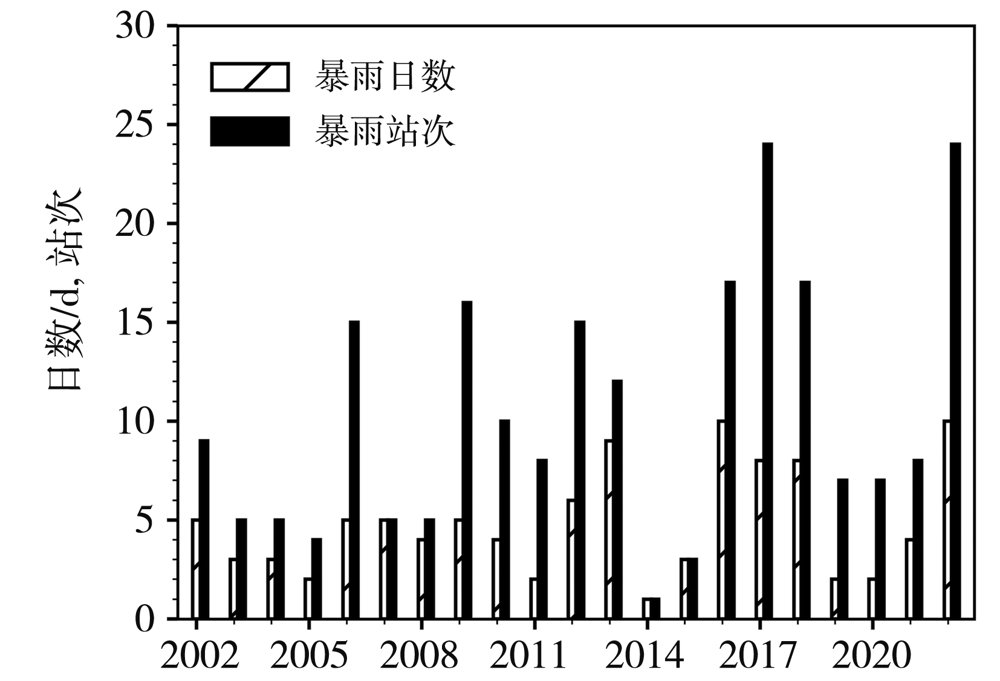
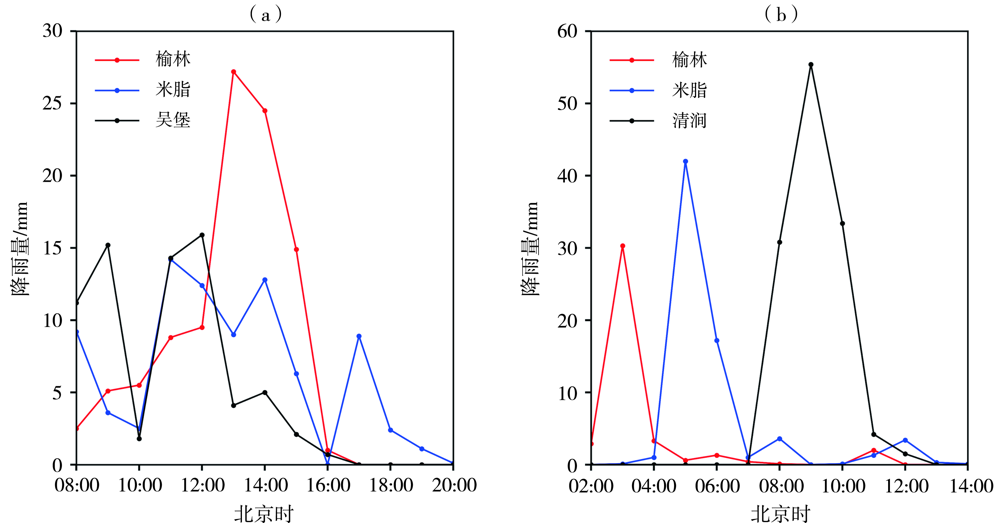
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 968-980.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-0968
• Study on rainstorm in arid region • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau
CHEN Xiaoting1,2( ), ZHAO Qiang1,2(
), ZHAO Qiang1,2( ), LIU Hui1, PENG Li3
), LIU Hui1, PENG Li3
- 1. Shaanxi Provincial Meteorological Observatory, Xi’an 710014,China
2. Key Laboratory of Eco-Environment and Meteorology for the Qinling Mountains and Loess Plateau,Xi'an 710016,China
3. Tongchuan Meteorological Observatory, Tongchuan 727031,Shaanxi ,China
-
Received:2022-10-27Revised:2022-12-20Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-10 -
Contact:ZHAO Qiang
黄土高原两次不同类型暴雨水汽特征分析
- 1.陕西省气象台,陕西 西安 710014
2.秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室,陕西 西安 710016
3.陕西省铜川市气象台,陕西 铜川 727031
-
通讯作者:赵强 -
作者简介:陈小婷(1984—),女,高级工程师,主要从事灾害天气机理及预报方法研究.E-mail:tsing_508@126.com。 -
基金资助:陕西省自然科学基础研究计划项目(2022JQ-248);秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室重点基金课题(2020K-1)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Xiaoting, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Hui, PENG Li. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 968-980.
