Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 755-766.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0755
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characterisation of total column water vapour in Jiangxi Province and its relationship with rainstorm
ZHENG Lijun1( ), XIAO An2,3(
), XIAO An2,3( ), LI Zhehua1
), LI Zhehua1
- 1. Shangrao Meteorological Bureau of Jiangxi Province, Shangrao 334000, Jiangxi, China
2. Jiangxi Meteorological Observatory, Nanchang 330096, China
3. Key Laboratory of Climate Change Risk and Meteorological Disaster Prevention of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang 330096, China
-
Received:2023-10-29Revised:2024-05-27Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-17
江西大气整层可降水量特征及其与暴雨的关系
- 1.江西省上饶市气象局,江西 上饶 334000
2.江西省气象台,江西 南昌 330096
3.气候变化风险与气象灾害防御江西点实验室,江西 南昌 330096
-
通讯作者:肖安(1979—),男,江西南昌人,正高级工程师,主要从事中短期天气预报研究。E-mail:mrxiaoan@sohu.com 。 -
作者简介:郑丽君(1990—),女,江西上饶人,高级工程师,主要从事天气预报研究。E-mail: karenzlj0818@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局复盘总结专项(FPZJ2023-069);江西省气象局面上项目(JX2021M01);华东区域气象科技协同创新基金合作项目(QYHZ202317);江西省气象局科技重点项目(JX2023Z05)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHENG Lijun, XIAO An, LI Zhehua. Characterisation of total column water vapour in Jiangxi Province and its relationship with rainstorm[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 755-766.
郑丽君, 肖安, 李浙华. 江西大气整层可降水量特征及其与暴雨的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 755-766.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0755
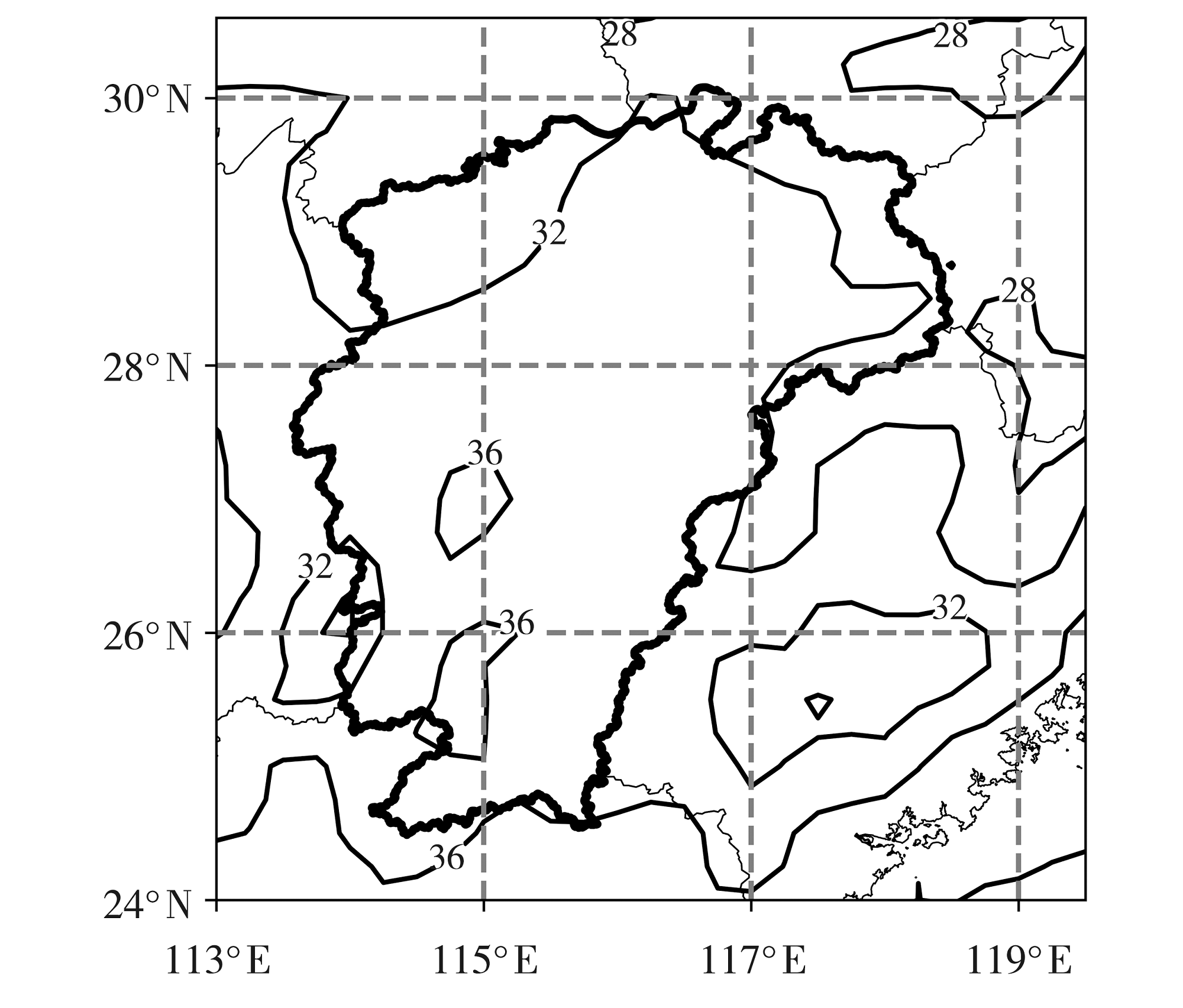
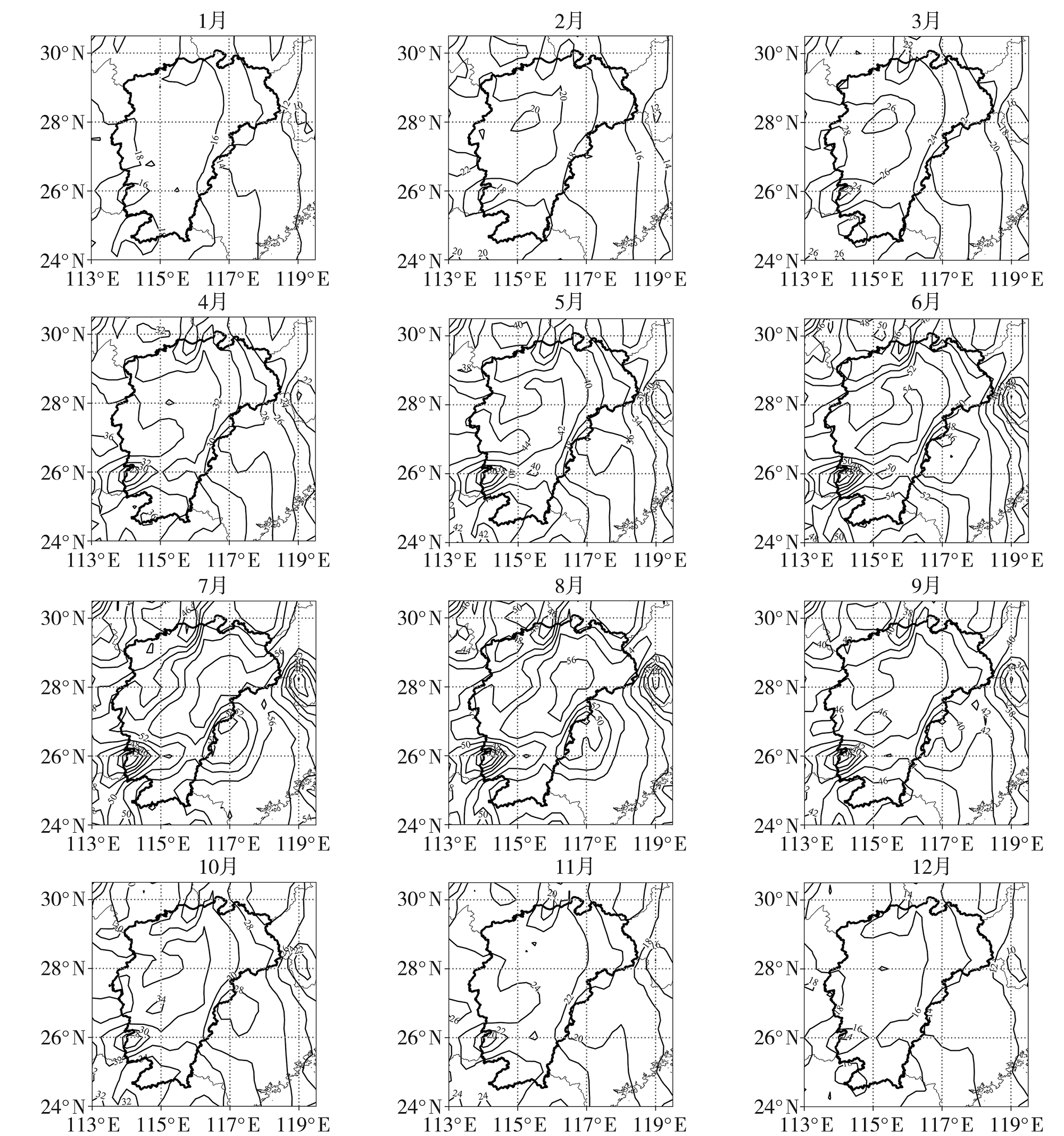
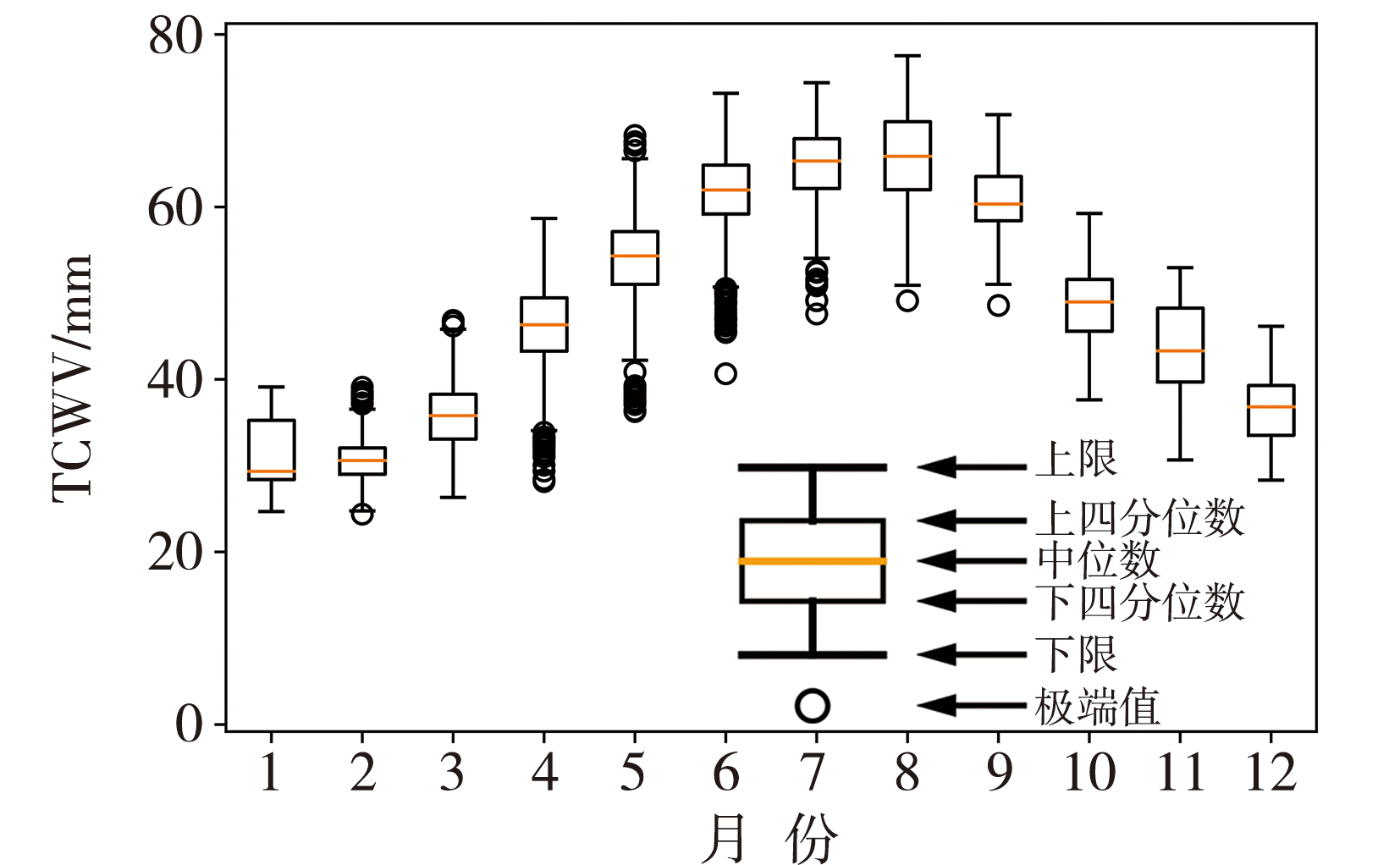
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of annual mean TCWV in Jiangxi Province during 1990-2022 (Unit: mm) (The thick solid line is the range of Jiangxi Province, the same as below)

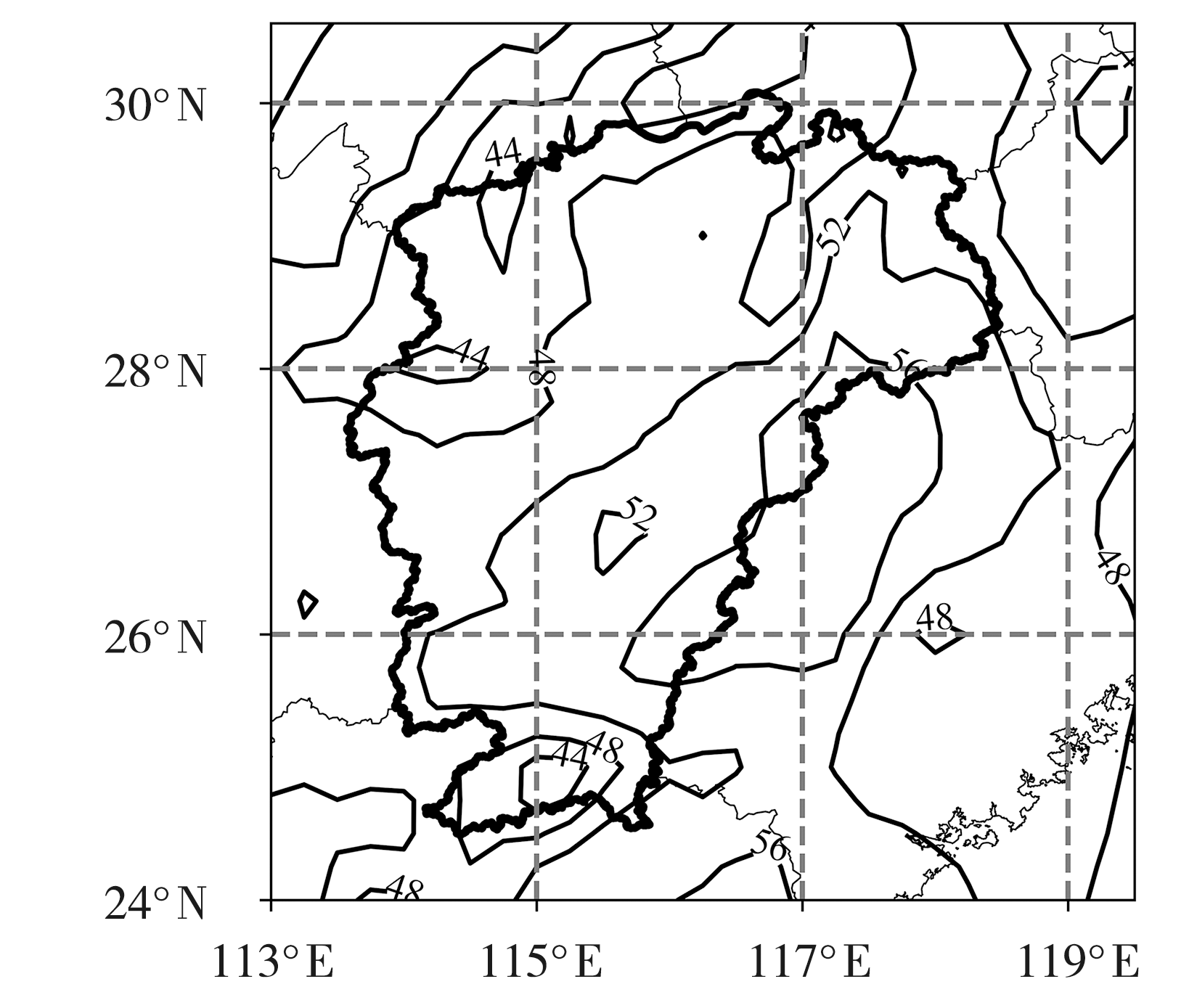
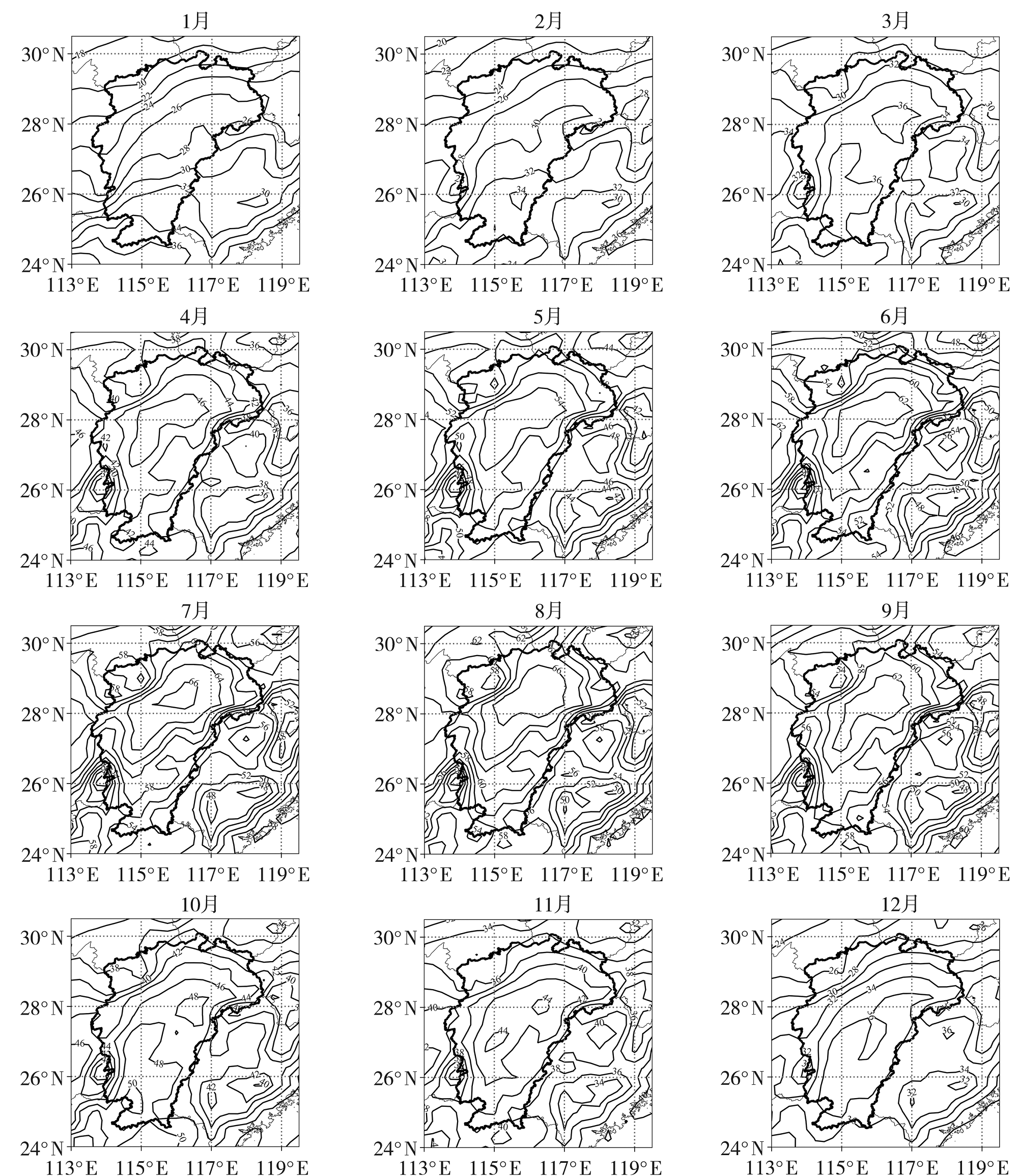
Fig.6 The spatial distribution of mean TCWV on rainstorm day in spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d) in Jiangxi Province during 1990-2022 (Unit:mm)

Fig.9 Distributions of maximum TCWV (isolines, Unit: mm) and stations with rainstorm and heavy rainstorm from 20:00 on May 4 to 07:00 on May 5 (a), 08:00 to 19:00 on May 5 (b), 20:00 on May 5 to 07:00 on May 6 (c), 08:00 to 19:00 on May 6 (d), 2023 (The red arrows indicate the locations of Tonggu, Le An, Congren and Xinfeng station, respectively)
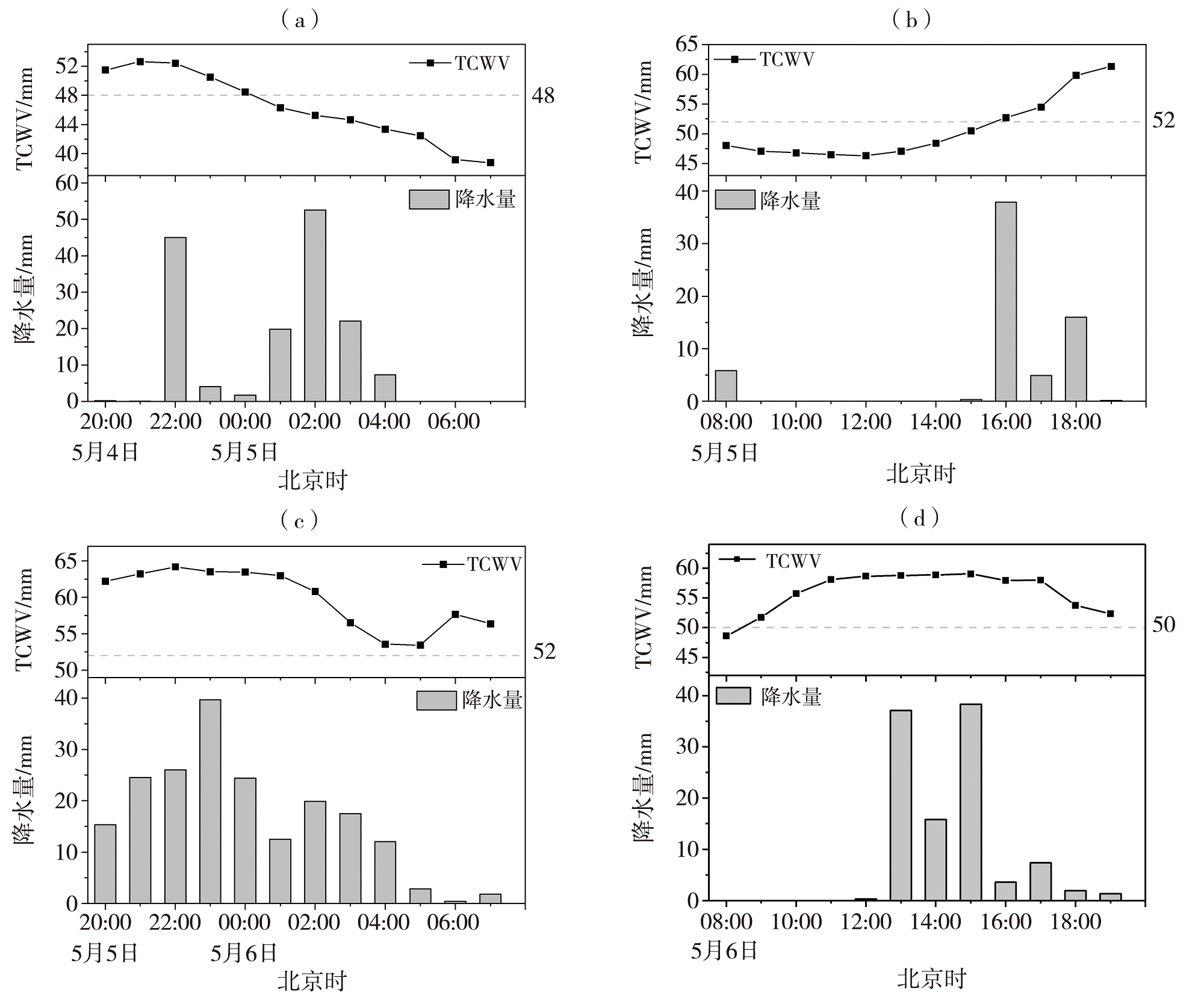
Fig.10 The hourly precipitation and TCWV of station from 20:00 on May 4 to 07:00 May 5 at Tonggu (a), 08:00 to 19:00 on May 5 at Le An (b), 20:00 on May 5 to 07:00 on May 6 at Chongren (c) and 08:00 to 19:00 on May 6 at Xinfeng (d), 2023 (The dotted lines represent the monthly mean TCWV of the stations)

Fig.11 Distributions of maximum TCWV (isolines, Unit: mm) and stations with rainstorm and heavy rainstorm from 08:00 to next 07:00 on June 22 (a), June 23 (b), June 24 (c), and July 22 (d), 2023, respectively (The red arrows indicate the location of Wuyuan, Yujiang, Lijiang and Pingxiang station, respectively)
