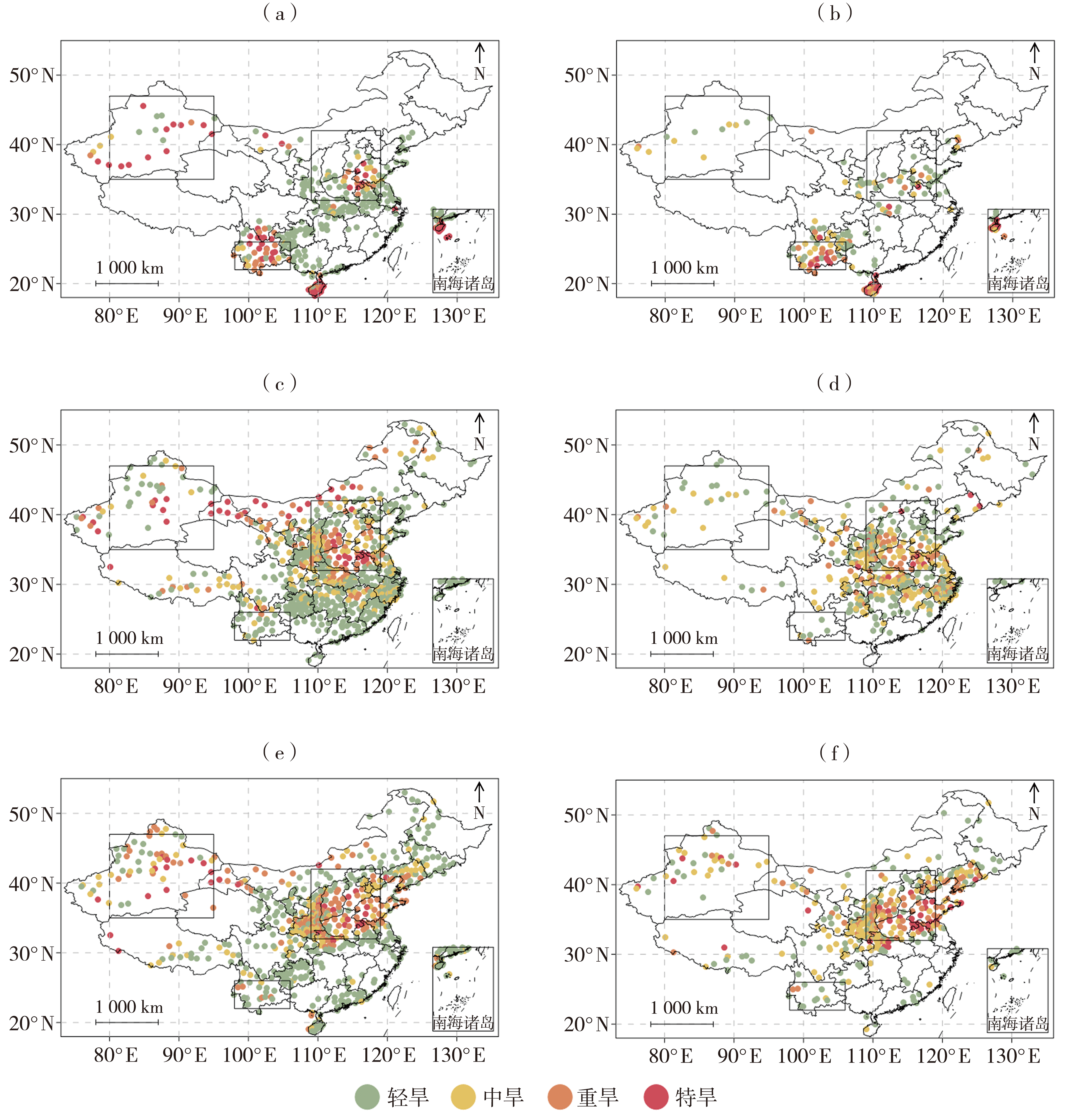
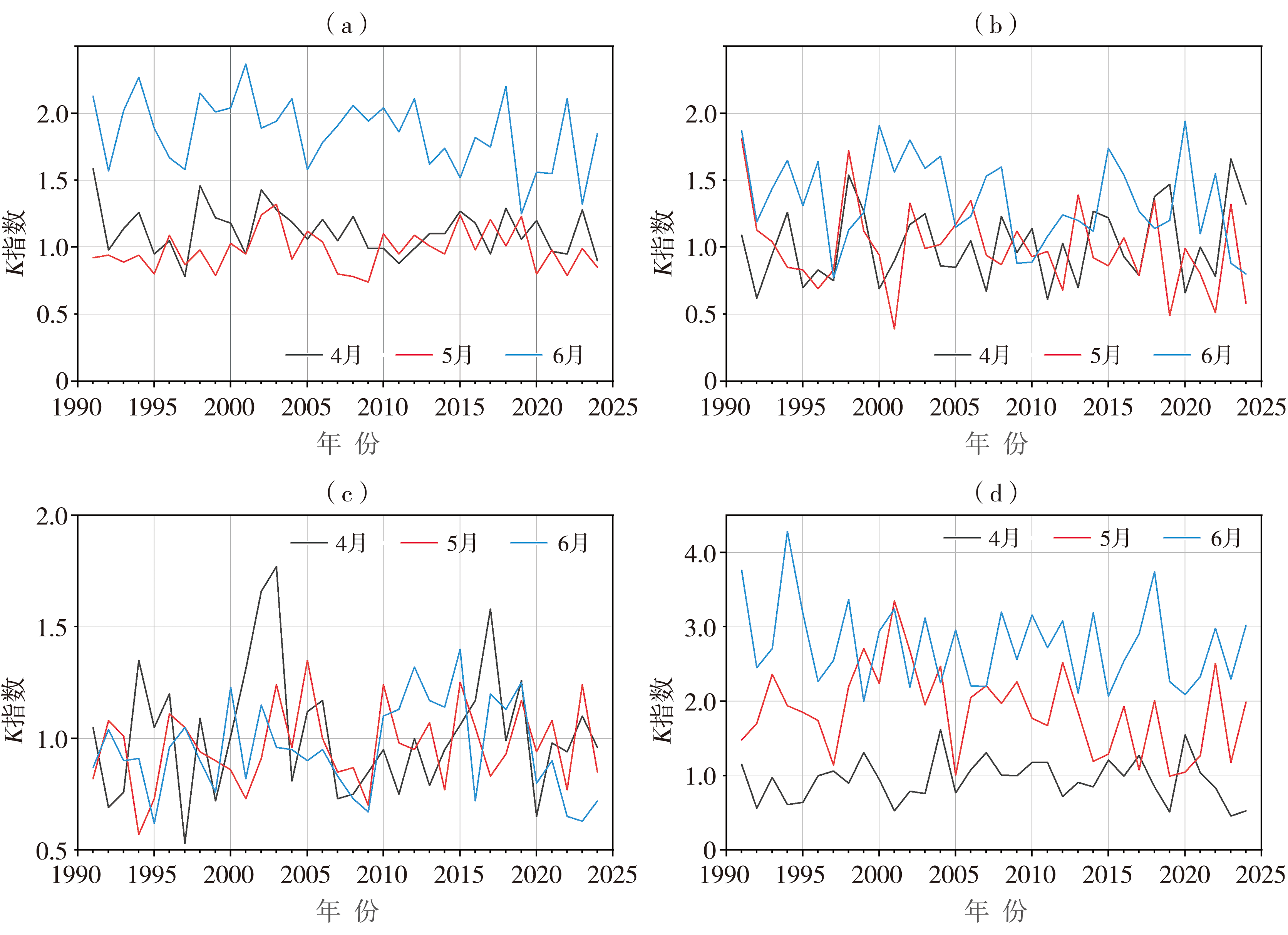
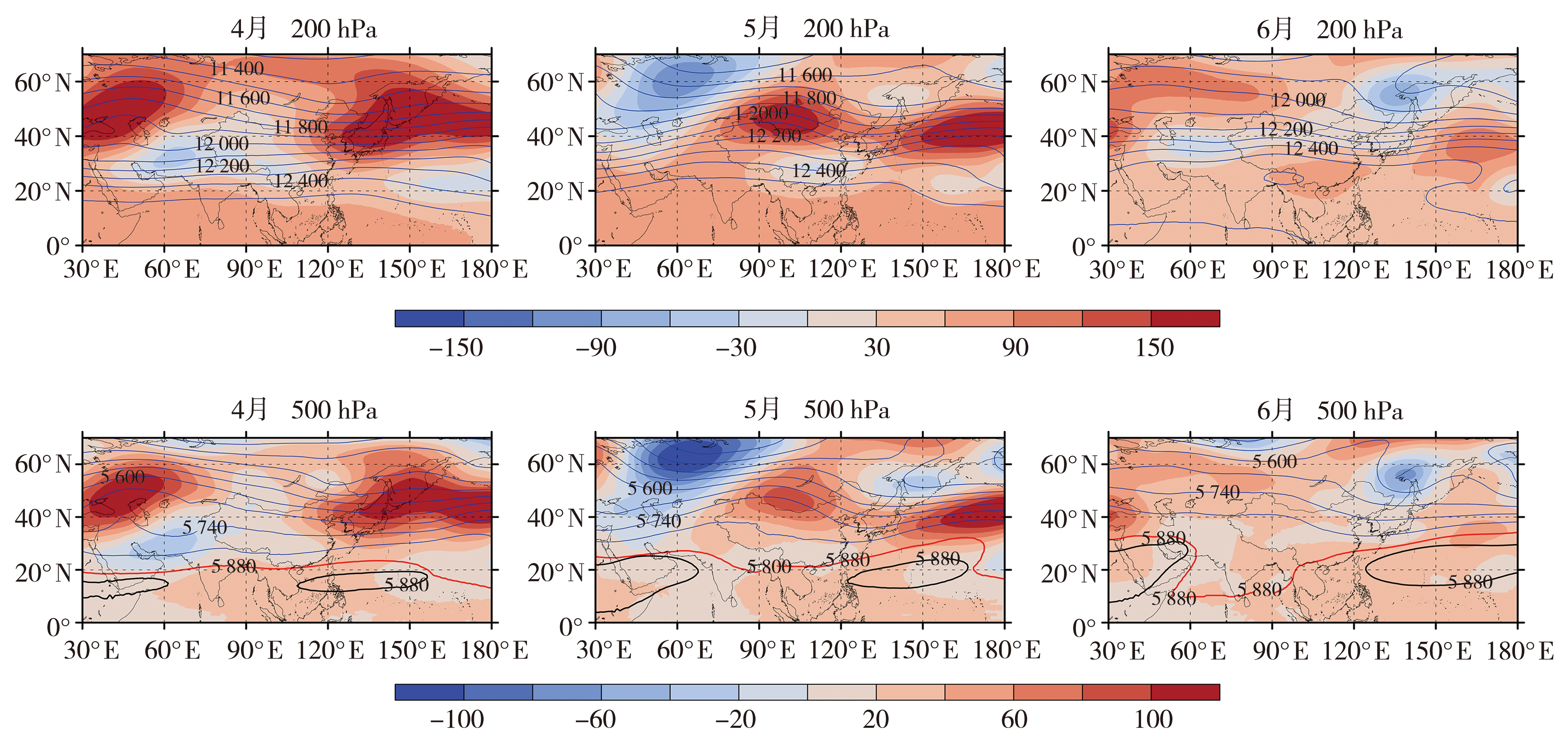
| [1] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 2022. 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 721-732.
DOI
|
| [2] |
姜雨彤, 侯爱中, 郝增超, 等, 2023. 长江流域2022年高温干旱事件演变及历史对比[J]. 水力发电学报, 42(8): 1-9.
|
| [3] |
李忆平, 张金玉, 