 | 15 602 273 | 34.57 | |
| >0.000 5 | >1.96 | 明显改善 | 14 966 410 | 33.17 |
| >0.000 5 | ≤1.96 | 轻微改善 | 10 915 416 | 24.19 |
Tab.5 Statistics on the trend of NDVI in the midwestern region of northwest China from 2003 to 2022
| NDVI趋势 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.000 5 | ≤1.96 | 轻微退化 | 2 926 009 | 6.48 |
| <-0.000 5 | >1.96 | 显著退化 | 716 410 | 1.59 |
| -0.000 5~0.000 5 | 稳定不变 | 15 602 273 | 34.57 | |
| >0.000 5 | >1.96 | 明显改善 | 14 966 410 | 33.17 |
| >0.000 5 | ≤1.96 | 轻微改善 | 10 915 416 | 24.19 |
| 2003—2012年 | 2013—2022年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI趋势 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% | NDVI趋势 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% |
| 轻微退化 | 8 013 340 | 17.72 | 轻微退化 | 9 291 888 | 20.54 |
| 明显退化 | 782 646 | 1.73 | 明显退化 | 1 099 378 | 2.43 |
| 稳定不变 | 11 958 309 | 26.45 | 稳定不变 | 11 165 730 | 24.68 |
| 明显改善 | 6 001 385 | 13.27 | 明显改善 | 5 199 594 | 11.49 |
| 轻微改善 | 18 455 916 | 40.83 | 轻微改善 | 18 487 780 | 40.86 |
Tab.6 Statistics of NDVI trends in the midwestern region of northwest China from 2003 to 2012 and from 2013 to 2022
| 2003—2012年 | 2013—2022年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI趋势 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% | NDVI趋势 | 像元个数 | 百分比/% |
| 轻微退化 | 8 013 340 | 17.72 | 轻微退化 | 9 291 888 | 20.54 |
| 明显退化 | 782 646 | 1.73 | 明显退化 | 1 099 378 | 2.43 |
| 稳定不变 | 11 958 309 | 26.45 | 稳定不变 | 11 165 730 | 24.68 |
| 明显改善 | 6 001 385 | 13.27 | 明显改善 | 5 199 594 | 11.49 |
| 轻微改善 | 18 455 916 | 40.83 | 轻微改善 | 18 487 780 | 40.86 |
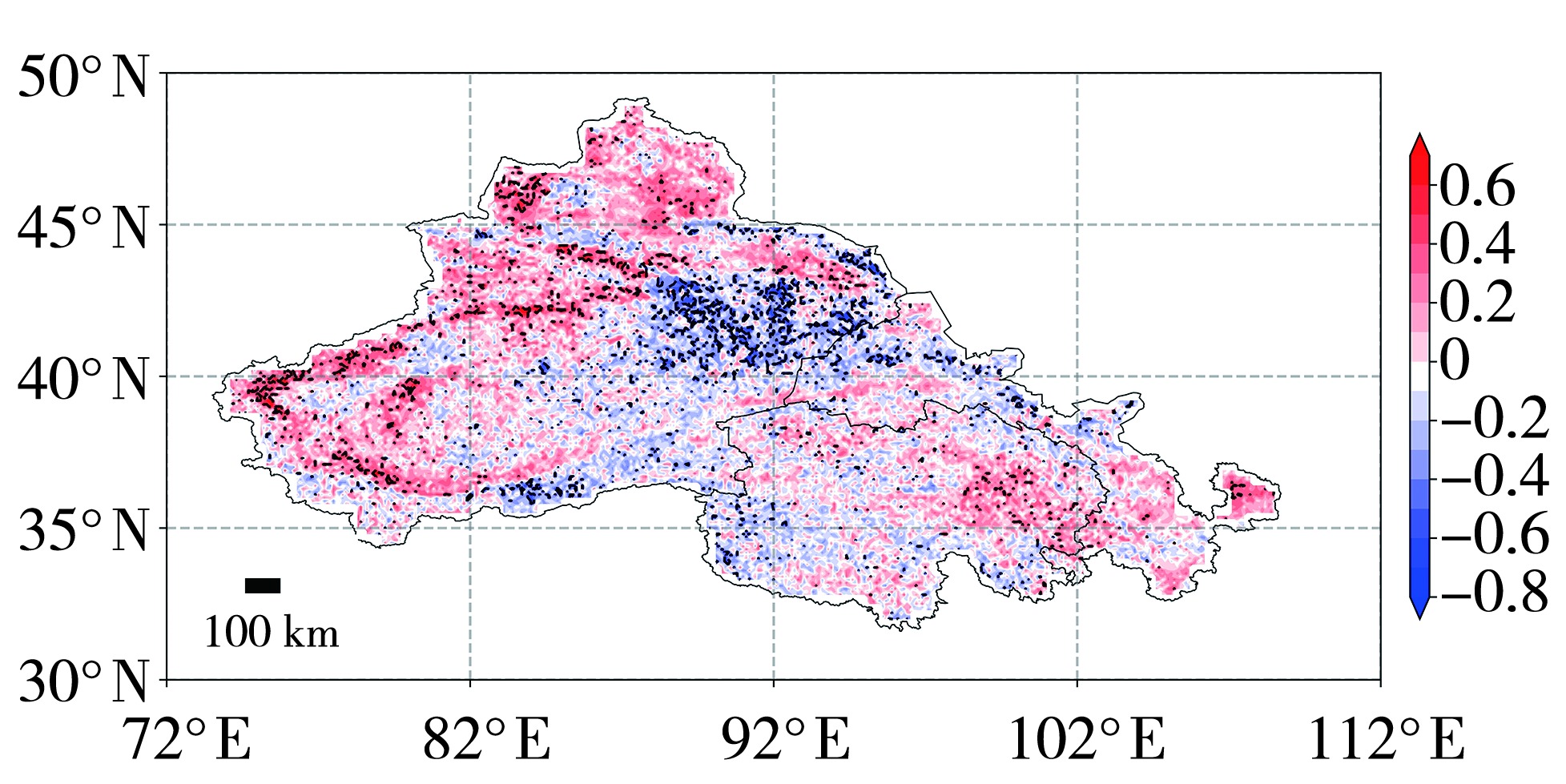
