干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 981-992.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-0981
有无台风影响下陕西西北涡暴雨特征对比分析
彭力1,2,4( ), 赵强3,4, 乔丹杨4,5, 张雄1,2, 徐浩天1,2, 倪闻1,2
), 赵强3,4, 乔丹杨4,5, 张雄1,2, 徐浩天1,2, 倪闻1,2
- 1.陕西省铜川市气象局,陕西 铜川 727031
2.陕西省铜川市中草药气象服务研究中心,陕西 铜川 727031
3.陕西省气象台,陕西 西安 710014
4.秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室,陕西 西安 710016
5.陕西省咸阳市气象局,陕西 咸阳 712000
-
收稿日期:2022-05-05修回日期:2022-06-14出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2023-01-10 -
作者简介:彭力(1990—),男,陕西商洛人,工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报技术研究工作. E-mail:sxpeng3677@qq.com。 -
基金资助:陕西省重点研发计划(2021NY-183);秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室开放研究基金课题(2019M-1);秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室开放研究基金课题(2020Y-7)
Comparative analysis on characteristics of rainstorms caused by northwest vortex in Shaanxi with and without influence of typhoon
PENG Li1,2,4( ), ZHAO Qiang3,4, QIAO Danyang4,5, ZHANG Xiong1,2, XU Haotian1,2, NI Wen1,2
), ZHAO Qiang3,4, QIAO Danyang4,5, ZHANG Xiong1,2, XU Haotian1,2, NI Wen1,2
- 1. Tongchuan Meteorological Bureau of Shaanxi Province, Tongchuan 727031, Shaanxi, China
2. Tongchuan Chinese Herbal Medicine Meteorological Service Research Center, Tongchuan 727031, Shaanxi, China
3. Shaanxi Meteorological Observatory, Xi’an 710014, China
4. Key Laboratory of Eco-Environment Meteorology for the Qinling Mountains and Loess Plateau, Xi’an 710016, China
5. Xianyang Meteorological Bureau of Shaanxi Province, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi, China
-
Received:2022-05-05Revised:2022-06-14Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-10
摘要:
基于2010—2020年地面日降水量资料、高空观测资料以及ERA5(0.25°×0.25°)逐小时再分析资料,对影响陕西的西北涡暴雨天气过程进行统计,并对有无台风影响下西北涡暴雨天气特征进行对比分析。结果表明:陕西西北涡暴雨多发生在7—8月,陕北为暴雨多发区,西北涡暴雨夜雨特征明显;有台风影响时暴雨强度更强,落区比无台风影响时偏北2个纬度。造成陕西暴雨的西北涡位于西太平洋副热带高压脊线北侧7~8个纬度处,西北涡具有低层辐合、高层辐散的动力特征,地形强迫抬升加强了西北涡上升运动,低层水汽输送和水汽辐合为西北涡暴雨发生提供了有利条件。台风影响时,副热带高压偏西偏北,台风外围水汽、能量随着西南低空急流向西北涡输送,西北涡低层呈对流不稳定,高空槽前正涡度平流及高空急流右侧强辐散促使西北涡发展加强,低涡东侧和南侧强上升运动触发不稳定能量释放,在陕北形成强锋区,锋生进一步增强了低涡东侧与南侧垂直运动,造成该区域大暴雨;无台风影响时,副热带高压偏东偏南,西南风风速较小,水汽输送较弱,高原槽前西南风将孟加拉湾和南海水汽向陕西输送,西北涡低层大气层结稳定,低涡中心南部为强上升运动区,冷暖空气在陕西中南部交汇,产生分散的弱锋区,造成低涡中心南部暴雨天气。
中图分类号:
引用本文
彭力, 赵强, 乔丹杨, 张雄, 徐浩天, 倪闻. 有无台风影响下陕西西北涡暴雨特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 981-992.
