Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 338-346.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-03-0338
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application study of three remote sensing drought monitoring indices in the eastern Loess Plateau
TIAN Guozhen1( ), REN Yuhuan1, YANG Qian1, HUANG Xiaoyan2(
), REN Yuhuan1, YANG Qian1, HUANG Xiaoyan2( ), ZHAO Sinan1, ZUO Xiaorui1, LI Zhicai1
), ZHAO Sinan1, ZUO Xiaorui1, LI Zhicai1
- 1. Shanxi Climate Center, Taiyuan 030006, China
2. The Institute of Arid Meteorology of CMA, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2024-01-02Revised:2024-03-08Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-11
三种遥感干旱监测指数在黄土高原东部的适用性研究
田国珍1( ), 任玉欢1, 杨茜1, 黄小燕2(
), 任玉欢1, 杨茜1, 黄小燕2( ), 赵斯楠1, 左小瑞1, 李智才1
), 赵斯楠1, 左小瑞1, 李智才1
- 1.山西省气候中心,山西 太原 030006
2.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:黄小燕(1984—),女,硕士,副研究员,主要从事气候变化相关研究。E-mail:89290228@qq.com 。 -
作者简介:田国珍(1981—),女,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事农业遥感研究。E-mail: 532588806@qq.com。 -
基金资助:山西省地方标准修订项目(2023-06202);山西省气象局软科学项目(2024ZZ01)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TIAN Guozhen, REN Yuhuan, YANG Qian, HUANG Xiaoyan, ZHAO Sinan, ZUO Xiaorui, LI Zhicai. Application study of three remote sensing drought monitoring indices in the eastern Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 338-346.
田国珍, 任玉欢, 杨茜, 黄小燕, 赵斯楠, 左小瑞, 李智才. 三种遥感干旱监测指数在黄土高原东部的适用性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 338-346.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-03-0338
| 等级 | 类型 | 土壤相对湿度(R) | CWSI | TVDI | VSWI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | 0.6<R≤1.0 | 0˂CWSI≤0.4 | 0˂TVDI≤0.55 | 0.9˂VSWI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | 0.5˂R≤0.6 | 0.4˂CWSI≤0.5 | 0.55˂TVDI≤0.65 | 0.8˂VSWI≤0.9 |