Fig.12 Spatial distribution of the correlation coefficient between NDVI and SPEI in the midwestern region of northwest China from 2003 to 2022 (The black areas indicate significance at the 95% confidence level)
| [1] | 柴荣繁, 陈海山, 孙善磊, 2018. 基于SPEI的中国干湿变化趋势归因分析[J]. 气象科学, 38(4):423-431. |
| [2] | 陈亚宁, 李忠勤, 徐建华, 等, 2023. 中国西北干旱区水资源与生态环境变化及保护建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 38(3):385-393. |
| [3] | 丁一汇, 柳艳菊, 徐影, 等, 2023. 全球气候变化的区域响应:中国西北地区气候“暖湿化”趋势、成因及预估研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 38(6):551-562. |
| [4] | 董文杰, 2005. 中国气象灾害年鉴2004[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [5] | 董文杰, 2007. 中国气象灾害年鉴2006[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [6] | 高婧, 井立红, 李海燕, 等, 2024. 近60 a新疆塔城地区降水及气象干旱变化特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(1):134-142. |
| [7] | 高鹏文, 阿里木江·卡斯木, 赵永玉, 等, 2020. 1988—2018年哈密绿洲植被覆盖度时空变化及其驱动力[J]. 水土保持通报, 40(6):273-280. |
| [8] |
郭兵, 孔维华, 姜琳, 2018. 西北干旱荒漠生态区脆弱性动态监测及驱动因子定量分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 33(3):412-424.
DOI |
| [9] | 郭冬, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 吴秀兰, 等, 2022. 四种气象干旱指数在新疆区域适用性研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(3):90-101. |
| [10] | 黄文君, 2021. 中国西北干旱区干旱时空演变及预估[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. |
| [11] | 姜萍, 胡列群, 肖静, 等, 2022. 新疆植被NDVI时空变化及定量归因[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(2):212-220. |
| [12] | 焦岩, 闫峰, 卢琦, 等, 2024. 西北干旱区绿洲时空变化及驱动力[J]. 应用生态学报, 35(8):2206-2 216. |
| [13] | 孔冬冬, 张强, 顾西辉, 等, 2016. 植被对不同时间尺度干旱事件的响应特征及成因分析[J]. 生态学报, 36(24):7908-7 918. |
| [14] | 李明, 张永清, 张莲芝, 2017. 基于Copula函数的长春市106年来的干旱特征分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 31(6):147-153. |
| [15] |
梁丹, 赵锐锋, 李洁, 等, 2015. 4种干旱指标在河西走廊地区的适用性评估[J]. 中国农学通报, 31(36):194-204.
