Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 967-975.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0967
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Evolution characteristics of water vapor and its relationship with atmospheric visibility during haze processes in Sichuan Basin
ZHU Yao1,2( ), TANG Lu1,2, NI Changjian1,2, LI Na1,2, TANG Dezhi1,2, LI Xinyi3(
), TANG Lu1,2, NI Changjian1,2, LI Na1,2, TANG Dezhi1,2, LI Xinyi3( )
)
1. School of Atmospheric Sciences ,Chengdu University of Information Technology Chengdu 610225, China 2. Chengdu Plain Urban Meteorology and Environment Observation and Research Station of Sichuan Province Chengdu 610225, China 3. Chengdu Meteorological Bureau Chengdu 611130, China
-
Received:2025-06-10Revised:2025-09-30Online:2025-12-31Published:2026-01-19
四川盆地霾天气过程水汽演化特征及与大气能见度的关系
朱瑶1,2( ), 唐露1,2, 倪长健1,2, 李娜1,2, 唐得智1,2, 李昕翼3(
), 唐露1,2, 倪长健1,2, 李娜1,2, 唐得智1,2, 李昕翼3( )
)
1.成都信息工程大学大气科学学院 四川 成都 610225 2.成都平原城市气象与环境四川省野外科学观测研究站 四川 成都 610225 3.成都市气象局 四川 成都 611130
-
通讯作者:李昕翼 -
作者简介:朱瑶(2000—),女,硕士生,主要从事大气环境与大气物理相关研究。E-mail: zyao0929@163.com。 -
基金资助:四川省科技教育联合基金项目(2024NSFSC1983);与国家重点研发计划项目(2023YFC3709301)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHU Yao, TANG Lu, NI Changjian, LI Na, TANG Dezhi, LI Xinyi. Evolution characteristics of water vapor and its relationship with atmospheric visibility during haze processes in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(6): 967-975.
朱瑶, 唐露, 倪长健, 李娜, 唐得智, 李昕翼. 四川盆地霾天气过程水汽演化特征及与大气能见度的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(6): 967-975.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0967
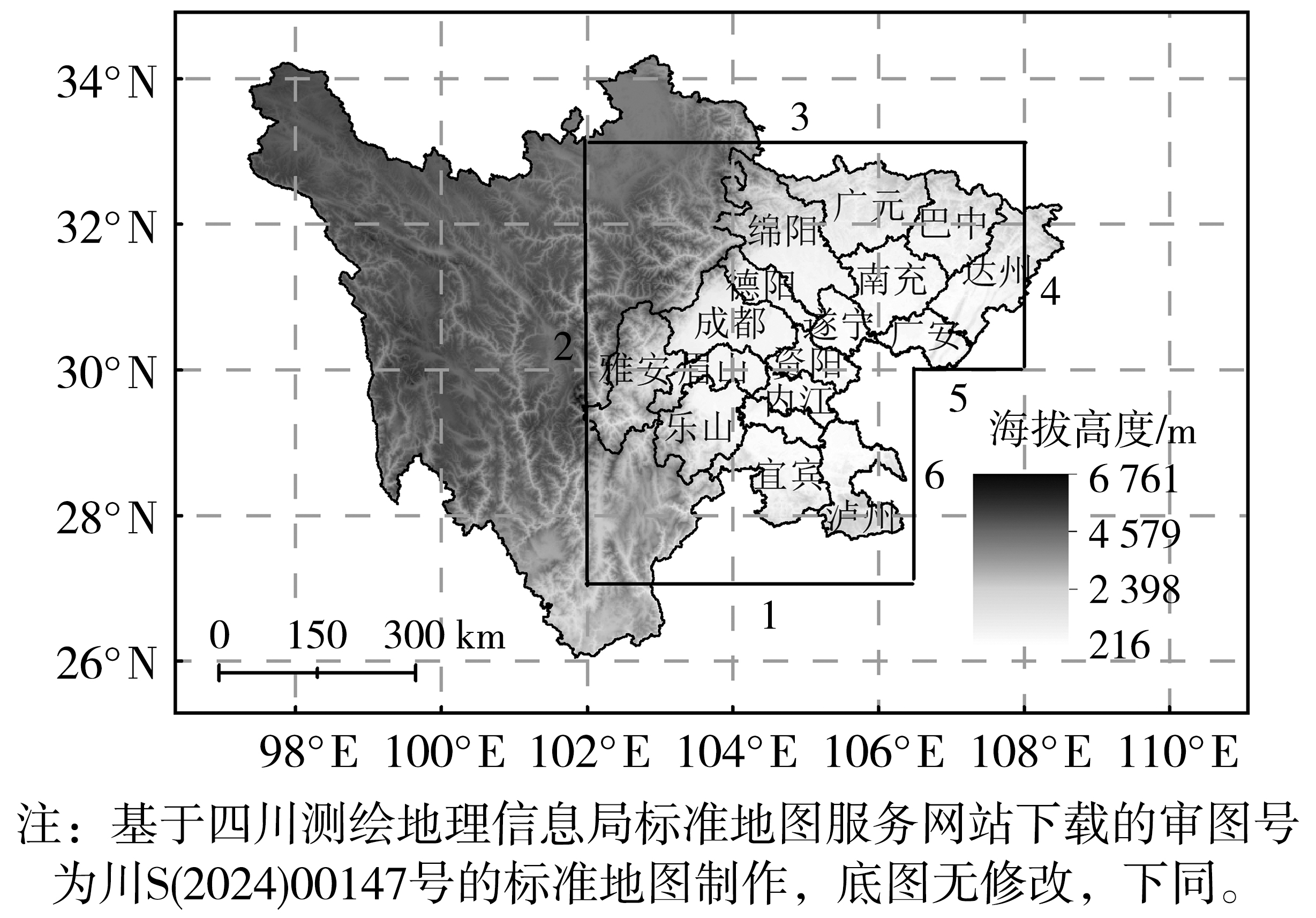
Fig.1 The boundaries of the Sichuan Basin and the distribution of cities (The numbers represent the boundaries of the study area, the number 1 and 5 are the southern boundary, 2 is the western boundary, 3 is the northern boundary, and 4 and 6 are the eastern boundary)
