Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 103-113.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0103
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Contrast analysis of dual-polarization signatures for the two extreme rainfall storms
GUO Feiyan1( ), DIAO Xiuguang2(
), DIAO Xiuguang2( ), CHU Yingjia3, LI Xin1, LU Xue1, ZHANG Shaobo1
), CHU Yingjia3, LI Xin1, LU Xue1, ZHANG Shaobo1
- 1. Qingdao Engineering Technology Research Center for Meteorological Disaster Prevention/Qingdao Meteorology Bureau, Qingdao 266003, China
2. Shandong Meteorological Observatory, Ji'nan 250031, China
3. Ji'nan Meteorology Bureau of Shandong, Ji'nan 250102, China
-
Received:2021-11-05Revised:2021-12-12Online:2023-02-28Published:2023-02-28
两次极端强降水风暴双偏振参量特征对比分析
郭飞燕1( ), 刁秀广2(
), 刁秀广2( ), 褚颖佳3, 李欣1, 陆雪1, 张少博1
), 褚颖佳3, 李欣1, 陆雪1, 张少博1
- 1.山东省青岛市气象灾害防御工程技术研究中心/青岛市气象局,山东 青岛 266003
2.山东省气象台,山东 济南 250031
3.山东省济南市气象局,山东 济南 250102
-
通讯作者:刁秀广(1964—),男,正高级工程师,主要从事天气雷达应用研究。E-mail: radardxg@126.com。
-
作者简介:郭飞燕(1986—),女,高级工程师,博士,主要从事强对流天气预报研究。E-mail: guofeiyan01@163.com。 -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2021QD028);山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2021MD062);山东省气象局科研项目(2019sdqxz01);山东省气象局科研项目(SDYBY2017-05);山东省气象局科研项目(SDYBY2020-04);山东省精准预报技术创新团队共同资助
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GUO Feiyan, DIAO Xiuguang, CHU Yingjia, LI Xin, LU Xue, ZHANG Shaobo. Contrast analysis of dual-polarization signatures for the two extreme rainfall storms[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 103-113.
郭飞燕, 刁秀广, 褚颖佳, 李欣, 陆雪, 张少博. 两次极端强降水风暴双偏振参量特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 103-113.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0103
| 北京时 | K(ΔT) /℃ | LI* /(℃) | CAPE*(CIN)/(J·kg-1) | 垂直风切变/(m·s-1) | 比湿/(g·kg-1) | 高度/km | SRH/ (m2·s-2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~6 km | 0~2 km | 700 hPa | 850 hPa | 925 hPa | 0 ℃ | -10 ℃ | -20 ℃ | -30 ℃ | |||||
