干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 516-523.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0516
2018年广东空中水物质评估及开发分析
高建秋1,2( ), 郑彬3, 游积平1, 何松蔚1, 余小嘉1, 杨博成4
), 郑彬3, 游积平1, 何松蔚1, 余小嘉1, 杨博成4
- 1.广东省突发事件预警信息发布中心/广东省人工影响天气中心,广东 广州 510640
2.中国气象局云雾物理环境重点开放实验室,北京 100081
3.中国气象局广州热带海洋气象研究所,广东 广州 510640
4.广东海洋大学海洋与气象学院,广东 湛江 524088
Assessment and development analysis of air water substances in Guangdong in 2018
GAO Jianqiu1,2( ), ZHENG Bin3, YOU Jiping1, HE Songwei1, YU Xiaojia1, YANG Bocheng4
), ZHENG Bin3, YOU Jiping1, HE Songwei1, YU Xiaojia1, YANG Bocheng4
- 1. Guangdong Provincial Emergency Early Warning Information Release Center/Guangdong Weather Modification Center, Guangzhou 510640, China
2. Key Laboratory for Cloud Physics of China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081,China
3. Institute of Tropical and Marine Meteorology of China Meteorological Administration, Guangzhou 510640, China
4. College of Ocean and Meteorology, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088,Guangdong,China
摘要:
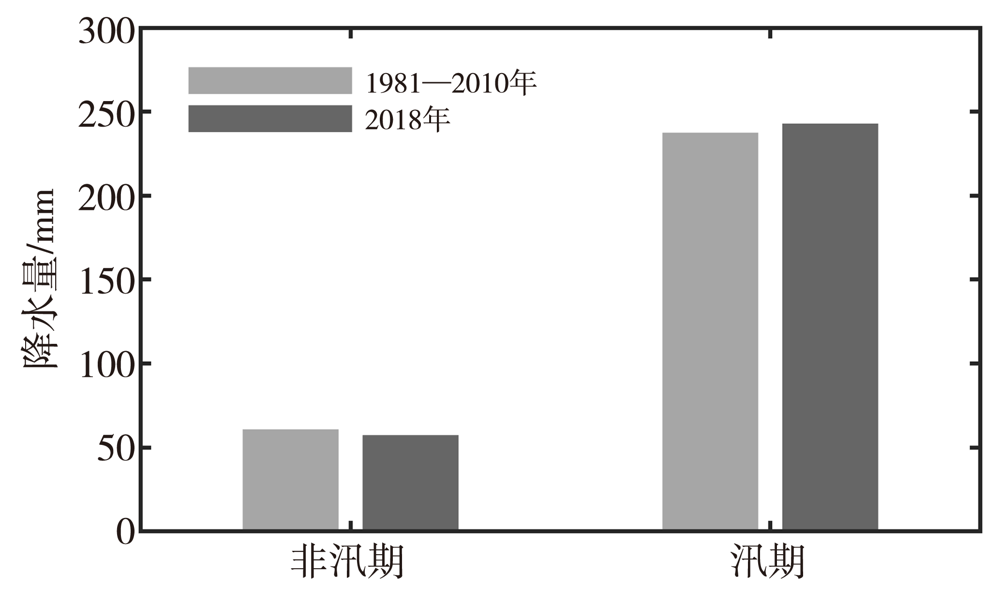
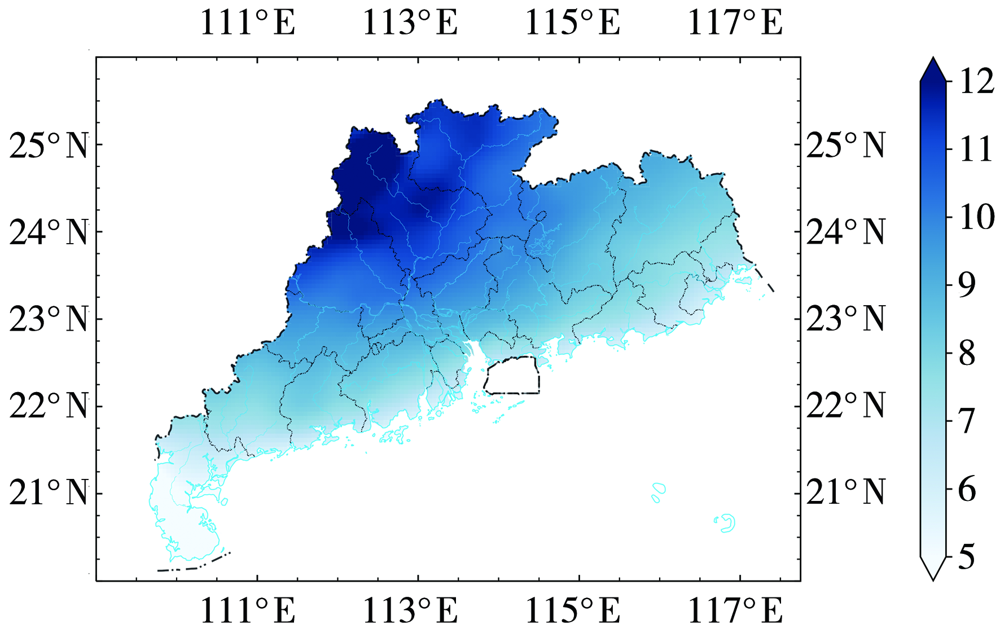
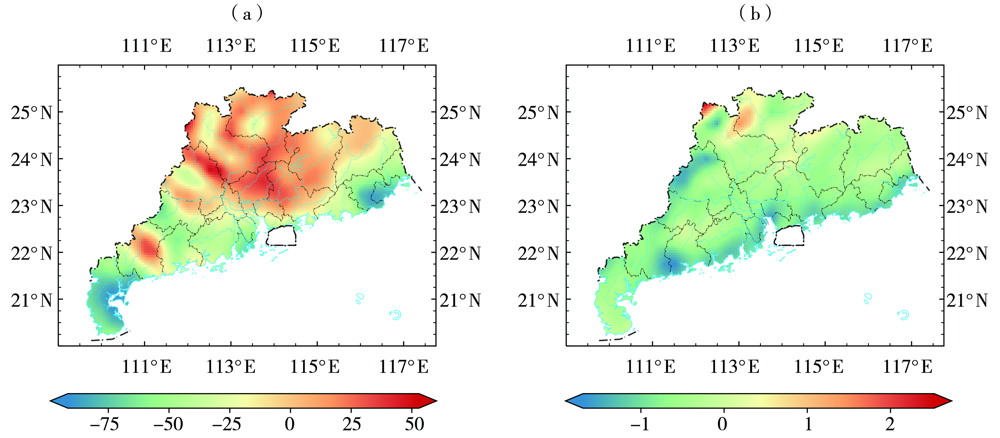
利用2018年1月1日至12月31日逐小时欧洲中期天气预报中心(European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts,ECMWF)第五代全球大气再分析产品——ERA5和中国气象局多源降水分析系统(CMA multi-source precipitation analysis system,CMPAS)中逐小时降水产品(CMPAS-hourly),采用基于大气水物质收支平衡方程的水物质评估方法对广东2018年空中云水资源及空中水汽、水凝物时空分布进行评估。对广东省整体而言,2018年水汽降水效率为5.1%,水凝物降水效率为89.6%,水汽和水凝物都为净输出。从空间分布来看,水汽总量自西南向东北逐渐减少,水凝物总量高值区在粤西云雾山、天露山及粤东莲花山的南坡,云水资源总量从北部山区向沿海地区逐渐减小,水凝物降水效率从沿海地区向北部山区逐渐减小。从时间变化来看,水汽总量在夏季最大,水凝物总量在8月下半月和9月上半月最大,云水资源总量非汛期高于汛期;水汽和云水资源的变化月内尺度大于天气尺度,水凝物的变化天气尺度大于月内尺度。
中图分类号: