Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 889-899.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0889
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative analysis of temperature and precipitation variations in Ningxia between different climatological normal periods
ZHANG Wen1,2( ), WANG Dai1,2(
), WANG Dai1,2( ), MA Yang1,2, CUI Yang1, KUAI Yixiong3, HUANG Ying1,2
), MA Yang1,2, CUI Yang1, KUAI Yixiong3, HUANG Ying1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory for Meteorological Disaster Monitoring and Early Warning and Risk Management of Characteristic Agriculture in Arid Regions, China Meteorological Administration, Yinchuan 750002, China
2. Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Climate Center, Yinchuan 750002, China
3. The Wuhai Branch of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Civil Airports Group Co., Ltd., Meteorological Observatory, Wuhai 016000, Inner Mongolia, China
-
Received:2023-10-27Revised:2024-04-03Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
不同气候态时段宁夏气温、降水变化对比分析
张雯1,2( ), 王岱1,2(
), 王岱1,2( ), 马阳1,2, 崔洋1, 蒯亦雄3, 黄莹1,2
), 马阳1,2, 崔洋1, 蒯亦雄3, 黄莹1,2
- 1.中国气象局旱区特色农业气象灾害监测预警与风险管理重点实验室,宁夏 银川 750002
2.宁夏回族自治区气候中心,宁夏 银川 750002
3.内蒙古自治区民航机场集团有限责任公司乌海分公司气象台,内蒙古 乌海 016000
-
通讯作者:王岱(1990—),女,宁夏银川人,工程师,主要从事气候变化及短期气候预测研究。E-mail:wangd123@126.com。 -
作者简介:张雯(1990—),女,宁夏银川人,工程师,主要从事短期气候预测及气候变化研究。E-mail:acaimeme@sina.cn。 -
