干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 251-259.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0251
内蒙古中部干旱半干旱区水汽和液态水特征研究
苏立娟1,2,3( ), 衣娜娜1,2,3, 郑旭程1,2,3, 史金丽1,2,3, 邓晓东4
), 衣娜娜1,2,3, 郑旭程1,2,3, 史金丽1,2,3, 邓晓东4
- 1.内蒙古自治区气象科学研究所,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010000
2.中国气象局云雾物理环境重点开放实验室,北京 100081
3.内蒙古自治区人工影响天气重点实验室,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010000
4.内蒙古自治区生态与农业气象中心,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010000
-
收稿日期:2021-12-20修回日期:2022-05-05出版日期:2023-04-30发布日期:2023-05-09 -
作者简介:苏立娟(1976—),女,内蒙古人,正高级工程师,主要从事云降水物理以及人工影响天气作业识别研究。E-mail:yinndongzhl@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划课题(2018YFC1507900);西北区域人工影响天气能力建设项目“巴彦淖尔人工防雹技术研究试验”(ZQC-R18217/RYSY201906);国家自然科学基金项目(42030604);内蒙古自治区科技创新项目(nmqxkjcx202203);及内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2020MS04015)
Characteristics of water vapor and liquid water in arid and semi-arid region in the central Inner Mongolia
SU Lijuan1,2,3( ), YI Nana1,2,3, ZHENG Xucheng1,2,3, SHI Jinli1,2,3, DENG Xiaodong4
), YI Nana1,2,3, ZHENG Xucheng1,2,3, SHI Jinli1,2,3, DENG Xiaodong4
- 1. Meteorological Science Institute of Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010000, China
2. Key Open Laboratory for Cloud Physics of China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
3. Key Laboratory for Weather Modification of Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010000, China
4. Ecological and Agricultural Meteorological Center of Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010000, China
-
Received:2021-12-20Revised:2022-05-05Online:2023-04-30Published:2023-05-09
摘要:
基于多通道微波辐射计数据与呼和浩特站逐小时降水数据分析 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部干旱和半干旱区35个降水日积分水汽含量、积分液态水含量月变化特征,进一步分析层状云稳定性降水和积状云对流性降水中液态水含量、水汽含量的垂直分布特征和积分液态水含量、积分水汽含量的相位特征。结果表明,降水日积分水汽含量和积分液态水含量具有明显的季节变化特征,两者均在夏季和初秋较大。降水发生前积分水汽含量与积分液态水含量有明显跃增,这种变化在对流性降水中更明显,且超过80%的样本显示积分水汽含量与积分液态水含量存在反相位变化。对流性降水水汽含量主要分布在0~6 km高度,且随高度递减,而液态水含量随高度先增加后减小;稳定性降水水汽含量和液态水含量的垂直分布与对流性降水一致,但两者均小于对流性降水。基于积分水汽含量与积分液态水含量的降水发生判断条件对指导当地人工增雨作业、缓解旱情有实际应用价值。
中图分类号:
引用本文
苏立娟, 衣娜娜, 郑旭程, 史金丽, 邓晓东. 内蒙古中部干旱半干旱区水汽和液态水特征研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 251-259.
SU Lijuan, YI Nana, ZHENG Xucheng, SHI Jinli, DENG Xiaodong. Characteristics of water vapor and liquid water in arid and semi-arid region in the central Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 251-259.
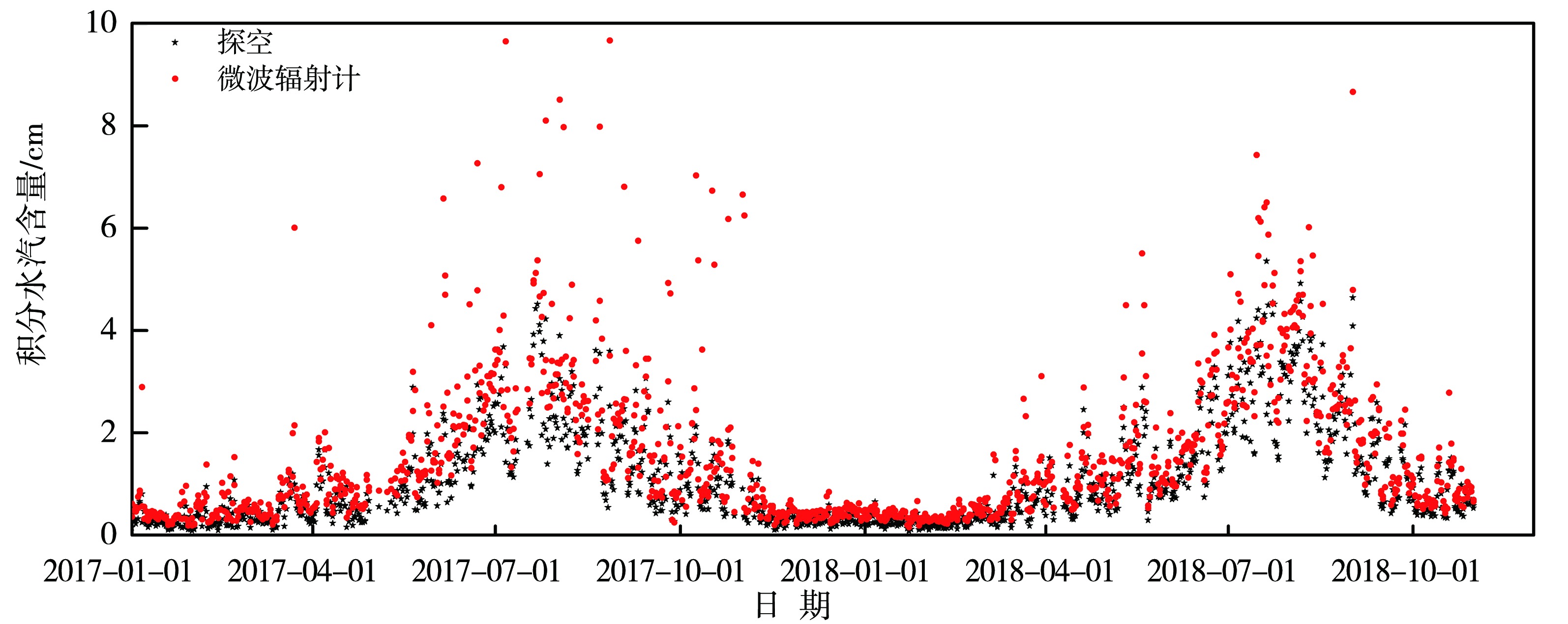
图1 2017年1月至2018年10月呼和浩特站微波辐射计和探空数据反演的积分水汽含量
Fig.1 The integrated water vapor content retrieved by the sounding data and microwave radiometer data at Hohhot station from January 2017 to October 2018
| 稳定性降水日 | 对流性降水日 | |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-06-05 | 2017-06-21 | 2018-07-06 |
| 2017-06-06 | 2017-06-22 | 2018-07-07 |
| 2017-09-10 | 2017-06-28 | 2018-07-20 |
| 2018-04-04 | 2017-07-22 | 2018-07-21 |
| 2018-04-13 | 2017-07-26 | 2018-08-06 |
| 2018-04-20 | 2017-08-22 | 2018-08-10 |
| 2018-06-23 | 2017-09-09 | 2018-08-11 |
| 2018-08-17 | 2017-09-25 | 2018-08-12 |
| 2018-09-27 | 2018-05-10 | 2018-08-28 |
| 2018-06-24 | 2018-06-16 | 2018-08-30 |
| 2018-09-10 | 2018-06-25 | 2018-09-01 |
| 2018-07-02 | 2018-08-07 | |
表1 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部35个降水日降水性质划分
Tab.1 Classification of precipitation properties about 35 rainfall days from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
| 稳定性降水日 | 对流性降水日 | |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-06-05 | 2017-06-21 | 2018-07-06 |
| 2017-06-06 | 2017-06-22 | 2018-07-07 |
| 2017-09-10 | 2017-06-28 | 2018-07-20 |
| 2018-04-04 | 2017-07-22 | 2018-07-21 |
| 2018-04-13 | 2017-07-26 | 2018-08-06 |
| 2018-04-20 | 2017-08-22 | 2018-08-10 |
| 2018-06-23 | 2017-09-09 | 2018-08-11 |
| 2018-08-17 | 2017-09-25 | 2018-08-12 |
| 2018-09-27 | 2018-05-10 | 2018-08-28 |
| 2018-06-24 | 2018-06-16 | 2018-08-30 |
| 2018-09-10 | 2018-06-25 | 2018-09-01 |
| 2018-07-02 | 2018-08-07 | |
| 月份 | 样本数 | 不同区间积分水汽含量样本数占比/% | 积分水汽含量/cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0≤w≤ 2 cm | 2<w≤ 3 cm | 3<w≤ 4 cm | 4<w≤ 5 cm | w>5 cm | 均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | ||
| 4 | 301 | 38.87 | 3.99 | 9.30 | 23.92 | 23.92 | 3.45 | 6.91 | 1.43 |
| 5 | 17 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.59 | 2.73 | 2.50 |
| 6 | 473 | 0.21 | 10.15 | 13.11 | 13.74 | 62.79 | 5.51 | 9.06 | 1.91 |
| 7 | 616 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8.60 | 69.97 | 21.43 | 4.85 | 14.54 | 3.49 |
| 8 | 628 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 2.07 | 39.49 | 57.96 | 5.86 | 12.00 | 1.38 |
| 9 | 747 | 1.34 | 5.22 | 4.82 | 17.14 | 71.49 | 6.14 | 13.69 | 0.82 |
表2 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部不同区间积分水汽含量样本数占比及积分水汽含量均值与最大、最小值逐月变化
Tab.2 The monthly change of sample number proportion of integrated water vapor content with different intervals and the maximum, minimum and mean value of integrated water vapor from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
| 月份 | 样本数 | 不同区间积分水汽含量样本数占比/% | 积分水汽含量/cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0≤w≤ 2 cm | 2<w≤ 3 cm | 3<w≤ 4 cm | 4<w≤ 5 cm | w>5 cm | 均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | ||
| 4 | 301 | 38.87 | 3.99 | 9.30 | 23.92 | 23.92 | 3.45 | 6.91 | 1.43 |
| 5 | 17 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.59 | 2.73 | 2.50 |
| 6 | 473 | 0.21 | 10.15 | 13.11 | 13.74 | 62.79 | 5.51 | 9.06 | 1.91 |
| 7 | 616 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8.60 | 69.97 | 21.43 | 4.85 | 14.54 | 3.49 |
| 8 | 628 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 2.07 | 39.49 | 57.96 | 5.86 | 12.00 | 1.38 |
| 9 | 747 | 1.34 | 5.22 | 4.82 | 17.14 | 71.49 | 6.14 | 13.69 | 0.82 |
| 月份 | 积分水汽含量/cm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w≥1.5 | w≥2.0 | w≥2.5 | w≥3.0 | w≥3.5 | w≥4.0 | w≥4.5 | w≥5.0 | |
| 4 | 82.30* | 61.13 | 58.14 | 57.14 | 55.48 | 47.84 | 36.21 | 23.92 |
| 5 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 94.12* | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 100.00 | 99.79 | 99.58 | 89.85 | 80.34* | 76.74 | 66.60 | 63.00 |
| 7 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.84 | 91.88* | 55.65 | 23.32 |
| 8 | 99.84 | 99.84 | 99.68 | 99.52 | 98.89 | 97.45* | 75.64 | 58.12 |
