干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 241-250.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-02-0241
1997—2021年四川省干旱时空变化特征分析
蔡怡亨1,2( ), 李帅3(
), 李帅3( ), 张强4, 邓彪1,2, 罗玉1,2, 孙蕊1,2
), 张强4, 邓彪1,2, 罗玉1,2, 孙蕊1,2
- 1.中国气象局成都高原气象研究所/高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
2.四川省气候中心,四川 成都 610072
3.中国长江三峡集团有限公司流域枢纽运行管理中心 湖北 宜昌 443133
4.国家气候中心,北京 100081
Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021
CAI Yiheng1,2( ), LI Shuai3(
), LI Shuai3( ), ZHANG Qiang4, DENG Biao1,2, LUO Yu1,2, SUN Rui1,2
), ZHANG Qiang4, DENG Biao1,2, LUO Yu1,2, SUN Rui1,2
- 1. Institute of Plateau Meteorology, CMA/ Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateau and Basin Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
2. Sichuan Provincial Climate Centre, Chengdu 610072, China
3. Operation and Administration Center for River Basin Hydro Complex, China Three Gorges Corporation, Yichang 443133, Hubei, China
4. National Climate Centre, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
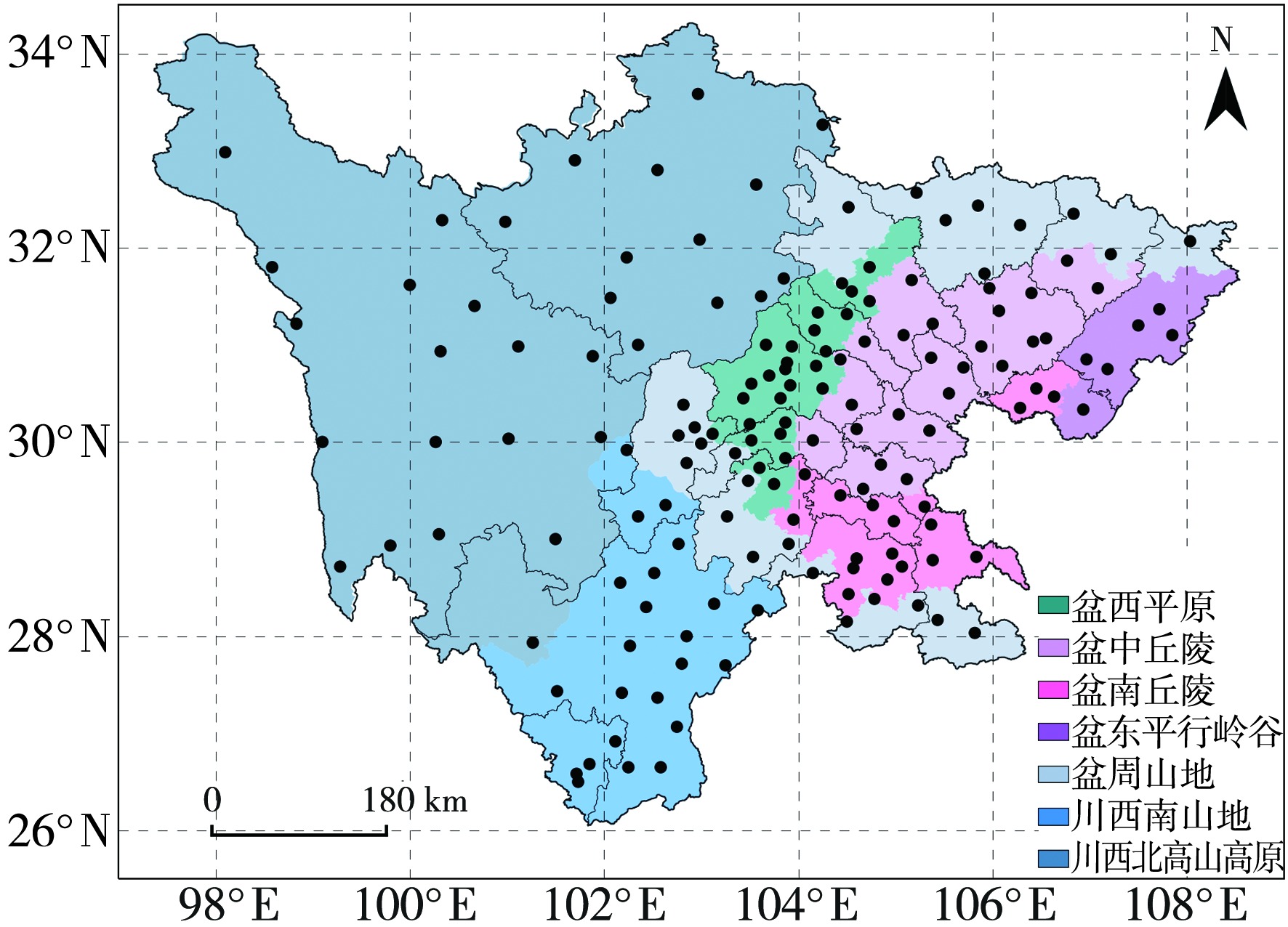
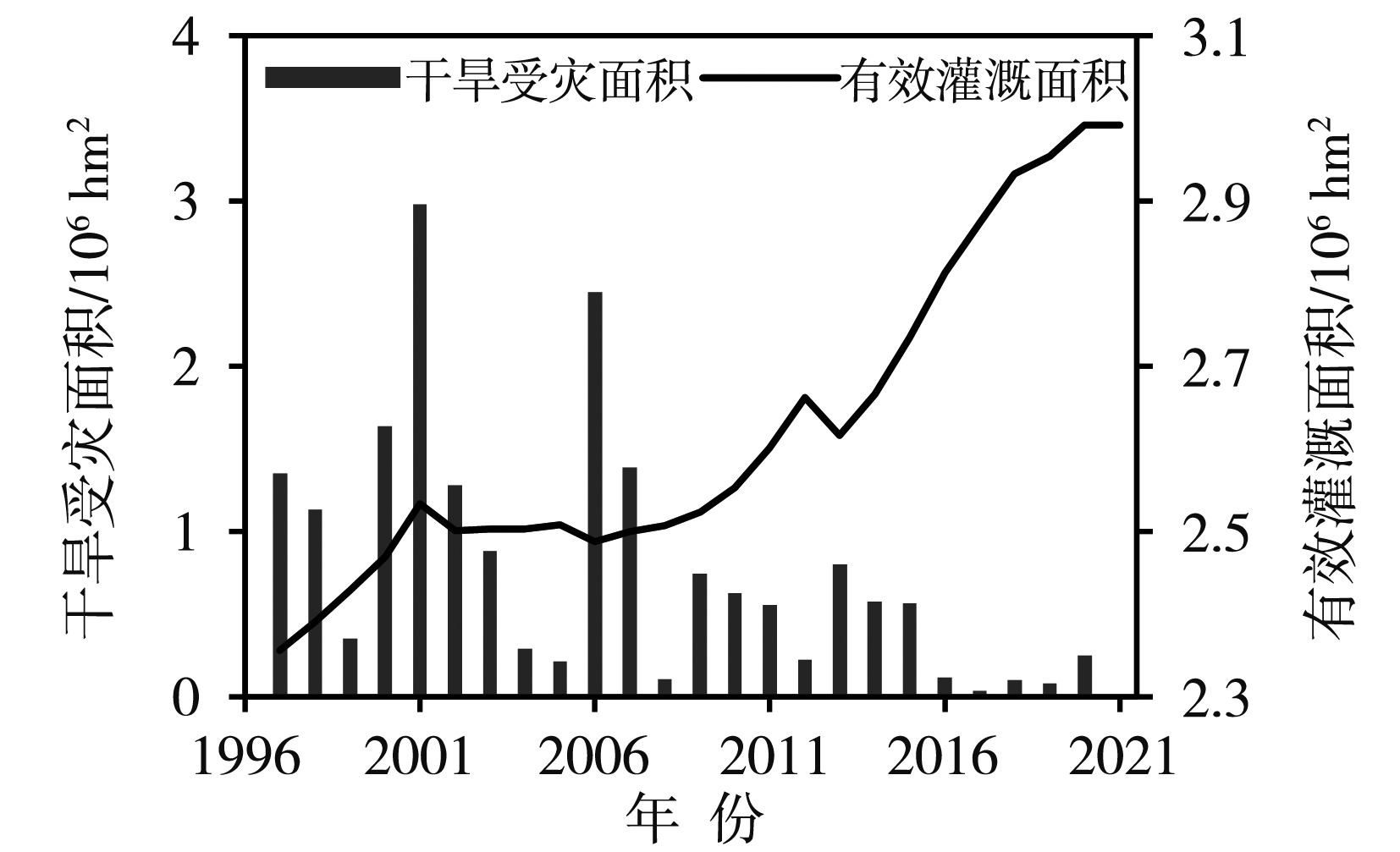
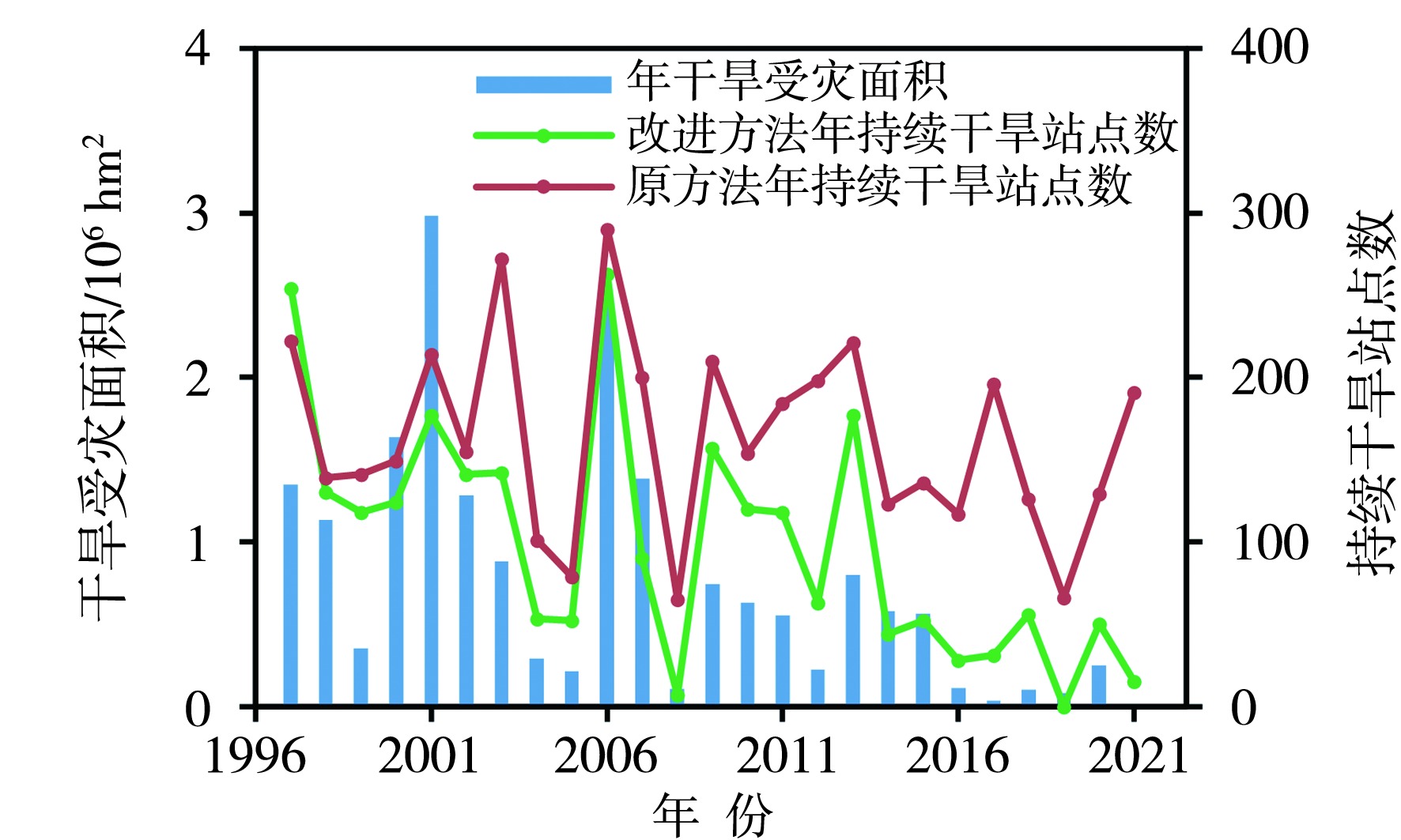
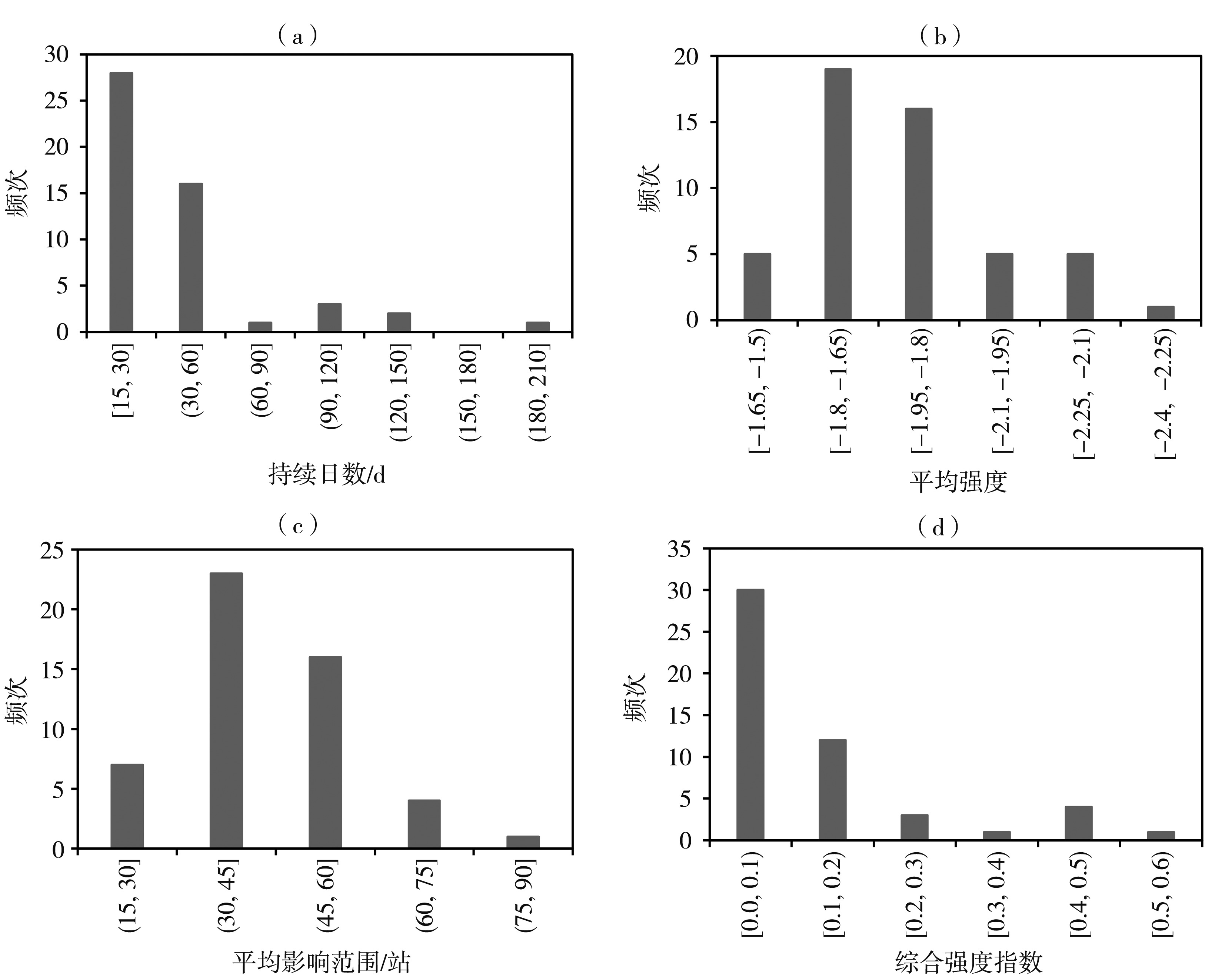
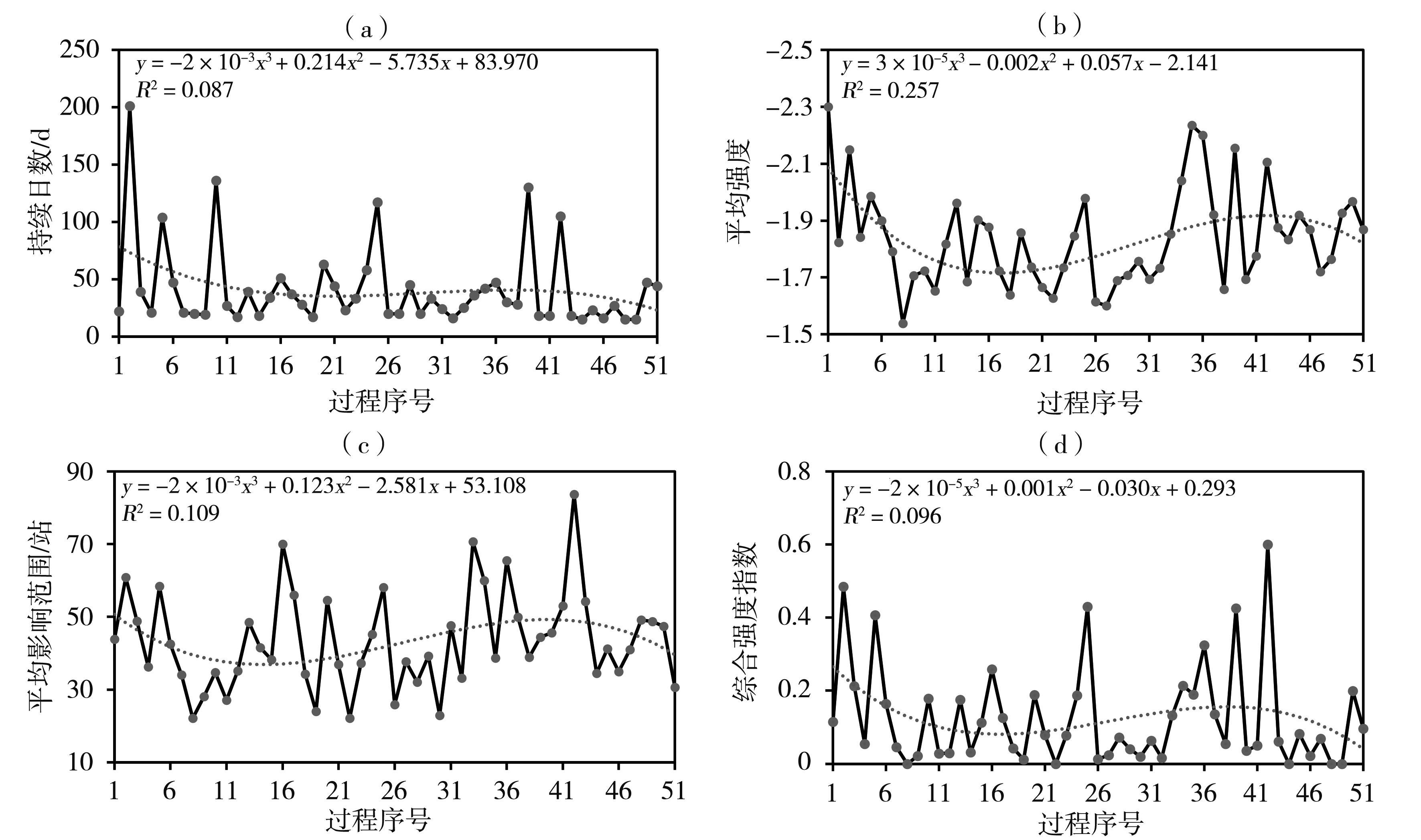
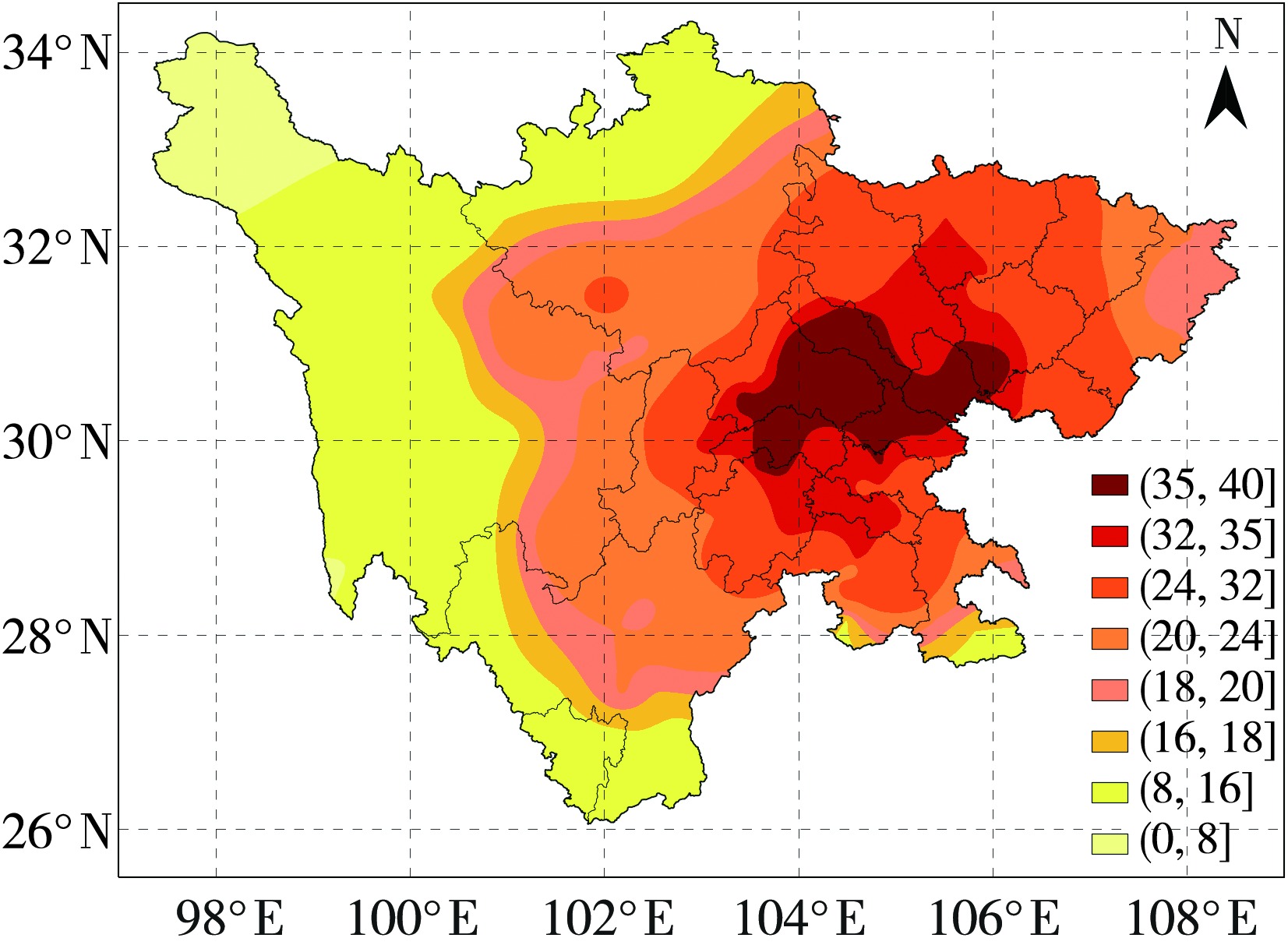
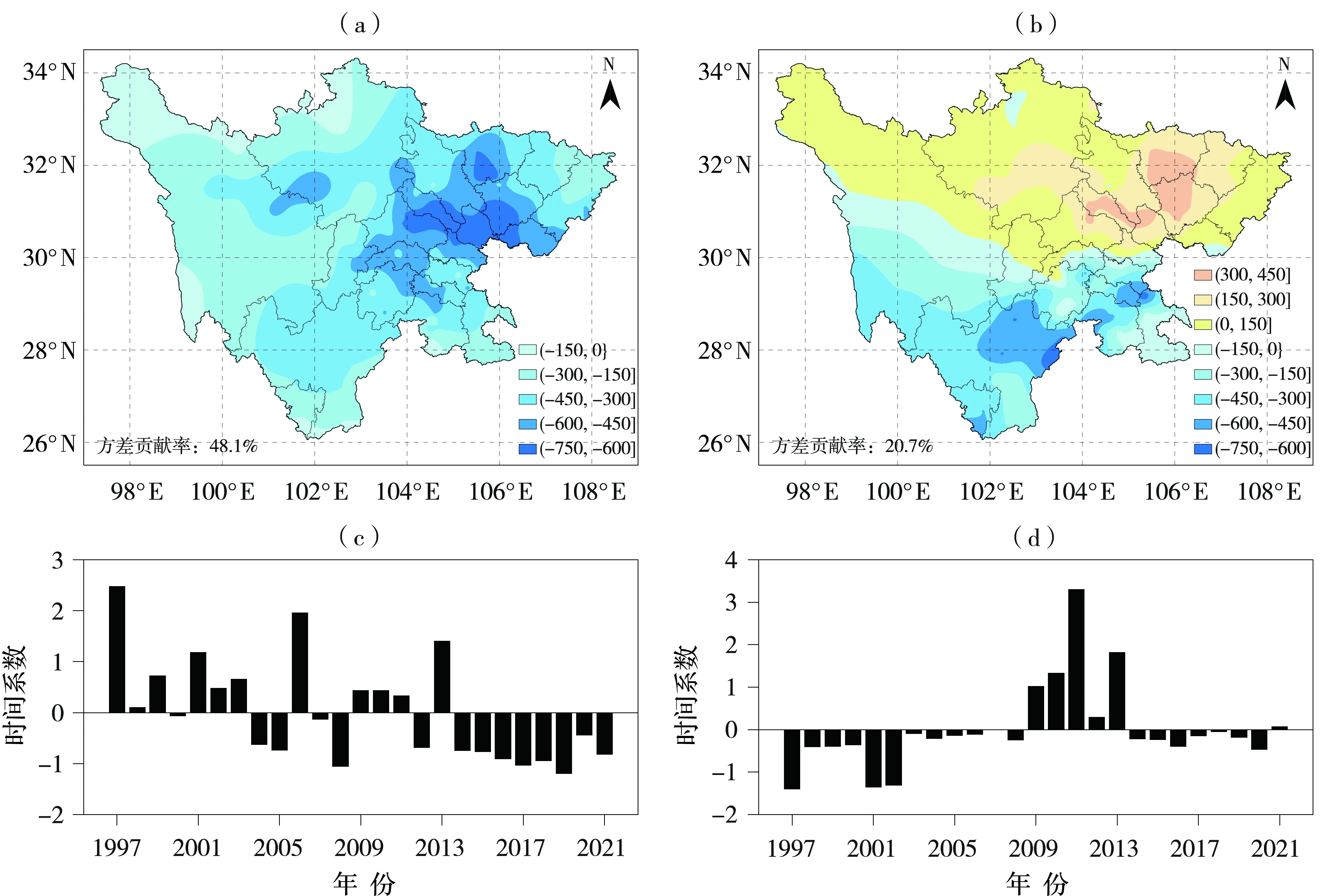
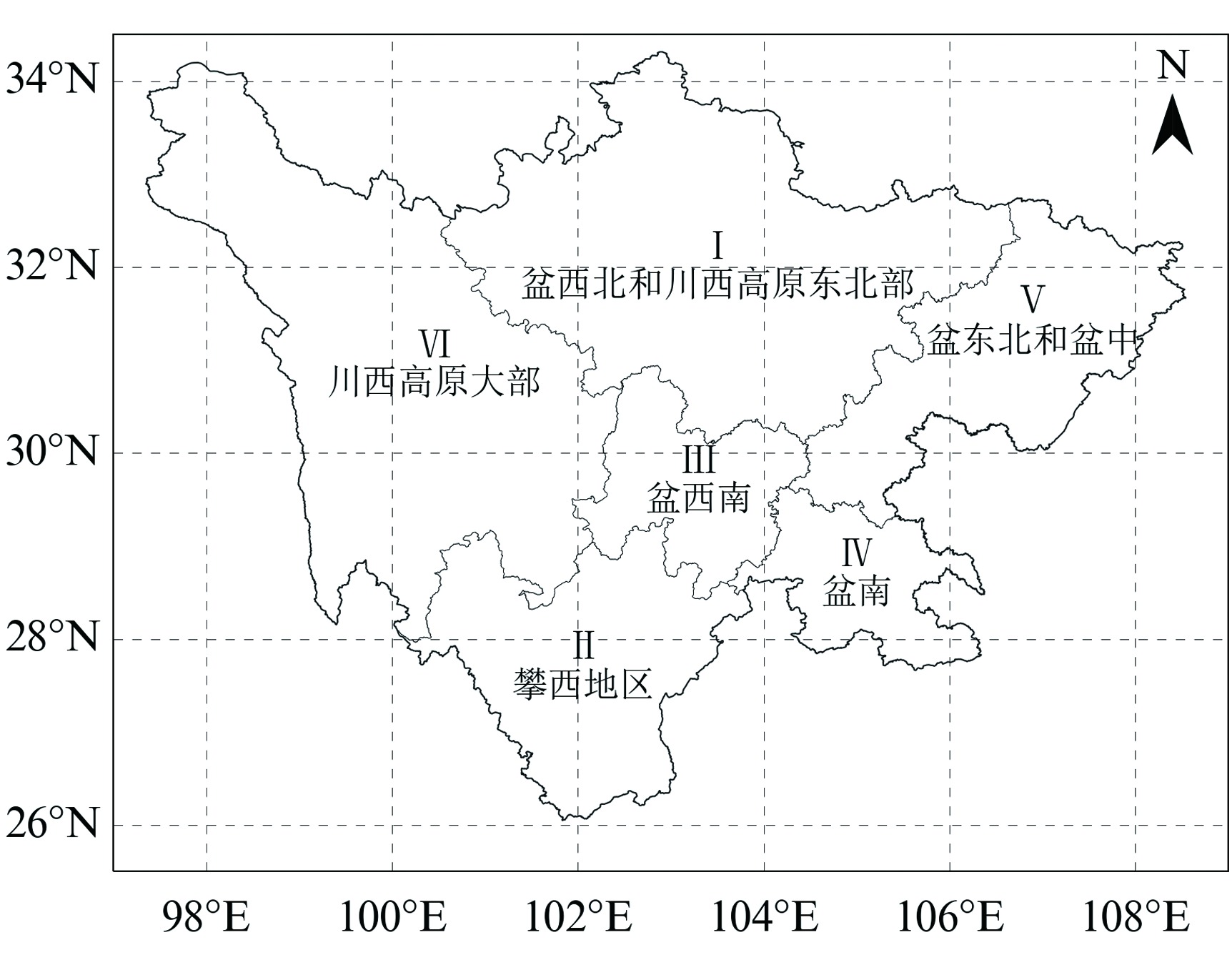
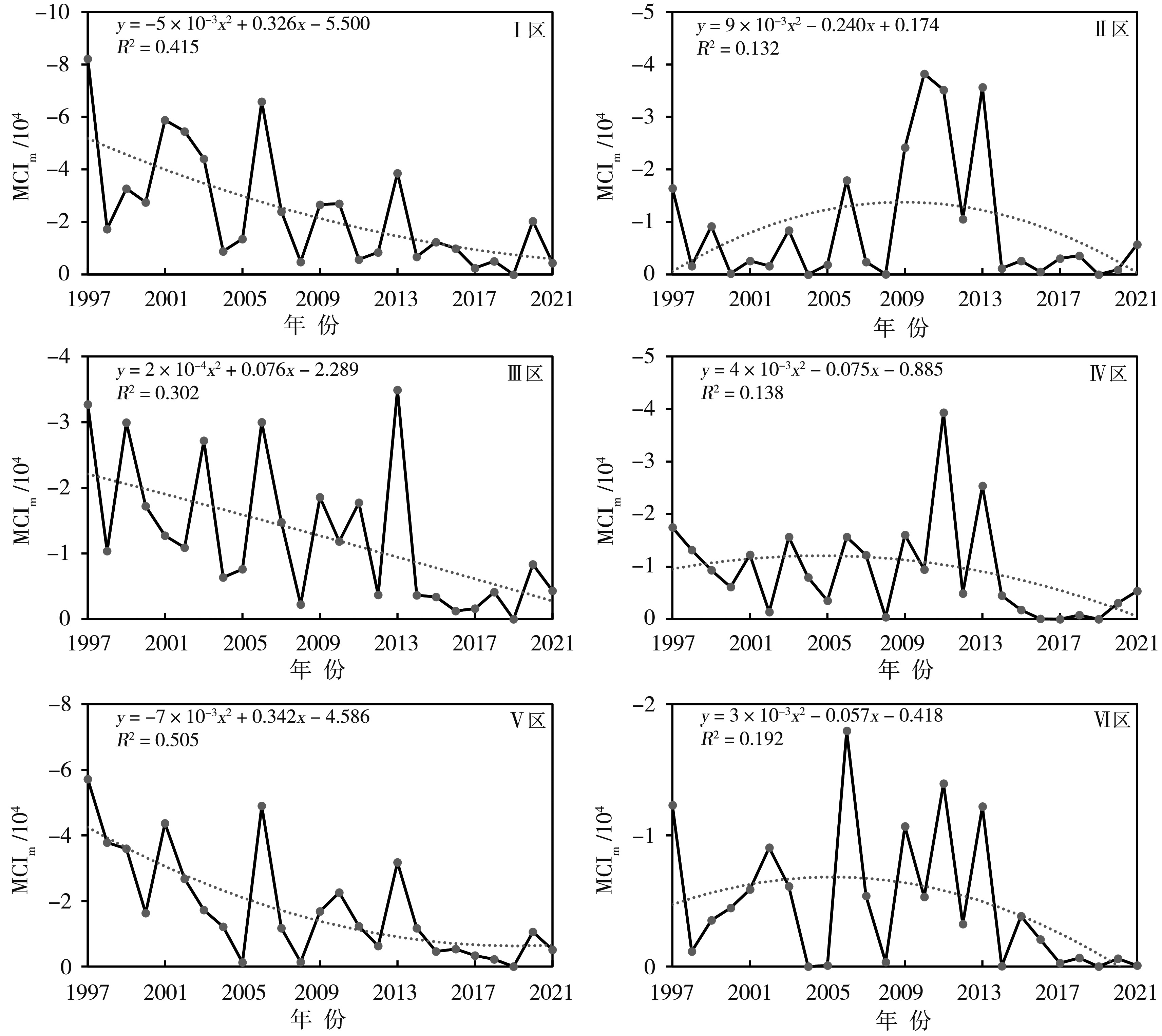
构建适宜的气象干旱指标是开展干旱监测和干旱评价业务服务的基础。基于1997—2021年四川省155个国家气象站逐日平均气温和降水,以及各县(市、区)农作物播种面积资料,通过改进气象干旱综合指数(Meteorological Drought Composite Index, MCI)中的季节调节系数,形成改进的气象干旱综合指数(Modified Meteorological Drought Composite Index, MCIm);再结合历年干旱受灾面积、有效灌溉面积修订区域性干旱过程识别方法,并识别出四川省历年区域性干旱过程51次,然后再利用经验正交函数(Empirical Orthogonal Function,EOF)、旋转经验正交函数(Rotated Empirical Orthogonal Function)、Morlet小波分析法,分析区域性干旱过程时空分布特征。结果表明:1997—2021年四川省发生区域性干旱过程的持续日数呈现出“先变短再增长再变短”,平均影响范围呈现出“先减小再增大再减小”,平均强度和综合强度呈现出“先减弱再增强再减弱”的变化趋势。平均年干旱过程累积日数总体呈现盆地多于盆周山区、盆周山区多于川西高原和攀西地区的特征。年累积MCIm距平EOF分解空间型存在全区一致特征,同时也存在南北反位相特征。四川省可划分为6个区域性干旱气候区,2009—2015年各区年累积MCIm周期变化比2001—2008年更明显。改进后的区域性干旱过程识别方法识别出的干旱过程与干旱灾情更为吻合,更能准确反映四川省干旱发生的实际状况。
中图分类号: