Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 385-394.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-03-0385
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
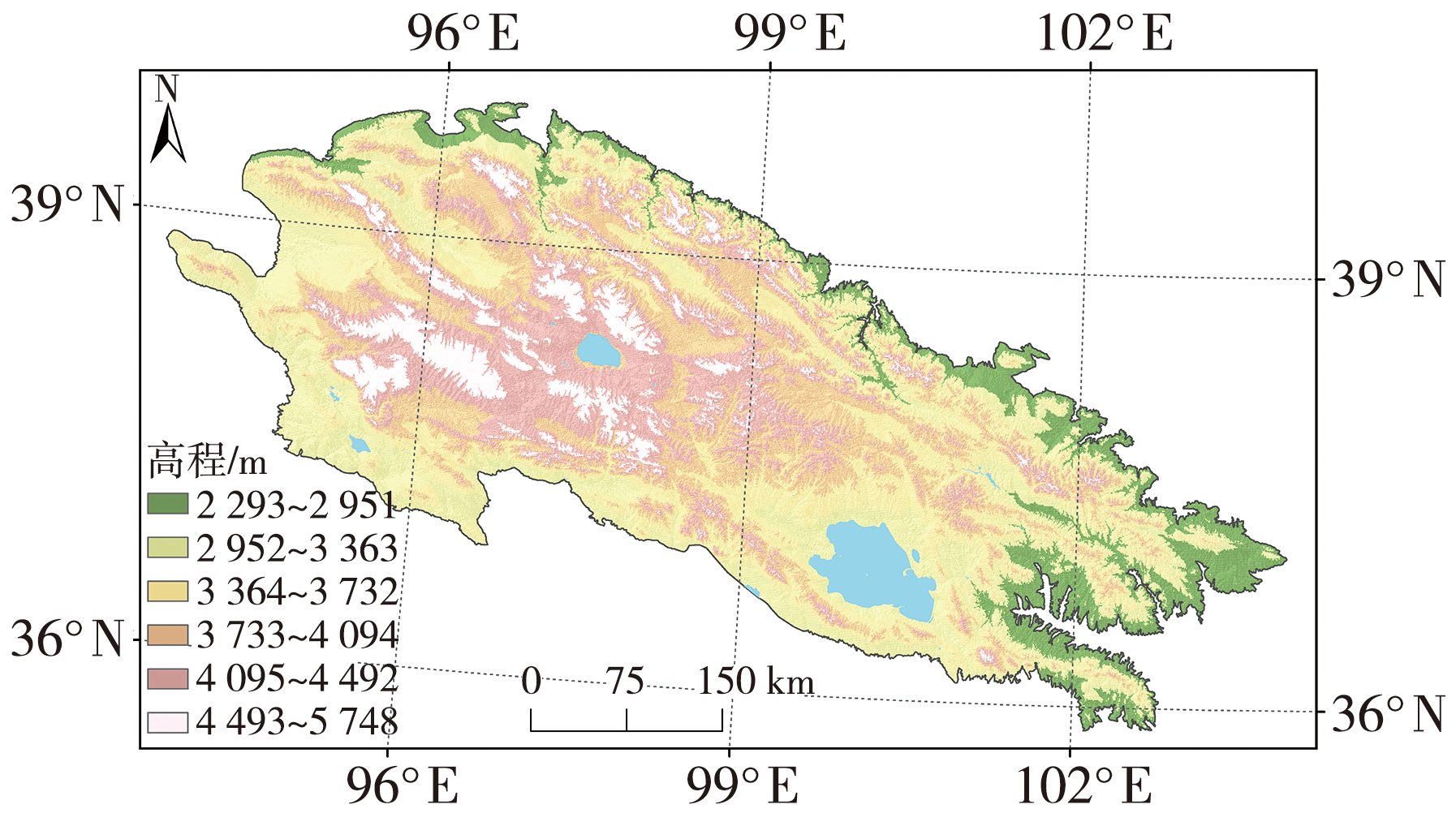
Characteristics of vegetation change and its relationship with climate in the Qilian Mountains over the past 40 years
YANG Fei1,2( ), FENG Xiang1, ZHANG Feimin1, WANG Chenghai1(
), FENG Xiang1, ZHANG Feimin1, WANG Chenghai1( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Resource and Environment of Gansu Province, College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
2. Gansu Academy of Eco-environmental Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2024-03-10Revised:2024-04-29Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-11
过去40 a来祁连山地区植被变化特征及其与气候的关系
- 1.甘肃省气候资源开发及防灾减灾重点实验室,兰州大学大气科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730000
2.甘肃省生态环境科学设计研究院,甘肃 兰州 730000
-
通讯作者:王澄海(1961—),男,教授,主要从事青藏高原气候学、短期气候预测研究。E-mail:wch@lzu.edu.cn 。 -
作者简介:杨斐(1992—),女,硕士,主要从事气候变化研究。E-mail: yangf21@lzu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42275004);国家自然科学基金项目(91837205);甘肃省重点研发计划项目(23YFFA0001);甘肃省重点实验室建设基金项目(20JR10RA654)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Fei, FENG Xiang, ZHANG Feimin, WANG Chenghai. Characteristics of vegetation change and its relationship with climate in the Qilian Mountains over the past 40 years[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 385-394.
杨斐, 冯祥, 张飞民, 王澄海. 过去40 a来祁连山地区植被变化特征及其与气候的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 385-394.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-03-0385

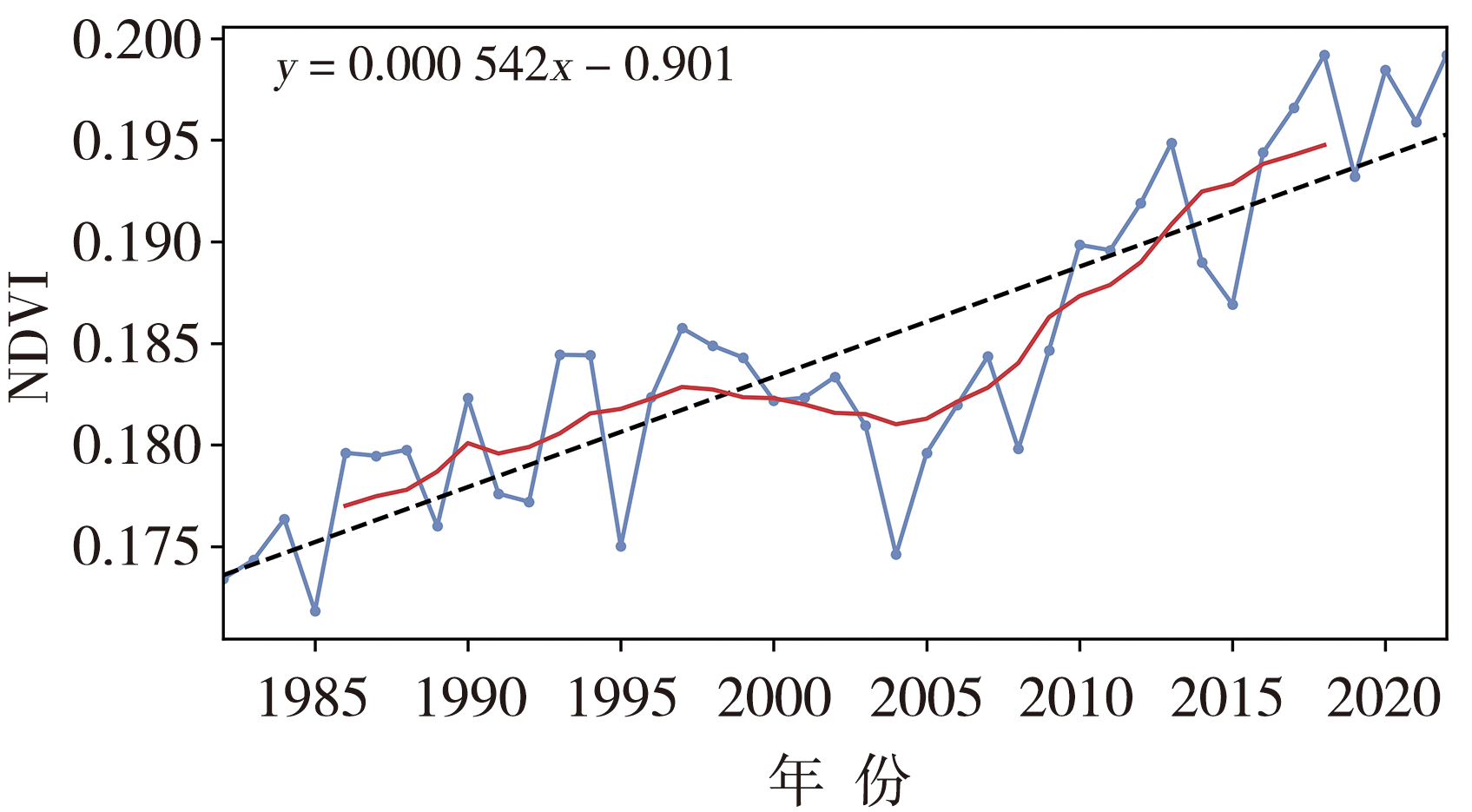
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of NDVI trends in annual (a), spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d) and growing season (e) in the Qilian Mountains from 1982 to 2022 (Unit: ×10-3 a-1) (the black slash areas passing the significance test at α=0.05)
| NDVI变化量 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 生长季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -0.004~0 | 10.19 | 39.30 | 7.90 | 15.37 | 7.69 |
| >0~0.001 | 62.75 | 53.97 | 36.97 | 39.73 | 41.70 |
| >0.001~0.002 | 23.67 | 5.28 | 32.89 | 27.18 | 34.19 |
| >0.002~0.003 | 3.11 | 1.08 | 15.52 | 12.27 | 12.66 |
| >0.003~0.004 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 5.54 | 4.24 | 3.25 |
Tab.1
| NDVI变化量 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 生长季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -0.004~0 | 10.19 | 39.30 | 7.90 | 15.37 | 7.69 |
| >0~0.001 | 62.75 | 53.97 | 36.97 | 39.73 | 41.70 |
| >0.001~0.002 | 23.67 | 5.28 | 32.89 | 27.18 | 34.19 |
| >0.002~0.003 | 3.11 | 1.08 | 15.52 | 12.27 | 12.66 |
| >0.003~0.004 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 5.54 | 4.24 | 3.25 |

Fig.5 The spatial distribution of the correlation coefficient r between NDVI and air temperature in annual (a), spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d) and growing season (e) in the Qilian Mountains from 1982 to 2022 (the black slash areas passing the significance test at α=0.05)
| 相关性 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 生长季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 显著负相关 | 0.32 | 4.36 | 1.61 | 0.14 | 2.29 |
| 不显著负相关 | 7.94 | 19.24 | 8.33 | 28.47 | 9.66 |
| 负相关 | 8.26 | 23.60 | 9.94 | 28.61 | 11.95 |
| 正相关 | 90.09 | 76.39 | 90.06 | 69.27 | 88.05 |
| 不显著正相关 | 33.12 | 39.34 | 28.47 | 59.76 | 30.47 |
| 显著正相关 | 56.97 | 37.05 | 61.59 | 9.51 | 57.58 |
