Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 661-670.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0661
• Special Column: Application of Artificial Intelligence in Drought Meteorology and Related Fields • Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and validation of summer drought prediction model in Hubei Province based on machine learning algorithms
WANG Yajun1,2( ), LUO Juying1, CHENG Liehai3(
), LUO Juying1, CHENG Liehai3( ), LI Wei4
), LI Wei4
- 1. Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture Meteorological Bureau of Hubei Province, Enshi 445000, Hubei, China
2. Hubei Key Laboratory for Heavy Rain Monitoring and Warning Research, Wuhan 430205, China
3. Shandong Electric Power Engineering Consulting Institute Company Limited, Jinan 250013, China
4. Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster of Ministry of Education, Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2024-08-03Revised:2024-09-15Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-17
基于机器学习的湖北省夏季干旱预测模型构建与检验
- 1.湖北省恩施土家族苗族自治州气象局,湖北 恩施 445000
2.暴雨监测预警湖北省重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430205
3.山东电力工程咨询院有限公司,山东 济南 250013
4.南京信息工程大学,气象灾害教育部重点实验室,气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210044
-
通讯作者:程烈海(1973—),男,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事风能太阳能等新能源气候预测。E-mail:chengliehai@sdepci.com 。 -
作者简介:王雅君(1996—),女,硕士,助理工程师,主要从事季节尺度干旱预测和区域气候变化研究。E-mail:1843984032@qq.com。 -
基金资助:湖北省气象局科研项目(2023Q15);山东省工信厅课题(202350100877)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Yajun, LUO Juying, CHENG Liehai, LI Wei. Construction and validation of summer drought prediction model in Hubei Province based on machine learning algorithms[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 661-670.
王雅君, 罗菊英, 程烈海, 李伟. 基于机器学习的湖北省夏季干旱预测模型构建与检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 661-670.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0661
| SPEI | 干旱等级 | 是否干旱 |
|---|---|---|
| -0.5<SPEI | 无旱 | 否 |
| -1.0<SPEI≤-0.5 | 轻旱 | 是 |
| -1.5<SPEI≤-1.0 | 中旱 | 是 |
| -2.0<SPEI≤-1.5 | 重旱 | 是 |
| SPEI≤-2.0 | 特旱 | 是 |
Tab.1 The drought classification standard based on SPEI
| SPEI | 干旱等级 | 是否干旱 |
|---|---|---|
| -0.5<SPEI | 无旱 | 否 |
| -1.0<SPEI≤-0.5 | 轻旱 | 是 |
| -1.5<SPEI≤-1.0 | 中旱 | 是 |
| -2.0<SPEI≤-1.5 | 重旱 | 是 |
| SPEI≤-2.0 | 特旱 | 是 |
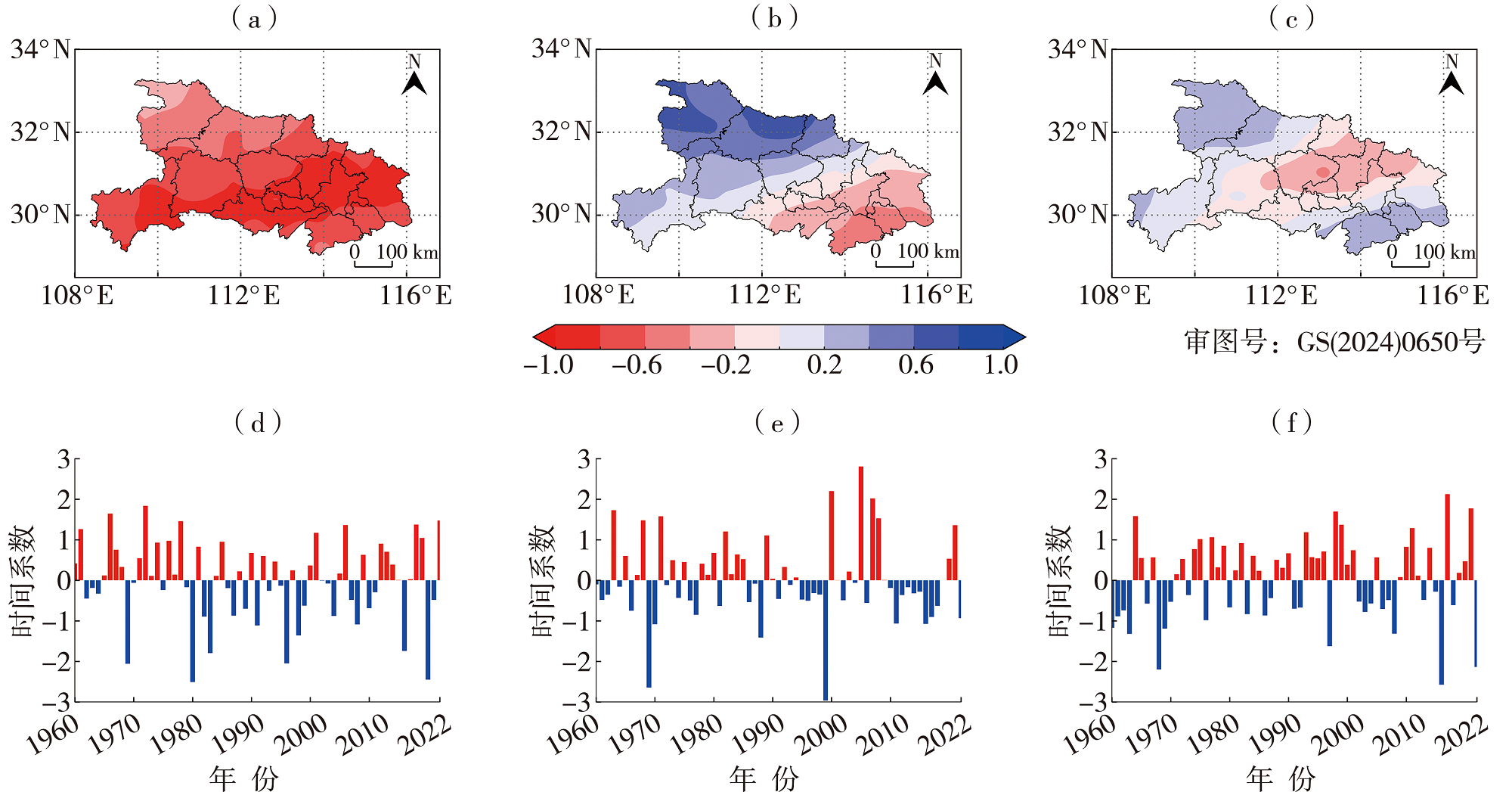
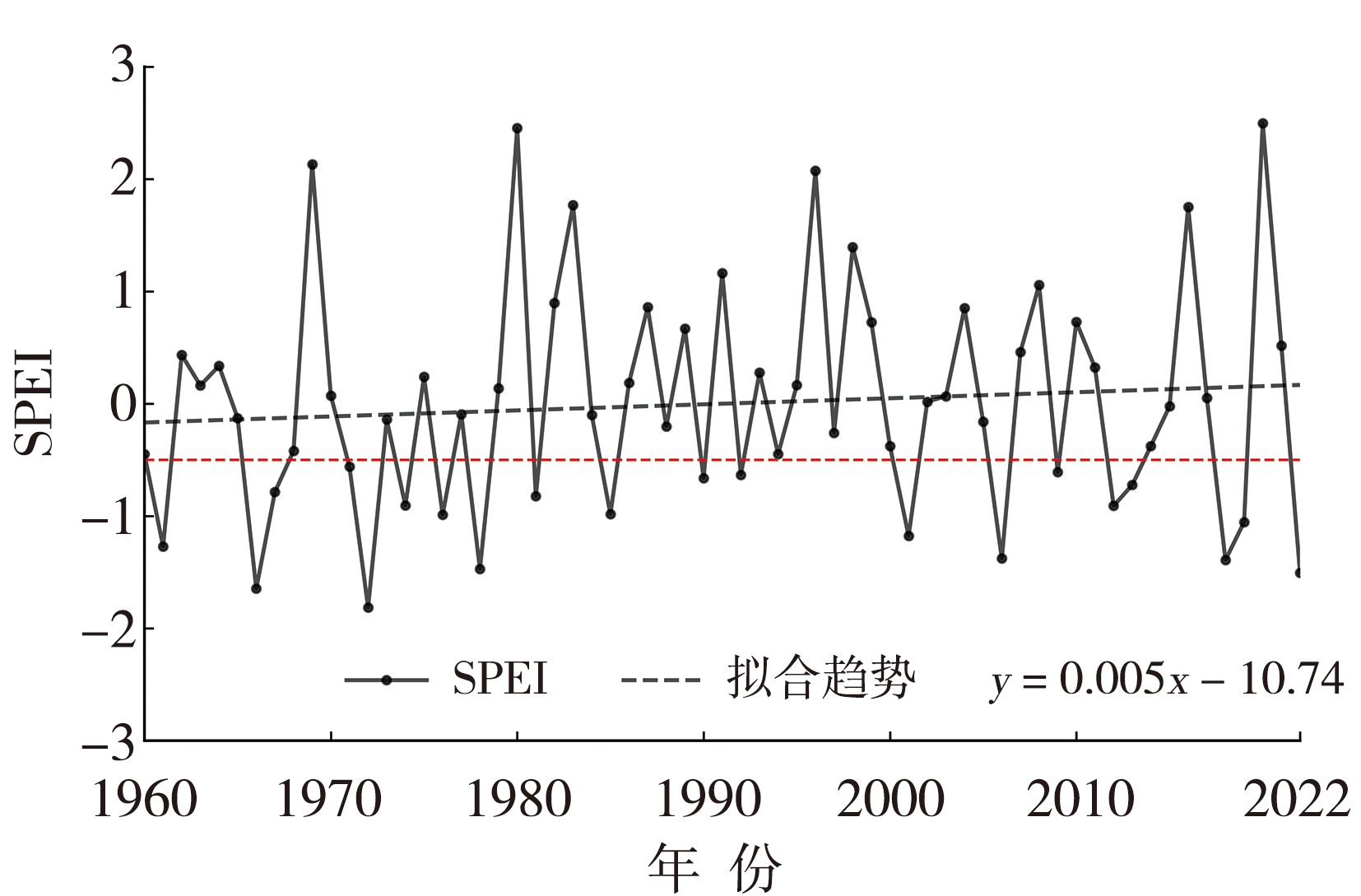
Fig.2 The spatial distribution (a, b, c) and their corresponding time coefficients (d, e, f) of the first (a, d), second (b, e), and third (c, f) modes by EOF decomposition of the summer SPEI in Hubei Province from 1960 to 2022
| 特征编号 | 影响因子 | 定义 | 相关 系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 热带南大西洋海温指数 | 30°W—10°E、20°S—0°区域内海表温度距平的区域平均值 | 0.19 |
| 2 | 亲潮区海温指数 | 165°E—175°E、40°N—45°N区域内海表温度距平的区域平均值 | -0.15 |
| 3 | 西风漂流区海温指数 | 160°E—160°W、35°N—45°N区域内海表温度距平的区域平均值 | -0.09 |
| 4 | 西太平洋副高脊线位置指数 | 110°E—150°E、10°N—60°N区域内500 hPa高度场逐条经线上副热带高压中心位置所在纬度的平均值 | -0.37** |
| 5 | 北美副高脊线位置指数 | 110°W—60°W、10°N—60°N区域内500 hPa高度场逐条经线上副热带高压中心位置所在纬度的平均值 | -0.24* |
| 6 | 北大西洋副高北界位置指数 | 55°W—25°W、10°N—60°N区域内500 hPa高度场逐条经线上副热带高压北侧5 880 gpm等值线所在纬度的平均值 | 0.26** |
| 7 | 亚洲区极涡面积指数 | 北半球60°E—150°E区域内500 hPa高度场极涡南界特征等高线以北所包围的扇形面积 | -0.30** |
| 8 | 亚洲纬向环流指数 | 60°E—150°E、45°N—65°N区域内500 hPa高度场以30个经度为间隔划分为3个区,计算平均纬向指数 | 0.07 |
| 9 | 斯堪的纳维亚遥相关型指数 | 0°—360°、20°N—90°N区域内,标准化500 hPa高度场经验正交函数分析所得的第九模态的时间系数 | -0.32** |
| 10 | AMO | 80°W—0°、0°—60°N区域内平均的海表面温度距平 | 0.26** |
| 11 | NAO | 90°W—50°E、20°N—85°N大西洋地区海平面气压距平场的经验正交函数分解第一主成分 | -0.24* |
Tab.2 The definition of summer drought impact factors and their correlation coefficient with SPEI in Hubei Province from 1960 to 2022
| 特征编号 | 影响因子 | 定义 | 相关 系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 热带南大西洋海温指数 | 30°W—10°E、20°S—0°区域内海表温度距平的区域平均值 | 0.19 |
| 2 | 亲潮区海温指数 | 165°E—175°E、40°N—45°N区域内海表温度距平的区域平均值 | -0.15 |
| 3 | 西风漂流区海温指数 | 160°E—160°W、35°N—45°N区域内海表温度距平的区域平均值 | -0.09 |
| 4 | 西太平洋副高脊线位置指数 | 110°E—150°E、10°N—60°N区域内500 hPa高度场逐条经线上副热带高压中心位置所在纬度的平均值 | -0.37** |
| 5 | 北美副高脊线位置指数 | 110°W—60°W、10°N—60°N区域内500 hPa高度场逐条经线上副热带高压中心位置所在纬度的平均值 | -0.24* |
| 6 | 北大西洋副高北界位置指数 | 55°W—25°W、10°N—60°N区域内500 hPa高度场逐条经线上副热带高压北侧5 880 gpm等值线所在纬度的平均值 | 0.26** |
| 7 | 亚洲区极涡面积指数 | 北半球60°E—150°E区域内500 hPa高度场极涡南界特征等高线以北所包围的扇形面积 | -0.30** |
| 8 | 亚洲纬向环流指数 | 60°E—150°E、45°N—65°N区域内500 hPa高度场以30个经度为间隔划分为3个区,计算平均纬向指数 | 0.07 |
| 9 | 斯堪的纳维亚遥相关型指数 | 0°—360°、20°N—90°N区域内,标准化500 hPa高度场经验正交函数分析所得的第九模态的时间系数 | -0.32** |
| 10 | AMO | 80°W—0°、0°—60°N区域内平均的海表面温度距平 | 0.26** |
| 11 | NAO | 90°W—50°E、20°N—85°N大西洋地区海平面气压距平场的经验正交函数分解第一主成分 | -0.24* |
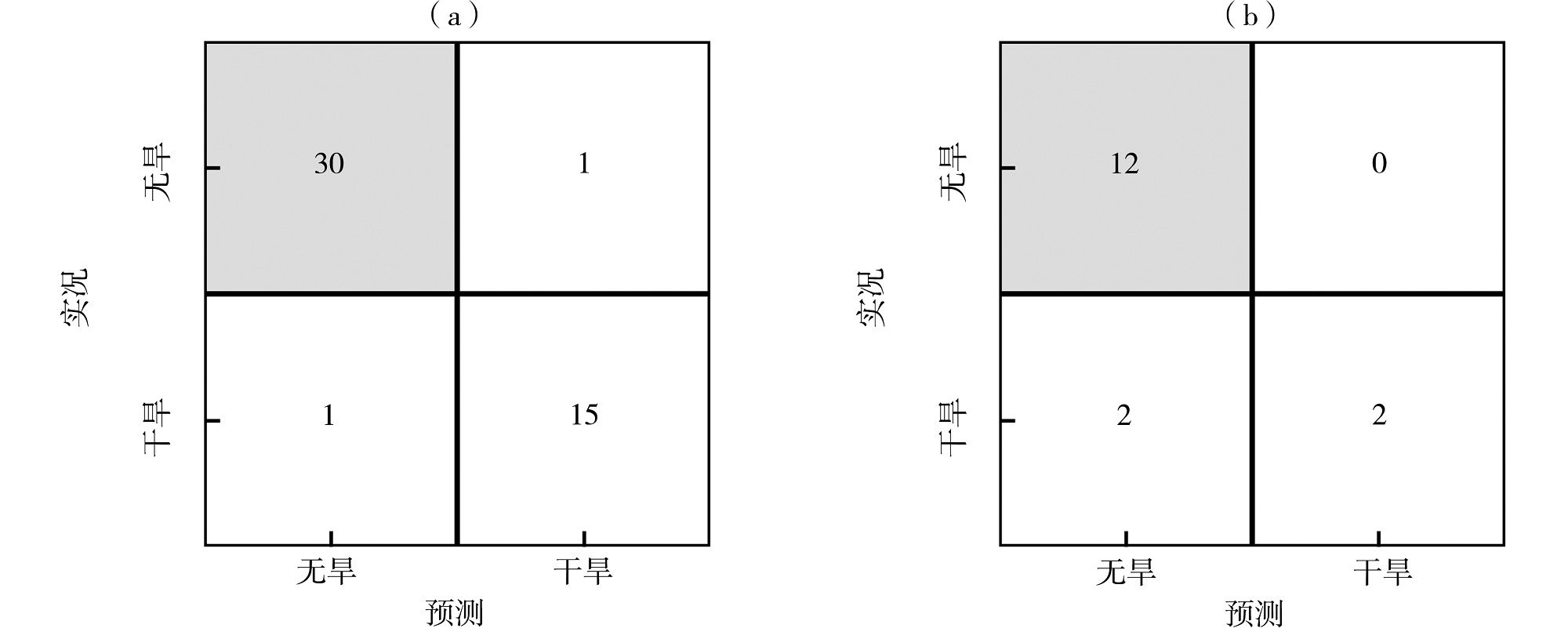
| 年份 | 分类回归树算法预测 | 随机森林算法预测 | 实况 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1962 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1963 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1966 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 1977 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1979 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1980 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1981 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 1983 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1986 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1987 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1991 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1995 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1997 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1999 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2001 | 干旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 2013 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
Tab.3 Comparison of the actual values and predict drought based on classification and regression tree algorithm and random forest algorithm in the test set
| 年份 | 分类回归树算法预测 | 随机森林算法预测 | 实况 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1962 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1963 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1966 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 1977 