| 4日20:00 | 40(22) | -3.9 | 2 700(324) | 13 | 3 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 5.2 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 10.2 | 30 |
| 5日08:00 | 35(20) | -3.4 | 1 152(38) | 6 | 2 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 5.3 | 7.2 | 8.9 | 10.2 | 6 |
| 6日08:00 | 39(24) | -5.2 | 2 700(96) | 8 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 16 | 5.3 | 7.2 | 8.8 | 10.3 | 120 |
| 6日20:00 | 35(23) | 0.2 | 126(43) | 13 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 16 | 5.4 | 7.5 | 9.1 | 10.5 | 79 |
Tab.1 The environmental physical parameters calculated by radiosonde data of Zhangqiu of Ji'nan
| 北京时 | K(ΔT) /℃ | LI* /(℃) | CAPE*(CIN)/(J·kg-1) | 垂直风切变/(m·s-1) | 比湿/(g·kg-1) | 高度/km | SRH/ (m2·s-2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~6 km | 0~2 km | 700 hPa | 850 hPa | 925 hPa | 0 ℃ | -10 ℃ | -20 ℃ | -30 ℃ | |||||
| 4日20:00 | 40(22) | -3.9 | 2 700(324) | 13 | 3 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 5.2 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 10.2 | 30 |
| 5日08:00 | 35(20) | -3.4 | 1 152(38) | 6 | 2 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 5.3 | 7.2 | 8.9 | 10.2 | 6 |
| 6日08:00 | 39(24) | -5.2 | 2 700(96) | 8 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 16 | 5.3 | 7.2 | 8.8 | 10.3 | 120 |
| 6日20:00 | 35(23) | 0.2 | 126(43) | 13 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 16 | 5.4 | 7.5 | 9.1 | 10.5 | 79 |

Fig.2 Combined reflectivity (Unit: dBZ) at 05:03 (a) and 07:16 (b), and ZH (c, Unit: dBZ), ZDR (d, Unit: dB), KDP (e, Unit:(°)·km-1), CC (f) at 0.5° elevation from Ji'nan radar at 07:16 on 5 August 2020 (The blue solid, dash and dotted isolines are 45, 50 and 55 dBZ isoline of ZH respecitvely, the green solid isoline is V convergence line. the same as below)

Fig.3 Combined reflectivity (Unit: dBZ) at 18:30 (a) and 19:22 (b), and ZH (c, Unit: dBZ), ZDR (d, Unit: dB), KDP (e, Unit:(°)·km-1), CC(f) at 0. 5° elevation from Ji'nan radar at 19:22 on 6 August 2020
| 站点 | 北京时 | ZH /dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/[(°)·km-1] | CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 均值 | 范围 | 均值 | 范围 | 均值 | 范围 | 均值 | ||
| 王庄集附近 | 8月5日07:16 | 53.0~58.0 | 56.2 | 1.0~1.8 | 1.4 | 2.7~3.6 | 3.1 | 0.96~0.99 | 0.98 |
| 大安站附近 | 8月6日19:22 | 47.0~54.0 | 50.8 | 1.1~2.5 | 1.8 | 2.0~3.5 | 2.9 | 0.96~0.99 | 0.98 |
| 新兖和兴隆庄附近 | 8月6日19:22 | 50.0~56.5 | 53.5 | 1.2~4.5 | 2.9 | 3.1~6.4 | 4.8 | 0.91~0.99 | 0.97 |
Tab.2 The dual-polarization parameters at 0.5 elevation and 20 range bins mean around the representative stations for the two extreme flash heavy rain
| 站点 | 北京时 | ZH /dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/[(°)·km-1] | CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 均值 | 范围 | 均值 | 范围 | 均值 | 范围 | 均值 | ||
| 王庄集附近 | 8月5日07:16 | 53.0~58.0 | 56.2 | 1.0~1.8 | 1.4 | 2.7~3.6 | 3.1 | 0.96~0.99 | 0.98 |
| 大安站附近 | 8月6日19:22 | 47.0~54.0 | 50.8 | 1.1~2.5 | 1.8 | 2.0~3.5 | 2.9 | 0.96~0.99 | 0.98 |
| 新兖和兴隆庄附近 | 8月6日19:22 | 50.0~56.5 | 53.5 | 1.2~4.5 | 2.9 | 3.1~6.4 | 4.8 | 0.91~0.99 | 0.97 |

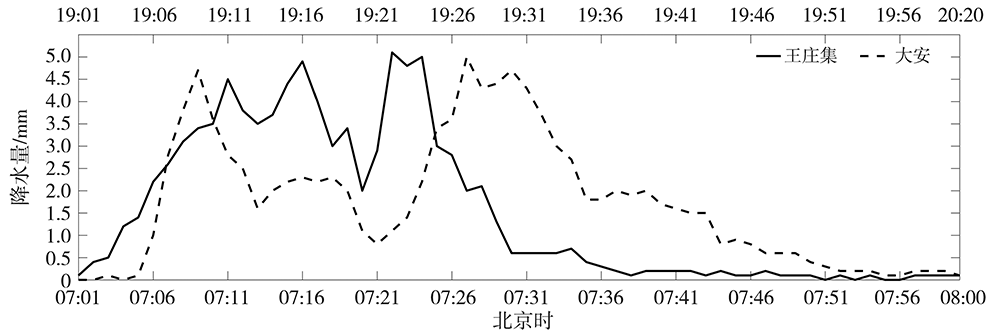
Fig.4 Vertical cross-section(VCS) of ZH (a, Unit: dBZ), ZDR (b, Unit: dB), KDP (c,Unit:(°)·km-1), CC (d),V(e,m·s-1), and VCS of ZH (Unit: dBZ) overlying ZDR, KDP, CC and zero velocity isoline from Ji'nan radar at 07:16 on 5 August 2020 (The blue solid, dash and dotted isolines are 45, 50 and 55 dBZ isoline of ZH respectively; the pink, red and blue isolines are the heights of 0 ℃, -10 ℃ and -20 ℃ layers respectively; the red isoline is 1 dB isoline of ZDR, the yellow isoline is 1.00(°)·km-1 isoline of KDP, the white isoline is 0 m·s-1 isoline of V in Fig.4(f). The same as below)
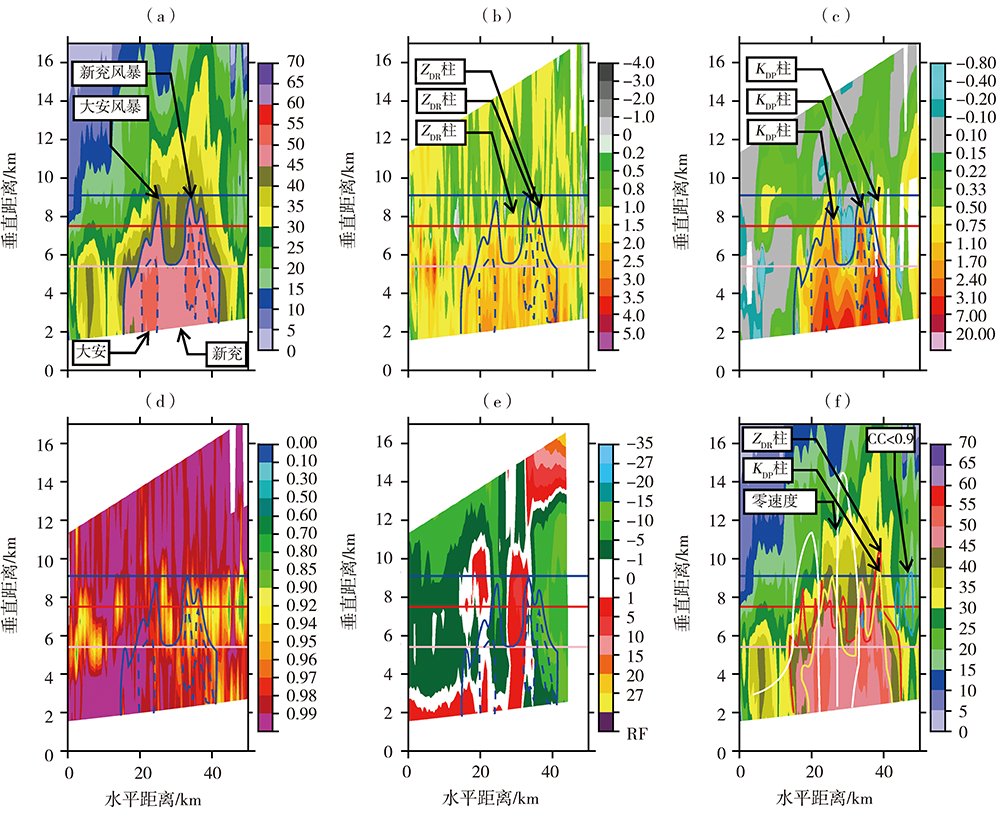
Fig.5 Vertical cross-section(VCS) of ZH (a, Unit: dBZ), ZDR (b, Unit: dB), KDP (c, Unit:(°)·km-1), CC (d),V(e,Unit:m·s-1), and VCS of ZH (Unit: dBZ) overlying ZDR, KDP, CC and zero velocity isolines from Ji'nan radar at 19:22 on 6 August 2020
| 北京时 | 风暴 | -10 ℃层高度以上 | -10~0 ℃层高度 | 0 ℃层高度以下 | 特征高度/km | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH/dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/ [(°)· km-1] | ZH/dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/ [(°)·km-1] | ZH/dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/ [(°)·km-1] | ZDR柱 | KDP柱 | 45 dBZ顶 | ||
| 8月5日07:16 | 王庄集风暴 | <55 | ≈0 | <1.5 | 45~59 | 0.3~1.6 | 0.5~2.5 | 45~61 | 1.0~2.7 | 0.5~3.8 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 11.7 |
| 8月6日19:22 | 大安风暴 | <45 | 0.2~1.0 | <1.0 | 40~52 | 0.5~1.7 | 0.5~2.5 | 45~55 | 1.0~2.6 | 0.5~3.7 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 8.8 |
Tab.3 Vertical structural characteristics for Wang Zhuangji and Da'an storms
| 北京时 | 风暴 | -10 ℃层高度以上 | -10~0 ℃层高度 | 0 ℃层高度以下 | 特征高度/km | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH/dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/ [(°)· km-1] | ZH/dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/ [(°)·km-1] | ZH/dBZ | ZDR/dB | KDP/ [(°)·km-1] | ZDR柱 | KDP柱 | 45 dBZ顶 | ||
| 8月5日07:16 | 王庄集风暴 | <55 | ≈0 | <1.5 | 45~59 | 0.3~1.6 | 0.5~2.5 | 45~61 | 1.0~2.7 | 0.5~3.8 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 11.7 |
| 8月6日19:22 | 大安风暴 | <45 | 0.2~1.0 | <1.0 | 40~52 | 0.5~1.7 | 0.5~2.5 | 45~55 | 1.0~2.6 | 0.5~3.7 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 8.8 |
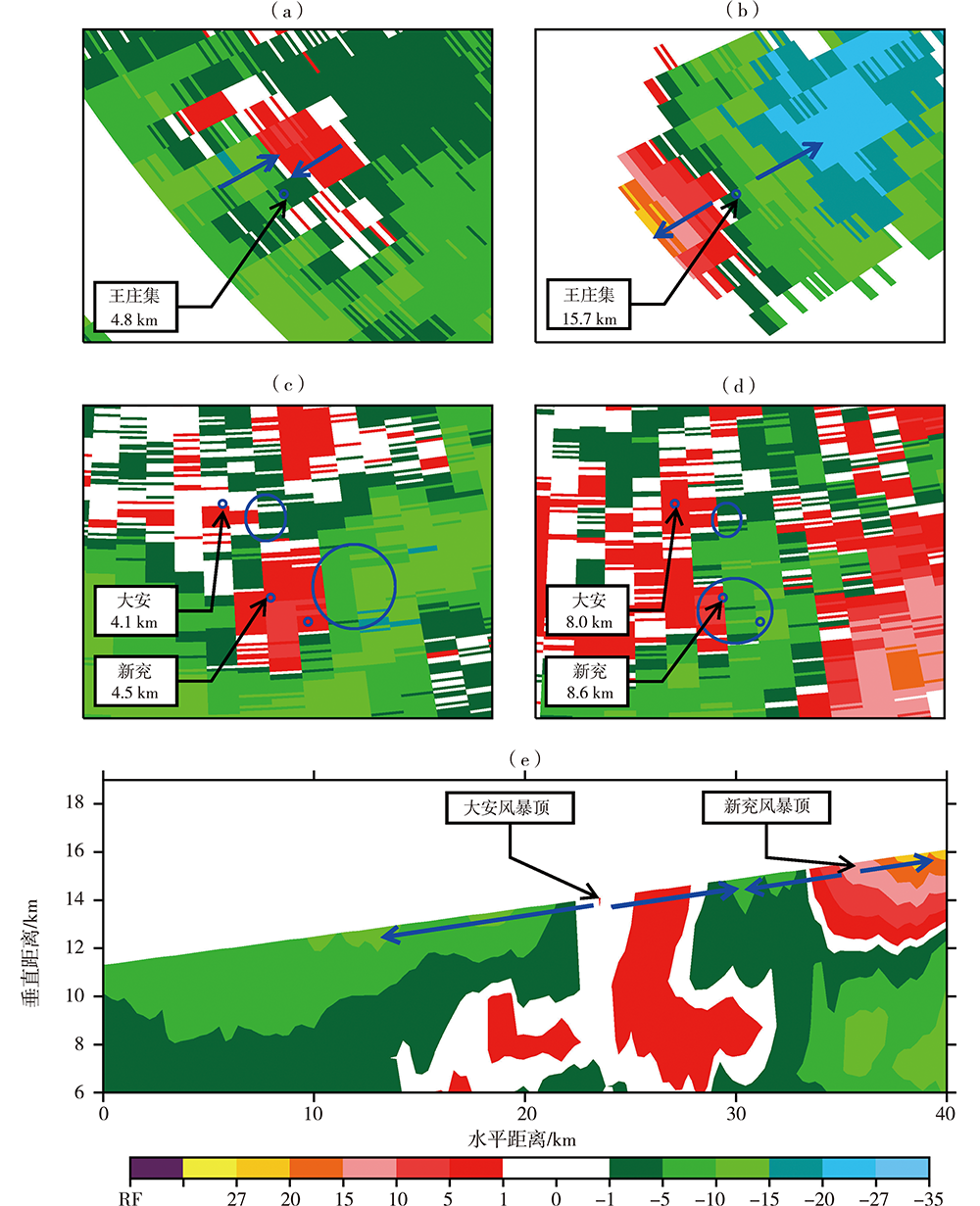
Fig.6 Radial velocity at 1.5° (a), 6.0° (b) elevations at 07:16 on 5 and at 1.5°(c), 3.3°(d) elevations at 19:22 on 6 and vertical section of radial velocity at 19:22 on 6 (e) August 2020 (Unit: m·s-1) (The vertical section is along dotted line in Fig.3(e))
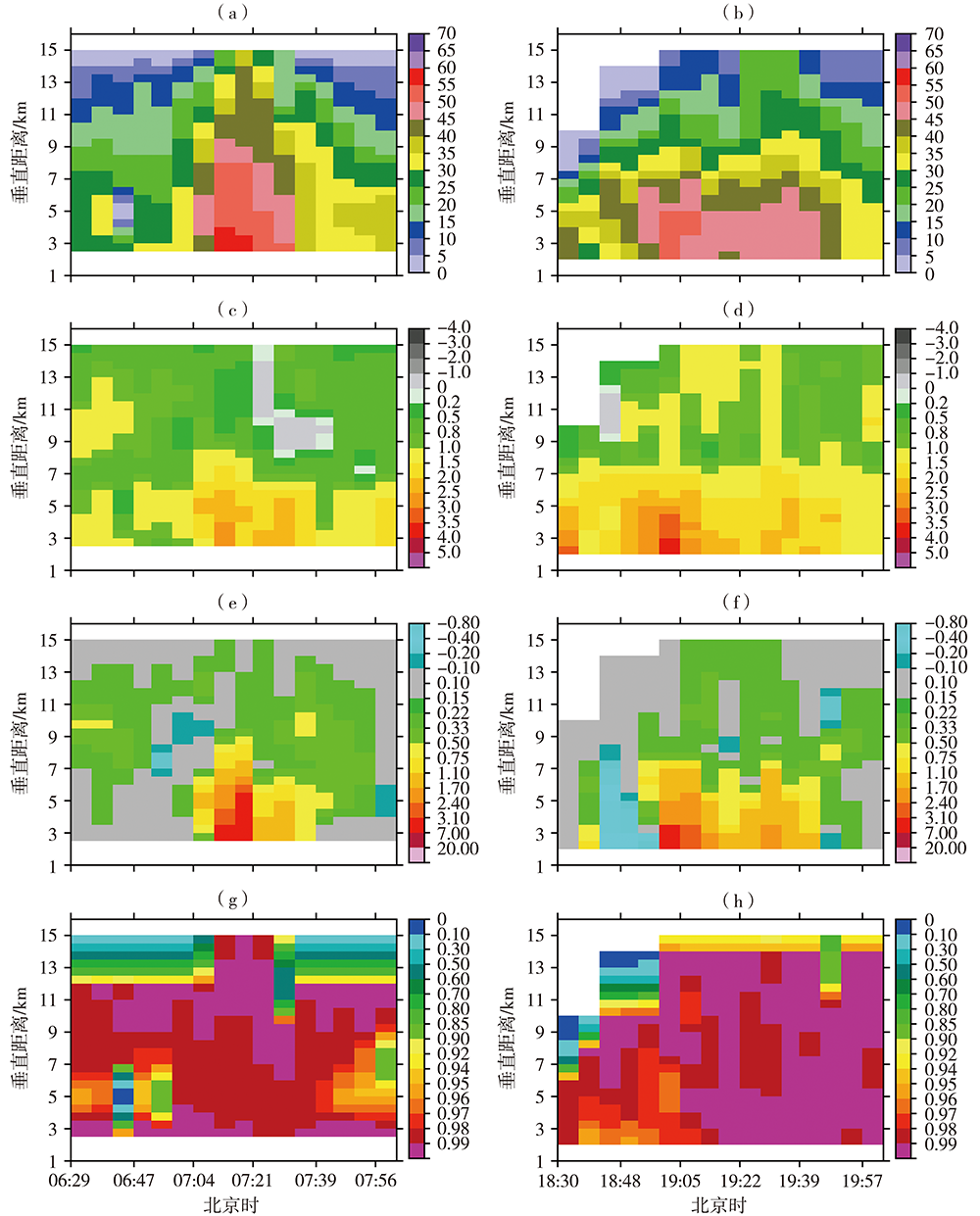
Fig.7 Time-height cross sections of ZH (Unit: dBZ)(a, b), ZDR (Unit: dB)(c,d), KDP (Unit:(°)·km-1)(e, f) and CC (g, h) at Wangzhuangji station from 06:30 to 08:00 on 5 (a, c, e, g) and Da'an station from 18:30 to 20:00 on 6 (b, d, f, h) August 2020
| [1] | 陈炯, 郑永光, 张小玲, 等, 2013. 中国暖季短时强降水分布和日变化特征及其与中尺度对流系统日变化关系分析[J]. 气象学报, 71(3): 367-382. |
| [2] | 刁秀广, 张磊, 孟宪贵, 等, 2020. 两次强降水风暴双偏振参量特征分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 40(3): 27-36. |
| [3] | 刁秀广, 郭飞燕, 2021. 2019年8月16日诸城着急单体风暴双偏振参量结构特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 79(2): 181-195. |
| [4] | 刘黎平, 葛润生, 张沛源, 2002. 双线偏振多普勒天气雷达遥测降水强度和液态含水量的方法和精度研究[J]. 大气科学, 26(5): 709-719. |
| [5] |
高晓梅, 孙雪峰, 秦瑜蓬, 等, 2018. 山东一次强对流天气的环境条件和对流风暴特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(3): 447-455.
DOI |
| [6] | 潘赫拉, 许东蓓, 陈明轩, 等, 2020. 天气雷达气候学研究新进展[J]. 干旱气象, 38(6): 887-894. |
| [7] | 魏庆, 胡志群, 流黎平, 等, 2016. C波段偏振雷达数据预处理及在降水估计中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 35(1): 594-601. |
| [8] | 荀爱萍, 张伟, 黄惠镕, 等, 2019. 厦门市S波段双偏振雷达测雨效果分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 42(4): 103-110. |
| [9] | 俞小鼎, 郑永光, 2020. 中国当代强对流天气研究与业务进展[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 391-418. |
| [10] | 俞小鼎, 周小刚, 王秀明, 2012. 雷暴与强对流临近天气预报技术进展[J]. 气象学报, 70(3): 311-337. |
| [11] | 杨吉, 郑媛媛, 徐芬, 2020. 江淮地区一次冰雹过程的双线偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 78(4): 568-579. |
| [12] | 张培昌, 魏鸣, 黄兴友, 等, 2018. 双线偏振多普勒天气雷达探测原理与应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 38-49. |
| [13] | 郑永光, 陶祖钰, 俞小鼎, 2017. 强对流天气预报的一些基本问题[J]. 气象, 43(6): 641-652. |
| [14] | 张羽, 胡东明, 李怀宇, 2017. 广州双偏振天气雷达在短时强降水中的初步应用[J]. 广东气象, 39(2): 26-29. |
| [15] | 郑铮, 潘灵杰, 钱燕珍, 等, 2021. 台风“利奇马”造成浙江沿海极端强降水的演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 269-278. |
| [16] |
HALL M P M, CHERRY S M, GODDARD J W F, et al, 1980. Rain drop sizes and rainfall rate measured by dual-polarization radar[J]. Nature, 285(5762): 195-198.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HUBBERT J C, WILSON J W, WECKWERTH T M, et al, 2018. S-Pol’s polarimetric data reveal detailed storm features (and insect behavior)[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 99(10): 2 045-2 060.