Tab.2
| 相关性 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 生长季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 显著负相关 | 0.32 | 4.36 | 1.61 | 0.14 | 2.29 |
| 不显著负相关 | 7.94 | 19.24 | 8.33 | 28.47 | 9.66 |
| 负相关 | 8.26 | 23.60 | 9.94 | 28.61 | 11.95 |
| 正相关 | 90.09 | 76.39 | 90.06 | 69.27 | 88.05 |
| 不显著正相关 | 33.12 | 39.34 | 28.47 | 59.76 | 30.47 |
| 显著正相关 | 56.97 | 37.05 | 61.59 | 9.51 | 57.58 |

Fig.6 The spatial distribution of the correlation coefficient between NDVI and precipitation in annual (a), spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d) and growing season (e) in the Qilian Mountains from 1982 to 2022 (the black slash areas passing the significance test at α=0.05)
| 相关性 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 生长季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 显著负相关 | 0.72 | 11.01 | 0.93 | 1.39 | 1.61 |
| 不显著负相关 | 13.80 | 51.14 | 18.06 | 43.88 | 14.99 |
| 负相关 | 14.52 | 62.15 | 18.99 | 45.27 | 16.60 |
| 正相关 | 85.48 | 37.84 | 81.01 | 54.72 | 83.40 |
| 不显著正相关 | 41.06 | 34.59 | 43.81 | 53.61 | 35.30 |
| 显著正相关 | 44.42 | 3.25 | 37.20 | 1.11 | 48.10 |
Tab.3
| 相关性 | 年 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 生长季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 显著负相关 | 0.72 | 11.01 | 0.93 | 1.39 | 1.61 |
| 不显著负相关 | 13.80 | 51.14 | 18.06 | 43.88 | 14.99 |
| 负相关 | 14.52 | 62.15 | 18.99 | 45.27 | 16.60 |
| 正相关 | 85.48 | 37.84 | 81.01 | 54.72 | 83.40 |
| 不显著正相关 | 41.06 | 34.59 | 43.81 | 53.61 | 35.30 |
| 显著正相关 | 44.42 | 3.25 | 37.20 | 1.11 | 48.10 |

Fig.7 The spatial distribution of the correlation coefficient between NDVI and temperature (a, b, c) as well as precipitation (d, e, f) in the previous season in spring (a, d), summer (b, e) and autumn (c, f) in the Qilian Mountains from 1982 to 2022 (the black slash areas passing the significance test at α=0.05)
| 相关性 | 气温 | 降水 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | |
| 显著负相关 | 1.18 | 4.36 | 6.68 | 1.57 | 0.58 | 1.51 |
| 不显著负相关 | 40.34 | 19.24 | 24.96 | 47.07 | 15.34 | 13.05 |
| 负相关 | 41.52 | 23.60 | 31.64 | 48.64 | 15.92 | 14.56 |
| 正相关 | 58.51 | 76.40 | 68.35 | 51.36 | 84.09 | 85.44 |
| 不显著正相关 | 52.83 | 39.34 | 42.74 | 48.39 | 64.81 | 38.20 |
| 显著正相关 | 5.68 | 37.06 | 25.61 | 2.97 | 19.28 | 47.24 |
Tab. 4
| 相关性 | 气温 | 降水 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | |
| 显著负相关 | 1.18 | 4.36 | 6.68 | 1.57 | 0.58 | 1.51 |
| 不显著负相关 | 40.34 | 19.24 | 24.96 | 47.07 | 15.34 | 13.05 |
| 负相关 | 41.52 | 23.60 | 31.64 | 48.64 | 15.92 | 14.56 |
| 正相关 | 58.51 | 76.40 | 68.35 | 51.36 | 84.09 | 85.44 |
| 不显著正相关 | 52.83 | 39.34 | 42.74 | 48.39 | 64.81 | 38.20 |
| 显著正相关 | 5.68 | 37.06 | 25.61 | 2.97 | 19.28 | 47.24 |

Fig.8 The spatial distribution of the time coefficients (a, d) corresponding to the first mode of the SVD of NDVI and simultaneous air temperature (a, b, c) and precipitation (d, e, f) in the Qilian Mountains from 1982 to 2022, as well as the anisotropic correlation coefficients of NDVI (b, e) and simultaneous air temperature (c) and precipitation (f)
| [1] | 曹晓云, 周秉荣, 周华坤, 等, 2022. 气候变化对青藏高原植被生态系统的影响研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 40 (6): 1 068-1 080. |
| [2] | 陈桂琛, 彭敏, 黄荣福, 等, 1994. 祁连山地区植被特征及其分布规律[J]. 植物学报, 36(1): 63-72. |
| [3] | 冯起, 李宗省, 王旭峰, 等, 2018. 祁连山生态变化评估报告[R]. 兰州: 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院. |
| [4] | 黄波, 2012. 祁连山地区降水的时空分布特征及数值模拟研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [5] | 黄星星, 2022. 祁连山国家公园水源涵养与土壤保持功能研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [6] | 贾文雄, 陈京华, 2018. 1982—2014年祁连山植被生长季NDVI变化及其对气候的响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(2): 264-268. |
| [7] | 马有绚, 张武, 向亚飞, 等, 2017. 西北干旱半干旱地区植被指数对气温和水分因子的响应[C]// 中国气象学会第34届中国气象学会年会 S4 重大气象干旱成因、物理机制、监测预测与影响论文集, 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [8] | 孙杰, 2007. 1982-2000年中国植被覆盖变化及典型区域与气候因子的响应关系[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| [9] |
孙树娇, 曹晓云, 肖建设, 等, 2023. 基于NDVI-Albedo特征空间的柴达木盆地荒漠化监测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 560-569.