PENG Li, ZHAO Qiang, QIAO Danyang, ZHANG Xiong, XU Haotian, NI Wen. Comparative analysis on characteristics of rainstorms caused by northwest vortex in Shaanxi with and without influence of typhoon[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 981-992.
| 暴雨日期 | 暴雨落区 | 暴雨 站数/个 | 最大日 降水量/mm | 影响系统 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有台风影响 | 2010年7月22—23日 | 关中、陕南 | 20 | 214.6 | 台风‘灿都’,500 hPa低涡,700 hPa西南风急流 |
| 2012年7月20—21日 | 陕北、陕南 | 7 | 125.2 | 南海热带低压,500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2012年8月17—18日 | 关中 | 6 | 100.5 | 台风‘启德’,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月21—22日 | 关中、陕南 | 28 | 149.8 | 南海热带低压,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月24—25日 | 陕北 | 6 | 140.5 | 南海热带低压,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2016年7月7—8日 | 陕北 | 5 | 106.6 | 台风‘尼伯特’,500 hPa低涡,700 hPa西南风急流 | |
| 2017年8月21—22日 | 陕北 | 10 | 105.4 | 台风‘天鸽’,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2019年8月2—3日 | 陕北、陕南 | 13 | 115.5 | 台风‘韦帕’,500 hPa低涡、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流 | |
| 2020年8月4—5日 | 陕北 | 12 | 182.1 | 台风 ‘黑格比’,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 无台风影响 | 2010年8月12—13日 | 关中 | 11 | 104.3 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 |
| 2010年8月17—18日 | 陕北 | 4 | 83.8 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2010年8月20—21日 | 陕北、陕南 | 15 | 146.1 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月3—4日 | 陕北 | 5 | 81.6 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月7—8日 | 陕北、陕南 | 5 | 116.4 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月11—12日 | 陕北 | 8 | 152.0 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2014年7月8—9日 | 陕北 | 13 | 98.5 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2014年8月5—6日 | 陕北、关中 | 12 | 152.4 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2014年9月10—11日 | 陕北、陕南 | 11 | 93.1 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2016年7月18—19日 | 陕北、陕南、关中 | 15 | 118.9 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2017年10月8—9日 | 陕北 | 5 | 59.8 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2019年7月21—22日 | 陕北、陕南 | 12 | 100.3 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 |
表1 2010—2020年陕西西北涡暴雨过程统计
Tab.1 Statistics of rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020
| 暴雨日期 | 暴雨落区 | 暴雨 站数/个 | 最大日 降水量/mm | 影响系统 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有台风影响 | 2010年7月22—23日 | 关中、陕南 | 20 | 214.6 | 台风‘灿都’,500 hPa低涡,700 hPa西南风急流 |
| 2012年7月20—21日 | 陕北、陕南 | 7 | 125.2 | 南海热带低压,500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2012年8月17—18日 | 关中 | 6 | 100.5 | 台风‘启德’,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月21—22日 | 关中、陕南 | 28 | 149.8 | 南海热带低压,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月24—25日 | 陕北 | 6 | 140.5 | 南海热带低压,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2016年7月7—8日 | 陕北 | 5 | 106.6 | 台风‘尼伯特’,500 hPa低涡,700 hPa西南风急流 | |
| 2017年8月21—22日 | 陕北 | 10 | 105.4 | 台风‘天鸽’,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2019年8月2—3日 | 陕北、陕南 | 13 | 115.5 | 台风‘韦帕’,500 hPa低涡、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流 | |
| 2020年8月4—5日 | 陕北 | 12 | 182.1 | 台风 ‘黑格比’,500 hPa西风槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 无台风影响 | 2010年8月12—13日 | 关中 | 11 | 104.3 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 |
| 2010年8月17—18日 | 陕北 | 4 | 83.8 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2010年8月20—21日 | 陕北、陕南 | 15 | 146.1 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月3—4日 | 陕北 | 5 | 81.6 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月7—8日 | 陕北、陕南 | 5 | 116.4 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2013年7月11—12日 | 陕北 | 8 | 152.0 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2014年7月8—9日 | 陕北 | 13 | 98.5 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2014年8月5—6日 | 陕北、关中 | 12 | 152.4 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa偏南风气流,高空急流 | |