| 3 | 中旱 | 0.4˂R≤0.5 | 0.5˂CWSI≤0.6 | 0.65˂TVDI≤0.75 | 0.7˂VSWI≤0.8 |
| 4 | 重旱 | 0.3˂R≤0.4 | 0.6˂CWSI≤0.7 | 0.75˂TVDI≤0.85 | 0.6˂VSWI≤0.7 |
| 5 | 特旱 | 0˂R≤0.3 | 0.7˂CWSI≤1.0 | 0.85˂TVDI≤1.00 | 0˂VSWI≤0.6 |
Tab.1 The index for classification of drought grades
| 等级 | 类型 | 土壤相对湿度(R) | CWSI | TVDI | VSWI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | 0.6<R≤1.0 | 0˂CWSI≤0.4 | 0˂TVDI≤0.55 | 0.9˂VSWI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | 0.5˂R≤0.6 | 0.4˂CWSI≤0.5 | 0.55˂TVDI≤0.65 | 0.8˂VSWI≤0.9 |
| 3 | 中旱 | 0.4˂R≤0.5 | 0.5˂CWSI≤0.6 | 0.65˂TVDI≤0.75 | 0.7˂VSWI≤0.8 |
| 4 | 重旱 | 0.3˂R≤0.4 | 0.6˂CWSI≤0.7 | 0.75˂TVDI≤0.85 | 0.6˂VSWI≤0.7 |
| 5 | 特旱 | 0˂R≤0.3 | 0.7˂CWSI≤1.0 | 0.85˂TVDI≤1.00 | 0˂VSWI≤0.6 |

Fig.2 The spatial distribution of 20 cm soil moisture (a, e) and CWSI (b, f), TVDI (c, g), VSWI (d, h) drought monitoring indices in Shanxi Province on May 5 (a, b, c, d) and 13 (e, f, g, h), 2022
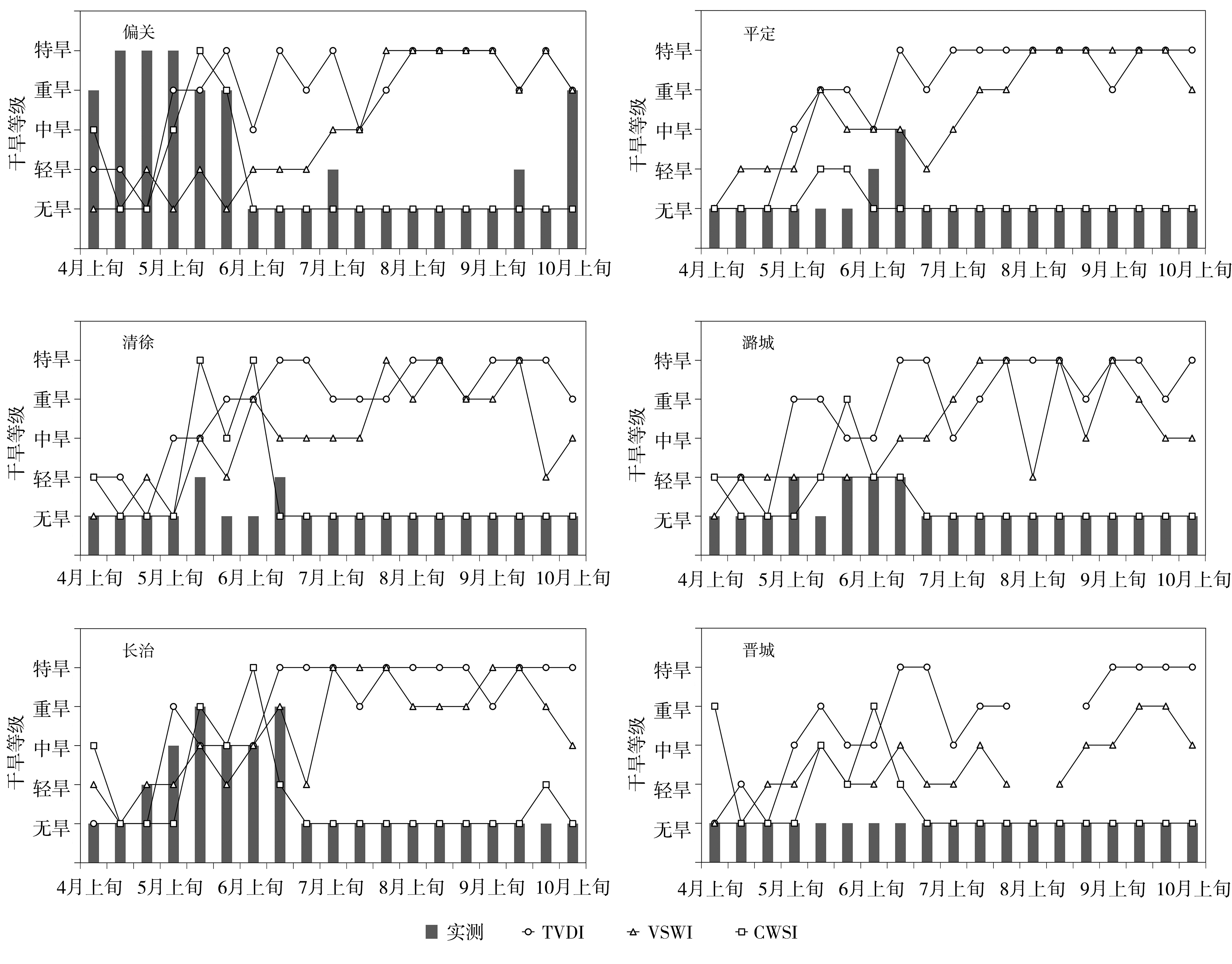
Fig.3 The ten days variation of drought grades of observation and CWSI, VSWI, TVDI at typical meteorological stations in Shanxi Province from April to early October in 2022
| 站点 | 时间段 | TVDI | VSWI | CWSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 偏关 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.39 | 0.57** | -0.70** |
| 4—5月 | -0.26 | 0.26 | 0.23 | |
| 6—10月上旬 | -0.17 | -0.04 | -0.24 | |
| 平定 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.10 | 0.33 | -0.66** |
| 4—5月 | -0.86** | -0.71* | -0.74* | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.07 | 0.37 | -0.74** | |
| 清徐 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.22 | 0.26 | -0.74** |
| 4—5月 | -0.74* | -0.46 | -0.77* | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.30 | 0.22 | -0.71** | |
| 潞城 | 4—10月上旬 | -0.11 | 0.29 | -0.68** |
| 4—5月 | -0.78* | -0.38 | -0.71* | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.09 | 0.37 | -0.76** | |
| 长治 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.16 | 0.47 | -0.76** |
| 4—5月 | -0.71* | -0.62 | -0.43 | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.03 | 0.49 | -0.83** | |
| 晋城 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.13 | 0.19 | -0.78** |
| 4—5月 | -0.42 | 0.14 | -0.90** | |
| 6—10月上旬 | -0.06 | -0.09 | -0.68** |
Tab.2 The correlation coefficients between observed relative humidity and CWSI, VSWI, TVDI at typical meteorological stations in Shanxi Province from April to early October in 2022
| 站点 | 时间段 | TVDI | VSWI | CWSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 偏关 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.39 | 0.57** | -0.70** |
| 4—5月 | -0.26 | 0.26 | 0.23 | |
| 6—10月上旬 | -0.17 | -0.04 | -0.24 | |
| 平定 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.10 | 0.33 | -0.66** |
| 4—5月 | -0.86** | -0.71* | -0.74* | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.07 | 0.37 | -0.74** | |
| 清徐 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.22 | 0.26 | -0.74** |
| 4—5月 | -0.74* | -0.46 | -0.77* | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.30 | 0.22 | -0.71** | |
| 潞城 | 4—10月上旬 | -0.11 | 0.29 | -0.68** |
| 4—5月 | -0.78* | -0.38 | -0.71* | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.09 | 0.37 | -0.76** | |
| 长治 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.16 | 0.47 | -0.76** |
| 4—5月 | -0.71* | -0.62 | -0.43 | |
| 6—10月上旬 | 0.03 | 0.49 | -0.83** | |
| 晋城 | 4—10月上旬 | 0.13 | 0.19 | -0.78** |
| 4—5月 | -0.42 | 0.14 | -0.90** | |
| 6—10月上旬 | -0.06 | -0.09 | -0.68** |
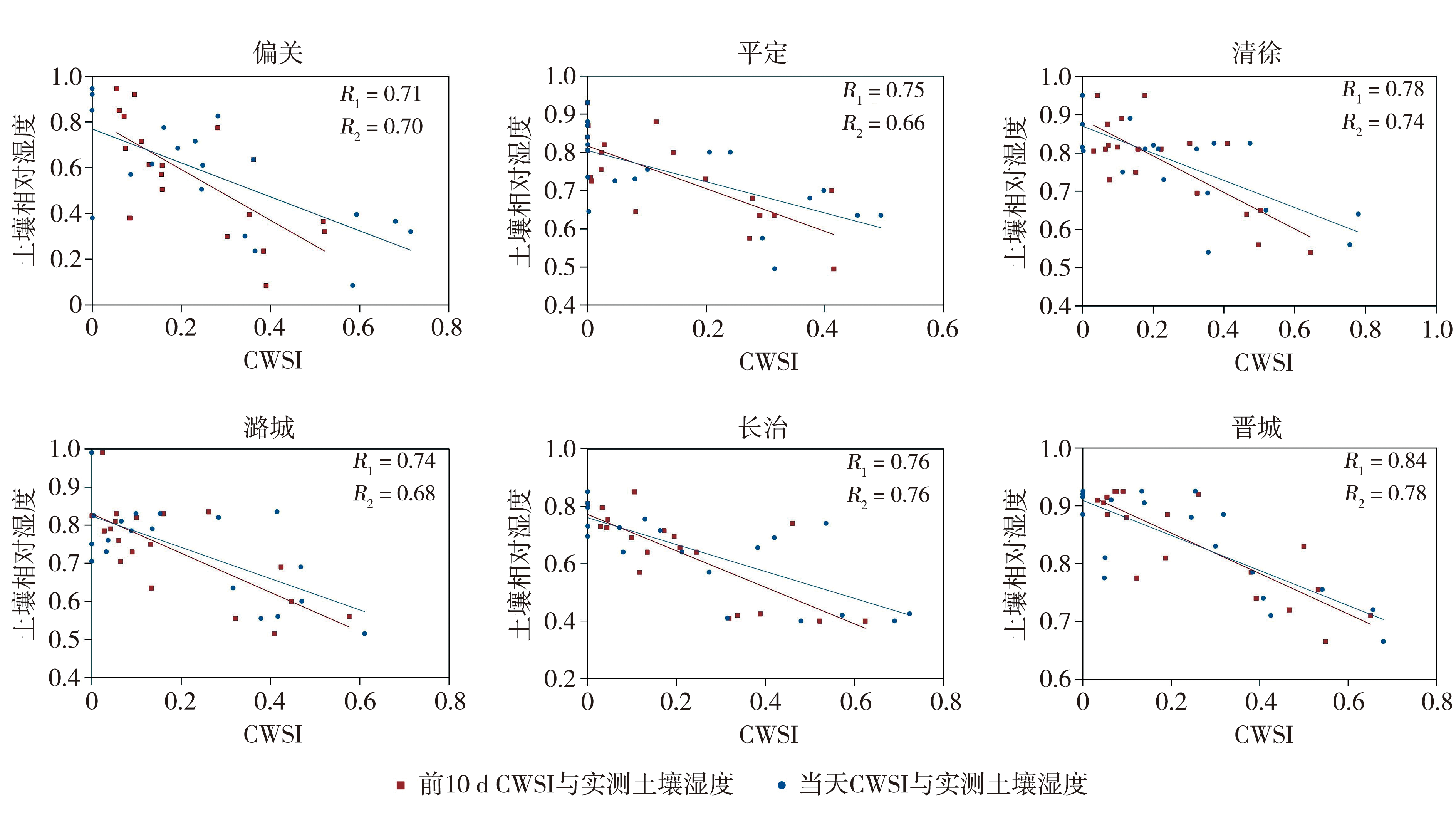
Fig.4 Correlation analysis of average CWSI in the first 10 days, CWSI on the same day and observed relative humidity at typical meteorological stations in Shanxi Province from April to early October in 2022
| [1] | 陈国茜, 祝存兄, 李林, 等, 2018. 青海高寒草地区曲麻莱县遥感干旱指数的适用性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 36(6): 905-910. |
| [2] | 陈亮, 张超, 常斌, 等, 2019. 通用温度-植被指数特征空间农田干旱遥感监测[J]. 遥感信息, 34(5): 29-34. |
| [3] | 高彦春, 龙笛, 2008. 遥感蒸散发模型研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 12(3): 515-528. |
| [4] |
郭铌, 王小平, 2015. 遥感干旱应用技术进展及面临的技术问题与发展机遇[J]. 干旱气象, 33(1): 1-18.
DOI |
| [5] | 国家气候中心, 中国气象局预报与网络司,中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [6] | 李芬, 张建新, 武永利, 等, 2013. 近50年山西终霜冻的时空分布及其影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 68(11): 1 472-1 480. |
| [7] | 梁任刚, 周旭, 李松, 等, 2022. 基于CWSI的贵州省干旱时空变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(3): 284-291. |
| [8] | 刘庆桐, 2005. 中国气象灾害大典: 山西卷[M]//温克刚. 中国气象灾害大典. 北京: 气象出版社: 10-11. |
| [9] |
刘志明, 张柏, 晏明, 等, 2003. 土壤水分与干旱遥感研究的进展与趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, 18(4): 576-583.
DOI |
| [10] | 马玉芬, 李火青, 2019. 不同土地利用数据对WRF模拟新疆高温天气的影响[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(1):52-62. |
| [11] | 钱锦霞, 王振华, 2008. 山西省春旱趋势及对农业的影响[J]. 自然灾害学报, 17(4): 105-110. |
| [12] | 任兆鹏, 卢宇坤, 谢丰, 2020. 东北半干旱地区夏季能量水分传输过程分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(3): 122-130 |
| [13] | 申广荣, 田国良, 2000. 基于GIS的黄淮海平原旱灾遥感监测研究-作物缺水指数模型的实现[J]. 生态学报, 20(2): 224-228. |
| [14] | 史尚渝, 王飞, 金凯, 等, 2020. 黄土高原地区植被指数对干旱变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 1-13. |
| [15] |
汪左, 王芳, 张运, 2018. 基于CWSI的安徽省干旱时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 33(5): 853-866.