DOI |
| [16] | 刘宇, 田济扬, 黄婷婷, 等, 2023. 长江流域NDVI变化及其驱动因素分析[J]. 地理科学, 43(6):1022-1 031. |
| [17] | 马楠, 白涛, 蔡朝朝, 2024. 2000—2021年新疆植被覆盖度变化及驱动力[J]. 水土保持研究, 31(1):385-394. |
| [18] | 马有绚, 2016. 干旱半干旱地区植被指数与气候的关系[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [19] | 梅静, 2023. 气候与植被变化对西北地区蒸散发影响评估[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| [20] | 全国气候与气候变化标准化技术委员会, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [21] | 宋佳颖, 2021. 西北五省植被NDVI的时空变化及驱动力研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| [22] | 宋连春, 2016. 中国气象灾害年鉴 2015[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [23] | 宋连春, 2018. 中国气象灾害年鉴 2017[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [24] | 滕怀颐, 2021. 西北地区近34 a干旱时空演变规律[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学. |
| [25] |
王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2020. 多种干旱指数在中国北方的适用性及其差异原因初探[J]. 高原气象, 39(3):628-640.
DOI |
| [26] | 王文举, 崔鹏, 刘敏, 等, 2012. 近50年湖北省多时间尺度干旱演变特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 28(29):279-284. |
| [27] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4):549-566.
DOI |
| [28] | 王芝兰, 李耀辉, 王素萍, 等, 2015. 1901—2012年中国西北地区东部多时间尺度干旱特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 35(6):1666-1 673. |
| [29] | 卫捷, 马柱国, 2003. Palmer干旱指数、地表湿润指数与降水距平的比较[J]. 地理学报(增刊1):117-124. |
| [30] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [31] | 温克刚, 丁一汇, 2008. 中国气象灾害大典. 综合卷[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [32] | 吴佳, 高学杰, 2013. 一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4):1102-1 111. |
| [33] | 吴万民, 刘涛, 陈鑫, 2023. 西北干旱半干旱区NDVI季节性变化及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究, 40(12):1969-1 981. |
| [34] | 肖子牛, 2009. 中国气象灾害年鉴2008[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [35] | 熊威, 2017. 基于Palmer旱度模式的四湖流域旱涝急转特征分析[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学. |
| [36] | 张强, 李栋梁, 姚玉璧, 等, 2024. 干旱形成机制与预测理论方法及其灾害风险特征研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 82(1):1-21. |
| [37] |
张强, 杨金虎, 马鹏里, 等, 2023. 西北地区气候暖湿化增强东扩特征及其形成机制与重要环境影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):351-358.
DOI |
| [38] | 张强, 张良, 崔显成, 等, 2011. 干旱监测与评价技术的发展及其科学挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 26(7):763-778. |
| [39] | 张强, 朱飙, 杨金虎, 等, 2021. 西北地区气候湿化趋势的新特征[J]. 科学通报, 66(28):3757-3 771. |
| [40] | 张燕, 王雪姣, 张新, 等, 2024. 北疆绿洲农业区气象干旱指数的确定及干旱特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(4):133-142. |
| [41] |
赵鸿, 蔡迪花, 王鹤龄, 等, 2023. 干旱灾害对粮食安全的影响及其应对技术研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2):187-206.
DOI |
| [42] |
赵惠珍, 何涛, 郭瑞霞, 等, 2023. 基于SPEI的甘南高原气象干旱变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5):688-696.
DOI |
| [43] | 赵林, 武建军, 吕爱锋, 等, 2011. 黄淮海平原及其附近地区干旱时空动态格局分析:基于标准化降雨指数[J]. 资源科学, 33(3):468-476. |
| [44] | 赵煜飞, 朱江, 许艳, 2014. 近50 a中国降水格点数据集的建立及质量评估[J]. 气象科学, 34(4):414-420. |
| [45] | 郑有飞, 徐芳, 关福来, 等, 2007. AVHRR植被产品在干旱研究中的应用[J]. 科技信息(29):20-22. |
| [46] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2005. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2004[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [47] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2007. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2006[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [48] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2009. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2008[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [49] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2016. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2015[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [50] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2018. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2018[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [51] | 中华人民共和国水利部, 2023. 中国水旱灾害防御公报2022[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [52] | 周俊菊, 冯炜, 向鹃, 等, 2022. 基于SPEI指数的近58 a甘肃省干旱特征分析[J]. 气象科学, 42(1):99-107. |
| [53] | GOCIC M, TRAJKOVIC S, 2014. Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in Serbia[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 510:110-123. |
| [54] | HUANG J, LI Y, FU C, et al, 2017. Dryland climate change: Recent progress and challenges[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 55(3): 719-778. |
| [55] |
LIU X B, YU S Y, YANG Z W, et al, 2024. The first global multi-timescale daily SPEI dataset from 1982 to 2021[J]. Scientific Data, 11:223. DOI:10.1038/s41597-024-03047-z.
