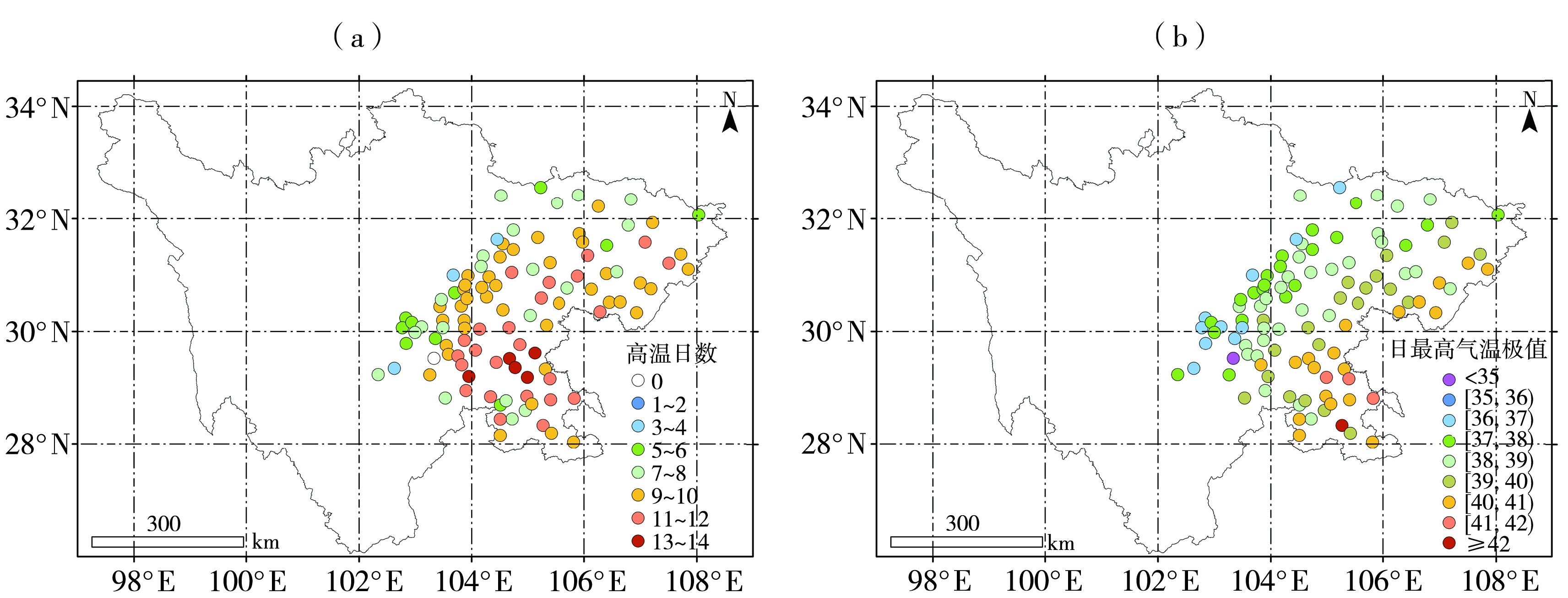
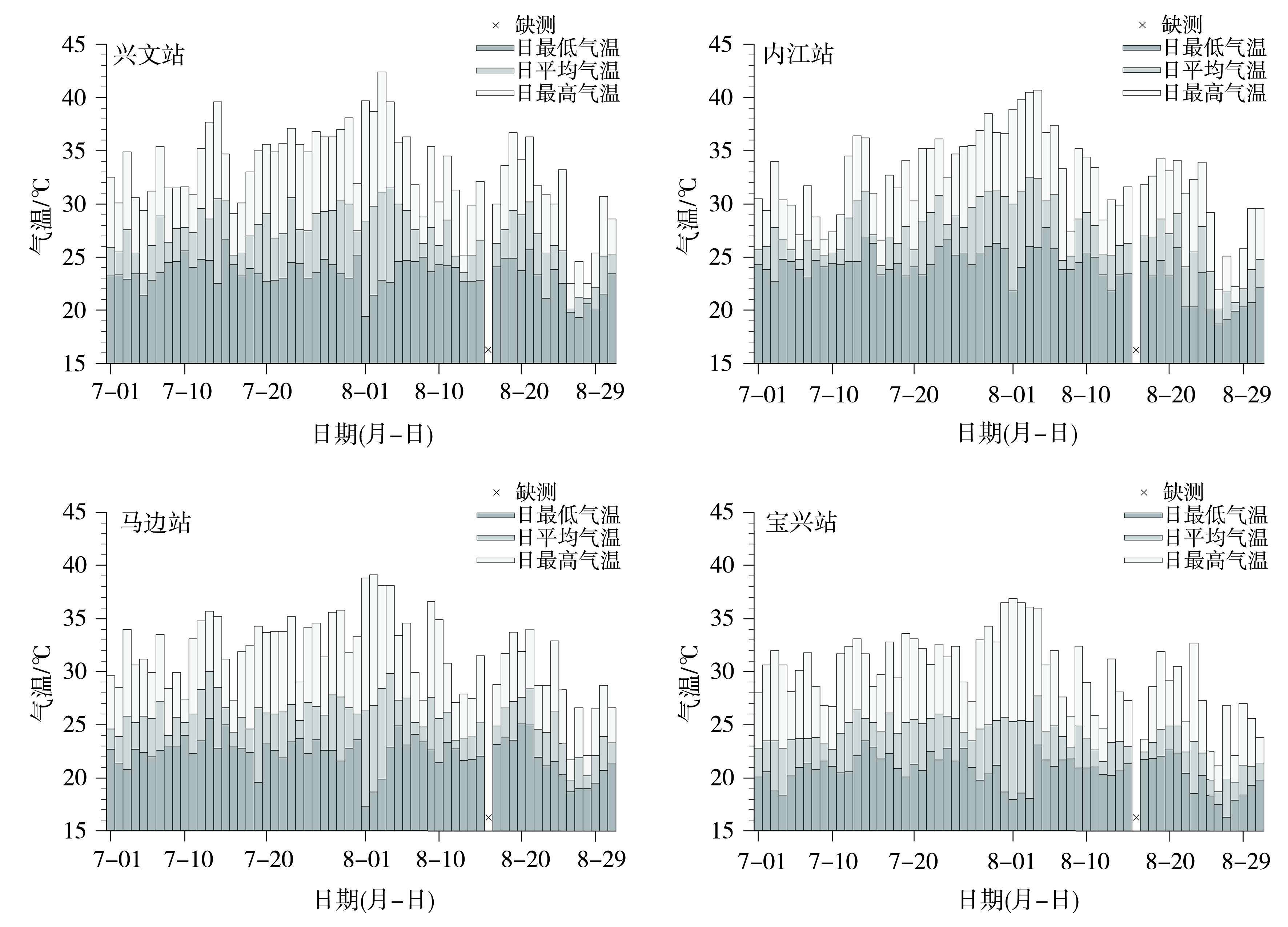
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 923-932.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0923
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of atmospheric circulation background and main impacts of heatwave in Sichuan Basin from July to August 2021
YU Haohui1( ), ZHOU Changyan2(
), ZHOU Changyan2( ), CHEN Chao2, CHEN Yongren1
), CHEN Chao2, CHEN Yongren1
- 1. Sichuan Meteorological Disaster Prevention Technology Center, Chengdu 610072, China
2. Institute of Plateau Meteorology, CMA, Key Laboratory of Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateau and Basin of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
-
Received:2022-07-02Revised:2022-12-07Online:2023-12-31Published:2024-01-03
2021年7—8月四川盆地高温热浪大气环流背景及影响分析
- 1.四川省气象灾害防御技术中心,四川 成都 610072
2.中国气象局成都高原气象研究所;高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
-
通讯作者:周长艳(1979—),女,研究员,主要从事气候及气候变化研究。E-mail:zcy001124@163.com 。 -
作者简介:于浩慧(1993—),女,工程师,主要从事气象灾害风险评估研究。E-mail: yuhaoh984264@163.com。 -
基金资助:四川省自然科学基金项目(2022NSFSC0230);国家自然科学基金项目(41775084)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Haohui, ZHOU Changyan, CHEN Chao, CHEN Yongren. Analysis of atmospheric circulation background and main impacts of heatwave in Sichuan Basin from July to August 2021[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 923-932.
于浩慧, 周长艳, 陈超, 陈永仁. 2021年7—8月四川盆地高温热浪大气环流背景及影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 923-932.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-06-0923
| 站名 | 最高气温/℃ | 出现日期 | 历史最高气温/℃ | 出现日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 内江 | 40.7 | 2021-08-04 | 40.4 | 2006-08-12 |
| 隆昌 | 40.5 | 2021-08-03 | 40.3 | 2011-08-17 |
| 泸县 | 41.9 | 2021-08-03 | 41.4 | 2011-08-17 |
| 富顺 | 41.5 | 2021-08-03 | 41.3 | 2006-08-12 |
| 马边 | 39.1 | 2021-08-02 | 37.1 | 2019-08-16 |
| 犍为 | 39.6 | 2021-08-03 | 39.3 | 2006-08-11 |
| 郫县 | 37.9 | 2021-08-02 | 37.5 | 2015-07-25 |
| 宝兴 | 36.9 | 2021-08-01 | 35.6 | 2015-07-25 |
| 彭山 | 39.1 | 2021-08-03 | 39.0 | 2020-07-27 |
| 新都 | 38.4 | 2021-08-02 | 38.2 | 2015-07-25 |
| 广汉 | 38.5 | 2021-08-02 | 37.8 | 2015-07-25 |
| 邛崃 | 38.3 | 2021-08-02 | 38.2 | 2020-07-26 |
| 绵竹 | 37.2 | 2021-08-02 | 36.2 | 2002-07-14 |
Tab.1 Statistics of meteorological stations with daily maximum temperature breaking the historical record in Sichuan from 25 July to 9 August 2021
| 站名 | 最高气温/℃ | 出现日期 | 历史最高气温/℃ | 出现日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 内江 | 40.7 | 2021-08-04 | 40.4 | 2006-08-12 |
| 隆昌 | 40.5 | 2021-08-03 | 40.3 | 2011-08-17 |
| 泸县 | 41.9 | 2021-08-03 | 41.4 | 2011-08-17 |
| 富顺 | 41.5 | 2021-08-03 | 41.3 | 2006-08-12 |
| 马边 | 39.1 | 2021-08-02 | 37.1 | 2019-08-16 |
| 犍为 | 39.6 | 2021-08-03 | 39.3 | 2006-08-11 |
| 郫县 | 37.9 | 2021-08-02 | 37.5 | 2015-07-25 |
| 宝兴 | 36.9 | 2021-08-01 | 35.6 | 2015-07-25 |
| 彭山 | 39.1 | 2021-08-03 | 39.0 | 2020-07-27 |
| 新都 | 38.4 | 2021-08-02 | 38.2 | 2015-07-25 |
| 广汉 | 38.5 | 2021-08-02 | 37.8 | 2015-07-25 |
| 邛崃 | 38.3 | 2021-08-02 | 38.2 | 2020-07-26 |
| 绵竹 | 37.2 | 2021-08-02 | 36.2 | 2002-07-14 |

Fig.3 Spatial distributions of daily highest temperature on 25 (a), 26 (b), 29 (c) July and 3 (d), 5 (e), 7 (f) August 2021 in the Sichuan Basin (Unit: ℃)
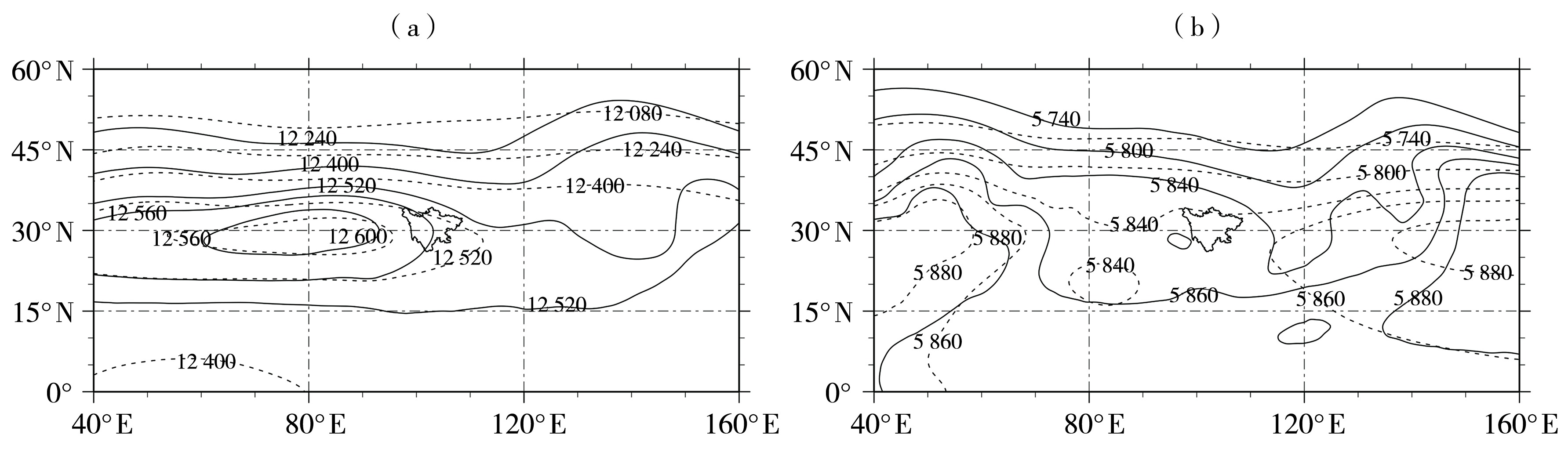
Fig.5 The average geopotential height from July to August during 1980-2010 (dashed lines) and from 25 July to 9 August 2021 (solid lines) at 200 hPa (a) and 500 hPa (b) (Unit: gpm)
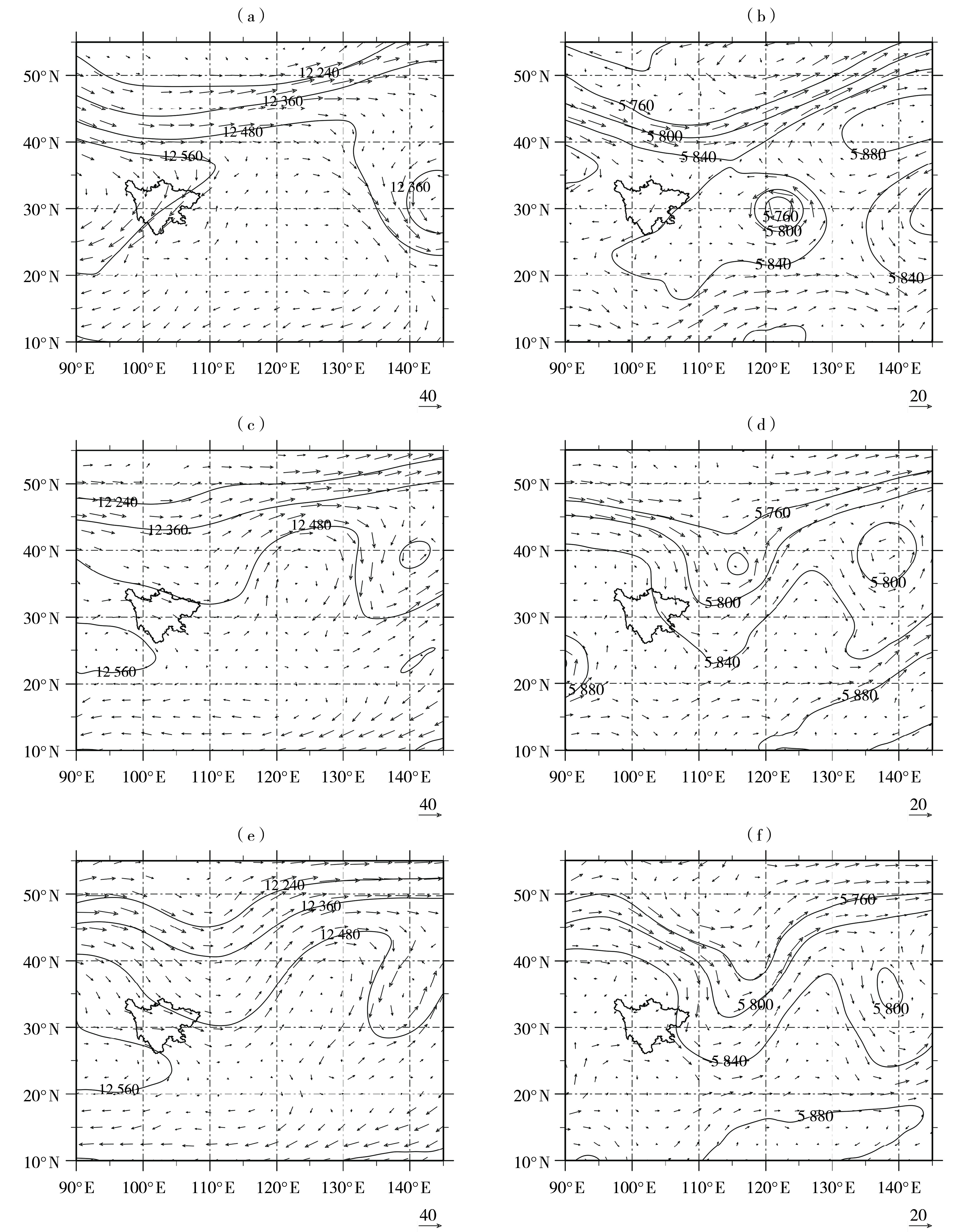
Fig.6 The 200 hPa (a, c, e) and 500 hPa (b, d, f) geopotential height field (contours, Unit: gpm) and wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) on 25 (a, b), 29 (c, d) and 30 (e, f) July 2021
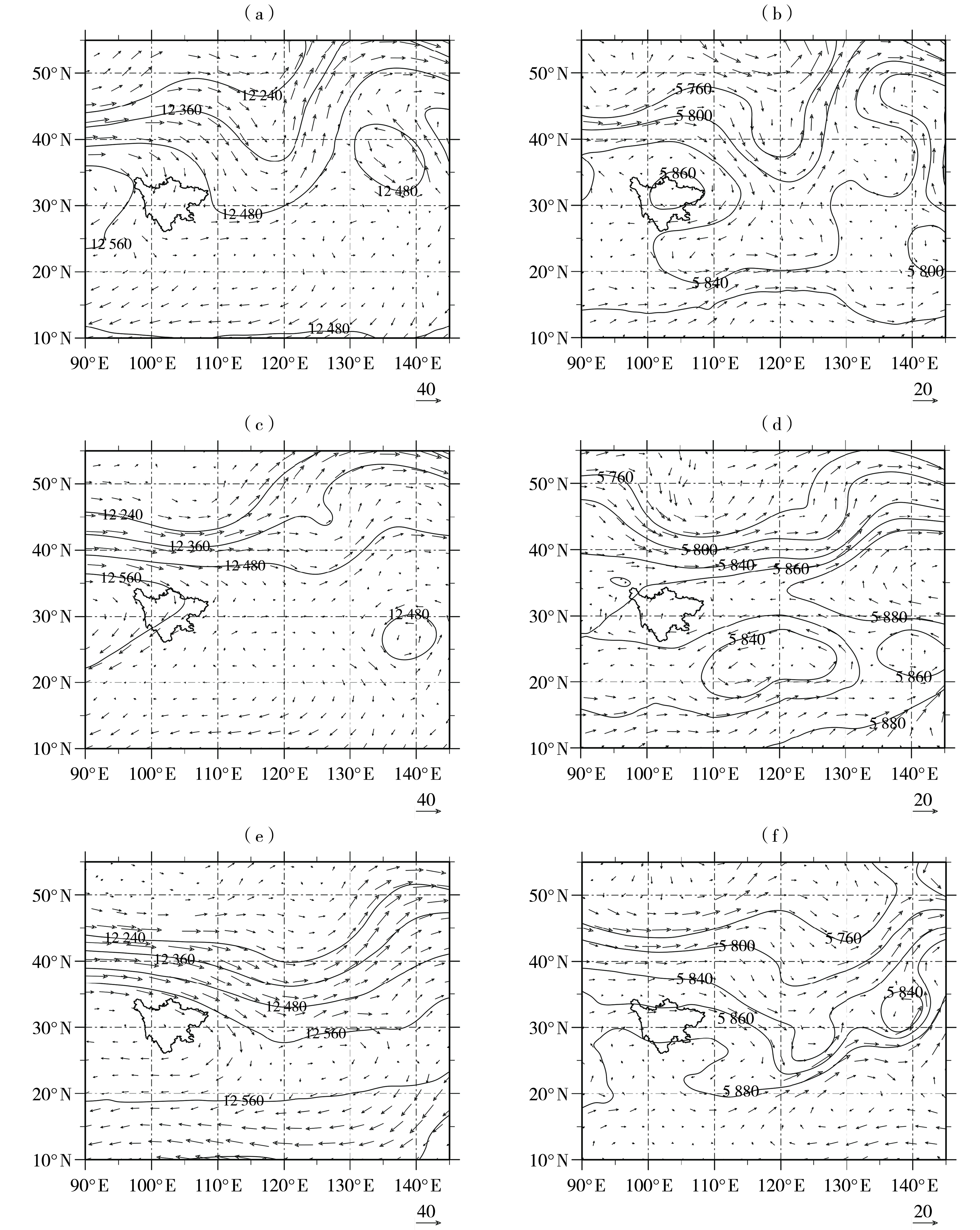
Fig. 7 The 200 hPa (a, c, e) and 500 hPa (b, d, f) geopotential height field (contours, Unit: gpm) and wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) on 1 (a, b), 3 (c, d) and 7 (e, f) August 2021