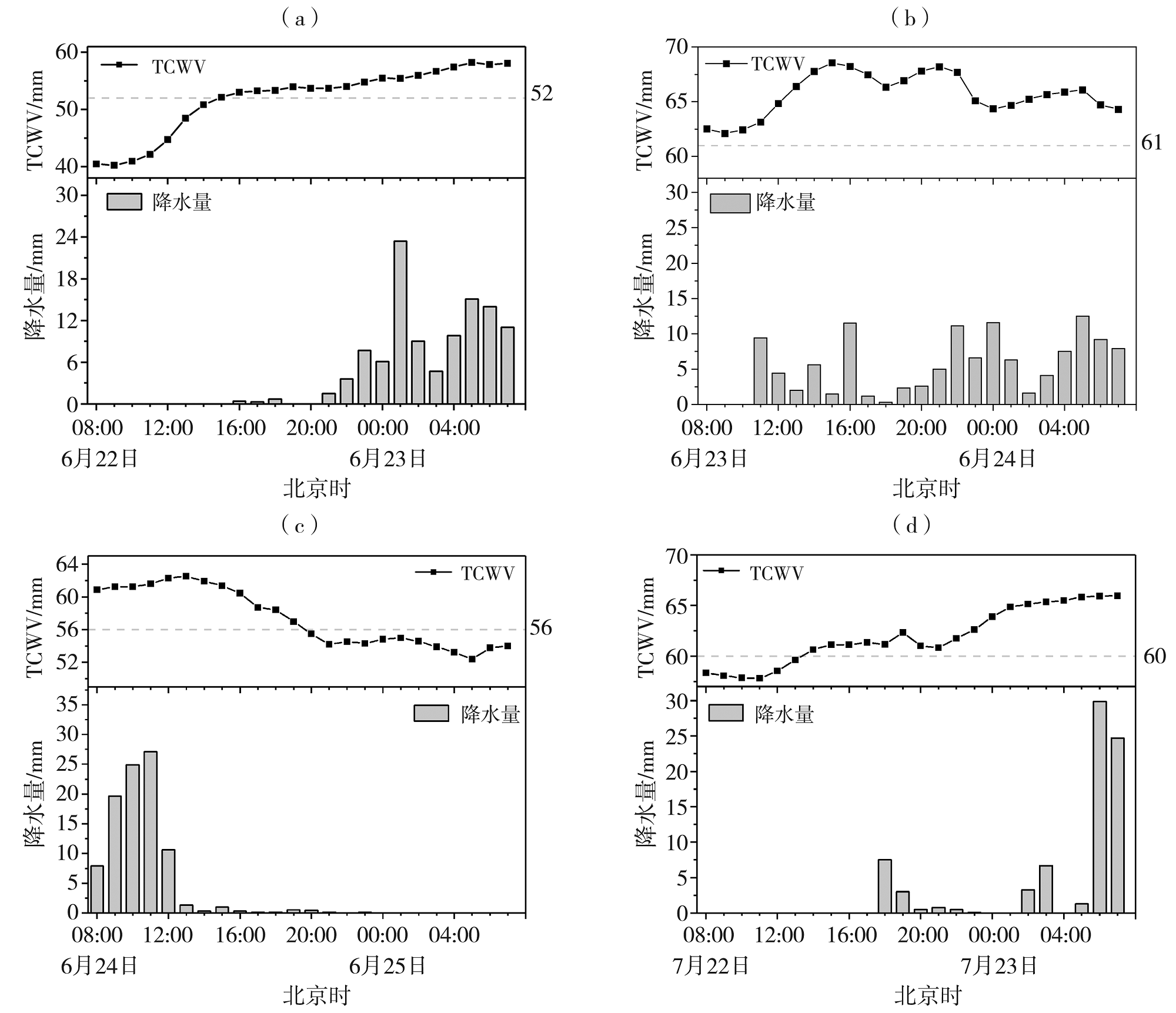
Fig.12 The hourly precipitation and TCWV of station from 08:00 to next 07:00 on June 22 at Wuyuan (a), June 23 at Yujiang (b), June 24 at Lichuan (c), and July 22 at Pingxiang (d), 2023 (The dotted lines represent the monthly mean TCWV of the stations)
| [1] | 蔡荣辉, 陈静静, 文萍, 等, 2019. 2017年湖南一次特大致洪暴雨过程的水汽特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(2): 288-300. |
| [2] |
蔡逸男, 杜岩, 陈泽生, 2021. 四种全球大洋水汽数据产品的比较分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(2): 17-26.