| 2014年9月10—11日 | 陕北、陕南 | 11 | 93.1 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2016年7月18—19日 | 陕北、陕南、关中 | 15 | 118.9 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2017年10月8—9日 | 陕北 | 5 | 59.8 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 | |
| 2019年7月21—22日 | 陕北、陕南 | 12 | 100.3 | 500 hPa西风槽、高原槽,700 hPa西南风急流,高空急流 |
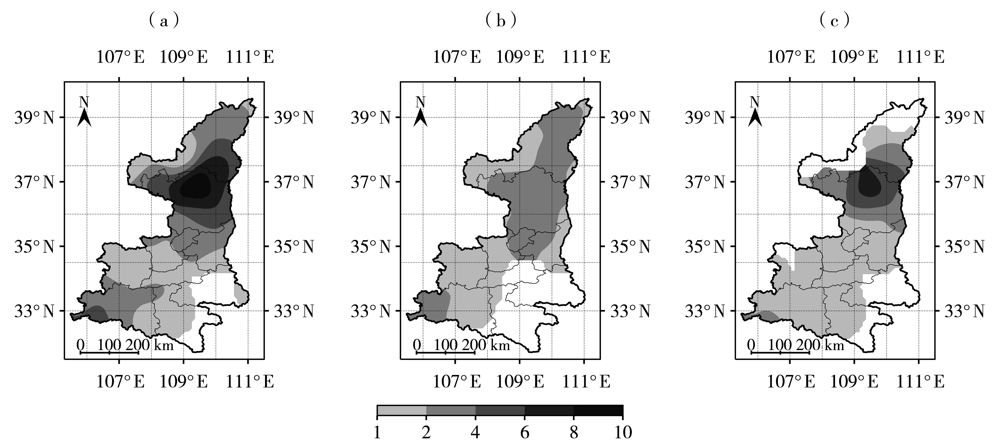
图1 2010—2020年陕西西北涡暴雨日数(a)及有(b)、无(c)台风影响时西北涡暴雨日数空间分布(单位:d)
Fig.1 The spatial distribution of rainstorm days caused by northwest vortex (a) and rainstorm days accompanying with (b) and without (c) typhoon in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020 (Unit: d)
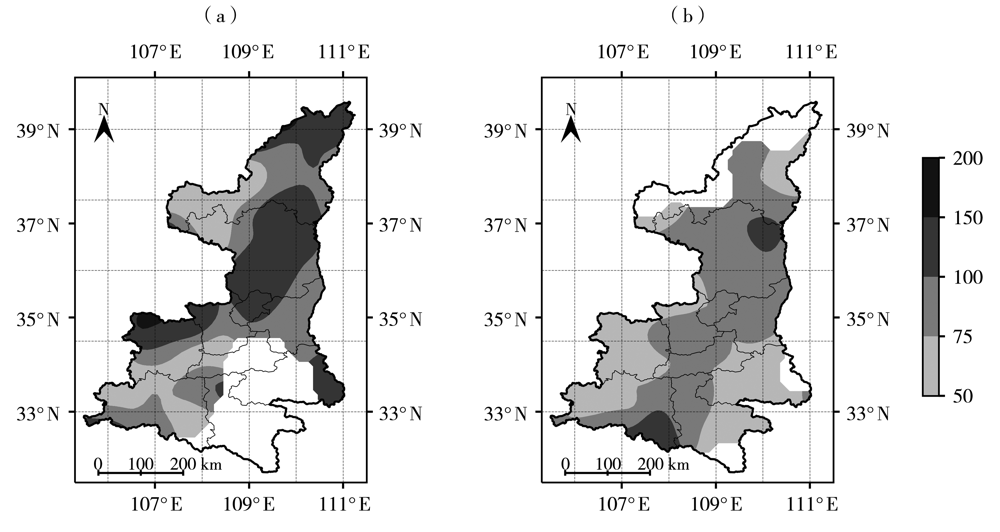
图2 2010—2020年有(a)、无(b)台风影响时陕西西北涡暴雨日最大降水量空间分布(单位:mm)
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of daily maximum precipitation during rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex accompanying with (a) and without (b) typhoon in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020 (Unit: mm)
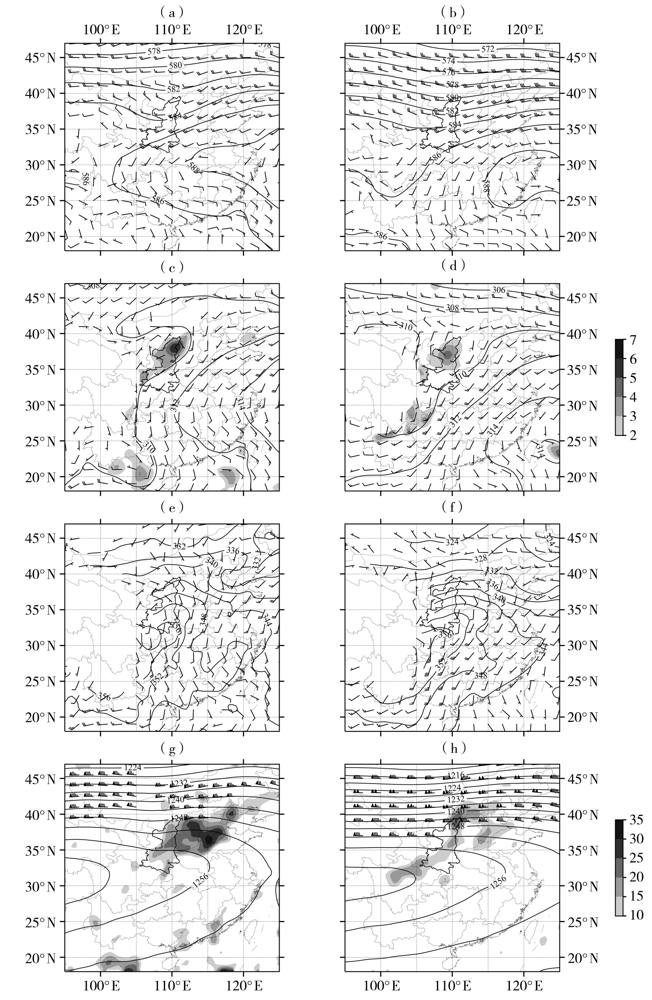
图3 2010—2020年有(a、c、e、g)、无(b、d、f、h)台风影响时陕西西北涡暴雨500 hPa高度场(实等值线,单位:dagpm)、风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(a、b),700 hPa高度场(实等值线,单位:dagpm)、风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)和涡度(阴影,单位:10-5 s-1)(c、d),800 hPa假相当位温(实等值线,单位:K)、风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(e、f),200 hPa高度场(实等值线,单位:dagpm)、风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)和散度(阴影,单位:10-6 s-1)(g、h)
Fig.3 The 500 hPa height field (solid contours, Unit: dagpm) and wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (a, b), 700 hPa height field (solid contours, Unit: dagpm), wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and vorticity (the shaded, Unit: 10-5 s-1) (c, d), 800 hPa pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (solid isolines, Unit: K) and wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (e, f), 200 hPa height field (solid contours, Unit: dagpm), wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and divergence (the shaded, Unit: 10-6 s-1) (g, h) during rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex with (a, c, e, g) and without(b, d, f, h) typhoon influence in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020