| 9 | 99.33 | 98.66 | 98.13 | 93.44 | 91.43 | 88.62 | 81.79* | 71.62 |
表3 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部降水日积分水汽含量分段累积样本数占比 单位:%
Tab.3 The cumulative sample number proportion of integrated water vapor content with different intervals on rainfall days from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
| 月份 | 积分水汽含量/cm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w≥1.5 | w≥2.0 | w≥2.5 | w≥3.0 | w≥3.5 | w≥4.0 | w≥4.5 | w≥5.0 | |
| 4 | 82.30* | 61.13 | 58.14 | 57.14 | 55.48 | 47.84 | 36.21 | 23.92 |
| 5 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 94.12* | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 100.00 | 99.79 | 99.58 | 89.85 | 80.34* | 76.74 | 66.60 | 63.00 |
| 7 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.84 | 91.88* | 55.65 | 23.32 |
| 8 | 99.84 | 99.84 | 99.68 | 99.52 | 98.89 | 97.45* | 75.64 | 58.12 |
| 9 | 99.33 | 98.66 | 98.13 | 93.44 | 91.43 | 88.62 | 81.79* | 71.62 |
| 月份 | 样本数 | 不同区间积分液态水含量样本数占比/% | 积分液态水含量/mm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0≤L≤2 mm | 2<L≤3 mm | 3<L≤4 mm | 4<L≤5 mm | L>5 mm | 均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | ||
| 4 | 301 | 11.30 | 31.23 | 14.29 | 4.65 | 38.54 | 4.09 | 6.60 | 0.11 |
| 5 | 17 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.01 |
| 6 | 473 | 22.41 | 12.47 | 29.60 | 20.51 | 15.01 | 3.35 | 9.19 | 0.03 |
| 7 | 616 | 8.12 | 8.60 | 6.82 | 16.56 | 59.90 | 4.89 | 14.65 | 0.44 |
| 8 | 628 | 28.66 | 10.99 | 12.26 | 7.48 | 40.61 | 3.86 | 15.20 | 0.08 |
| 9 | 748 | 22.36 | 20.88 | 16.73 | 14.06 | 25.97 | 3.86 | 22.77 | 0.09 |
表4 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部不同区间积分液态水含量样本数占比及积分液态水含量均值与最大、最小值逐月变化
Tab.4 The monthly change of sample number proportion of integrated liquid water content with different intervals and the maximum, minimum and mean values of integrated liquid water content from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