DOI |
| [16] |
王丽娟, 郭铌, 沙莎, 等, 2016. 混合像元对遥感干旱指数监测能力的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 34(5): 772-778.
DOI |
| [17] | 王玲玲, 何巍, 罗米娜, 等, 2021. 基于归一化旱情综合指数的川西高原草地伏旱监测分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6): 884-893. |
| [18] | 王万同, 2012. 基于遥感技术的区域地表蒸散估算研究——以伊洛河流域为例[D]. 开封: 河南大学. |
| [19] | 王小平, 郭铌, 2003. 遥感监测干旱的方法及研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 21(4): 76-81. |
| [20] | 王玉娟, 王树东, 曾红娟, 等, 2014. 基于作物缺水指数法的渭河流域干旱特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 31(1): 118-124. |
| [21] | 王志伟, 武永利, 2019. 农业干旱卫星遥感监测预报技术研究[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [22] | 武永利, 相栋, 2013. FY2号气象卫星估算地面太阳辐射研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 28(12): 2 117-2 126. |
| [23] | 谢婷, 马育军, 张午朝, 2021. 青海湖北岸大气向下长波辐射特征及云的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 288-295. |
| [24] | 易雪, 杨森, 刘鸣彦, 等, 2021. 辽宁省植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 252-261. |
| [25] | 张红卫, 陈怀亮, 申双和, 等, 2010. NDVI-ST特征空间及干湿边变化特征[J]. 气象科技, 38(1): 86-95. |
| [26] |
张小平, 秦璐, 范卫东, 等, 2022. 山西最大冻土深度时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1): 49-54.
DOI |
| [27] | 张学艺, 李剑萍, 秦其明, 等, 2009. 几种干旱监测模型在宁夏的对比应用[J]. 农业工程学报, 25(8): 18-23. |
| [28] | 张艳红, 吕厚荃, 李森, 2008. 作物水分亏缺指数在农业干旱监测中的适用性[J]. 气象科技, 36(5): 596-600. |
| [29] | 赵杰鹏, 张显峰, 廖春华, 等, 2011. 基于TVDI的大范围干旱区土壤水分遥感反演模型研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 26(6): 742-750. |
| [30] | 赵伟, 李召良, 2007. 利用MODIS/EVI时间序列数据分析干旱对植被的影响[J]. 地理科学进展, 26(6): 40-47. |
| [31] | 赵亚迪, 刘永和, 李建林, 等, 2018. 1960—2013年中国地表潜在蒸散发时空变化及其对气象因子的敏感性[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 12(3): 1-9. |
| [32] | CARLSON T N, GILLIES R R, PERRY E M, 1994. A method to make use of thermal infrared temperature and NDVI measurements to infer surface soil water content and fractional vegetation cover[J]. Remote Sensing Review, 9(1/2): 161-173. |
| [33] | GOETZ S J, 1997. Multi-sensor analysis of NDVI, surface temperature and biophysical variables at a mixed grassland site[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 18(1): 71-94. |
| [34] | HU X, SHI L, LIN L, et al, 2019. Nonlinear boundaries of land surface temperature-vegetation index space to estimate water deficit index and evaporation fraction[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 279, 107736. DOI: 10. 1016/j.agrformet.2019.107736. |
| [35] | JACKSON R D, IDSO S B, REGINATO R J, et al, 1981. Canopy temperature as a crop water stress indicator[J]. Water Resources Research, 17(4): 1 133-1 138. |
| [36] | JIANG Y, TANG R, JIANG X, et al, 2019. Impact of clouds on the estimation of daily evapotranspiration from MODIS-derived instantaneous evapotranspiration using the constant global shortwave radiation ratio method[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(5/6): 1 930-1 944. |
| [37] | LAMBIN E F, EHRLICH D, 1996. The surface temperature-vegetation index space for land cover and land-cover change analysis[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(3): 463-487. |
| [38] | MA Z C, SUN P, ZHANG Q, et al, 2021. Characterization and evaluation of MODIS-derived crop water stress index (CWSI) for monitoring drought from 2001 to 2017 over Inner Mongolia[J]. Sustainability, 13(2): 916. DOI:10.3390/su13020916. |
| [39] | MENENTI M, CHOUDHURY B J, 1993. Parameterization of land surface evaporation by means of location dependent potential evaporation and surface temperature range[C]// Yokohama: Progress in Physical Geography. |
| [40] | OKE T R, JOHNSON G T, STEYN D G, et al, 1991. Simulation of surface urban heat islands under ‘ideal’ conditions at night part 2: Diagnosis of causation[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 56(4): 339-358. |
| [41] | PRICE J C, 1990. Using spatial context in satellite data to infer regional scale evapotranspiration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 28(5): 940-948. |
| [42] | RICHARD G A, LUIS S P, DIRK R, et al. Crop evapotranspiration, FAO irrigation and drainage paper NO. 56[R]. Rome: FAO, 1998: 24-25. |
| [43] | SU Z, 2002. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 6(1): 85-100. |
| [1] |
CHEN Xiaoxiao, , HUANG Zhiyong , QIN Pengcheng , XIA Zhihong , YAO Yao , TANG Xingzhi , WANG Yingqiong.
Atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature characteristics of summer high temperature anomaly in the middle
reaches of the Yangtze River
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 553-562.
|
| [2] |
XIAO Ying, , GAO Yaqi, , DU Liangmin, , REN Yongjian, .
Analysis on the characteristics and causes of intraseasonal differences of the continuous rainfall in Hanjiang River Basin
during the summer and autumn in 2021
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 563-575.
|
| [3] | LU Xiaojuan, WANG Zhilan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, HU Die, SHA Sha, WANG Suping, LI Yiping. The synergistic effect of sea temperature and MJO on spring drought in southwestern China in 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 166-179. |
| [4] | YANG Jing, ZHANG Yajie, CHEN Jinwei, ZHU Jingjing, ZHANG Mingjie, Lin Shaowu. Research on the applicability of three vegetation indices based on MODIS data in vegetation monitoring of Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 274-282. |
| [5] | LIU Wei, ZHAO Yanli, GAO Jing, LI Linhui, WANG Huimin. Cause analysis of flood-drought alternation event in July 2022 in arid and semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 11-18. |
| [6] | SHA Sha, WANG Lijuan, WANG Xiaoping, HU Die, ZHANG Liang. Study on monitoring method of agricultural drought in Gansu Province based on Temperature Vegetation Dryness Index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 27-38. |
| [7] | DONG Jingwei, WEN Lijuan, YU Tao, YANG Yongshun, LUO Ying, WANG Mengxiao, NIU Ruijia. Prediction of the future temperature in Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 64-74. |
| [8] | ZHU Li, LYU Xiaoyu, GUO Hao, MENG Xiangchen, TIAN Yunfei. Suitability study of ERA5-Land precipitation product for drought monitoring in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 677-687. |
| [9] | ZHAO Huizhen, HE Tao, GUO Ruixia, WANG Chengfu, ZHANG Yanrong, LI Qi. Meteorological drought variation characteristics in the Gannan Plateau based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 688-696. |
| [10] | GUO Jingyan, XIAO Dong. Changes of summer water vapor in Bengal region and its linkage with the interdecadal Pacific oscillation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 380-389. |
| [11] | YANG Yang, WANG Lijuan, HUANG Xiaoyan, QI Yue, XIE Rui. Analysis on spatio-temporal variation of evapotranspiration in the Yellow River Basin based on ERA5-Land products [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 390-402. |
| [12] | ZHAO Hong, CAI Dihua, WANG Heling, YANG Yang, WANG Runyuan, ZHANG Kai, QI Yue, ZHAO Funian, CHEN Fei, YUE Ping, WANG Xing, YAO Yubi, LEI Jun, WEI Xingxing. Progress and prospect on impact of drought disaster on food security and its countermeasures [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 187-206. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaochen, MA Xueqing, HE Huayun, REN Siqi, TANG Shuyue, ZHAO Jinyuan, PAN Zhihua, WANG Jing, PAN Xuebiao, HU Qi. Characteristics of dry and wet changes in sunflower growing areas in northern China and their causes from 1961 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1033-1041. |
| [14] | CHEN Yanli, TANG Meirong, ZHANG Hui, MO Jianfei, QIAN Shuan. Response difference of fractional vegetation cover and net primary productivity to SPEI drought index in karst areas of Guangxi [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1042-1050. |
| [15] | LI Liang, YANG Zesu, HE Hang. Evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength response to hydrothermal factors over northern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 791-803. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