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KUMJIAN M R, 2013a. Principles and applications of dual-polarization weather radar. Part II: warm-and cold-season applications[J]. Journal of Operational Meteorology, 1 (20): 243-264.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KUMJIAN M R, 2013b. Principles and applications of dual-polarization weather radar. Part I: description of the polarimetric radar variables[J]. Journal of Operational Meteorology, 1(19): 226-242.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
KUMJIAN M R, RYZHKOV A V, PHILLIPS V T, 2014. The anatomy and physics of ZDR columns: investigating a polarimetric radar signature with a spectral bin microphysical model[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 53(7): 1 820-1 842.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SACHIDANANDA M, ZRNIC D S, 1987. Rain rate estimates from differential polarization measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 4: 588-598.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SNYDER J C, BLUESTEIN H B, DAWSON D T, II, et al, 2017. Simulations of polarimetric, X-band radar signatures in supercells. Part II:ZDR columns and rings and KDP columns[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 56(7): 2 001-2 026.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SUN J Z, ZHANG Y, BAN J M, et al, 2020. Impact of combined assimilation of radar and rainfall data on short-term heavy rainfall prediction: a case study[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 148(5): 2 211-2 232.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Van LIER-WALQUI M, FRIDLIND A M, ACKERMAN A S, et al, 2016. On polarimetric radar signatures of deep convection for model evaluation: columns of specific differential phase observed during MC3E[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 144(2): 737-758.
DOI URL |
| [1] | CHU Yingjia, GUO Feiyan, GAO Fan, HU Peng, ZHENG Lina, LIU Yichen, LU Qi. Comparative analysis of two different types of severe convective processes under the influence of cold vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 279-289. |
| [2] | FU Zhao, LIU Weicheng, SONG Xingyu, XU Lili, SHA Honge, MA Li, CUI Yu. Local enhanced convective environment characteristics of an extreme rainstorm event in arid region of Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 909-921. |
| [3] | ZHANG Junxia, HUANG Wubin, YANG Xiumei, LIU Weicheng, ZHOU Zihan, SHA Honge. Analysis on precipitation extremity of a torrential rain event in semi-arid region of eastern Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 922-932. |
| [4] | SHA Honge, FU Zhao, LIU Weicheng, XU Lili, LIU Na, LIU Xinyu, MA Yihao. Mechanism of trigger and maintenance during an extremely torrential rain in semi-arid region of eastern Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 933-944. |
| [5] | LI Chenrui, FU Jing, LIU Weicheng, WANG Jixin, WANG Yicheng, FU Zhao, ZHEN Xin. Cloud characteristics analysis of a torrential rainfall event use FY satellite in semi-arid region of Eastern Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 954-967. |
| [6] | CHEN Xiaoting, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Hui, PENG Li. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [7] | XU Min, SHEN Fang, LIU Xuan, LIU Yanjie, ZHANG Xianghan. Environmental conditions and mesoscale characteristics of severe convective weather in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei on 5 July 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 993-1002. |
| [8] | PENG Li, ZHAO Qiang, QIAO Danyang, ZHANG Xiong, XU Haotian, NI Wen. Comparative analysis on characteristics of rainstorms caused by northwest vortex in Shaanxi with and without influence of typhoon [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 981-992. |
| [9] | XU Min, SHEN Fang, LIU Qiqi, LI Na, WANG Jie. Formation conditions and characteristics of heavy precipitation with quasi-linear MCSs [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 596-604. |
| [10] | ZHANG Haiyao, HUANG Yuxia, WU Huiyan, LI Xia, MU Lamei, YANG Huining. Comparative analysis of two consecutive hail weathers in complex terrain area of loecs plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 646-655. |
| [11] | LAN Mingcai, ZHOU Li, JIANG Shuai, YIN Yiwen, XU Lin. Causes of a short-term heavy rainfall under the control of the western Pacific subtropical high in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 656-666. |
| [12] | LIN Chunying, WANG Qihua, LI Hongmei, GUO Qiang, HOU Yonghui, ZHOU Wanfu, ZHANG Liyan. Characteristics and disaster risk analysis of hail in agricultural area of eastern Qinghai Province in recent 60 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 436-443. |
| [13] | ZHANG Guilian, LIU Lanbo, MENG Xuefeng, ZHANG Lu, LI Linhui. Causes of a backflow snowstorm in southeastern Inner Mongolia under the background of cold pad and its radar echoes characteristics [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 500-506. |
| [14] | LEI Yu, HUANG Wubin, LI Qian, HUANG Yuxia, ZHANG Junxia, LIU Na. Characteristics of Doppler radar products of strong hails under different weather classification in Hedong region of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 234-243. |
| [15] | SHEN Xiaoling, PAN Lingjie, ZUO Jun, SANG Minghui, ZHANG Lina. Comparative analysis on two similar falling area rainstorms during Meiyu period in western Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 244-255. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||