| 霾天气过程编号 | 日期 | 霾天气过程编号 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2015年1月20—26日 | 8 | 2017年1月19—29日 |
| 2 | 2015年2月8—15日 | 9 | 2017年2月12—20日 |
| 3 | 2015年12月25日—2016年1月5日 | 10 | 2017年12月18日—2018年1月2日 |
| 4 | 2016年1月25日—2016年2月11日 | 11 | 2018年1月9—23日 |
| 5 | 2016年2月16—20日 | 12 | 2018年2月6—17日 |
| 6 | 2016年12月18—23日 | 13 | 2018年12月13—18日 |
| 7 | 2016年12月28日—2017年1月8日 |
Tab.1 Persistent haze processes in the Sichuan Basin during winter from 2015 to 2018
| 霾天气过程编号 | 日期 | 霾天气过程编号 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2015年1月20—26日 | 8 | 2017年1月19—29日 |
| 2 | 2015年2月8—15日 | 9 | 2017年2月12—20日 |
| 3 | 2015年12月25日—2016年1月5日 | 10 | 2017年12月18日—2018年1月2日 |
| 4 | 2016年1月25日—2016年2月11日 | 11 | 2018年1月9—23日 |
| 5 | 2016年2月16—20日 | 12 | 2018年2月6—17日 |
| 6 | 2016年12月18—23日 | 13 | 2018年12月13—18日 |
| 7 | 2016年12月28日—2017年1月8日 |
| 霾天气过程 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.03 | -27.00 | 15.85 | -3.25 | 3.63 |
| 2 | 17.67 | -32.60 | 17.72 | -0.77 | 2.01 |
| 3 | 11.53 | -36.36 | 13.59 | 8.41 | -2.83 |
| 4 | 21.59 | -30.39 | 15.62 | -3.70 | 3.12 |
| 5 | 39.93 | -42.03 | 5.83 | 1.54 | 5.27 |
| 6 | 23.94 | -37.15 | 25.38 | -6.43 | 5.73 |
| 7 | 23.36 | -50.29 | 36.81 | -7.21 | 2.67 |
| 8 | 20.83 | -33.73 | 17.00 | -2.54 | 1.56 |
| 9 | 17.85 | -30.41 | 32.70 | -12.57 | 7.58 |
| 10 | 30.87 | -44.23 | 18.60 | -2.60 | 2.64 |
| 11 | 20.64 | -28.63 | 13.07 | -2.16 | 2.92 |
| 12 | 30.62 | -41.27 | 14.24 | -2.19 | 1.40 |
| 13 | 44.78 | -63.60 | 29.30 | -1.95 | 8.54 |
| 平均 | 24.74±9.43 | -38.28±10.19 | 19.67±8.82 | -2.72±4.82 | 3.40±2.92 |
Tab.2 Water vapor transportation of the boundaries and net water vapor budget of the Sichuan Basin during the haze processes in winter from 2015 to 2018 单位:106 kg·s-1
| 霾天气过程 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.03 | -27.00 | 15.85 | -3.25 | 3.63 |
| 2 | 17.67 | -32.60 | 17.72 | -0.77 | 2.01 |
| 3 | 11.53 | -36.36 | 13.59 | 8.41 | -2.83 |
| 4 | 21.59 | -30.39 | 15.62 | -3.70 | 3.12 |
| 5 | 39.93 | -42.03 | 5.83 | 1.54 | 5.27 |
| 6 | 23.94 | -37.15 | 25.38 | -6.43 | 5.73 |
| 7 | 23.36 | -50.29 | 36.81 | -7.21 | 2.67 |
| 8 | 20.83 | -33.73 | 17.00 | -2.54 | 1.56 |
| 9 | 17.85 | -30.41 | 32.70 | -12.57 | 7.58 |
| 10 | 30.87 | -44.23 | 18.60 | -2.60 | 2.64 |
| 11 | 20.64 | -28.63 | 13.07 | -2.16 | 2.92 |
| 12 | 30.62 | -41.27 | 14.24 | -2.19 | 1.40 |
| 13 | 44.78 | -63.60 | 29.30 | -1.95 | 8.54 |
| 平均 | 24.74±9.43 | -38.28±10.19 | 19.67±8.82 | -2.72±4.82 | 3.40±2.92 |

Fig.2 Net water vapor input and output (a) and net water vapor budget (b) in four stages of the winter haze processes over the Sichuan Basin from 2015 to 2018 (The error bar above the bars represents standard error)
| 阶段 | 700 hPa及以下 | 700~500 hPa | 500~300 hPa | 1 000~300 hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形成期 | 9.08±1.91 | 2.63±0.74 | 0.51±0.17 | 13.30±4.48 |
| 发展期 | 10.37±2.27 | 3.01±0.88 | 0.62±0.21 | 22.75±8.05 |
| 持续期 | 12.58±2.56 | 3.81±0.95 | 0.87±0.39 | 27.23±9.50 |
| 消亡期 | 12.04±2.12 | 3.49±1.01 | 0.67±0.36 | 25.48±9.08 |
| 平均 | 11.63±2.60 | 3.44±1.01 | 0.73±0.36 | 24.44±9.57 |
Tab.3 Water vapor content in different layers in four stages of the winter haze processes over the Sichuan Basin from 2015 to 2018
| 阶段 | 700 hPa及以下 | 700~500 hPa | 500~300 hPa | 1 000~300 hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形成期 | 9.08±1.91 | 2.63±0.74 | 0.51±0.17 | 13.30±4.48 |
| 发展期 | 10.37±2.27 | 3.01±0.88 | 0.62±0.21 | 22.75±8.05 |
| 持续期 | 12.58±2.56 | 3.81±0.95 | 0.87±0.39 | 27.23±9.50 |
| 消亡期 | 12.04±2.12 | 3.49±1.01 | 0.67±0.36 | 25.48±9.08 |
| 平均 | 11.63±2.60 | 3.44±1.01 | 0.73±0.36 | 24.44±9.57 |

Fig.3 Spatial distribution of water vapor content in the lower troposphere during the formation stage (a), development stage (b), persistence stage (c), and dissipation stage (d) of the winter haze processes over the Sichuan Basin from 2015 to 2018 (Unit: mm)
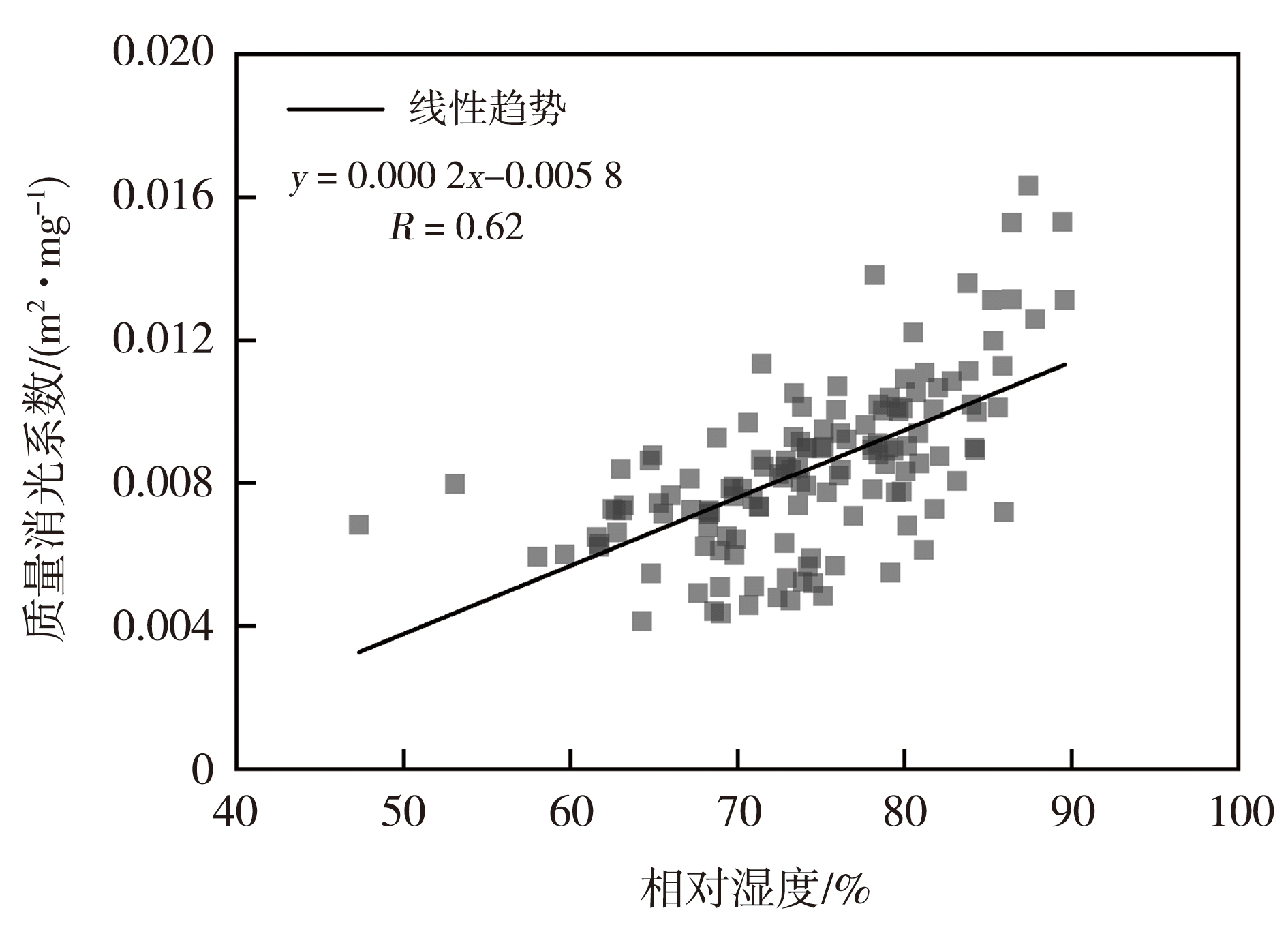
Fig.4 Scatter plot of relative humidity and extinction coefficient per unit mass of particulate matter during the winter haze processes over the Sichuan Basin from 2015 to 2018
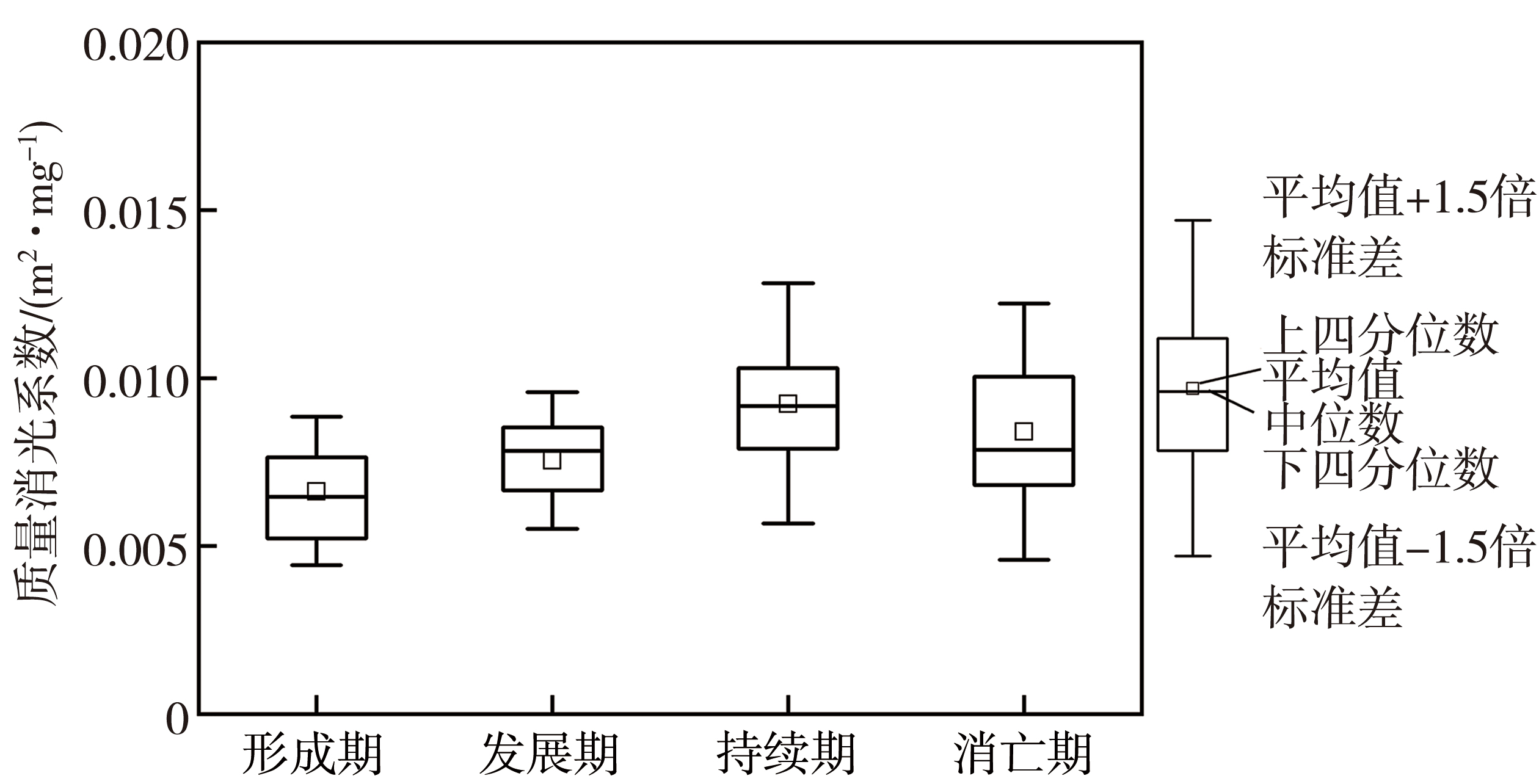
Fig.5 Box plot of extinction coefficient per unit mass of particulate matter during four stages of the winter haze processes over the Sichuan Basin from 2015 to 2018
| [1] | 白永清, 祁海霞, 刘琳, 等, 2016. 武汉大气能见度与PM2.5浓度及相对湿度关系的非线性分析及能见度预报[J]. 气象学报, 74(2):189-199. |
| [2] | 陈丹, 周长艳, 邓梦雨, 2016. 西南地区夏季大气水汽含量及其与南亚高压关系[J]. 应用气象学报, 27(4):473-479. |
| [3] | 崔蕾, 倪长健, 孙欢欢, 等, 2016. 成都颗粒物吸湿增长特征及订正方法研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(11):3938-3 943. |
| [4] | 范灵悦, 2022. 近几十年中国典型地区地表太阳辐射变化特征及其影响因素分析[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| [5] | 黄荣辉, 张振洲, 黄刚, 等, 1998. 夏季东亚季风区水汽输送特征及其与南亚季风区水汽输送的差别[J]. 大气科学, 22(4):460-469. |
| [6] | 刘凡, 谭钦文, 江霞, 等, 2018. 成都市冬季相对湿度对颗粒物浓度和大气能见度的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(4):1466-1 472. |
| [7] | 刘建西, 龙美希, 杜远林, 等, 2010. 川渝地区空中水资源分布及水汽输送特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 30(2):31-35. |
| [8] | 刘景卫, 周天军, 吴春强, 等, 2011. 海气耦合模式FGOALS_gl模拟的水汽和云辐射反馈过程[J]. 大气科学, 35(3):531-546. |
| [9] | 罗玉, 陈超, 赵鹏国, 等, 2023. 冬季四川盆地霾天气的环流特征及其对前期青藏高原热力作用的响应[J]. 大气科学, 47(5): 1 626-1 640. |
| [10] | 罗玉, 马振峰, 李小兰, 等, 2021. 四川盆地冬季霾日数的分布特征及其与气象条件和海温关系[J]. 高原气象, 40(1):189-199. |
| [11] | 罗玉, 王顺久, 张菁, 等, 2024. 初冬四川盆地霾的变化特征及其成因分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(1):111-116. |
| [12] | 孟子圣, 倪长健, 王思媛, 等, 2023. 霾过程大气消光系数时间序列混沌特性分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(3):353-362. |
| [13] | 权建农, 徐祥德, 贾星灿, 等, 2020. 影响我国霾天气的多尺度过程[J]. 科学通报, 65(9):810-824. |
| [14] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2010. 霾的观测和预报等级:QX/T113—2010[S]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [15] | 全国气象仪器与观测方法标准化技术委员会, 2018. 霾的观测识别:GB/T36542—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [16] | 任鑫冰, 杨显玉, 文军, 等, 2024. 2016年冬季四川盆地一次重度灰霾事件形成机制研究[J]. 高原气象, 43(3):775-789. |
| [17] | 邵龙义, 王文华, 幸娇萍, 等, 2018. 大气颗粒物理化特征和影响效应的研究进展及展望[J]. 地球科学, 43(5):1691-1 708. |
| [18] | 孙蕊, 马振峰, 张亮, 等, 2021. 1981—2019年四川省霾日时空变化特征及成因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(3):85-92. |
| [19] | 陶金花, 王子峰, 徐谦, 等, 2015. 北京地区颗粒物质量消光吸湿增长模型研究[J]. 遥感学报, 19(1):12-24. |
| [20] | 王佳津, 肖红茹, 杨康权, 等, 2023. 四川盆地一次持续性暴雨的水汽输送特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):474-482. |
| [21] | 王平, 范广洲, 董一平, 等, 2010. 四川空中水资源的稳定性与可开发性研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 25(10):1762-1 776. |
| [22] | 王同美, 吴国雄, 万日金, 2008. 青藏高原的热力和动力作用对亚洲季风区环流的影响[J]. 高原气象, 27(1):1-9. |
| [23] | 吴兑, 毕雪岩, 邓雪娇, 等, 2006. 珠江三角洲大气灰霾导致能见度下降问题研究[J]. 气象学报, 64(4):510-517. |
| [24] | 谢启玉, 巩远发, 杨蓉, 2015. 冬季青藏高原湿中心区域水汽收支及其与中国降水的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 33(5):732-739. |
| [25] | 徐祥德, 王寅钧, 赵天良, 等, 2015. 中国大地形东侧霾空间分布“避风港”效应及其“气候调节”影响下的年代际变异[J]. 科学通报, 60(12):1132-1 145. |
| [26] | 杨健博, 蔡子颖, 杨旭, 等, 2023. 气溶胶辐射效应对气象和环境影响的观测与模拟研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 43(1):38-51. |
| [27] | 杨茜, 高阳华, 李振亮, 2019. 重庆市霾天气下大气能见度与颗粒污染物的关系[J]. 西南大学学报:自然科学版, 41(9):134-140. |
| [28] | 杨素英, 田芷洁, 张铁凝, 等, 2019. 霾天气下城市气溶胶吸湿性的观测[J]. 环境科学, 40(6):2546-2 555. |
| [29] | 张华, 王菲, 汪方, 等, 2022. 全球气候变化中的云辐射反馈作用研究进展[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 52(3):400-417. |
| [30] | 张人禾, 李强, 张若楠, 2014. 2013年1月中国东部持续性强雾霾天气产生的气象条件分析[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 44(1):27-36. |
| [31] | 周长艳, 李跃清, 李薇, 等, 2005. 青藏高原东部及邻近地区水汽输送的气候特征[J]. 高原气象, 24(6):880-888. |
| [32] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等, 2002. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:636-643. |
| [33] | 邹进上, 刘惠兰, 1981. 我国平均水汽含量分布的基本特点及其控制因子[J]. 地理学报, 36(4):377-391. |
| [34] | CHEN J, ZHAO C S, MA N, et al, 2014. Aerosol hygroscopicity parameter derived from the light scattering enhancement factor measurements in the North China Plain[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14(15): 8 105-8 118. |
| [35] | DAY D E, MALM W C, 2001. Aerosol light scattering measurements as a function of relative humidity: A comparison between measurements made at three different sites[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 35(30): 5 169-5 176. |
| [36] | KOSCHMIEDER H, 1924. Theorie der horizontalen Sichtweite[J]. Beitrage zur Physik der freien Atmosphäre, 12: 33-55. |
| [37] | LI X, GAO Z Q, LI Y B, et al, 2019. Meteorological conditions for severe foggy haze episodes over North China in 2016-2017 winter[J]. Atmospheric Environment,199:284-298. |
| [38] | LIU X G, ZHANG Y H, CHENG Y F, et al, 2012. Aerosol hygroscopicity and its impact on atmospheric visibility and radiative forcing in Guangzhou during the 2006 PRIDE-PRD campaign[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 60: 59-67. |
| [39] | MCMURRY P H, WILSON J C, 1983. Droplet phase (Heterogeneous) and gas phase (homogeneous) contributions to secondary ambient aerosol formation as functions of relative humidity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 88(C9): 5 101-5 108. |
| [40] | PILINIS C, SEINFELD J H, GROSJEAN D, 1989. Water content of atmospheric aerosols[J]. Atmospheric Environment: 1967, 23(7): 1 601-1 606. |
| [41] | YANG K, DING B H, QIN J, et al, 2012. Can aerosol loading explain the solar dimming over the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(20):L20710. DOI: 10.1029/2012GL053733. |
| [42] | YANG Y C, GE B Z, CHEN X S, et al, 2021. Impact of water vapor content on visibility: Fog-haze conversion and its implications to pollution control[J]. Atmospheric Research, 256: 105565. DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105565. |
| [43] | YEH T C, 1950. The circulation of the high troposphere over China in the winter of 1945-46[J]. Tellus, 2(3): 173-183. |
| [44] | ZHAO S P, YU Y, QIN D H, et al, 2019. Analyses of regional pollution and transportation of PM2.5 and ozone in the city clusters of Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 10(2): 374-385. |
| [1] | LI Zhehua, XIAO An, TU Manhong, WU Wenxin. Analysis of short-term heavy rainfall change trend and its causes in Jiangxi Province from April to September during 1979-2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(4): 595-606. |
| [2] | YANG Xiaoling, SUN Xuying, YANG Jinhu, WU Wen, ZHAO Huihua, CHEN Jing. Identification and evolution characteristics of compound high-temperature and drought events in the Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 836-843. |
| [3] | DENG Peiyun, CHANG Zhuolin, HE Jia, YANG Meng, CHEN Deyuan, LIN Tong, MU Jianhua, DAI Yanbo. Research on temporal and spatial differences of atmospheric water vapor and its driving factors over Liupan Mountain area [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 376-384. |
| [4] | WEI Juanjuan, WAN Yu, PAN Ning, XIAO Junʼan. Analysis of water vapor characteristics and unstable mechanism of extreme rainstorm in spring in Yili River Valley [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 395-404. |
| [5] | ZHOU Jinhong, WANG Xiuming, TIAN Xiaoting, ZHANG Zexiu, LI Shuwen, CAI Xiaofang. Study on circulation characteristics and water vapor anomaly of extreme rainstorm events in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 426-436. |
| [6] | YU Haohui, ZHOU Changyan, CHEN Chao, CHEN Yongren. Analysis of atmospheric circulation background and main impacts of heatwave in Sichuan Basin from July to August 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 923-932. |
| [7] | WANG Wenyan, WANG Ruiying, LEI Lianfa, FAN Chao, LI Guoping. Distribution characteristics of atmospheric vapor and liquid water in central Guanzhong Plain based on observation data of ground-based microwave radiometer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 774-782. |
| [8] | NIE Haohao, WANG Wan, GUO Xiaojun, LIN Xiaomeng. Distribution characteristics of typical stratiform clouds water vapor and liquid water in Tianjin area based on airborne microwave radiometer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 599-606. |
| [9] | GUO Yang, SHI Chunxiang, XU Bin, SI Peng, XU Mei, WANG Min, SUN Meiling. Accuracy analysis of fog and haze identification based on CLDAS land surface fusion data in Tianjin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 657-665. |
| [10] | GUO Jingyan, XIAO Dong. Changes of summer water vapor in Bengal region and its linkage with the interdecadal Pacific oscillation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 380-389. |
| [11] | WANG Jiajin, XIAO Hongru, YANG Kangquan, WANG Binyan. Water vapor transport characteristics of a continuous rainstorm in Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 474-482. |
| [12] | SU Lijuan, YI Nana, ZHENG Xucheng, SHI Jinli, DENG Xiaodong. Characteristics of water vapor and liquid water in arid and semi-arid region in the central Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 251-259. |
| [13] | BA Li, XI Lizong, CAI Dihua, PANG Zhaoyun, ZHANG Xinhai, YIN Chun. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of atmospheric water vapor and liquid water in eastern section of the Qilian Mountains based on microwave radiometer data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 64-72. |
| [14] | CHEN Xiaoting, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Hui, PENG Li. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [15] | WEN Xiaopei, WU Wei, LI Changyi, LI Ji, XiAO Mingjing, LIU Shijun, ZHU Wengang. Influences of updated land-use datasets on WRF simulations for high-temperature weather in Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 868-878. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