DOI |
| [3] |
陈小婷, 赵强, 刘慧, 等, 2022. 黄土高原两次不同类型暴雨水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 968-980.
DOI |
| [4] | 陈玥, 谌芸, 陈涛, 等, 2016. 长江中下游地区暖区暴雨特征分析[J]. 气象, 42(6): 724-731. |
| [5] | 崔慧慧, 李荣, 郜彦娜, 等, 2023. "7·20"郑州极端特大暴雨降水细节特征和成灾过程研究[J]. 灾害学, 38(2): 114-120. |
| [6] | 崔晓鹏, 杨玉婷, 2022. “21·7”河南暴雨水汽源地追踪和定量贡献分析[J]. 大气科学, 46(6): 1 543-1 556. |
| [7] | 黄荣辉, 陈际龙, 2010. 我国东、西部夏季水汽输送特征及其差异[J]. 大气科学, 34(6): 1 035-1 045. |
| [8] | 黄荣辉, 陈际龙, 刘永, 2011. 我国东部夏季降水异常主模态的年代际变化及其与东亚水汽输送的关系[J]. 大气科学, 35(4): 589-606. |
| [9] | 江志红, 任伟, 刘征宇, 等, 2013. 基于拉格朗日方法的江淮梅雨水汽输送特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 71(2): 295-304. |
| [10] | 蒋贤玲, 马柱国, 巩远发, 2015. 全球典型干湿变化区域水汽收支与降水变化的对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 34(5): 1 279-1 291. |
| [11] | 金米娜, 2009. 江西省汛期暴雨气候特点及预报方法综合分析[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 32(1): 69-72. |
| [12] | 李方腾, 刘飞, 柴静, 2021. 过去500年印度夏季风降水与ENSO的关系[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(4): 558-572. |
| [13] | 刘丹, 邱新法, 史岚, 等, 2013. 基于NCEP资料的我国大气可降水量的计算及其时空分布[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报, 5(2): 113-119. |
| [14] |
马志敏, 王将, 连钰, 等, 2023. 云南一次强对流暴雨天气学成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 629-638.
DOI |
| [15] |
钱正安, 蔡英, 宋敏红, 等, 2018. 中国西北旱区暴雨水汽输送研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 37(3): 577-590.
DOI |
| [16] | 阙志萍, 凌婷, 吴凡, 等, 2021. 江西一次连续大暴雨的水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(1): 76-86. |
| [17] | 冉令坤, 李舒文, 周玉淑, 等, 2021. 2021年河南"7.20"极端暴雨动、热力和水汽特征观测分析[J]. 大气科学, 45(6):1366-1 383. |
| [18] | 饶晨泓, 毕鑫鑫, 陈光华, 等, 2022. 近海台风对"21·7"河南极端暴雨过程水汽通量和动,热力条件影响的模拟[J]. 大气科学, 46(6): 1 577-1 594. |
| [19] | 孙继松, 2017. 短时强降水和暴雨的区别与联系[J]. 暴雨灾害, 36(6): 498-506. |
| [20] | 汤彬, 王宗明, 胡文婷, 等, 2023. 2021年河南省一次罕见暴雨过程的降水特征及成因[J]. 大气科学, 47(2): 517-533. |
| [21] | 唐传师, 甘瑞杰, 程宗佩, 等, 2021. 江西暴雨气候特征及降水极值重现期分析[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 44(3): 164-171. |
| [22] |
王佳津, 肖红茹, 杨康权, 等, 2023. 四川盆地一次持续性暴雨的水汽输送特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 474-482.