岳平, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季长江流域重大干旱特征及其成因研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 733-747.
DOI
|
| [4] |
陆晓娟, 李忆平, 王劲松, 2024a. 中国北方干旱多发带极端春夏连旱的主要影响因子特征[J/OL]. 高原气象, 1-16 [2024-07-29]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1061.P.20240716.1117.008.html.
|
| [5] |
陆晓娟, 王芝兰, 张金玉, 等, 2024b. 海温和MJO对2023年西南春旱的协同影响[J]. 干旱气象, 42(2): 166-179.
|
| [6] |
聂波, 2024. 华北高温干旱花生出现“过山车”行情[N]. 粮油市场报, 2024-06-15(B03).
|
| [7] |
彭京备, 张庆云, 布和朝鲁, 2007. 2006年川渝地区高温干旱特征及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(3): 464-474.
|
| [8] |
王劲松, 郭江勇, 倾继祖, 2007. 一种K干旱指数在西北地区春旱分析中的应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 22(5): 709-717.
|
| [9] |
王劲松, 李忆平, 任余龙, 等, 2013. 多种干旱检测指标在黄河流域应用的比较[J]. 自然资源学报, 28(8): 1 337-1 349.
|
| [10] |
王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2020. 多种干旱指数在中国北方的适用性及其差异原因初探[J]. 高原气象, 39(3): 628-640.
