Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 390-402.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0390
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis on spatio-temporal variation of evapotranspiration in the Yellow River Basin based on ERA5-Land products
YANG Yang1( ), WANG Lijuan1, HUANG Xiaoyan1(
), WANG Lijuan1, HUANG Xiaoyan1( ), QI Yue1, XIE Rui2
), QI Yue1, XIE Rui2
- 1. The Institute of Arid Meteorology of CMA, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. Tianshui Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Tianshui 741000, Gansu, China
-
Received:2022-08-31Revised:2022-12-23Online:2023-06-30Published:2023-07-02 -
Contact:HUANG Xiaoyan
基于ERA5-Land产品的黄河流域蒸散时空变化特征
- 1.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.甘肃省天水市气象局,甘肃 天水 741000
-
通讯作者:黄小燕 -
作者简介:杨扬(1988—),女,副研究员,主要从事陆-气相互作用研究。E-mail:yangmeng07.happy@163.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省青年科技基金计划(20JR10RA450);国家自然科学基金项目(42105131);国家自然科学基金项目(419751111);甘肃省气象局气象科研项目(人才专项——2122rc2x-青年优秀科技人才-09);陕西省气象局秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室开放研究基金项目(2022-G13)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Yang, WANG Lijuan, HUANG Xiaoyan, QI Yue, XIE Rui. Analysis on spatio-temporal variation of evapotranspiration in the Yellow River Basin based on ERA5-Land products[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 390-402.
杨扬, 王丽娟, 黄小燕, 齐月, 谢蕊. 基于ERA5-Land产品的黄河流域蒸散时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 390-402.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-03-0390

Fig.1 The regional division (green boxs) of the Yellow River Basin and spatial distribution of average annual precipitation (color filled areas, Unit: mm) from 1961 to 2018 (The blue solid line represents the Yellow River. the same as below)
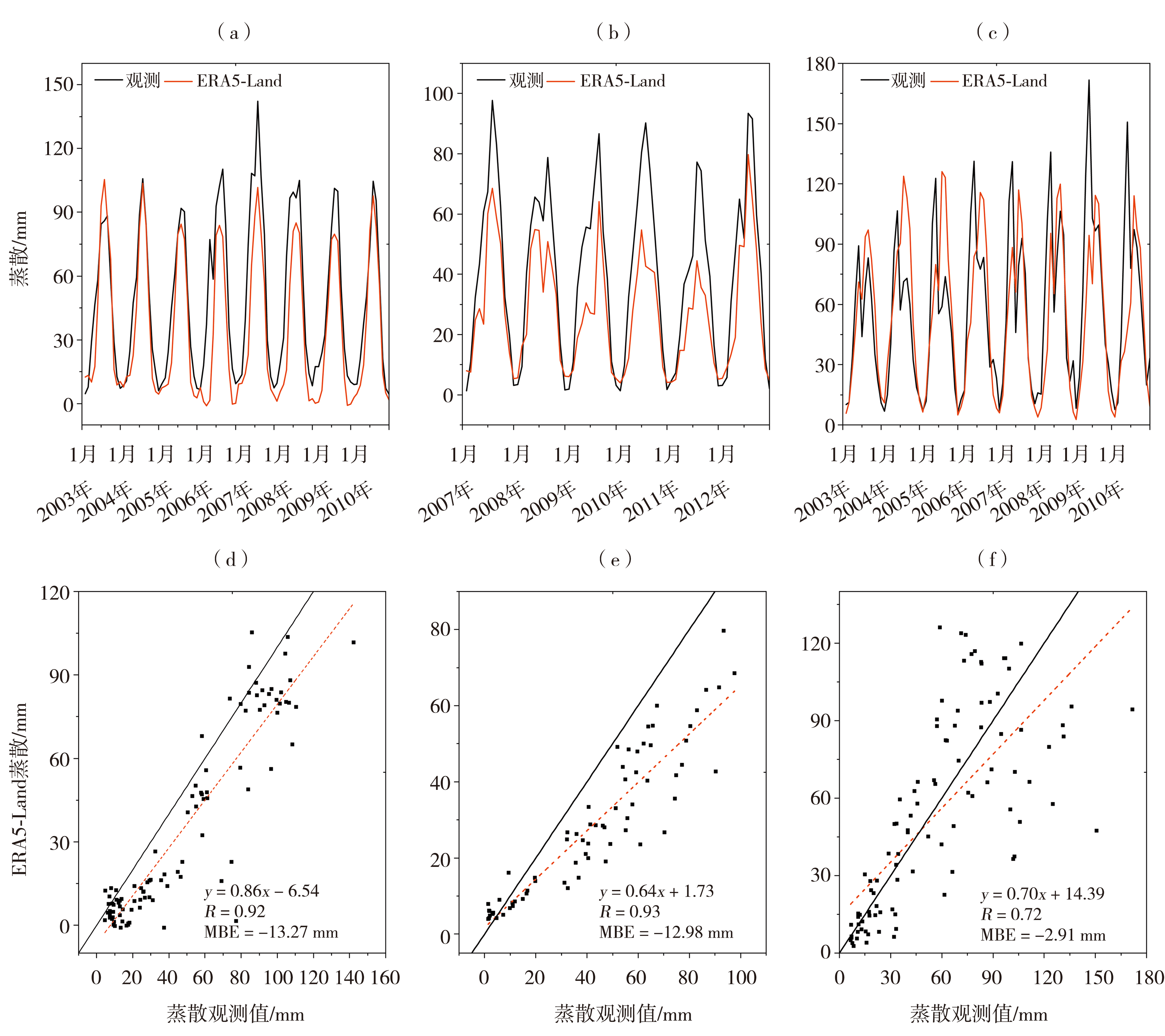
Fig.2 Monthly variation (a, b, c) and scatter plots (d, e, f) of evapotranspiration between ERA5-Land data and the observation at Haibei (a, d) and Yucheng (c, f) station from 2003 to 2010, SACOL station (b, e) from 2007 to 2012

Fig.3 The spatial distribution of annual and seasonal mean evapotranspiration in the Yellow River Basin during 1980-2021 (Unit: mm) (a) the whole year, (b) spring, (c) summer, (d) autumn, (e) winter

Fig.4 Inter-annual variation (b, d, f, h) of evapotranspiration and spatial distribution of variation trend (a, c, e, g) (Unit: mm·a-1) in the whole year and different seasons in the different area of the Yellow River Basin during 1980-2021 (a, b) annual, (c, d) spring, (e, f) summer, (g, h) autumn(The black dot areas passed the confidence level at 95%. the same as below)
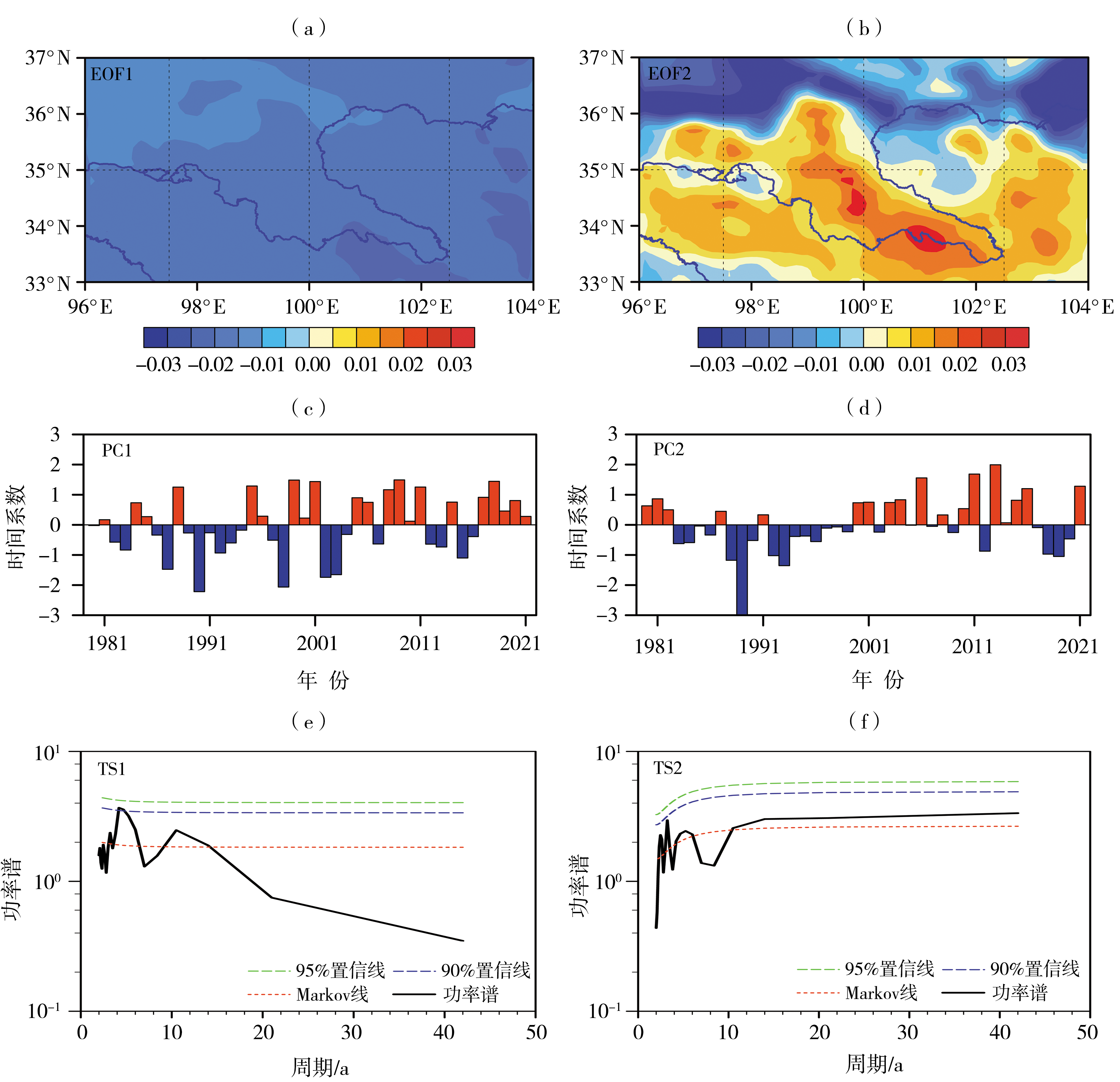
Fig.5 Spatial patterns (a, b), standardized time coefficients (c, d) and their power spectrum (e, f) of the first two modes of EOF analysis of annual evapotranspiration in source region of the Yellow River Basin during 1980-2021

Fig.6 Spatial patterns (a, b), standardized time coefficients (c, d) and their power spectrum (e, f) of the first two modes of EOF analysis of annual evapotranspiration in Hetao area during 1980-2021
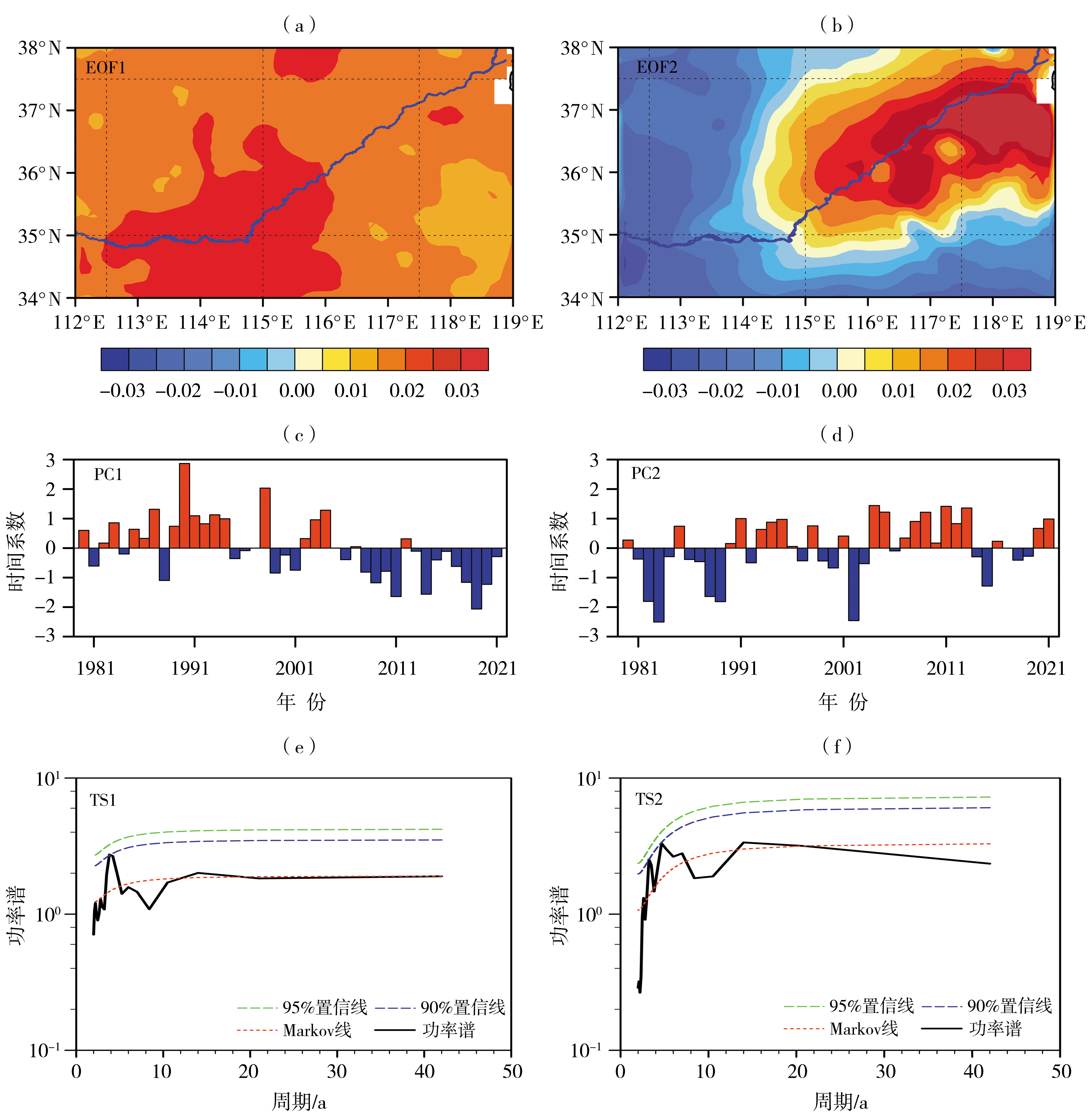
Fig.7 Spatial patterns (a, b), standardized time coefficients (c, d) and their power spectrum (e, f) of the first two modes of EOF analysis of annual evapotranspiration in the lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin during 1980-2021

Fig.8 Inter-annual variation (b, d, f) of evapotranspiration and variation trend spatial distribution (a, c, e) (Unit: mm·a-1) in different areas of the Yellow River Basin based on GLEAM (a, b)、GLDAS (c, d) and Eta (e, f) data
| [1] |
安琳莉, 黄建平, 任钰, 等, 2022. 中国北方旱区陆地水储量变化特征及其归因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2):169-178.
DOI |
| [2] | 黄珊, 杨扬, 王含嘉, 等, 2020. 中国西南地区地表感热和潜热通量时空变化特[J]. 干旱气象, 38(4): 601-611. |
| [3] |
马守存, 保广裕, 郭广, 等, 2018. 1982—2013年黄河源区植被变化趋势及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 36(2): 226-233.
DOI |
| [4] | 童瑞, 杨肖丽, 任立良, 等, 2015. 黄河流域1961—2012年蒸散发时空变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 水资源保护, 31(3): 16-21. |
| [5] | 魏凤英, 1999. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 115-135. |
| [6] | 王澄海, 杨金涛, 杨凯, 等, 2022. 过去近60 a黄流流域降水时空变化特征及未来30 a变化趋势[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(3): 708-722. |
| [7] | 王丽娟, 2022. 蒸散及其关键参数的多源卫星遥感反演与应用研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [8] | 吴佳, 高学杰, 2013. 一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其他资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1 102-1 111. |
| [9] | 肖风劲, 徐雨晴, 黄大鹏, 等, 2021. 气候变化对黄河流域生态安全影响及适应对策[J]. 人民黄河, 43(1): 10-14. |
| [10] | 徐宗学, 隋彩虹, 2005. 黄河流域平均气温变化趋势分析[J]. 气象, 31(11): 8-11. |
| [11] | 杨特群, 饶素秋, 陈冬伶, 2009. 1951年以来黄河流域气温和降水变化特点分析[J]. 人民黄河, 31(10): 76-77. |
| [12] | 杨扬, 杨启东, 王芝兰, 等, 2021. 中国区域陆气耦合强度的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 374-385. |
| [13] | 张镭, 黄建平, 梁捷宁, 等, 2020. 气候变化对黄河流域的影响及应对措施[J]. 科技导报, 38(17): 42-51. |
| [14] | 张亚春, 马耀明, 马伟强, 等, 2021. 青藏高原不同下垫面蒸散量及其与气象因子的相关性[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 366-373. |
| [15] | 郑子彦, 吕美霞, 马柱国, 2020. 黄河源区气候水文和植被覆盖变化及面临问题的对策建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 35(1): 61-72. |
| [16] |
CHADWICK R, GOOD P, WILLETT K, 2016. A simple moisture advection model of specific humidity change over land in response to SST warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 29(21): 7 613-7 632.
DOI URL |
| [17] | CHENG W, MMCMARTIN D G, DAGON K, et al, 2019. Soil moisture and other hydrological changes in a stratospheric aerosol geoengineering large ensemble[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 124(23):12 773-12 793. |
| [18] | FENG T C, SU T, JI F, et al, 2018. Temporal characteristics of actual evapotranspiration over China under global warming[J]. Journal of Geophysical research, 123: 5 845-5 858. |
| [19] | FISHER B, MELTON F, MIDDLETON E, et al, 2017. The future of evapotranspiration: global requirements for ecosystem functioning, carbon and climate feedbacks, agricultural management, and water resources[J]. Water Resources Research, 53: 2 618-2 626. |
| [20] |
GAO G, CHEN D L, XU C Y, et al, 2007. Trend of estimated actual evapotranspiration over China during 1960-2002[J]. Journal of Geophysical research, 112, D11120. DOI:10.1029/2006JD008010.
DOI URL |
| [21] | HERSBACH H, COAUTHORS, 2020. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 146(730): 1 999-2 049. |
| [22] | IPCC, 2019. Climate Change and land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, degradationland, sustainable land management, securityfood, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystem[R/OL].(2019-08)[2023-05-29]. https://www.ipcc.ch/srccl/. |
| [23] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change 2021:The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M/OL]. United Kinodom and New York, NY USA: Cambridge University Press. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/. |
| [24] |
JUNG M, REICHSTEIN M, CIAIS P, et al, 2010. Recent decline in the global land evapotranspiration trend due to limited moisture supply[J]. Nature, 467: 951-954.
DOI |
| [25] | KOSTER R D, DIRMEYER P A, GUO Z, et al, 2004, Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation[J]. Science, 305(5 687), 1 138-1 140. |
| [26] |
LI C C, ZHANG Y Q, SHEN Y J, et al, 2020. LUCC-driven changes in gross primary production and actual evapotranspiration in North China[J]. Journal of Geophysical research, 125, e2019JD031705.DOI:10.1029/2019JD031705.
DOI |
| [27] |
LV M X, MA Z G, PENG S M, 2019. Responses of terrestrial water cycle components to afforestation within and around the Yellow River Basin[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 12: 116-123.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MADELEINE P C, JONH T R, HRISHIKESH A, et al, 2021. A 10 percent increase in global land evapotranspiration from 2003 to 2019[J]. Nature, 593: 543-547.
DOI |
| [29] | MARTENS B, SCHUMACHER D L, WOUTERS H, et al, 2020. Evaluating the land-surface energy partitioning in ERA5[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 13: 4 159-4 181. |
| [30] |
QIAO L, ZUO Z, XIAO D, et al, 2021. Evaluation of soil moisture in CMIP6 simulations[J]. Journal of Climate, 35: 779-800.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, CORTI T, DAVIN E L, et al, 2010. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 99(3):125-161.
DOI URL |
| [32] | WANG C, GRAHAM R M, WANG K, et al, 2019. Comparison of ERA5 and ERA-Interim near-surface air temperature, snowfall and precipitation over Arctic sea ice: effects on sea ice thermodynamics and evolution[J]. The Cryosphere, 13: 1 661-1 679. |
| [33] |
WANG K, DICKINSON R, 2012. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 50(2), RG2005. DOI: 10,1029/2011 RG000373.
DOI |
| [34] |
WU Z Y, FENG H H, HE H, et al, 2021. Evaluation of soil moisture climatology and anomaly components derived from ERA5-land and GLDAS-2.1 in China[J]. Water Resources Management, 35: 629-643.
DOI |
| [35] |
XU S, YU Z, YANG C, et al, 2018. Trends in evapotranspiration and their responses to climate change and vegetation greening over the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 263: 118-129.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
YANG Q, DAN L, LV M, et al, 2021. Quantitative assessment of the parameterization sensitivity of the Noah-MP land surface model with dynamic vegetation using ChinaFLUX data[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 307(2), 108542. DOI:10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108542.
DOI URL |
| [37] | YANG Z S, ZHANG Q, HAO X C, et al, 2019. Changes in evapotranspiration over global semiarid regions 1984-2013[J]. Journal of Geophysical research, 124: 2 946-2 963. |
| [38] |
YUAN L, CHEN X L, MA Y M, et al, 2022. A monthly 0.01° terrestrial evapotranspiration product (1982-2018) for the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth System Science Data, DOI: 10.5194/eesd-2022-195.
DOI |
| [39] |
YUE P, ZHANG Q, YANG Y, et al, 2018. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of the Bowen smith ratio over a semiarid grassland in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 252: 99-108.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHANG K, KIMBALL J S, NEMANI R R, et al, 2015. Vegetation greening and climate change promote multidecadal rises of global land evapotranspiration[J]. Scientific Reports, 5, 15956. DOI:10.1038/srep15956.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
ZHAO J, WEI L, YANG Y T, et al, 2017. Separating vegetation greening and climate change controls on evapotranspiration trend over the Loess Plateau[J]. Scentific Reports, 7, 8191. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-08477-x.
DOI |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||