DOI |
| [10] |
王澄海, 张晟宁, 张飞民, 等, 2021. 论全球变暖背景下中国西北地区降水增加问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 36(9): 980-989.
DOI |
| [11] |
王芝兰, 李耀辉, 王劲松, 2015. SVD分析青藏高原冬春积雪异常与西北地区春、夏季降水的相关关系[J]. 干旱气象, 33(3): 363-370.
DOI |
| [12] | 尤联元, 杨景春, 2013. 中国地貌[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| [13] | 尤南山, 蒙吉军, 孙慕天, 2019. 2000—2015年黑河流域中上游NDVI时空变化及其与气候的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 55(1): 171-181. |
| [14] |
张金丹, 刘明春, 李兴宇, 等, 2023. 石羊河流域干湿气候变化特征及对NDVI的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41 (5): 697-704.
DOI |
| [15] | 张景华, 封志明, 姜鲁光, 2011. 土地利用/土地覆被分类系统研究进展[J]. 资源科学, 33(6): 1 195-1 203. |
| [16] | 张强, 张存杰, 白虎志, 等, 2010. 西北地区气候变化新动态及对干旱环境的影响——总体暖干化,局部出现暖湿迹象[J]. 干旱气象, 28(1): 1-7. |
| [17] | 周伟, 王倩, 章超斌, 等, 2013. 黑河中上游草地NDVI时空变化规律及其对气候因子的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 22(1): 138-147. |
| [18] | DENG S F, YANG T B, ZENG B, et al, 2013. Vegetation cover variation in the Qilian Mountains and its response to climate change in 2000-2011[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 10(6): 1 050-1 062. |
| [19] |
DING M J, ZHANG Y L, LIU L S, et al, 2007. The relationship between NDVI and precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 17(3): 259-268.
DOI |
| [20] | GAO X, HUANG X X, LO K, et al, 2021. Vegetation responses to climate change in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve, Northwest China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 28, e01698. DOI: 10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01698. |
| [21] | IPCC, 2023. Summary for Policymakers[R]// Climate Change 2023:Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland. DOI: 10.59327/IPCC/AR6-9789291691647.001. |
| [22] | LIU L, GU H T, XIE J K, et al, 2021. How well do the ERA-Interim, ERA‐5, GLDAS‐2.1 and NCEP‐R2 reanalysis datasets represent daily air temperature over the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 41(2): 1 484-1 505. |
| [23] | PEARSON K, 1894. Contributions to the mathematical theory of evolution[J]. Proceeding of the Royal Society of London, 54: 326-330. |
| [24] | PIAO S L, LIU Q, CHEN A P, et al, 2019. Plant phenology and global climate change: Current progresses and challenges[J]. Global Change Biology, 25(6): 1 922-1 940. |
| [25] | SEN P K, 1968. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's tau[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 63(324): 1 379-1 389. |
| [26] | TIAN H Z, YANG T B, LIU Q P, 2014. Climate change and glacier area shrinkage in the Qilian Mountains, China, from 1956 to 2010[J]. Annals of Glaciology, 55(66): 187-197. |
| [27] | WANG C H, 2023. Climatology in Cold Regions[M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. DOI:10.1002/9781119702689. |
| [28] | WOODWARD F I, MCKEE I F, 1991. Vegetation and climate[J]. Environment International, 17(6): 535-546. |
| [29] | WU X J, SU J B, REN W W, et al, 2023. Statistical comparison and hydrological utility evaluation of ERA5-Land and IMERG precipitation products on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 620, 129384. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129384. |
| [30] | YANG H, LUO P, WANG J, et al, 2015. Ecosystem evapotranspiration as a response to climate and vegetation coverage changes in northwest Yunnan, China[J]. PLOS ONE, 10(8), e0134795. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134795. |
| [31] | YANG J T, YANG K, ZHANG F M, et al, 2023. Contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to historical changes in vegetation cover and its future projections in the Yellow River Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 43(14): 6 434-6 449. |
| [1] | TIAN Guozhen, REN Yuhuan, YANG Qian, HUANG Xiaoyan, ZHAO Sinan, ZUO Xiaorui, LI Zhicai. Application study of three remote sensing drought monitoring indices in the eastern Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 338-346. |
| [2] | DUAN Jing, WANG Xin, CHEN Yong, GUO Qiang, WANG Tiantian, CHEN Tianyu, CHEN Baojun. Characteristics of rainfall and convection in summer in the middle of the Qilian Mountains [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 405-414. |
| [3] | YANG Jing, ZHANG Yajie, CHEN Jinwei, ZHU Jingjing, ZHANG Mingjie, Lin Shaowu. Research on the applicability of three vegetation indices based on MODIS data in vegetation monitoring of Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 274-282. |
| [4] | SHA Sha, WANG Lijuan, WANG Xiaoping, HU Die, ZHANG Liang. Study on monitoring method of agricultural drought in Gansu Province based on Temperature Vegetation Dryness Index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 27-38. |
| [5] | ZHANG Jindan, LIU Mingchun, LI Xingyu, DING Wenkui, YANG Hua, JIANG Jufang. Characteristics of dry-wet climate change and its influence on NDVI in Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 697-704. |
| [6] | SUN Shujiao, CAO Xiaoyun, XIAO Jianshe, SUN Weijie, ZHU Cunxiong. Desertification monitoring in the Qaidam Basin based on NDVI-Albedo feature space [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 560-569. |
| [7] | BA Li, XI Lizong, CAI Dihua, PANG Zhaoyun, ZHANG Xinhai, YIN Chun. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of atmospheric water vapor and liquid water in eastern section of the Qilian Mountains based on microwave radiometer data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 64-72. |
| [8] | CHEN Yanli, TANG Meirong, ZHANG Hui, MO Jianfei, QIAN Shuan. Response difference of fractional vegetation cover and net primary productivity to SPEI drought index in karst areas of Guangxi [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1042-1050. |
| [9] | CAO Xiaoyun, ZHOU Bingrong, ZHOU Huakun, QIAO Bin, YAN Yuqian, ZHAO Tong, CHEN Qi, ZHAO Huifang, YU Hongyan. Research progress on the impact of climate change on vegetation ecosystem in the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1068-1080. |
| [10] | FAN Jinjin, QIN Pengcheng, SHI Ruiqin, LI Mengrong, DU Liangmin. Characteristics of compound hot and drought disasters in Hubei under the background of climate change [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 780-790. |
| [11] | CEHN Xiaochen, TANG Zhenfei, CHEN Xikuan, ZHENG Chaoyu, LI Xinxin, YANG Ting. Projection of extreme temperature in Fujian based on CMIP6 output [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 415-423. |
| [12] | WU Bin, QIAN Ye, WANG Ruifang, ZHAO Xin, JIN Lei. Assessment of Largescale Environmental Factors Affecting Typhoon Intensity in Northwest Pacific Simulated by Global Climate Models [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 466-479. |
| [13] | LIU Mingyan, FANG Yihe, SUN Fenghua, ZHAO Chunyu, HOU Yiling, CUI Yan, ZHOU Xiaoyu. Contributions of Climate Changes and Human Activities to Runoff Change in the Taizihe Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 244-251. |
| [14] | YI Xue, YANG Sen, LIU Mingyan, LI Tao, HOU Yiling, CUI Yan. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Vegetation Coverage and Its Response to Climate Change in Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 252-261. |
| [15] | ZHAO Lin, WANG Changke, AI Wanxiu. Analysis of Gender Differences in Public Perception and Adaptation to Climate Change in Northern Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 168-174. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||