陈小婷, 赵强, 刘慧, 彭力. 黄土高原两次不同类型暴雨水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 968-980.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-0968

Fig.2 The spatial distribution of 24 h accumulated precipitation in Shaanxi from 20:00 BST 10 to 20:00 BST 11 July (a) , and from 20:00 BST 8 to 20:00 BST 9 August (b) 2022 (Unit: mm)

Fig.4 Geopotential height filed (contour, Unit: dagpm) and wind field (wind vector, Unit: m·s-1) at 500 hPa at 08:00 BST 11 July (a), at 08:00 BST 9 August (c), and 700 hPa wind field (red wind vector for 700 hPa wind speed greater than 12 m·s-1, the shaded area for 700 hPa wind speed greater than 10 m·s-1) and wind field (black wind vector, Unit: m·s-1) and geopotential height (contour, Unit: dagpm) at 850 hPa at 14:00 BST 11 July (b), at 02:00 BST 9 August (d) 2022 (The blue dot represents Yulin station. the same as below)
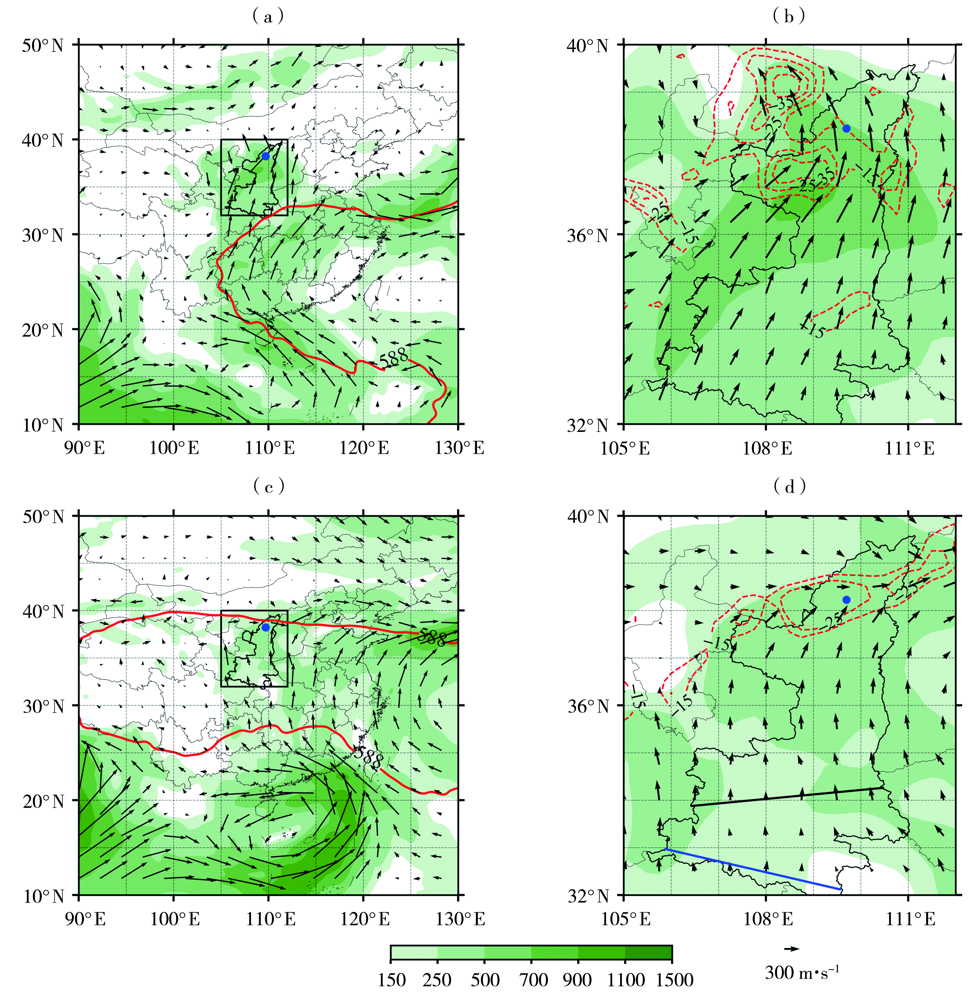
Fig.5 The vertically integrated water vapor fluxes from ground to 300 hPa (arrow vector and color shaded area, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1, only plotting the value greater than 100 kg·m-1·s-1) (a, c) and its divergence (isoline,Unit:10-4 kg·m-2·s-1) (b, d) at 08:00 BST 11 July (a, b) and 02:00 BST 9 August (c, d) 2022 (The box in Fig.5 (a) and Fig.5 (c) represent Fig.5 (b) and Fig.5 (d) region, the red contours in Fig.5 (a, c) represent the 588 dagpm isoline, the solid black and blue lines in Fig.5 (d) represent the approximate locations of Qinling Mountains and Daba Moutain respectively)

Fig.6 700 hPa (a, c) and 850 hPa (b, d) water vapor flux (arrow, Unit:10-1 kg·hPa-1·m-1·s-1) and its divergence (color shaded areas,Unit:10-6 kg·hPa-1·m-2·s-1) at 08:00 BST 11 July (a, b) and 02:00 BST 9 August (c,d) 2022
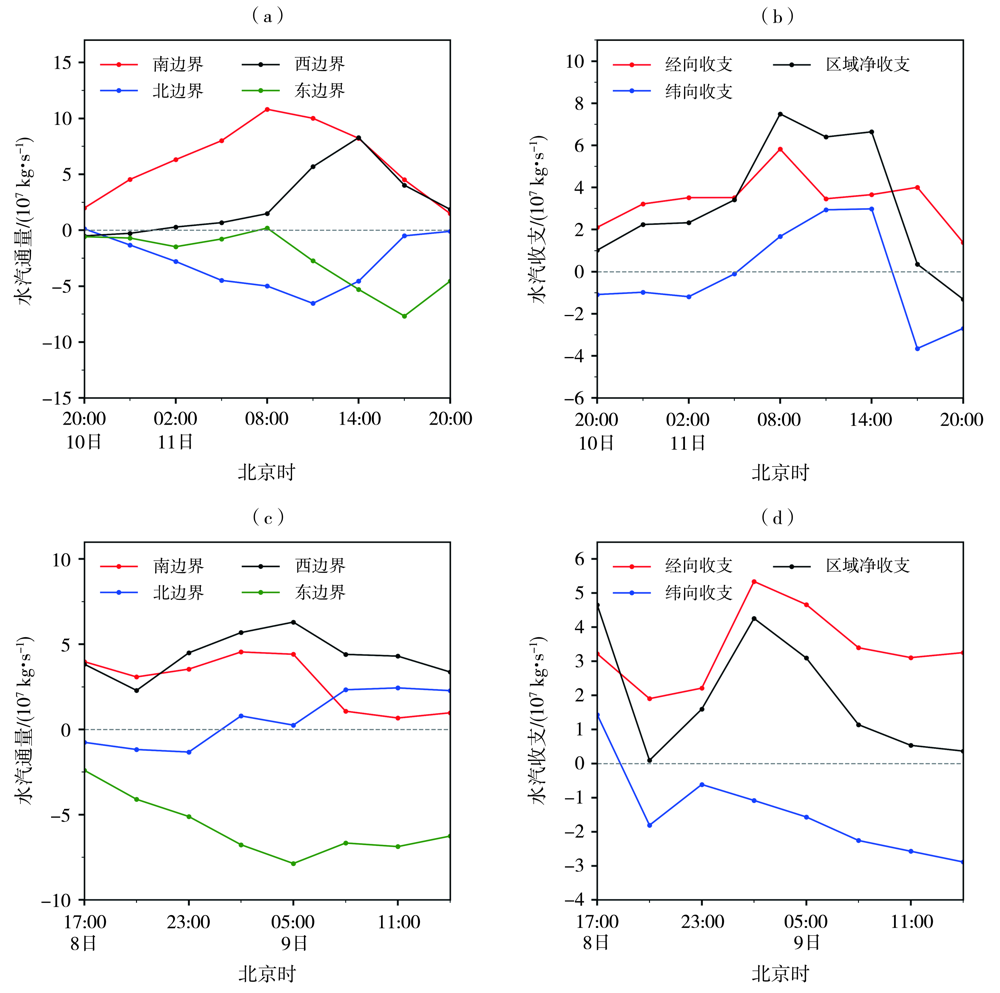
Fig.7 The evolution of water vapor flux (a, c) at each boundary and water vapor budget (b, d) over the rainstorm area (109°E-111°E, 37°N-39°N) from 20:00 BST 10 to 20:00 BST 11 July (a, b) and 17:00 BST 8 to 14:00 BST 9 August (c, d) 2022
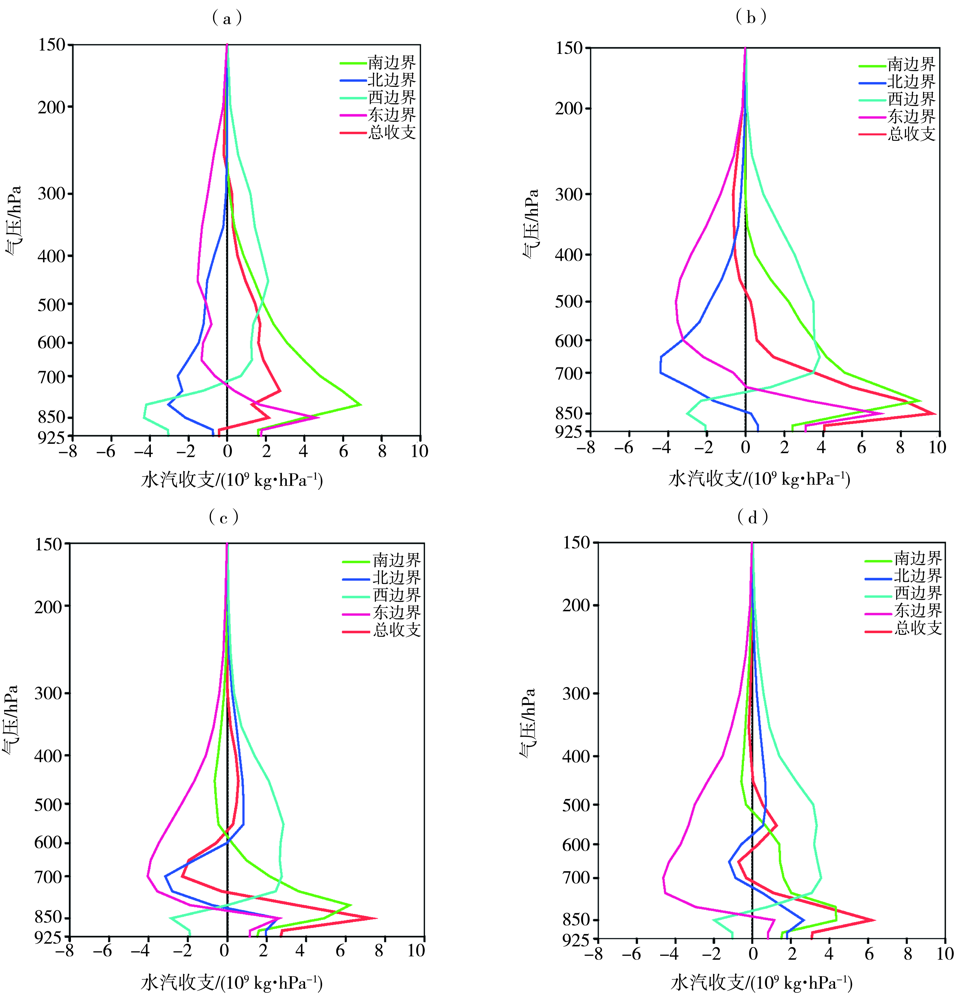
Fig.8 The vertical profile of water vapor budget at four boundaries from 02:00 BST to 08:00 BST 11 July (a), from 08:00 BST to 14:00 BST 11 July (b), from 20:00 BST 8 to 02:00 BST 9 August (c) and from 02:00 BST to 08:00 BST 9 August (d) 2022

Fig.9 The time evolution of meridional water vapor budget (a, d), zonal water vapor budget (b, e) and net water vapor budget (c, f) from ground to 800 hPa, from 800 to 500 hPa and from 500 to 300 hPa from 20:00 BST 10 to 20:00 BST 11 July (a, b, c) and 17:00 BST 8 to 14:00 BST 9 August (d, e, f) 2022

Fig.10 Water vapor transport trajectory cluster analysis at 1500 m (a, c)and 3000 m (b, d) height for the heavy rain process on 11 July (a, b) and 9 August (c, d) 2022 (The number in the brackets represents the contribution rate of water vapor in the channel)
| [1] |
刘勇, 郭大梅, 胡启元. 2012年7月27日陕北佳县特大暴雨天气的成因[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(3):424-430.
DOI |
| [2] | 井喜, 井宇, 陈闯, 等. 黄土高原β中尺度致洪暴雨特征及成因[J]. 气象, 2014, 40(10):1183-1193. |
| [3] | 王文, 程攀. “7·27”陕北暴雨数值模拟与诊断分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2013, 36(2):174-183. |
| [4] | 刘慧敏, 马晓华, 梁生俊, 等. 2017年7月25日陕北局地特大暴雨过程的β中尺度特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40(4):374-382. |
| [5] | 赵强, 韩洁, 陈小婷. 黄土高原一次副高外围暴雨的对流环境及触发条件分析[J]. 陕西气象, 2020(3):1-18. |
| [6] | 赵强, 王楠, 李萍云, 等. 两次陕北暴雨过程热力动力机制诊断[J]. 应用气象学报, 2017, 28(3):340-356. |
| [7] | 蒋伊蓉, 李晓利, 刘慧敏, 等. 引起陕北暴雨的西北涡特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2022, 41(3):614-654. |
| [8] | 赵强, 王楠, 陈小婷, 等. “8·21”陕西中北部暴雨成因对比及预报偏差分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4):559-568. |
| [9] | 黄勤, 黄鑫, 李亚丽. 陕西榆林地区一次暴雨过程三维风场结构演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 747-754. |
| [10] | 赵榆飞, 杜继稳. 陕北地区突发性暴雨和系统性暴雨的对比分析[J]. 气象科技, 2005, 33(5):414-418. |
| [11] | 廖晓农, 倪允琪, 何娜, 等. 导致“7·21”特大暴雨过程水汽异常充沛的天气尺度动力过程分析研究[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71(6):997-1011. |
| [12] | 赵强, 彭力, 李文耀, 等. 2021年4月陕西一次极端暴雨过程的成因诊断[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2022, 41(2):109-118. |
| [13] | 孔祥伟, 杨建才, 李红, 等. 河西走廊西部干旱区一次极端暴雨天气的水汽特征分析[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(4):412-423. |
| [14] | 井喜, 贺文彬, 毕旭, 等. 远距离台风影响陕北突发性暴雨成因分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 2005, 16(5):655-662. |
| [15] | 张弘, 陈卫东, 孙伟. 一次台风与河套低涡共同影响的陕北暴雨分析[J]. 高原气象, 2006, 25(2):52-59. |
| [16] |
张雅斌, 武麦凤, 侯建忠, 等. 陕西 4 次台风远距离暴雨过程的水汽条件对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(5):788-797.
DOI |
| [17] | 武麦凤, 王旭仙, 孙健康, 等. 2003年渭河流域5场致洪暴雨过程的水汽场诊断分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 2007, 418(2):225-231. |
| [18] | 师锐, 何光碧, 周春花. 四川一次持续性暴雨过程的水汽特征及多尺度系统影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3):415-425. |
| [19] | 江志红, 任伟, 刘征宇, 等. 基于拉格朗日方法的江淮梅雨水汽输送特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71(2): 295-304. |
| [20] | 陈红专, 叶成志, 陈静静, 等. 2017年盛夏湖南持续性暴雨过程的水汽输送和收支特征分析[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(9):1213-1226. |
| [21] | 熊秋芬, 姜晓飞, 鞠英芹. 湖北省三次春季暴雨过程水汽来源与输送特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2022, 12(3):25-33. |
| [22] | 张芳丽, 李国平, 李武阶. 2020年7月5—6日武汉江夏特大暴雨水汽源地和输送特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2022, 41(4):375-383. |
| [23] | 阙志萍, 凌婷, 吴凡, 等. 江西一次连续大暴雨的水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 76-86. |
| [24] |
钱正安, 蔡英, 宋敏红, 等. 中国西北旱区暴雨水汽输送研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37(3): 577-590.
DOI |
| [25] |
庄晓翠, 李博渊, 赵江伟, 等. 天山南坡暖季暴雨过程的水汽来源及输送特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1):30-40.
DOI |
| [26] | 布和朝鲁, 诸葛安然, 谢作威, 等. 2021年“7·20”河南暴雨水汽输送特征及其关键天气尺度系统[J]. 大气科学, 2022, 46(3): 725-744. |
| [27] |
赵桂香, 薄燕青, 邱贵强, 等. 黄河中游一次大暴雨的观测分析与数值模拟[J]. 高原气象, 2017, 36(2):436-454.
DOI |
| [1] | GUO Jingyan, XIAO Dong. Changes of summer water vapor in Bengal region and its linkage with the interdecadal Pacific oscillation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 380-389. |
| [2] | WANG Jiajin, XIAO Hongru, YANG Kangquan, WANG Binyan. Water vapor transport characteristics of a continuous rainstorm in Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 474-482. |
| [3] | SONG Lin, ZHANG Guoping, WANG Shudong, WAN Fujing, SUN Hao. Evaluation of FY-4A lightning mapping imager applied in arid region and its comparison with multi-source data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 25-33. |
| [4] | LI Yuan, LI Ruifen, ZHANG Xi. Influence of El Niño Events with Different Patterns on the Following Summer Precipitation in Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 762-770. |
| [5] | SUN Junkui, WANG Jiang, KANG Daojun, YAN Liping, ZHOU Xi. Precipitation Forecast of Wudongde Hydropower Station Based on SVM Model Optimized by Multiple Algorithms [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 670-675. |
| [6] | WANG Siqi, ZHANG Xiang, CHEN Nengcheng, ZHOU Jiaxiang, HU Chuli, PENG Xiaoting. Monitoring and Comparison of Drought in Five Provinces of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Based on the Multiple Drought Indices [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 209-217. |
| [7] | WANG Huiqing, FU Yanan, MENG Xuefeng. Analysis on Characteristics of Water Vapor Transportation During an Extreme Snowfall Process in the Northeast of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 277-287. |
| [8] | CAI Ronghui, CHEN Jingjing, WEN Ping, HE Weiwei, CHEN Hongzhuan, LI Wei. Water Vapour Characteristics During a Flood-causing Torrential Rainfall Process in Hunan Province in 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 288-300. |
| [9] | YANG Shuhua, ZHAO Guixiang, CHENG Haixia, WANG Yijie,,LI Laping, SONG Shihua. Comparative Analysis of Three Hail Weather Processes Caused by Pulse Storms in Northern Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 67-75. |
| [10] | WANG Hongjun, WANG Zichen, WANG Ke,PENG Chong, ZHU Yaguang. Anomalous Circulation Characteristics of Autumn Rain and Its Cause over West China in 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(5): 743-750. |
| [11] | ZHAO Xi, LI Jingmeng, TONG Hongmei. Comparative Analysis of Low Visibility and Low Runway Visual Range at Jinan Airport [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(5): 847-856. |
| [12] | GAN Lu, GUO Wenli, DENG Changju. Comparative Analysis of Two Torrential Rain Processes in Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 239-249. |
| [13] | XU Dong, KONG Ying, WANG Chenghai. Changes of Water Vapor Budget in Arid Area of Northwest China and Its Relationship with Precipitation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(3): 431-439. |
| [14] | XIE Qiyu, GONG Yuanfa, YANG Rong. Water Vapor Budget of High Water Vapor Content Region over Tibet Plateau in Winter and Its Relationship with Precipitation of China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(5): 732-739. |
| [15] | DUAN Wei1,DUAN Xu1,FAN Feng1, SUN Jihua2. Climatic Characteristics of Dry and Wet Season in the Southeast Side of the Tibetan Plateau and Its Causes [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 546-554. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||