图4 2010—2020年陕西西北涡暴雨有(a、b)、无(c、d)台风影响时700 hPa(a、c)、800 hPa(b、d)水汽通量(矢量,单位:g·hPa-1·cm-1·s-1)与水汽通量散度(阴影,单位: 10-8 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1)分布
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of water vapor flux (vectors, Unit: g·hPa-1·cm-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence (the shaded, Unit:10-8 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1) at 700 hPa (a, c) and 800 hPa (b, d) during rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex with (a, b) and without (c, d) typhoon influence in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020
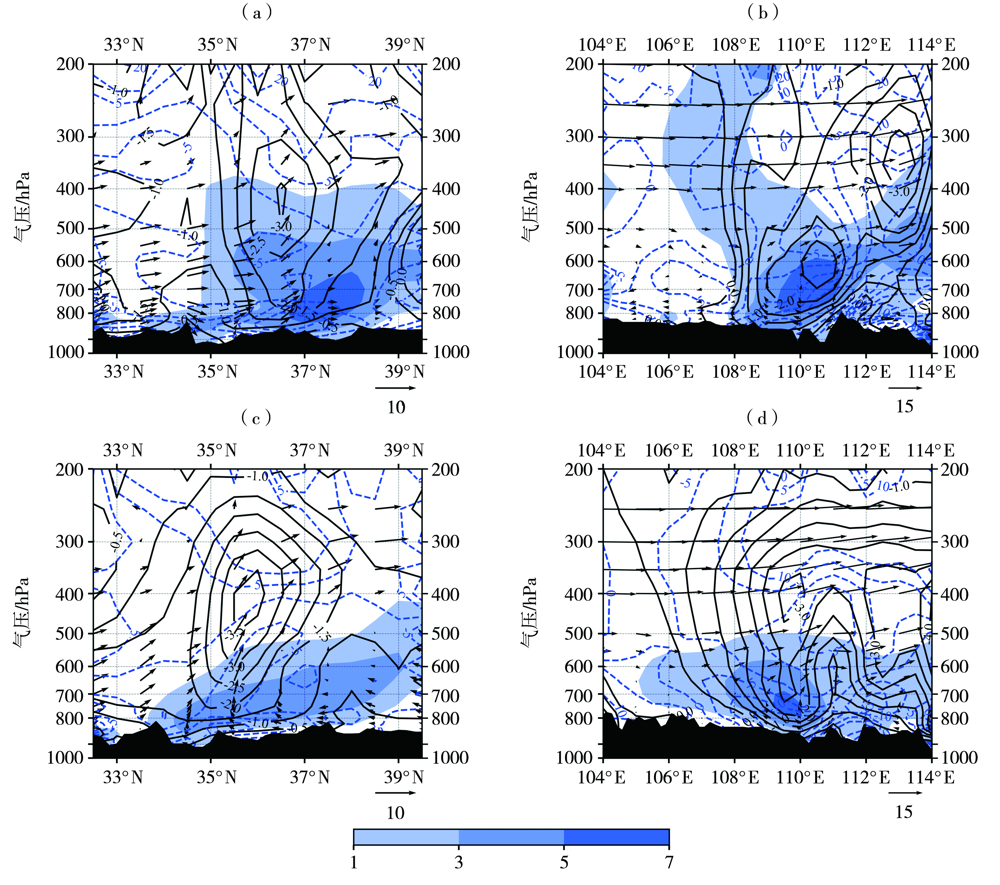
图5 2010—2020年陕西西北涡暴雨过程有(a、b)、无(c、d)台风影响时涡度(填色区,单位:10-5 s-1)、散度(蓝色虚线,单位:10-6 s-1)、垂直速度(黑色实线,单位:10-1 Pa·s-1)、流场(矢量,经向:v,ω×10,纬向:u,ω×10,单位:m·s-1)沿110°E(a)与109°E(c)的纬度-高度剖面,及沿38°N(b)与37°N(d)的经度-高度剖面 (黑色阴影为地形,下同)
Fig.5 The latitude-height profiles along 110°E (a) and 109°E (c) and longitude-height profiles along 38°N (b) and 37°N (d) of vorticity (the color shaded, Unit: 10-5 s-1), divergence (blue dashed lines, Unit: 10-6 s-1), vertical velocity (black solid lines, Unit: 10-1 Pa·s-1) and stream field (vectors, longitude: v,ω×10, latitude: u, ω×10, Unit: m·s-1) during rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex with (a, b) and without (c, d) typhoon influence in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020 (The black shaded is terrain. the same as below)
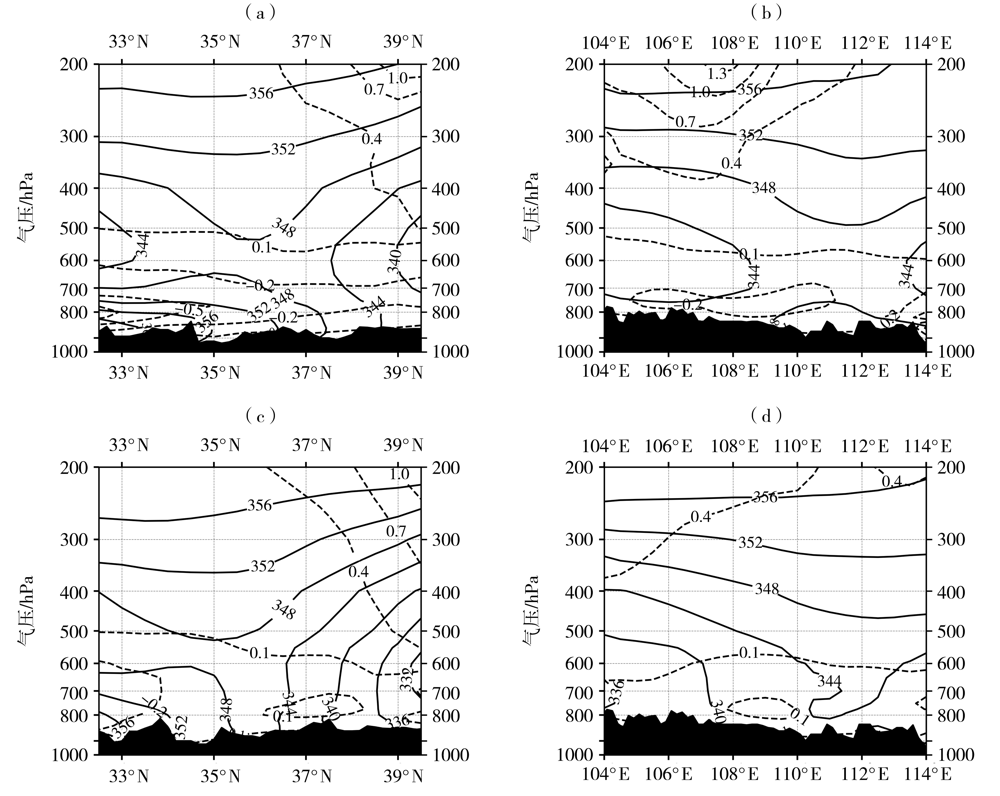
图6 2010—2020年陕西西北涡暴雨有(a、b)和无(c、d)台风影响时 θ s e(实线,单位:K)与湿位涡(MPV1)(虚线,单位: 10-6 m2·s-1·K·kg-1)沿110°E(a)及109°E(c)的纬度-高度剖面和沿38°N(b)及37°N(d)的经度-高度剖面