| 月份 | 样本数 | 不同区间积分液态水含量样本数占比/% | 积分液态水含量/mm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0≤L≤2 mm | 2<L≤3 mm | 3<L≤4 mm | 4<L≤5 mm | L>5 mm | 均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | ||
| 4 | 301 | 11.30 | 31.23 | 14.29 | 4.65 | 38.54 | 4.09 | 6.60 | 0.11 |
| 5 | 17 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.01 |
| 6 | 473 | 22.41 | 12.47 | 29.60 | 20.51 | 15.01 | 3.35 | 9.19 | 0.03 |
| 7 | 616 | 8.12 | 8.60 | 6.82 | 16.56 | 59.90 | 4.89 | 14.65 | 0.44 |
| 8 | 628 | 28.66 | 10.99 | 12.26 | 7.48 | 40.61 | 3.86 | 15.20 | 0.08 |
| 9 | 748 | 22.36 | 20.88 | 16.73 | 14.06 | 25.97 | 3.86 | 22.77 | 0.09 |
| 月份 | 积分液态水含量/mm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥1.50 | ≥2.00 | ≥2.50 | ≥3.00 | ≥3.50 | ≥4.00 | ≥4.50 | ≥5.00 | |
| 4 | 94.35 | 88.70* | 71.43 | 57.48 | 49.83 | 43.19 | 40.20 | 38.54 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 81.40* | 77.59 | 70.61 | 65.12 | 50.95 | 35.52 | 22.83 | 15.01 |
| 7 | 94.64 | 91.88 | 86.69 | 83.28 | 80.19* | 76.46 | 84.58 | 59.90 |
| 8 | 81.05* | 71.34 | 64.65 | 60.35 | 55.41 | 48.09 | 43.79 | 40.61 |
| 9 | 85.01* | 77.64 | 67.34 | 56.76 | 46.45 | 40.03 | 32.26 | 25.97 |
表5 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部降水日积分液态水含量分段累积样本数占比 单位:%
Tab.5 The cumulative sample number proportion of integral liquid water content with different intervals on precipitation days from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
| 月份 | 积分液态水含量/mm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥1.50 | ≥2.00 | ≥2.50 | ≥3.00 | ≥3.50 | ≥4.00 | ≥4.50 | ≥5.00 | |
| 4 | 94.35 | 88.70* | 71.43 | 57.48 | 49.83 | 43.19 | 40.20 | 38.54 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 81.40* | 77.59 | 70.61 | 65.12 | 50.95 | 35.52 | 22.83 | 15.01 |
| 7 | 94.64 | 91.88 | 86.69 | 83.28 | 80.19* | 76.46 | 84.58 | 59.90 |
| 8 | 81.05* | 71.34 | 64.65 | 60.35 | 55.41 | 48.09 | 43.79 | 40.61 |
| 9 | 85.01* | 77.64 | 67.34 | 56.76 | 46.45 | 40.03 | 32.26 | 25.97 |