基金资助:宁夏回族自治区第七批青年科技人才托举工程;宁夏自然科学基金项目(2022AAC05065);宁夏自然科学基金项目(2023AAC03792);宁夏智能数字预报技术研究与应用科技创新团队(2024CXTD006)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Wen, WANG Dai, MA Yang, CUI Yang, KUAI Yixiong, HUANG Ying. Comparative analysis of temperature and precipitation variations in Ningxia between different climatological normal periods[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 889-899.
张雯, 王岱, 马阳, 崔洋, 蒯亦雄, 黄莹. 不同气候态时段宁夏气温、降水变化对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 889-899.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0889
| 新气候态时段 | 旧气候态时段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 标准差 | ||
| 年 | 9.0 | 0.6 | 8.5 | 0.7 | |
| 春季 | 10.5 | 1.0 | 9.9 | 0.9 | |
| 夏季 | 21.4 | 0.7 | 20.9 | 0.7 | |
| 秋季 | 8.7 | 0.7 | 8.4 | 0.9 | |
| 冬季 | -5.0 | 1.2 | -5.4 | 1.2 | |
Tab.1 The annual and seasonal mean and standard deviation of temperature in the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia 单位:℃
| 新气候态时段 | 旧气候态时段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 标准差 | ||
| 年 | 9.0 | 0.6 | 8.5 | 0.7 | |
| 春季 | 10.5 | 1.0 | 9.9 | 0.9 | |
| 夏季 | 21.4 | 0.7 | 20.9 | 0.7 | |
| 秋季 | 8.7 | 0.7 | 8.4 | 0.9 | |
| 冬季 | -5.0 | 1.2 | -5.4 | 1.2 | |

Fig.2 The differences of annual (a), spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d) and winter (e) average temperature between the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia (Unit: ℃) (The black triangles are meteorological stations that passed the significant test at a 95% confidence level, the same as below)
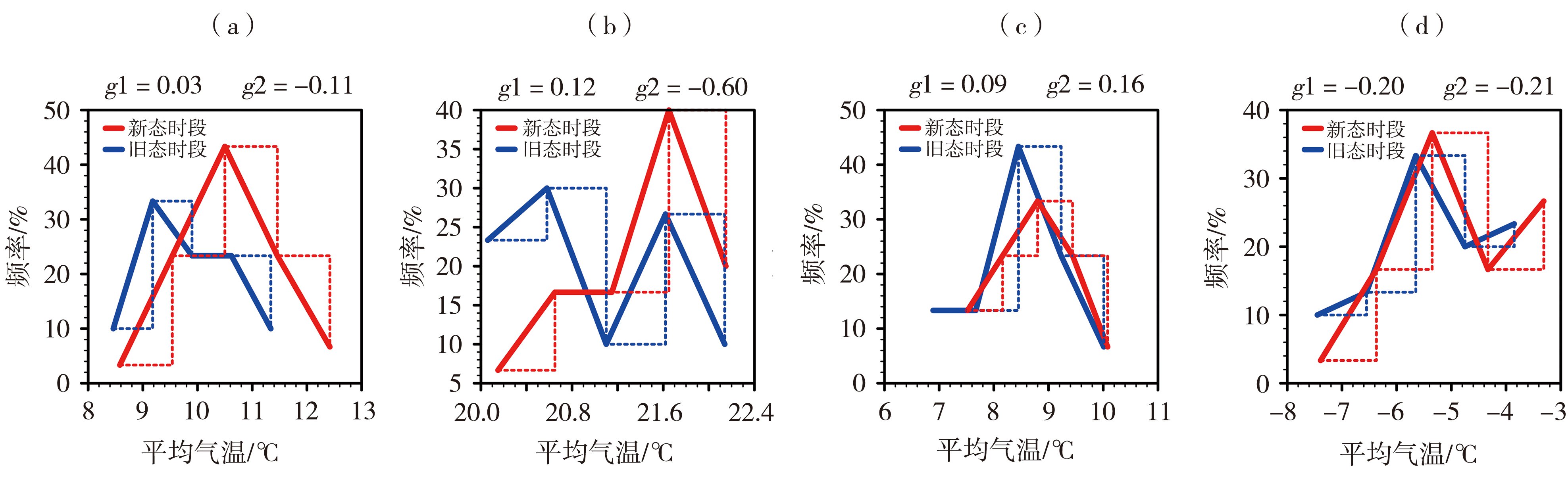
Fig.3 The frequency density histograms (dashed line) and distribution lines (solid line) of average temperature in spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c) and winter (d) in the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia (g2 and g1 are the skewness coefficients in the new and old climatological normal periods, respectively, the same as below)

Fig.4 The frequency density histograms (dashed line) and distribution lines (solid line) of extreme maximum temperature (a, b, c, d) and extreme minimum temperature (e, f, g, h) in spring (a, e), summer (b, f), autumn (c, g) and winter (d, h) in the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia

Fig.5 The differences of extreme high temperature threshold (a) and intensity (b) in summer, and extreme low temperature threshold (c) and intensity (d) in winter between the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia (Unit: ℃)
| 新态时段 | 旧态时段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 标准差 | ||
| 年 | 281.2 | 44.5 | 268.8 | 49.6 | |
| 春季 | 47.4 | 23.7 | 49.4 | 26.5 | |
| 夏季 | 161.9 | 40.4 | 154.9 | 36.3 | |
| 秋季 | 65.3 | 24.2 | 58.2 | 20.9 | |
| 冬季 | 6.7 | 3.2 | 6.4 | 3.7 | |
Tab.2 The annual and seasonal mean and standard deviation of precipitation in the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia 单位:mm
| 新态时段 | 旧态时段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 标准差 | ||
| 年 | 281.2 | 44.5 | 268.8 | 49.6 | |
| 春季 | 47.4 | 23.7 | 49.4 | 26.5 | |
| 夏季 | 161.9 | 40.4 | 154.9 | 36.3 | |
| 秋季 | 65.3 | 24.2 | 58.2 | 20.9 | |
| 冬季 | 6.7 | 3.2 | 6.4 | 3.7 | |

Fig.6 The differences of the annual (a), spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d) and winter (e) precipitation between the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia (Unit: mm)
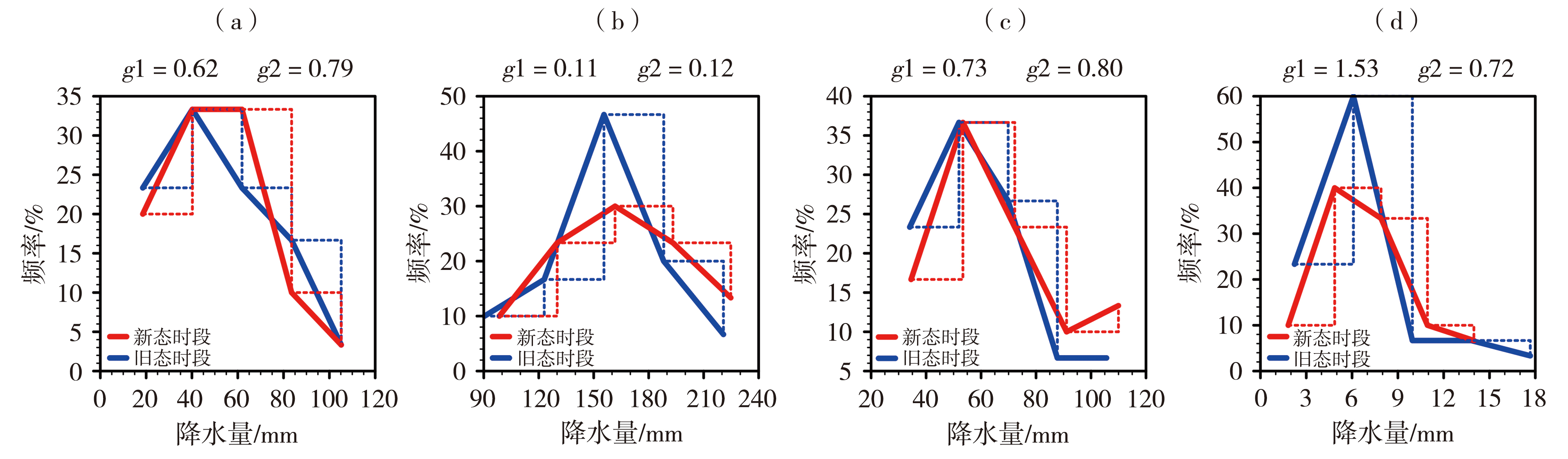
Fig.7 The frequency density histograms (dashed line) and distribution lines (solid line) of precipitation in spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d) in the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia

Fig.8 The frequency density histograms (dashed line) and distribution lines (solid line) of extreme precipitation in spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d) in the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia
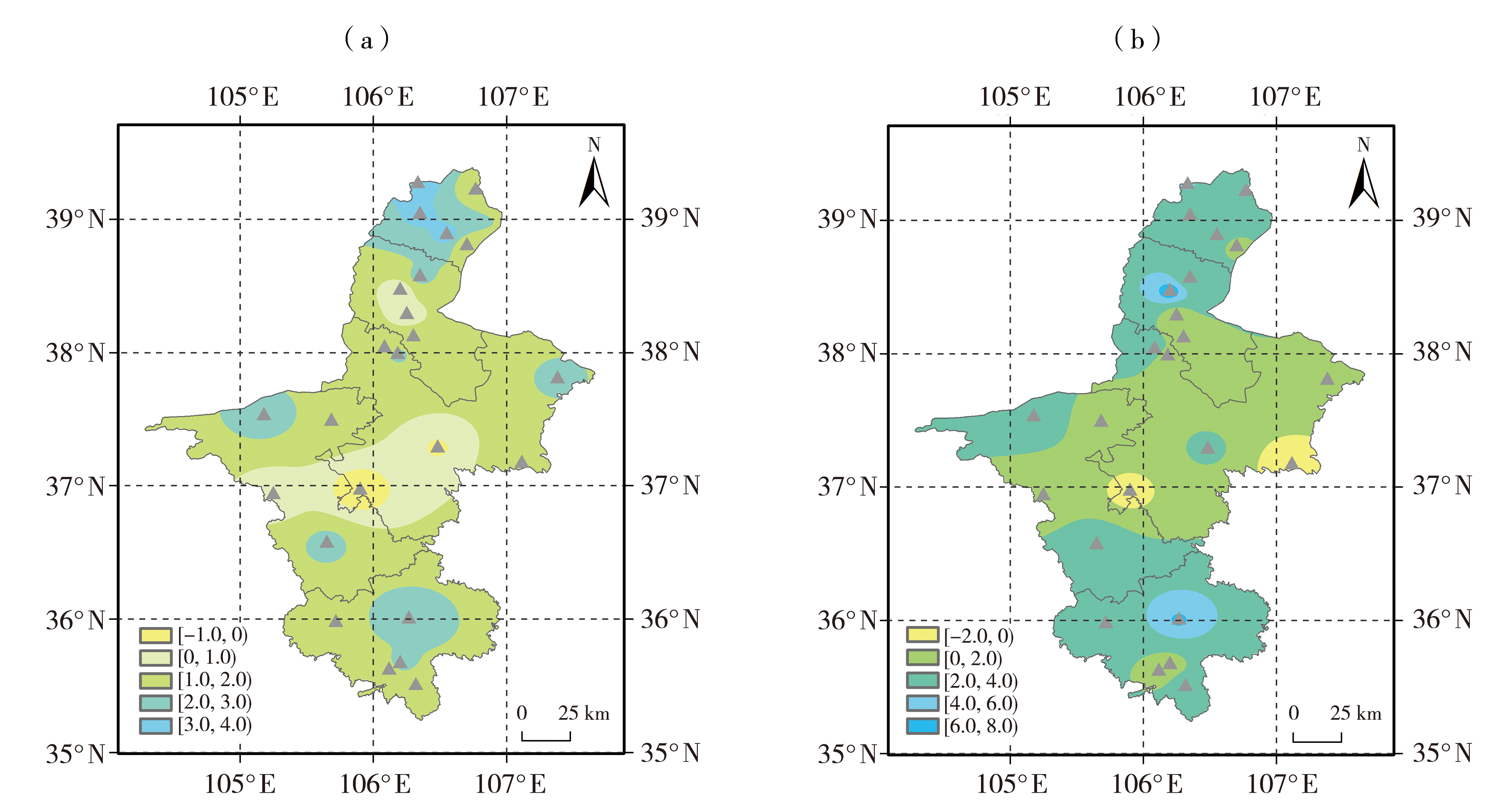
Fig.9 The differences of extreme precipitation threshold (a) and intensity (b) in summer between the new and old climatological normal periods in Ningxia (Unit: mm)
| [1] | 崔晓军, 王一飞, 吴明亮, 等, 2022. 气候变化研究中“气候平均值”等术语标准化问题探析[J]. 标准科学(10): 80-88. |
| [2] |
丁一汇, 柳艳菊, 徐影, 等, 2023. 全球气候变化的区域响应:中国西北地区气候“暖湿化”趋势、成因及预估研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 38(6): 551-562.
DOI |
| [3] | 丁一汇, 王会军, 2016. 近百年中国气候变化科学问题的新认识[J]. 科学通报, 61(10): 1 029-1 041 |
| [4] | 丁裕国, 江志红, 2009. 极端气候研究方法导论:诊断及模拟与预测[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [5] | 房一禾, 赵春雨, 王颖, 等, 2016. 新、旧气候态的差异及对东北地区气候业务的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 12(3): 193-201. |
| [6] | 李晓帆, 于长文, 龚志强, 等, 2023. 气候态调整对华北冬、夏季气候监测的影响研究[J]. 大气科学, 47(3): 599-615. |
| [7] | 林婧婧, 张强, 2015. 中国气候态变化特征及其对气候变化分析的影响[J]. 高原气象, 34(6): 1 593-1 600 |
| [8] |
马金龙, 庞雪琪, 杨建玲, 2017. 中国西北东部汛期降水主模态的年代际差异及其大气环流特征[J]. 干旱气象, 35(6): 940-948.
DOI |
| [9] | 马柱国, 符淙斌, 杨庆, 等, 2018. 关于我国北方干旱化及其转折性变化[J]. 大气科学, 42(4): 951-961. |
| [10] | 梅梅, 侯威, 周星妍, 2022. 新、旧气候态差异及对中国地区气候和极端事件评估业务的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 18(6): 653-669. |
| [11] | 施雅风, 沈永平, 李栋梁, 等, 2003. 中国西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的特征和趋势探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 23(2): 152-164. |
| [12] | 童宣, 严中伟, 李珍, 等, 2018. 近百年中国两次年代际气候变暖中的冷、暖平流背景[J]. 气象学报, 76(4): 554-565. |
| [13] | 王澄海, 李健, 许晓光, 2012. 中国近50年气温变化准3年周期的普遍性及气温未来的可能变化趋势[J]. 高原气象, 31(1): 126-136. |
| [14] |
王澄海, 张晟宁, 张飞民, 等, 2021. 论全球变暖背景下中国西北地区降水增加问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 36(9): 980-989.
DOI |
| [15] |
王岱, 杨建玲, 张雯, 等, 2024. 北极海冰对中国西北地区东部主汛期7月降水分布型的可能影响[J]. 高原气象, 43(2): 318-328.
DOI |
| [16] | 王劲廷, 马振峰, 杨小波, 等, 2014. 新旧气候平均值的差异及其对西南气候业务的影响[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 34(1): 46-50. |
| [17] | 王永光, 2002. 多年平均值的改变对中国气候业务的影响[J]. 气象, 28(8): 41-43. |
| [18] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [19] | 晏红明, 袁媛, 王永光, 2022. 气候变暖背景下气候平均值更替对中国气候业务的影响[J]. 气象, 48(3): 284-298. |
| [20] | 翟盘茂, 周佰铨, 陈阳, 等, 2021. 气候变化科学方面的几个最新认知[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6): 629-635. |
| [21] | 张强, 杨金虎, 王朋岭, 等, 2023a. 西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望[J]. 科学通报, 68(14): 1 814-1 828 |
| [22] | 张强, 杨金虎, 马鹏里, 等, 2023b. 西北地区气候暖湿化增强东扩特征及其形成机制与重要环境影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 351-358. |
| [23] | 张强, 朱飙, 杨金虎, 等, 2021. 西北地区气候湿化趋势的新特征[J]. 科学通报, 66(增刊2): 3 757-3 771 |
| [24] |
张雯, 马阳, 王素艳, 等, 2023. 西北地区东部春夏季旱涝转换环流特征及其与大西洋海温的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 14-24.
DOI |
| [25] | GU W, LI C Y, WANG X, et al, 2009. Linkage between Mei-yu precipitation and North Atlantic SST on the decadal timescale[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 26(1): 101-108. |
| [26] | IPCC, 2022. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [27] | MANTUA N J, HARE S R, ZHANG Y, et al, 1997. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 78(6): 1 069-1 079 |
| [28] | WANG L, CHEN W, 2014. The East Asian winter monsoon: Re-amplification in the mid-2000s[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(4): 430-436. |
| [29] | WANG X J, TUO Y, LI X F, et al, 2023. Features of the new climate normal 1991-2020 and possible influences on climate monitoring and prediction in China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 14(6): 930-940. |
| [30] | WMO, 2007. The role of climatological normals in a changing climate[R]. Geneva: WMO. |
| [31] | WMO, 2017. WMO guidelines on the calculation of climate normals[R]. Geneva: WMO. |
| [32] | WU P, DING Y H, LIU Y J, et al, 2019. The characteristics of moisture recycling and its impact on regional precipitation against the background of climate warming over Northwest China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 39(14): 5 241-5 255 |
| [33] |
XING W Q, WANG W G, SHAO Q X, et al, 2016. Periodic fluctuation of reference evapotranspiration during the past five decades: Does evaporation paradox really exist in China?[J]. Scientific Reports, 6: 39503. DOI: 10.1038/srep39503.