DOI |
| [23] |
肖安, 尹小飞, 刘献耀, 2022. 江西省降水日变化时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 840-848.
DOI |
| [24] | 徐爽, 胡鹏宇, 贾越, 等, 2023. 2020—2021年沈阳地区4次短时强降水过程的大气可降水量变化对比分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 39(2): 28-34. |
| [25] | 徐元泰, 丁一汇, 1988. 气象场的客观分析和中尺度滤波[J]. 大气科学, 12(3): 274-282. |
| [26] | 杨景梅, 邱金桓, 2002. 用地面湿度参量计算我国整层大气可降水量及有效水汽含量方法的研究[J]. 大气科学, 26(1): 9-22. |
| [27] | 俞小鼎, 2012. 2012年7月21日北京特大暴雨成因分析[J]. 气象, 38(11): 1 313-1 329. |
| [28] | 赵文灿, 龙余良, 阙志萍, 等, 2018. 江西省电线积冰特征及温度层结分析[J]. 气象科技, 46(1): 178-181. |
| [29] | KAHRAMAN A, KENDON E J, CHAN S C, et al, 2021. Quasi-stationary intense rainstorms spread across Europe under climate change[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(13). DOI: 10.1029/2020GL092361. |
| [30] | MUKHOPADHYAY P, BECHTOLD P, ZHU Y J, et al, 2021. Unraveling the mechanism of extreme (more than 30 Sigma) precipitation during August 2018 and 2019 over Kerala, india[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 36(4): 1 253-1 273. |
| [31] | XIONG Y T, REN X J, 2021. Contribution of atmospheric rivers to precipitation and precipitation extremes in East Asia: Diagnosis with moisture flux convergence[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 35(5): 831-843. |
| [32] | YOUNG M, LAMB D, LANE A, et al, 2020. Comparison of short-period daytime convective rainfall accumulations with total column precipitable water: Derivation of an operational forecasting technique[J]. Meteorological Applications, 27(2): 1-16. |
| [1] | LIN Hongjie, WEN Xiaohang, HUANG Xiaolu, LI Ruiqing. Numerical simulation study of Typhoon “Ambi” degeneration mechanism and its impact on heavy rainstorm in Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 588-597. |
| [2] | WEI Juanjuan, WAN Yu, PAN Ning, XIAO Junʼan. Analysis of water vapor characteristics and unstable mechanism of extreme rainstorm in spring in Yili River Valley [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 395-404. |
| [3] | ZHOU Jinhong, WANG Xiuming, TIAN Xiaoting, ZHANG Zexiu, LI Shuwen, CAI Xiaofang. Study on circulation characteristics and water vapor anomaly of extreme rainstorm events in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 426-436. |
| [4] | ZHAO Wei, LIU Jianhong, WANG Kun, ZHANG Chaohua, CHE Jingjing, HAN Yinjuan. Construction of an integrated rainstorm hazard risk warning model in semi-arid areas and its application in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 458-464. |
| [5] | SHI Yanzhao, LIU Weicheng, FU Zhao, FU Zhengxu, XU Lili, ZHENG Xin. Comparative analysis of two rainstorm cases in Longnan of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 107-116. |
| [6] | WU Guhui, PENG Fang, QI Dapeng, DU Xiaoling, YANG Xiuzhuang. Analysis on mesoscale feature of a extremely rainstorm process caused by the convergence line frontogenesis in Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 753-763. |
| [7] | MA Zhimin, WANG Jiang, LIAN Yu, ZHANG Wancheng, NIU Fabao, YANG Suyu. Analysis on synoptic causes of a severe convective rainstorm in Yunnan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 629-638. |
| [8] | WANG Jiajin, XIAO Hongru, YANG Kangquan, WANG Binyan. Water vapor transport characteristics of a continuous rainstorm in Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 474-482. |
| [9] | FU Zhao, LIU Weicheng, SONG Xingyu, XU Lili, SHA Honge, MA Li, CUI Yu. Local enhanced convective environment characteristics of an extreme rainstorm event in arid region of Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 909-921. |
| [10] | CHEN Xiaoting, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Hui, PENG Li. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [11] | PENG Li, ZHAO Qiang, QIAO Danyang, ZHANG Xiong, XU Haotian, NI Wen. Comparative analysis on characteristics of rainstorms caused by northwest vortex in Shaanxi with and without influence of typhoon [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 981-992. |
| [12] | XIAO An, YIN Xiaofei, LIU Xianyao. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of diurnal variation of precipitation in Jiangxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 840-848. |
| [13] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia. Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [14] | MA Simin, MU Jianhua, SHU Zhiliang, SUN Yanqiao, DENG Peiyun, ZHOU Nan. Topography sensitivity simulation test of a typical rainstorm process in Liupan Mountain region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 457-468. |
| [15] | YANG Xia, XU Tingting, ZHANG Linmei, HUA Ye, ZHOU Hongkui. Characteristics and differences of rainstorm in the southern Xinjiang during warm season under different climatic backgrounds [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 222-233. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||