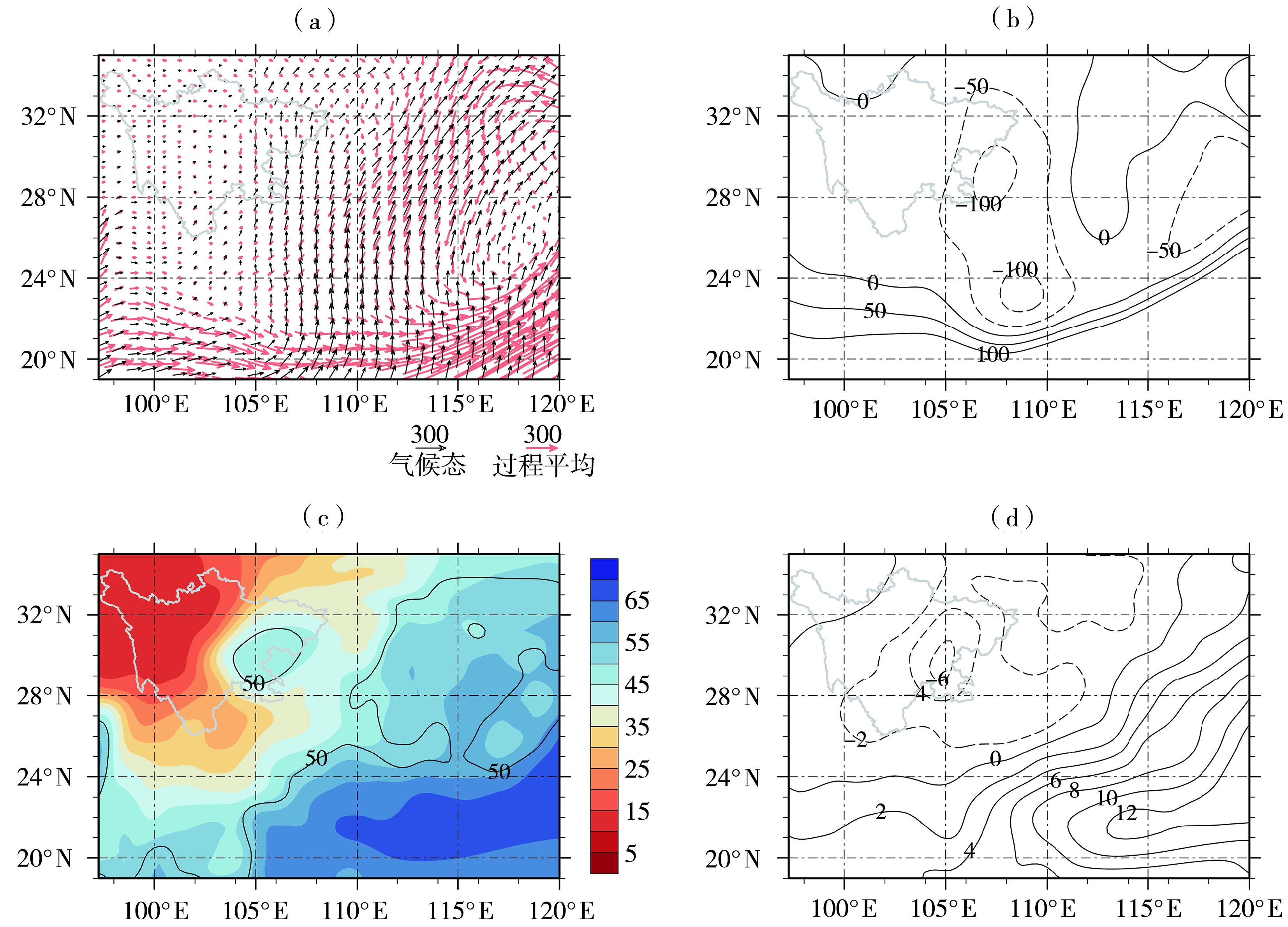
Fig.8 The process average (a, arrow vectors) and anomaly field (b) of the vertically integrated water vapor flux (Unit: kg·m-1·s-1), and the process average (c, color shaded and isolines) and anomaly field (d) of atmospheric precipitable water ( Unit: kg·m-2) in Sichuan and its surrounding areas from 25 July to 9 August 2021

Fig.9 Heat island intensity of Chengdu city from 25 July to 9 August 2021 (a) and spatial distribution of ground temperature on 1 (b) and 2 (c) August 2021 (Unit: ℃)
| [1] | 曹文静, 孙傅, 刘益宏, 等, 2018. 极端高温事件对城市用水量和供水管网系统的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 14(5): 485-494. |
| [2] | 陈超, 庞艳梅, 张玉芳, 2010. 近50年来四川盆地气候变化特征研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 32(9): 115-120. |
| [3] | 丁金才, 叶其欣, 丁长根, 2001. 上海地区高温分布的诊断分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 14(4): 494-499. |
| [4] | 丁金才, 张志凯, 奚红, 等, 2002. 上海地区盛夏高温分布和热岛效应的初步研究[J]. 大气科学, 26(3): 412-420. |
| [5] | 郭渠, 孙卫国, 程炳岩, 等, 2009. 重庆近48年来高温天气气候特征及其环流形势[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 18(1): 52-59. |
| [6] | 黄楚惠, 李国平, 张芳丽, 等, 2020. 近10 a气候变化影响下四川山地暴雨事件的演变特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 39(4): 335-343. |
| [7] | 黄小梅, 赵旋, 肖丁木, 2019. 1961—2016年四川盆地夏季高温热浪变化特征分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 39(2): 14-22. |
| [8] |
何泽能, 张德军, 叶勤玉, 等, 2022. 近40 a重庆城市热岛特征及其与天气状况的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 683-689.
DOI |
| [9] |
吉莉, 司云燕, 徐前进, 等, 2018. 1951—2016年重庆北碚高温热浪变化特征及其对花木生长的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 34(27): 152-158.
DOI |
| [10] |
贾佳, 胡泽勇, 2017. 中国不同等级高温热浪的时空分布特征及趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, 32(5): 546-559.
DOI |
| [11] | 金爱浩, 2019. 华南夏季极端高温年际、年代际变化及其与海温的可能联系[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| [12] | 李超骕, 朱鹏辉, 李可欣, 等, 2023. 城市形态与气候韧性的关联性实证研究——以澳门的雨洪事件为例[J]. 国际城市规划, 38(4): 48-57. |
| [13] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 748-763.
DOI |
| [14] | 彭京备, 张庆云, 布和朝鲁, 2007. 2006年川渝地区高温干旱特征及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(3): 464-474. |
| [15] | 仕仁睿, 齐冬梅, 陈丹, 等, 2021. 2016年四川省持续性高温天气时空变化特征及其成因[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 41(2): 77-82. |
| [16] | 四川省气候中心, 2021. 四川省气候公报[R]. |
| [17] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 764-770.
DOI |
| [18] | 田颖, 张书余, 罗斌, 等, 2013. 热浪对人体健康影响的研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 3(2): 49-54. |