PMID |
| [34] | ZHANG Q, YANG J H, WANG W, et al, 2021. Climatic warming and humidification in the arid region of Northwest China: Multi-scale characteristics and impacts on ecological vegetation[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 35(1): 113-127. |
| [35] | ZHOU T J, 2021. New physical science behind climate change: What does IPCC AR6 tell us?[J]. Innovation (Cambridge (Mass.)), 2(4): 100173. DOI: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100173. |
| [36] | ZHU Y L, LIU Y, WANG H J, et al, 2019. Changes in the interannual summer drought variation along with the regime shift over Northwest China in the late 1980s[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 124(6): 2 868-2 881 |
| [1] | ZHANG Yucui, TAN Jianghong, YAN Caixia. Variability characteristics and risk assessment of regional high temperature, drought and their compound events in Hubei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 825-835. |
| [2] | YANG Xiaoling, SUN Xuying, YANG Jinhu, WU Wen, ZHAO Huihua, CHEN Jing. Identification and evolution characteristics of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 836-843. |
| [3] | REN Zhihan, NI Changjian, SHI Qiaoyu, CHEN Ning. Analysis of drought characteristics in Chengdu over the past 63 years based on the optimal probability distribution function [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 844-853. |
| [4] | HAN Jing, JIAO Meiling, CAO Yanchao, WANG Juan, HE Tao, XU Geng, ZHOU Zhongwen, JIN Manhui. Deviation characteristics in intelligent grid forecast of flood season precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu based on CRA spatial forecast verification [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 976-986. |
| [5] | HE Liwei, CHEN Yingying, ZHAI Hongnan, WANG Yaxin, LU Jing. Research on temperature characteristics and prediction model of Wuhan Tianxingzhou bridge deck in winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 987-993. |
| [6] | YANG Jingkun, LI Xiehui, LEI Qinya, GONG Guangze. Correlation impact of extreme temperature events and urbanization development in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 744-754. |
| [7] | ZHENG Lijun, XIAO An, LI Zhehua. Characterisation of total column water vapour in Jiangxi Province and its relationship with rainstorm [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 755-766. |
| [8] | SUN Linhai, ZHU Xiaying, LI Xiang, AI Wanxiu, YANG Mingzhu. Assessment of monthly climate prediction in China from 1971 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 794-803. |
| [9] | SUN Tao, LI Yue, WANG Jin, LI Xiaoqin, HE Jinmei, ZHAO Wenjing, LYU Meixia. Research on risk assessment and early warning method for geological hazards induced by heavy precipitation in Longnan power grid [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 813-823. |
| [10] | CHEN Xiaoxiao, HUANG Zhiyong, QIN Pengcheng, XIA Zhihong, YAO Yao, TANG Xingzhi, WANG Yingqiong. Atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature characteristics of summer high temperature anomaly in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 553-562. |
| [11] | XIAO Ying, GAO Yaqi, DU Liangmin, REN Yongjian. Analysis on the characteristics and causes of intraseasonal differences of the continuous rainfall in Hanjiang River Basin during the summer and autumn in 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 563-575. |
| [12] | TIAN Guozhen, REN Yuhuan, YANG Qian, HUANG Xiaoyan, ZHAO Sinan, ZUO Xiaorui, LI Zhicai. Application study of three remote sensing drought monitoring indices in the eastern Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 338-346. |
| [13] | DUAN Yunxia, CUI Jin, LI Deqin, WANG Yue, BAN Weilong, LIU Qing. Comparative analysis of the characteristics of dry intrusions during two heavy rainfall processes under Northeast Cold Vortex background [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 357-366. |
| [14] | HAN Qinzhe, LIU Hailei, FAN Jiazhi, WU Hao, CHEN Leishi, OU Xiaofeng, HAN Qinzhen. Surface high temperature remote sensing evaluation index construction and characteristic analysis in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 367-375. |
| [15] | ZHAO Wei, LIU Jianhong, WANG Kun, ZHANG Chaohua, CHE Jingjing, HAN Yinjuan. Construction of an integrated rainstorm hazard risk warning model in semi-arid areas and its application in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 458-464. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