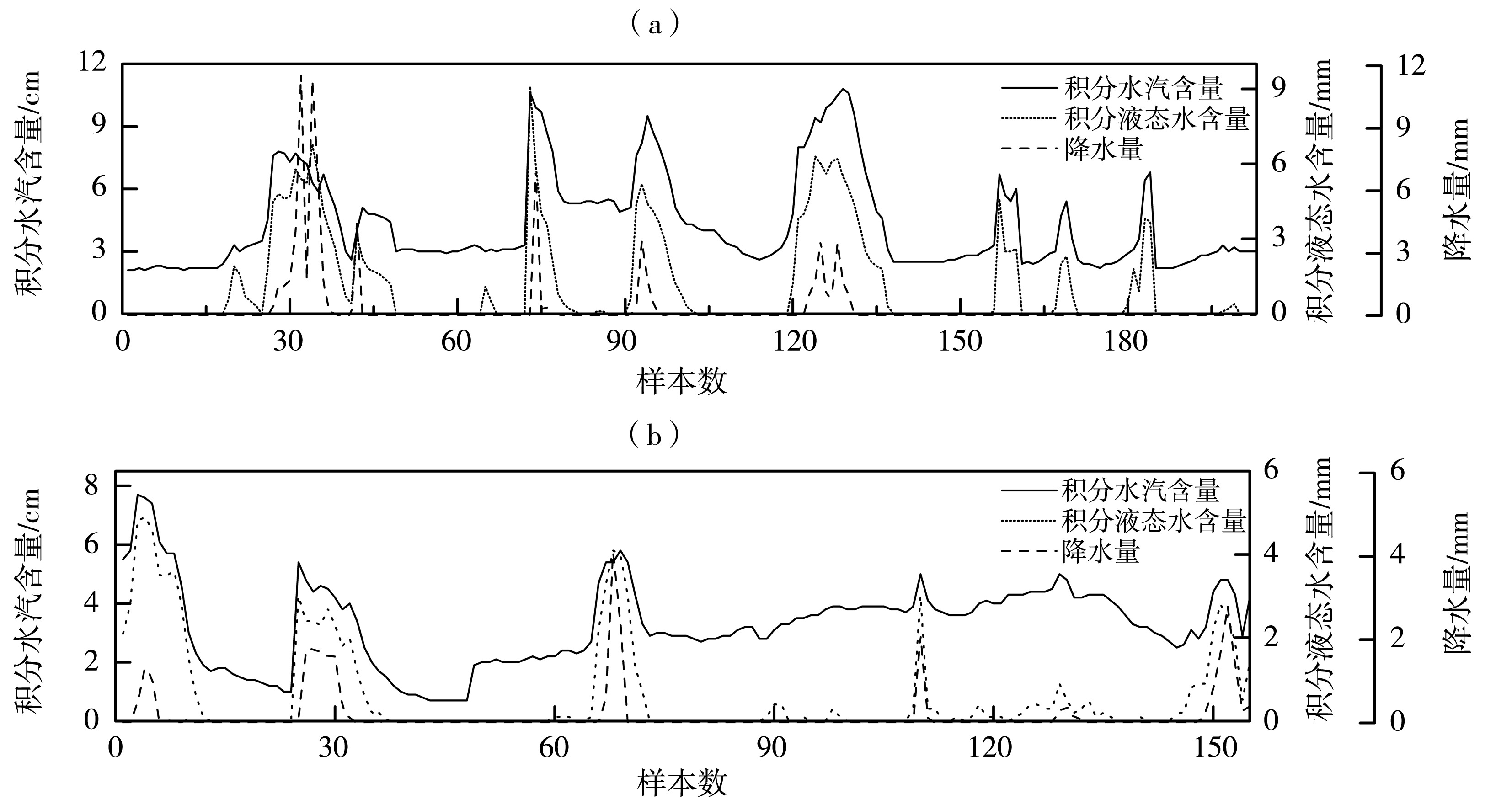
图2 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部降水日对流性降水(a)和稳定性降水(b)中积分水汽含量、积分液态水含量与小时降水量变化
Fig.2 The integrated water vapor, the integrated liquid water content and one-hour precipitation under convective (a) and steady (b) precipitation processes from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
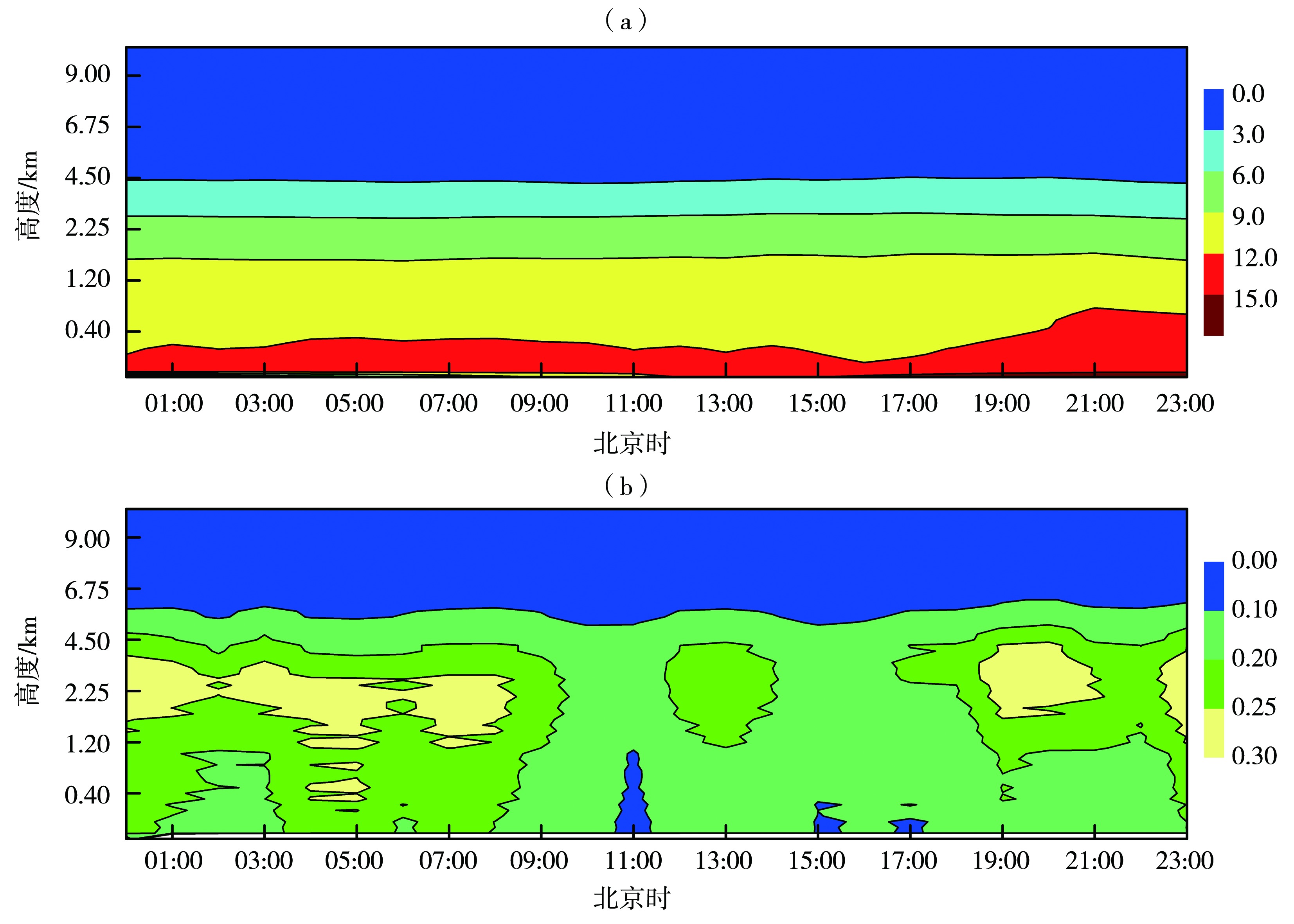
图3 2017、2018年4—9月内蒙古中部地区对流性降水水汽含量(a,单位:cm)和液态水含量(b,单位:mm)垂直分布的日变化
Fig.3 The diurnal variation of vertical distribution of water vapor (a, Unit: cm) and liquid water content (b, Unit: mm) during convective precipitation processes from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia

图4 内蒙古中部地区2017、2018年4—9月稳定性降水水汽含量(a,单位:cm)和液态水含量(b,单位:mm)垂直分布的日变化
Fig.4 The diurnal variation of vertical distribution of water vapor (a, Unit: cm) and liquid water content (b, Unit: mm) during steady precipitation processes from April to September in 2017 and 2018 in the middle region of Inner Mongolia

图5 内蒙古中部地区积分液态水含量与积分水汽含量的同相位(a)和反相位变化(b)个例
Fig.5 Cases of integrated liquid water and integrated water vapor content changes in phase (a) and anti-phase (b) in the middle region of Inner Mongolia
| [1] | 敖雪, 王振会, 徐桂荣, 等, 2011. 地基微波辐射计资料在降水分析中的应用[J]. 暴雨灾害, 30(4): 358-365. |
| [2] | 白婷, 丁建芳, 刘艳华, 等, 2021. 微波辐射计在监测水汽特征及降水分析中的应用[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(6): 102-107. |
| [3] | 陈银, 2021. 地基微波辐射计质量控制和反演算法研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 9-10. |
| [4] | 程鹏, 樊旭, 胡晓辉, 等, 2021. 基于微波辐射计的张掖地区水汽、液态水变化特征分析[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 36(2): 230-237. |
| [5] | 陈添宇, 陈乾, 丁瑞津, 2007. 地基微波辐射仪监测的张掖大气水汽含量与雨强的关系[J]. 干旱区地理, 2007, 30(4):501-506. |
| [6] | 方莎莎, 陆鹏程, 廖可文, 等, 2020. 基于微波辐射计资料对武汉市冬季典型大雾个例的探测分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 43(4): 81-87. |
| [7] | 巩宁刚, 孙美平, 闫露霞, 等, 2017. 1979—2016年祁连山地区大气水汽含量时空特征及其与降水的关系[J]. 干旱区地理, 40(4): 762-771. |