Fig.6 The latitude-height profiles along 110°E (a) and 109°E (c) and longitude-height profiles along 38°N (b) and 37°N (d) of pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (solid lines, Unit: K) and moist potential vorticity (MPV1) (dashed lines, Unit:10-6 m2·s-1·K·kg-1) during rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex with (a, b) and without (c, d) typhoon influence in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020
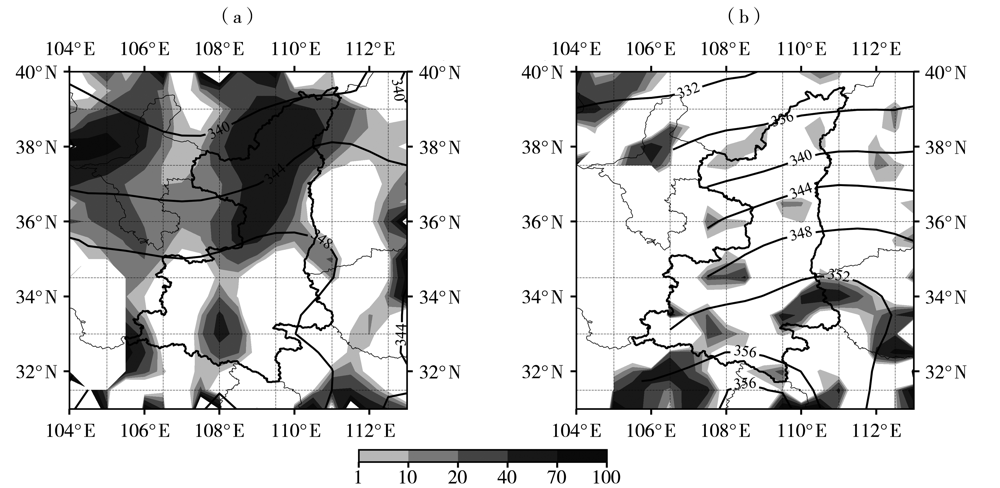
图7 2010—2020年陕西西北涡暴雨过程有台风影响时700 hPa(a)及无台风影响时800 hPa(b) θ s e(实线,单位:K)和锋生函数(阴影,单位:10-9 K·m-1·s-1)分布
Fig.7 Spatial distribution of pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (solid lines, Unit: K) and frontgenesis function (the shaded, Unit: 10-9 K·m-1·s-1) at 700 hPa under the influence of typhoon (a) and 800 hPa without influence of typhoon (b) during rainstorm processes caused by northwest vortex in Shaanxi from 2010 to 2020

图8 有台风影响(a)与无台风影响(b)时陕西西北涡暴雨环流配置
Fig.8 The circulation situation configuration for rainstorms caused by northwest vortex with (a) and without (b) typhoon influence in Shaanxi
| [1] | 刘晓冉, 李国平. 青藏高原低涡研究的回顾与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 2006, 24(1): 60-66. |
| [2] | 李江萍, 王式功, 孙国武. 高原低涡研究的回顾与展望[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(4): 53-60. |
| [3] |
LI L, ZHANG R H, WEN M. Diagnostic analysis of the evolution mechanism for a vortex over the Tibetan Plateau in June 2008[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 28(4): 797-808.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI L, ZHANG R H, WEN M. Diurnal variation in the occurrence frequency of the Tibetan Plateau vortices[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 2014, 125(3/4):135-144.
DOI URL |
| [5] | SUGIMOTO S, UENO K. Formation of mesoscale convective systems over the eastern Tibetan Plateau affected by plateau-scale heating contrasts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(D16):1-15. |
| [6] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007: 343-345. |
| [7] | 王丛梅, 丁治英. 河北夏季低涡暴雨的统计研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2006, 15(5): 69-75. |
| [8] | 李江萍, 沙宏娥, 郭勇涛, 等. 1980—2010年西北涡发生频数的时空分布特征[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(6): 733-737. |
| [9] | 荣涛. 柴达木低涡特征及其预报[J]. 干旱气象, 2004, 22(3): 26-31. |
| [10] | 丁治英, 吕君宁. 一次西北涡生成移动过程的数值试验[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 1993, 16(2): 226-232. |
| [11] | 陆倩, 付娇, 胡赛安. 承德市一次西北涡暴雨成因分析[J]. 内蒙古气象, 2016(2): 23-26. |
| [12] | 彭力, 徐浩天, 刘嘉慧敏, 等. 西北涡作用下陕西一次强降水过程成因分析[J]. 陕西气象, 2020(5): 1-5. |
| [13] |
WANG B, ORANSKI I. Study of a heavy rain vortex formed over the eastern flank of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1987, 115: 1370-1393.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG B. The development mechanism for Tibetan Plateau warm vortices[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1987, 44: 2978-2994.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 缪强, 刘波, 袁立新. 青藏高原天气系统与背风坡浅薄天气系统耦合相互作用的特征分析[J]. 四川气象, 1999, 19(3): 18-22. |
| [16] | 周丽峰, 李韬. 2007年夏季河套地区两次区域性大暴雨过程模拟分析[J]. 科技导报, 2008, 26(24): 43-50. |
| [17] | 李江萍, 李文弘, 郭勇涛, 等. 西北涡东移的大尺度环流特征分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(5): 629-634. |
| [18] | 王丛梅, 丁治英, 张金艳, 等. 西北涡暴雨的湿位涡诊断分析[J]. 气象, 2005, 31(11): 28-33. |
| [19] | 马晓华, 马青, 屈丽玮, 等. 低涡影响下的西北地区东部暴雨个例分析[J]. 陕西气象, 2021(4): 1-8. |
| [20] | 侯书勋, 张婉莹, 陈震, 等. 一次东移西北涡暴雨过程的诊断分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2018, 34(5): 9-15. |
| [21] | 李明, 高维英, 王兴慧. 西北涡和登陆台风共同影响的一次暴雨过程分析[J]. 陕西气象, 2016(5): 1-6. |
| [22] | 武麦凤, 曹玲玲, 马耀荣, 等. 西北涡与登陆台风相互作用个例的诊断分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2015, 34(4): 309-315. |
| [23] | 杜继稳, 侯明全, 梁生俊, 等. 陕西省短期天气预报技术手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007: 37-38. |
| [24] | 侯建忠, 王川, 鲁渊平, 等. 台风活动与陕西极端暴雨的相关特征分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2006, 22(2): 203-208. |
| [25] | 武麦凤, 王旭仙, 王桂梅, 等. 陕西中部一次远距离台风暴雨过程成因分析[J]. 气象科技, 2013, 41(1): 138-145. |
| [26] | 郭大梅, 刘瑞芳, 侯建忠, 等. 陕西一次远距离台风持续性暴雨的成因分析[J]. 气象科学, 2012, 32(3): 325-331. |
| [27] |
张雅斌, 武麦凤, 侯建忠, 等. 陕西4次台风远距离暴雨过程的水汽条件对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(5): 788-797.
DOI |
| [28] | 赵强, 王楠, 李萍云, 等. 两次陕北暴雨过程热力动力机制诊断[J]. 应用气象学报, 2017, 28(3): 340-356. |
| [29] | 王宏, 马凤莲, 王万筠, 等. 湿位涡分析在河北东北部暴雨预报中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2008, 26(4): 86-90. |
| [30] | SHOU S W, LI Y H. Study on moist potential vorticity and symmetric instability during a heavy rain event occurred in the Jiang-Huai Valleys[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 1999, 16(2): 312-321. |
| [31] | LI Y H, SHOU S W, FAN K. Isentropic potential vorticity analysis on the mesoscale cyclone development in a torrential rain process[J]. Acta Meteorological Scinica, 2002, 16(4): 75-85. |
| [1] | 王一丞, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 张文光.
卫星降水产品在陇东 2022年 7月特大暴雨事件中的适用性评估
[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 997-1007. |
| [2] | 吴古会, 彭芳, 齐大鹏, 杜小玲, 杨秀庄. 贵州一次辐合线锋生极端暴雨过程的中尺度特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 753-763. |
| [3] | 马志敏, 王将, 连钰, 张万诚, 牛法宝, 杨素雨. 云南一次强对流暴雨天气学成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 629-638. |
| [4] | 王佳津, 肖红茹, 杨康权, 王彬雁. 四川盆地一次持续性暴雨的水汽输送特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 474-482. |
| [5] | 邢蕊, 杨健博, 田梦, 邱晓滨, 庄庭, 朱晓晶. 不同边界层参数化方案对台风“烟花”北上阶段暴雨模拟的影响试验[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 91-102. |
| [6] | 傅朝, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 徐丽丽, 沙宏娥, 马莉, 崔宇. 西北干旱区一次极端暴雨局地性增强的对流环境特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 909-921. |
| [7] | 张君霞, 黄武斌, 杨秀梅, 刘维成, 周子涵, 沙宏娥. 陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 922-932. |
| [8] | 沙宏娥, 傅朝, 刘维成, 徐丽丽, 刘娜, 刘新雨, 马绎皓. 西北东部半干旱区一次极端特大暴雨的触发和维持机制[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 933-944. |
| [9] | 陈小婷, 赵强, 刘慧, 彭力. 黄土高原两次不同类型暴雨水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [10] | 于慧珍, 马艳, 韩旭卿, 时晓曚. 台风“摩羯”路径转折预报和诊断分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1014-1023. |
| [11] | 焦洋, 张永婧, 尹承美, 褚颖佳. 山东夏季暴雨对青藏高原东南部及邻近区域春季大气热源变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [12] | 郑林晔, 谌芸, 冯恬, 姚梦颖. 登陆华东台风降水分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 424-435. |
| [13] | 马思敏, 穆建华, 舒志亮, 孙艳桥, 邓佩云, 周楠. 六盘山区一次典型暴雨过程的地形敏感性模拟试验[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 457-468. |
| [14] | 张桂莲, 刘澜波, 孟雪峰, 张璐, 李林惠. 冷垫背景下回流暴雪成因与雷达回波特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 500-506. |
| [15] | 杨霞, 许婷婷, 张林梅, 华烨, 周鸿奎. 不同气候背景下南疆暖季暴雨特征和差异[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 222-233. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