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1979 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1980 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1981 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 1983 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1986 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1987 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1991 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1995 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1997 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 1999 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2001 | 干旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 2013 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
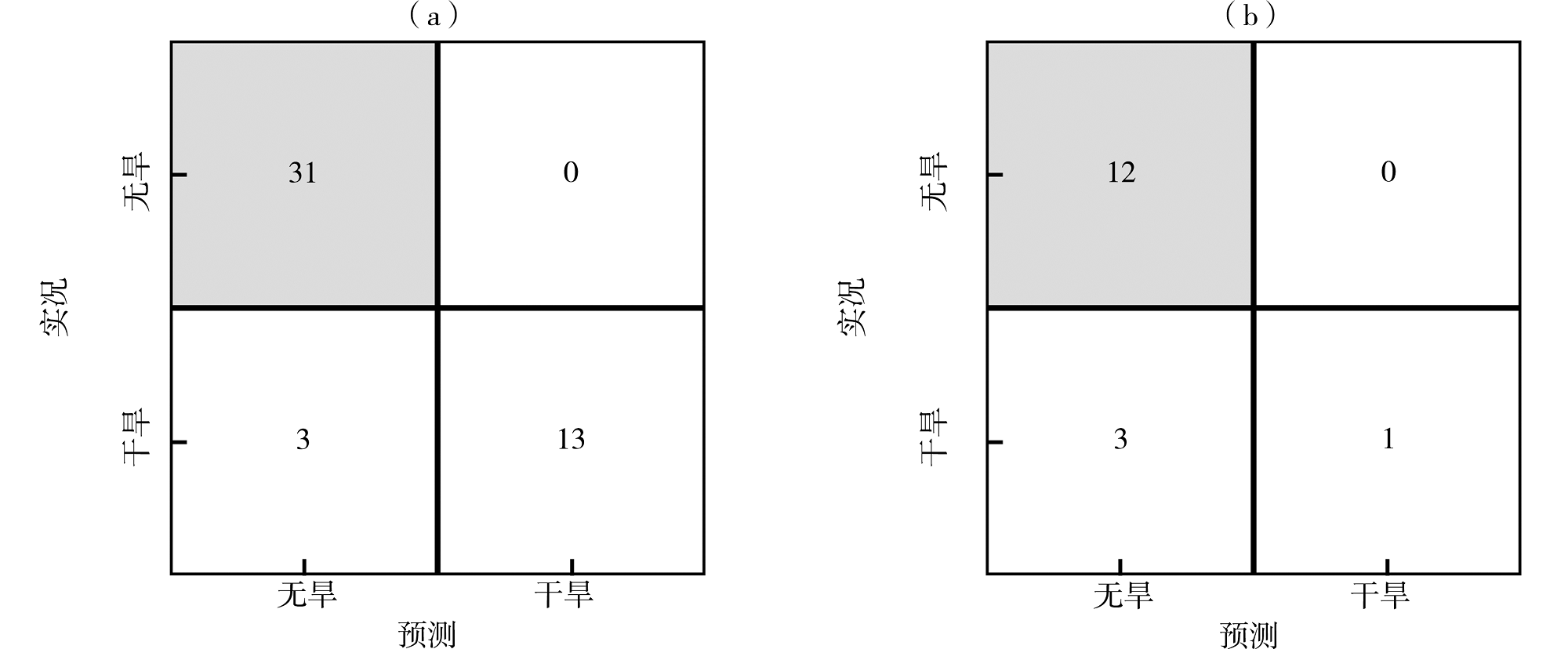
| 年份 | 分类回归树算法预测 | 随机森林算法预测 | 业务发布预测 | 实况 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2012 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
| 2013 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
| 2014 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2015 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2016 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2017 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2018 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
| 2019 | 干旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 2020 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 | 无旱 |
| 2021 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 | 无旱 |
| 2022 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
Tab.4 Comparison between the actual drought and the two machine learning algorithms prediction and operational prediction from 2011 to 2022
| 年份 | 分类回归树算法预测 | 随机森林算法预测 | 业务发布预测 | 实况 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2012 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
| 2013 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
| 2014 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2015 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2016 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2017 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 |
| 2018 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 干旱 |
| 2019 | 干旱 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
| 2020 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 | 无旱 |
| 2021 | 无旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 | 无旱 |
| 2022 | 干旱 | 干旱 | 无旱 | 干旱 |
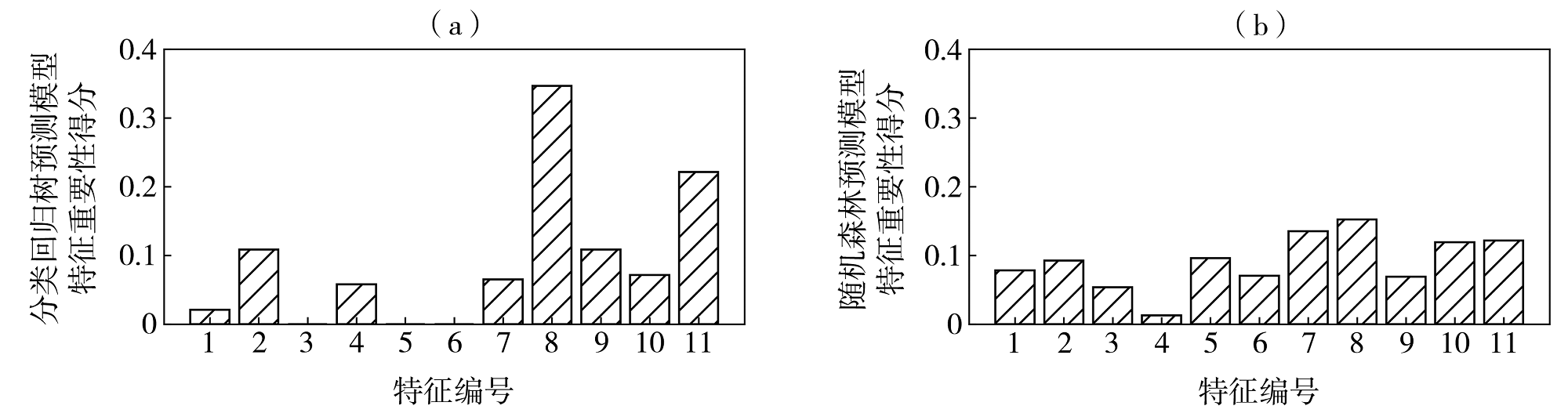
Fig.6 Importance scores of features in the prediction model based on classification and regression tree (a) and random forest (b) (The number of features corresponds to the influencing factors in table 2)
| [1] | 丁一汇, 司东, 柳艳菊, 等, 2018. 论东亚夏季风的特征、驱动力与年代际变化[J]. 大气科学, 42(3): 533-558. |
| [2] | 董亮, 陆桂华, 吴志勇, 等, 2014. 基于大气环流因子的西南地区干旱预测模型及应用[J]. 水电能源科学, 32(8): 5-8. |
| [3] | 董新宁, 向波, 周杰, 等, 2022. 两种机器学习方法在重庆夏季旱涝预测中的应用[J]. 气象科学, 42(1): 124-135. |
| [4] |
范进进, 秦鹏程, 史瑞琴, 等, 2022. 气候变化背景下湖北省高温干旱复合灾害变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 780-790.