| [19] | 王国复, 叶殿秀, 张颖娴, 等, 2018. 2017年我国区域性高温过程特征及异常大气环流成因分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 14(4): 341-349. |
| [20] | 吴遥, 唐红玉, 蒋兴文, 等, 2019. 重庆市一次特强区域性高温天气过程诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 817-826. |
| [21] | 肖安, 周长艳, 2017. 基于超热因子的中国热浪事件气候特征分析[J]. 气象, 43(8): 943-952. |
| [22] | 徐金芳, 邓振镛, 陈敏, 2009. 中国高温热浪危害特征的研究综述[J]. 干旱气象, 27(2): 163-167. |
| [23] | 杨续超, 陈葆德, 胡可嘉, 2015. 城市化对极端高温事件影响研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 34(10): 1 219-1 228. |
| [24] |
周斌, 王春学, 张顺谦, 2021. 1961—2018年四川盆地极端伏旱日数准2 a周期变化特征及其可能成因[J]. 干旱气象, 39(5): 727-733.
DOI |
| [25] | 周冠博, 高拴柱, 2021. 2021年8月大气环流和天气分析[J]. 气象, 47(11): 1 426-1 432. |
| [26] | 周长春, 汪丽, 郭善云, 等, 2014. 四川盆地高温热浪时空特征及预报模型研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 34(3): 51-57. |
| [27] | 周长艳, 张顺谦, 齐冬梅, 等, 2013. 近50年四川高温变化特征及其影响[J]. 高原气象, 32(6): 1 720-1 728. |
| [28] | 周惜荫, 李谢辉, 2021. 1978—2017年西南地区干湿时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 357-365. |
| [29] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等, 2007. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [30] |
张渝晨, 田宏伟, 2023. 近17 a郑州城市热岛时空演变及驱动机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 403-412.
DOI |
| [31] | DAI A, TRENBERTH K E, KARL T R, 1999. Effects of clouds, soil moisture, precipitation, and water vapor on diurnal temperature range[J]. Journal of Climate, 12(8): 2 451-2 473. |
| [32] | FOUNDA D, PIERROS F, PETRAKIS M, et al, 2015. Interdecadal variations and trends of the urban heat island in athens (Greece) and its response to heat waves[J]. Atmospheric Research, 161/162: 1-13. |
| [33] | LUO M, NGAR C L, 2018. Increasing heat stress in urban areas of eastern China: acceleration by urbanization[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(23): 13 060-13 069. |
| [34] | SCHÄR C, VIDALE P L, LÜTHI D, et al, 2004. The role of increasing temperature variability in European summer heatwaves[J]. Nature, 427(6972): 332-336. |
| [35] | ZHAO L, OPPENHEIMER M, ZHU Q, et al, 2018. Interactions between urban heat islands and heat waves[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 13(3). DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa9f73 |
| [1] | ZHANG Yuchen, TIAN Hongwei. Analysis of spatial-temporal variation of urban heat island and driving mechanism in Zhengzhou in recent 17 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 403-412. |
| [2] | LI Yiping, ZHANG Jinyu, YUE Ping, WANG Suping, ZHA Pengfei, WANG Lijuan, SHA Sha, ZHANG Liang, ZENG Dingwen, REN Yulong, HU Die. Study on characteristics of severe drought event over Yangtze River Basin in summer of 2022 and its causes [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 733-747. |
| [3] | HE Zeneng, ZHANG Dejun, YE Qinyu, CHEN Zhijun, YANG Shiqi, GAO Yanghua. Characteristics of urban heat island in Chongqing in recent 40 years and its association with weather conditions [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 683-689. |
| [4] | MA Yan, GUO lina. Impact of Climate Change and Urbanization on Precipitation in Qingdao [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 920-928. |
| [5] | LIU Xin, LIU Linchun, ZHAO Yanli, ZHONG Xia, SHEN Ziwei, LIU Shimeng. Variation Characteristics of Atmosphere Self-cleaning Ability and Its Influencing Factors in Hohhot City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(4): 632-638. |
| [6] | HUANG Helou, DING Yeyi, TU Xiaoping, ZHAO Changyu, YAO Risheng. Impact of Urbanization on Extreme Temperature and Human Comfort Degree in Ningbo City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 396-403. |
| [7] | DONG Junling, LIU Chao, SU Aifang. Impact of Urbanization on a Torrential Rain Process in Zhengzhou Region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(6): 922-932. |
| [8] | ZHAO Caiping, ZHOU Jinhong, LI Zhaoqi, LI Yanhong. Influence of Urbanization on the Change of Rainstorm in Taiyuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 109-118. |
| [9] | SHANG Jianshe, LI Benliang, SUN Xiaoli, XIA Baoxun. Characteristic Analysis of Urban Heat Island Effect in Summer in Ji’nan City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 70-74. |
| [10] | LI Yizhi, LUO Boliang, ZHOU Bi. Impact of Urbanization on Air Temperature Change in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Region of Hu’nan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(2): 257-262. |
| [11] | HUANG Shaoni1, WANG Jianpeng1, WANG Dan2, CHENG Lu3. Simulation and Diagnosis of a Temperature Anomaly Increase Event at Night in Xi’an Region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(2): 270-277. |
| [12] | . A Case Study on the Effect of Urban Underlying Expansion on Atmosphere Boundary Layer Characteristics in Taiyuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(6): 916-925. |
| [13] | CONG Bo,SUN Yitao,LIU Yanjie,ZHOU Heling. Influence of Urbanization on Precipitation Characteristics in Langfang of Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(5): 738-743. |
| [14] | YU Hua,ZHANG Huiqin,BAO Ronggang. Variation Characteristics of Temperature During 1952 -2012 and the Urbanization Impact in Turpan of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(2): 215-219. |
| [15] | WANG Xiaomo,DONG Ning. Effects of the Urbanization Process on Temperature in Ji’ning of Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(4): 732-737. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||