PMID |
| [56] |
LIU X F, ZHU X F, PAN Y Z, et al, 2018. Performance of different drought indices for agriculture drought in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 10(4): 507-516.
DOI |
| [57] | THORNTHWAITE C W, 1948. An approach toward a rational classification of climate[J]. Geographical Review, 38(1):55-94. |
| [58] | VICENTE-SERRANO S M, BEGUERÍA, LÓPEZ-MORENO J I, 2010. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(7): 1 696-1 718. |
| [59] | YAO J Q, ZHAO Y, CHEN Y N, et al, 2018. Multi-scale assessments of droughts: A case study in Xinjiang, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 630: 444-452. |
| [1] |
HE Huigen, ZHANG Chi, CHENG Qingyan, LI Yonghua, GAN Weiwei, JIN Yan.
Analysis on differences of characteristics and atmospheric circulation causes of meteorological drought during summer in Sichuan-Chongqing region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 355-365. |
| [2] |
NIE Zhenling, WU Guoming, DONG Hangyu.
Risk assessment of drought disasters on apple cultivation in Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 375-384. |
| [3] | TANG Yurui, QI Yue, WANG Heling, YANG Yang, ZHAO Hong, ZHANG Kai, WEI Xingxing, WANG Renkui. Photosynthetic characteristics and response mechanism of spring maize at seven-leaf stage under drought stress [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 176-185. |
| [4] | LIU Yulian, LI Xiufen, KANG Hengyuan, SUN Shuang, YUAN Fang, ZHOU Heling, SHEN Yuezhao. Multi-scale drought spatiotemporal characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from 1961 to 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 186-194. |
| [5] | PAN Yongdi, XIAO Jingjing, PAN Yanhua, SHI Jie. A meteorological drought index based on cumulative precipitation and cumulative evaporation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 1-10. |
| [6] | ZHOU Jianqin, LI Meng, TAO Yun, DOU Xiaodong, WANG Yuyouting. Study on the evolutionary characteristics of agricultural drought disasters and the relationship with climatic factors in Yunnan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 21-31. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yucui, TAN Jianghong, YAN Caixia. Variability characteristics and risk assessment of regional high temperature, drought and their compound events in Hubei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 825-835. |
| [8] | YANG Xiaoling, SUN Xuying, YANG Jinhu, WU Wen, ZHAO Huihua, CHEN Jing. Identification and evolution characteristics of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 836-843. |
| [9] | REN Zhihan, NI Changjian, SHI Qiaoyu, CHEN Ning. Analysis of drought characteristics in Chengdu over the past 63 years based on the optimal probability distribution function [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 844-853. |
| [10] | YIN Fei, BAI Bing, HUANG Pengcheng, MA Yulong. Impact of climate and human activities on NDVI change in Gansu section of the Yellow River main stream [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 934-943. |
| [11] | WANG Min, SUN Shujun, ZHANG Jian, LI Tianfang, CHEN Rui, YANG Xing, XIAO Yawen. Characteristics of vegetation cover change and its relationship with climate factors in Ganzi Prefecture [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 944-952. |
| [12] | XIE Ziyang, LI Changshun, CAI Jiayi, WANG Shanshan. Bibliometric analysis and visualization of the relationship between climate change and soil moisture from 1988 to 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 953-964. |
| [13] | WANG Yajun, LUO Juying, CHENG Liehai, LI Wei. Construction and validation of summer drought prediction model in Hubei Province based on machine learning algorithms [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 661-670. |
| [14] | WANG Yuetong, HE Dongpo, LI Zhongyan, WANG Shuo, CHEN Zaoyang. Analysis of two meteorological drought events in Guizhou Province and establishment of drought prediction model based on machine learning [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 671-682. |
| [15] | LI Bin, SUN Xiaolong, LU Shiqing, WANG Yuchen, XIA Ningyue, HAN Fang. Retrieval of net primary productivity in grassland of Inner Mongolia based on FY-3D/MERSI2 data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 734-743. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||