DOI
|
| [11] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI
|
| [12] |
王昀, 王丽娟, 陆晓娟, 等, 2023. 2023年上半年我国干旱的特征及其成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6): 884-896.
|
| [13] |
吴鹏, 2024. 农业生产如何应对?[N]. 中国气象报, 2024-06-14(003).
|
| [14] |
肖冰霜, 2017. 中国大陆高温与干旱指数的关系及典型城市高温天气对人群健康的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学.
|
| [15] |
熊少堂, 赵铜铁钢, 郭成超, 等, 2024. 我国各大流域复合高温干旱事件变化趋势与归因分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 54(1): 83-96.
|
| [16] |
许金朵, 侯渲, 马荣华, 等, 2023. 2022年强高温期长江中游通江湖泊干旱数据集[J]. 中国科学数据(中英文网络版), 8(4): 308-321.
|
| [17] |
张强, 李栋梁, 姚玉璧, 等, 2024. 干旱形成机制与预测理论方法及其灾害风险特征研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 1-21.
|
| [18] |
张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3):500-521.
|
| [19] |
张强, 姚玉璧, 王莺, 等, 2017. 中国南方干旱灾害风险特征及其防控对策[J]. 生态学报, 37(21): 7 206-7 218.
|
| [20] |
CHEN M Y, XIE P P, JANOWIAK J E, et al, 2002. Global land precipitation: A 50-yr monthly analysis based on gauge observations[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 3(3): 249-266.
|
| [21] |
HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al, 2020. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 146(730): 1 999-2 049.
|
| [22] |
HUANG B Y, THORNE P W, BANZON V F, et al, 2017. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature, version 5 (ERSSTv5): Upgrades, validations, and intercomparisons[J]. Journal of Climate, 30(20): 8 179-8 205.
|
| [23] |
LI J, YU R C, YUAN W H, et al, 2011. Changes in duration-related characteristics of late-summer precipitation over Eastern China in the past 40 years[J]. Journal of Climate, 24(21): 5 683-5 690.
|
| [24] |
CAMPBELL S, REMENYI T A, WHITE C J, et al, 2018. Heatwave and health impact research: A global review[J]. Health & Place, 53: 210-218.
|
| [25] |
SU B D, HUANG J L, FISCHER T, et al, 2018. Drought losses in China might double between the 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(42): 10 600-10 605.
|
| [26] |
ZENG J N, LI H X, SUN B, et al, 2024. Summertime compound heat wave and drought events in China: Interregional and subseasonal characteristics, and the associated driving factors[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 19(7), 074046. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/ad5576.
|
| [27] |
ZHOU L T, TAM C Y, ZHOU W, et al, 2010. Influence of South China Sea SST and the ENSO on winter rainfall over South China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 27(4): 832-844.
|
| [28] |
ZSCHEISCHLER J, SENEVIRATNE S I, 2017. Dependence of drivers affects risks associated with compound events[J]. Science Advances, 3(6), e1700263. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.1700263.
|
 ), LI Yiping1(
), LI Yiping1( ), ZENG Dingwen1, WANG Lijuan1, ZHANG Jinyu1, LU Xiaojuan1, YUE Ping1,2, JIN Jie4
), ZENG Dingwen1, WANG Lijuan1, ZHANG Jinyu1, LU Xiaojuan1, YUE Ping1,2, JIN Jie4
 ), 李忆平1(
), 李忆平1( ), 曾鼎文1, 王丽娟1, 张金玉1, 陆晓娟1, 岳平1,2, 靳洁4
), 曾鼎文1, 王丽娟1, 张金玉1, 陆晓娟1, 岳平1,2, 靳洁4