DOI |
| [5] | 方匡南, 吴见彬, 朱建平, 等, 2011. 随机森林方法研究综述[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 26(3): 32-38. |
| [6] | 高琦, 徐明, 2021. 2019年长江中下游伏秋连旱的异常特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 37(4): 93-99. |
| [7] | 官雨洁, 王伟, 刘寿东, 2018. 基于CART算法的夏季高温预测模型构建与应用[J]. 气象科学, 38(4): 539-544. |
| [8] | 国家气候中心, 中国气象局预报与网络司, 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [9] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 2022. 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 721-732.
DOI |
| [10] | 黄海新, 吴迪, 文峰, 2016. 决策森林研究综述[J]. 电子技术应用, 42(12): 5-9. |
| [11] |
李忆平, 张金玉, 岳平, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季长江流域重大干旱特征及其成因研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 733-747.
DOI |
| [12] | 吕红燕, 冯倩, 2019. 随机森林算法研究综述[J]. 河北省科学院学报, 36(3): 37-41. |
| [13] | 邵末兰, 向纯怡, 2009. 湖北省主要气象灾害分类及其特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 28(2): 179-185. |
| [14] | 王海燕, 温泉沛, 王珊珊, 等, 2019. 2014年6—7月湖北地区干旱特征及其异常环流分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(6): 82-87. |
| [15] | 王劲松, 李耀辉, 王润元, 等, 2012. 我国气象干旱研究进展评述[J]. 干旱气象, 30(4): 497-508. |
| [16] | 王伟, 薛丰昌, 史达伟, 等, 2016. 基于CART算法的夏季干旱预测模型研究及应用[J]. 气象科学, 36(5): 661-666. |
| [17] | 王文, 许金萍, 蔡晓军, 等, 2017. 2013年夏季长江中下游地区高温干旱的大气环流特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(6): 1 595-1 607. |
| [18] | 王文举, 崔鹏, 刘敏, 等, 2012. 近50年湖北省多时间尺度干旱演变特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 28(29): 279-284. |
| [19] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [20] | 吴晶, 陈元芳, 余胜男, 2016. 基于随机森林模型的干旱预测研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电(11): 17-22. |
| [21] | 夏扬, 徐海明, 2017. 2013年长江中下游地区夏季高温事件的环流特征及成因[J]. 气象科学, 37(1): 60-69. |
| [22] | 谢南茜, 熊立华, 李家誉, 等, 2023. 基于SPEI的长江流域气象干旱时空特征分析[J]. 水电与新能源, 37(6): 30-35. |
| [23] |
杨英杰, 曹倩, 税玥, 2024. 中亚复合高温干旱事件识别与特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(1): 19-26.
DOI |
| [24] | 殷浩, 吴志勇, 何海, 2021. 基于机器学习的季尺度干旱预测研究[J]. 人民长江, 52(增刊2): 60-63. |
| [25] | 余兴湛, 蒲义良, 康伯乾, 2022. 基于SPEI的广东省近50 a干旱时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 051-1 058. |
| [26] | 袁星, 马凤, 李华, 等, 2020. 全球变化背景下多尺度干旱过程及预测研究进展[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(1): 225-237. |
| [27] | 张乐园, 王弋, 陈亚宁, 2020. 基于SPEI指数的中亚地区干旱时空分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 37(2): 331-340. |
| [28] | 张玲, 智协飞, 2010. 南亚高压和西太副高位置与中国盛夏降水异常[J]. 气象科学, 30(4): 438-444. |
| [29] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等, 2015. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 73(6): 1 092-1 103. |
| [30] | 张强, 李栋梁, 姚玉璧, 等, 2024. 干旱形成机制与预测理论方法及其灾害风险特征研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 1-21. |
| [31] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [32] | 赵林, 于家烁, 薄岩, 等, 2015. 基于SPEI的湖北省近52年干旱时空格局变化[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 24(7): 1 230-1 237. |
| [33] | 赵萍, 傅云飞, 郑刘根, 等, 2005. 基于分类回归树分析的遥感影像土地利用/覆被分类研究[J]. 遥感学报, 9(6): 708-716. |
| [34] | 赵紫竹, 张宝林, 潘丽杰, 等, 2023. 基于SPEI的内蒙古东部干旱诊断与预测[J]. 环境生态学, 5(7): 39-48. |
| [35] | 郑力嘉, 宋冰, 2023. 决策树分类算法的预剪枝与优化[J]. 自动化仪表, 44(5): 56-62. |
| [36] | 郑治斌, 刘可群, 2020. 湖北省干旱灾害特征及其影响分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 59(8): 35-40. |
| [37] | 庄少伟, 左洪超, 任鹏程, 等, 2013. 标准化降水蒸发指数在中国区域的应用[J]. 气候与环境研究, 18(5): 617-625. |
| [38] | BREIMAN L, 2001. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 45(1): 5-32. |
| [39] | DING Y H, SI D, SUN Y, et al, 2014. Inter-decadal variations, causes and future projection of the Asian summer monsoon[J]. Engineering, 12(2): 22-28. |
| [40] | GUYON I, ELISSEEFF A, 2003. An introduction to variable and feature selection[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,3: 1 157-1 182. |
| [41] | HOU L W, JIN D C, 2016. The interannual relationship between anomalous precipitation over Southern China and the south eastern tropical Indian Ocean sea surface temperature anomalies during boreal summer[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 17(11): 610-615. |
| [42] | LOH W Y, 2011. Classification and regression trees[J]. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 1(1): 14-23. |
| [43] | SI D, DING Y H, 2016. Oceanic forcings of the interdecadal variability in East Asian summer rainfall[J]. Journal of Climate, 29(21): 7 633-7 649. |
| [1] | ZHANG Yucui, TAN Jianghong, YAN Caixia. Variability characteristics and risk assessment of regional high temperature,drought and their compound events in Hubei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 825-835. |
| [2] | WANG Yuetong, HE Dongpo, LI Zhongyan, WANG Shuo, CHEN Zaoyang. Analysis of two meteorological drought events in Guizhou Province and establishment of drought prediction model based on machine learning [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 671-682. |
| [3] | SU Hongmei, ZHANG Nan, RAN Xinmin, KANG Chao. Machine learning flood early warning model for small and medium watersheds in arid and semi-arid regions and its application [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 683-693. |
| [4] | YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping, ZENG Dingwen, WANG Lijuan, ZHANG Jinyu, LU Xiaojuan, YUE Ping, JIN Jie. Characteristics of regional high temperature and drought in China from April to June 2024 and their influence factors [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 507-518. |
| [5] | XIAO Ying, GAO Yaqi, DU Liangmin, REN Yongjian. Analysis on the characteristics and causes of intraseasonal differences of the continuous rainfall in Hanjiang River Basin during the summer and autumn in 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 563-575. |
| [6] | HAO Lisheng, HE Liye, MA Ning, HAO Yuqian. Relationship between interannual variability of El Niño events and summer droughts in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 829-840. |
| [7] | XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922. |
| [8] | ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Qiang, WANG Runyuan, YUE Ping, WANG Sheng, ZENG Jian, YANG Zesu, LI Hongyu, QIAO Liang, WANG Wenyu, ZHANG Hongli, YANG Siqi, ZHAO Funian. New progresses in the study of land-atmosphere interaction in summer monsoon transition zone in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 519-530. |
| [9] | HAN Yaojie, PENG Jiyong, ZHANG Xihe, LI Shuyan. Spatial and temporal variations of heat resources utilization efficiency of summer maize in growth season under climate change in Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 639-647. |
| [10] | KANG Hengyuan, LIU Yulian, ZHOU Heling, YUAN Fang. Heterogeneity characteristics and influencing factors of summer precipitation in Heilongjiang Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 268-278. |
| [11] | WANG Yehong, ZHAO Yuchun. Verification and assessment of persistent rainfall forecasts of GRAPES-REPS in pre-summer of 2017 in southern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 328-340. |
| [12] | FENG Liangmin, ZHOU Qiuxue, CAO Pingping, WANG Jiajin. Study of 2 m temperature variation correction during transitional processes of temperature in Sichuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 164-172. |
| [13] | LI Yiping, ZHANG Jinyu, YUE Ping, WANG Suping, ZHA Pengfei, WANG Lijuan, SHA Sha, ZHANG Liang, ZENG Dingwen, REN Yulong, HU Die. Study on characteristics of severe drought event over Yangtze River Basin in summer of 2022 and its causes [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 733-747. |
| [14] | LIN Shu, LI Hongying, HUANG Pengcheng, DUAN Xinyu. Characteristics of high temperature, drought and circulation situation in summer 2022 in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 748-763. |
| [15] | WEI Huabing, CHEN Zhenghong, LUO Xiang, XIAO Yun, LUO Yu, ZHANG Peng. Refined division of ecological suitability of loquat planting in southeastern Hubei Province based on GIS [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 823-830. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||