| [8] | 郭学良, 付丹红, 胡朝霞, 2013. 云降水物理与人工影响天气研究进展(2008—2012)[J]. 大气科学, 37(2): 351-363. |
| [9] | 郝巨飞, 袁雷武, 李芷霞, 等, 2018. 激光雷达和微波辐射计对邢台市一次沙尘天气的探测分析[J]. 高原气象, 37(4): 1 110-1 119. |
| [10] | 韩经纬, 王海梅, 乌兰, 等, 2009. 内蒙古雷暴、冰雹灾害的评估分析与防御对策研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 23(7): 31-38. |
| [11] | 侯叶叶, 2016. 地基微波辐射计的精度分析和资料同化试验[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 1-2. |
| [12] | 李成伟, 李伟, 夏江峰, 等, 2021. 不同天气条件下微波辐射计温度探测效果评估[J]. 陕西气象, (6): 43-46. |
| [13] | 李军霞, 李培仁, 晋立军, 等, 2017. 地基微波辐射计在遥测大气水汽特征及降水分析中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5): 767-775. |
| [14] | 李静, 何清, 姚俊强, 等, 2014. 内蒙古西部地区气候变化特征及影响因子分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 28(5): 186-191. |
| [15] | 李剑婕, 郑佳锋, 吴凌华, 等, 2021. 一次山地冬季“霰-雪-云-雾”天气的云降水垂直结构和演变特征研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 43(7): 165-175. |
| [16] | 刘红燕, 2011. 三年地基微波辐射计观测温度廓线的精度分析[J]. 气象学报, 69(4): 719-728. |
| [17] | 刘建忠, 张蔷, 2010. 微波辐射计反演产品评价[J]. 气象科技, 38(3): 325-331. |
| [18] | 林彤, 桑建人, 姚展予, 等, 2021. 基于微波辐射计的宁夏六盘山西侧大气水汽变化特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 44(4):923-933. |
| [19] | 卢士庆, 闫宾, 刘晓东, 2009. 几种求算大气可降水量方法比较[J]. 内蒙古气象, (1): 15-18. |
| [20] | 史金丽, 2017. 基于微波辐射计测量呼和浩特地区水汽特征的初步分析[J]. 内蒙古气象, (4):17-23. |
| [21] | 苏立娟, 郑旭程, 达布希拉图, 等, 2020. 基于雨滴谱仪建立不同性质降水 Z-I关系并与雷达作对比分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 34(6): 103-108. |
| [22] | 唐仁茂, 李德俊, 向玉春, 等, 2012. 地基微波辐射计对咸宁一次冰雹天气过程的监测分析[J]. 气象学报, 70(4): 806-813. |
| [23] | 王叶红, 赖安伟, 赵玉春, 2010. 地基微波辐射计资料同化对一次特大暴雨过程影响的数值试验研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 29(3): 201-207. |
| [24] | 冼星河, 张玮, 陈楚梦, 2021. 新型观测数据在东莞一次大暴雨过程中的综合应用[J]. 气象研究与应用, 42(2): 63-67. |
| [25] | 许皓琳, 郑佳锋, 姜涛, 等, 2020. 乌鲁木齐和成都两地机场雷暴降水水汽条件的分析研究[J]. 气象, 46(11): 1 440-1 449. |
| [26] | 许焕斌, 2009. 关于在人工影响天气中更新学术观念的探讨[J]. 干旱气象, 27(4): 305-307. |
| [27] |
杨莲梅, 李霞, 赵玲, 等, 2013. MP-3000A型地基微波辐射计探测性能及其在乌鲁木齐降水天气中的初步应用[J]. 干旱气象, 31(3): 570-578.
DOI |
| [28] | 衣娜娜, 苏立娟, 郑旭程, 等, 2021. 内蒙古西部地区降水云宏观特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 406-414. |
| [29] | 张成福, 王雨晴, 闫冬, 等, 2020. 内蒙古荒漠草原区气候变化及干旱趋势分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 39(增刊2): 20-25. |
| [30] | 张秋晨, 龚佃利, 王俊, 等, 2017. 基于地基微波辐射计反演的济南地区水汽及云液态水特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 33(5): 35-43. |
| [31] | 张文刚, 徐桂荣, 万蓉, 等, 2015. 基于地基微波辐射计的大气液态水及水汽特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 34(4): 367-374. |
| [32] | 郑飒飒, 2020. 基于地基微波辐射计反演四川盆地水汽及云液态水的初步分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 40(2): 83-88. |
| [33] | 朱雯娜, 王清平, 王春红, 等, 2018. 微波辐射计在乌鲁木齐机场浓雾监测中的应用[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 12(5): 23-31. |
| [34] |
COSSU F, HOCKER K, MARTYNOV A, et al, 2015. Atmospheric water parameters measured by a ground-based microwave radiometer and compared with the WRF mode[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 16(4): 465-472.
DOI URL |
| [35] | NAVAS-GUZMáN F, KäMPFER N, SCHRANZ F, et al, 2017. Intercomparison of stratospheric temperature profiles from a ground-based microwave radiometer with other techniques[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 17(22): 1-28. |
| [36] |
STEINKE S, LOHNERT U, CREWELL S, et al, 2014. Water vapor tomography with two microwave radiometers[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 11(2): 419-423.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 郭静妍, 肖 栋. 孟加拉地区夏季水汽变化及其与太平洋年代际振荡的联系[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 380-389. |
| [2] | 蔡 怡, 徐枝芳, 龚 玺, 钟若嵋, 黄观胜, 龙海川. 2021年夏季CMA-MESO模式降水预报评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 503-515. |
| [3] | 张存厚, 崔崴, 越昆, 赵杏花, 吴英杰, 森迪. 干旱半干旱区土壤水分对降水的脉动响应:以荒漠草原达茂旗为例[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 260-267. |
| [4] | 康恒元, 刘玉莲, 周贺玲, 袁芳. 黑龙江省夏季降水非均匀性特征及其影响因素[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 268-278. |
| [5] | 王叶红, 赵玉春. GRAPES-REPS对我国南方2017年初夏持续性降水预报的检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 328-340. |
| [6] | 邢红艳, 何清, 普宗朝, 王国胜, 金晨. 西北干旱区乌鲁木齐河流域植被生长季降水特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 34-42. |
| [7] | 把黎, 奚立宗, 蔡迪花, 庞朝云, 张鑫海, 尹春. 基于微波辐射计资料的祁连山东段大气水汽和液态水时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 64-72. |
| [8] | 郭飞燕, 刁秀广, 褚颖佳, 李欣, 陆雪, 张少博. 两次极端强降水风暴双偏振参量特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 103-113. |
| [9] | 吴薇, 黄晓龙, 徐晓莉, 李施颖, 杜冰, 蒋雨荷. 四川省降水实况分析产品影响因素综合评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 143-151. |
| [10] | 叶茂, 吴钲, 高松, 陈良吕, 游婷. 对流尺度集合预报对川渝地区降水的预报性能分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 152-163. |
| [11] | 张君霞, 黄武斌, 杨秀梅, 刘维成, 周子涵, 沙宏娥. 陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 922-932. |
| [12] | 杨丽杰, 曹彦超, 刘维成, 徐丽丽, 张洪芬, 孙子茱. 陇东黄土高原旱区短时强降水的时空分布特征及地形影响研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 945-953. |
| [13] | 李晨蕊, 伏晶, 刘维成, 王基鑫, 王一丞, 傅朝, 郑新. 应用FY卫星产品分析陇东半干旱区特大暴雨事件云特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 954-967. |
| [14] | 陈燕丽, 唐梅蓉, 张会, 莫建飞, 钱拴. 广西喀斯特地区植被覆盖度和净初级生产力对SPEI干旱指数的响应差异[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1042-1050. |
| [15] | 李光伟, 黄光瑞, 邢峰华, 敖杰. 海口地区GPS反演大气可降水量中加权平均温度模型构建及其应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1081-1091. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
