Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 339-354.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0339
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatial distribution and intensity variation characteristics of land-atmosphere coupling in the Northern Hemisphere over the past 70 years
WANG Chenghai( ), SHANG Junxiang, ZHANG Feimin, YANG Kai
), SHANG Junxiang, ZHANG Feimin, YANG Kai
- Key Laboratory of Climate Resource Development and Disaster Prevention in Gansu Province, College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730000,China
-
Received:2025-03-20Revised:2025-05-18Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
北半球近70 a陆气耦合空间分布及其强度变化特征
- 甘肃省气候资源开发及防灾减灾重点实验室,兰州大学大气科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730000
-
作者简介:王澄海(1962—),男,教授, 主要从事青藏高原气候学、短期气候预测研究。E-mail:wch@lzu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42175064)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Chenghai, SHANG Junxiang, ZHANG Feimin, YANG Kai. Spatial distribution and intensity variation characteristics of land-atmosphere coupling in the Northern Hemisphere over the past 70 years[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 339-354.
王澄海, 尚君翔, 张飞民, 杨凯. 北半球近70 a陆气耦合空间分布及其强度变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 339-354.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0339
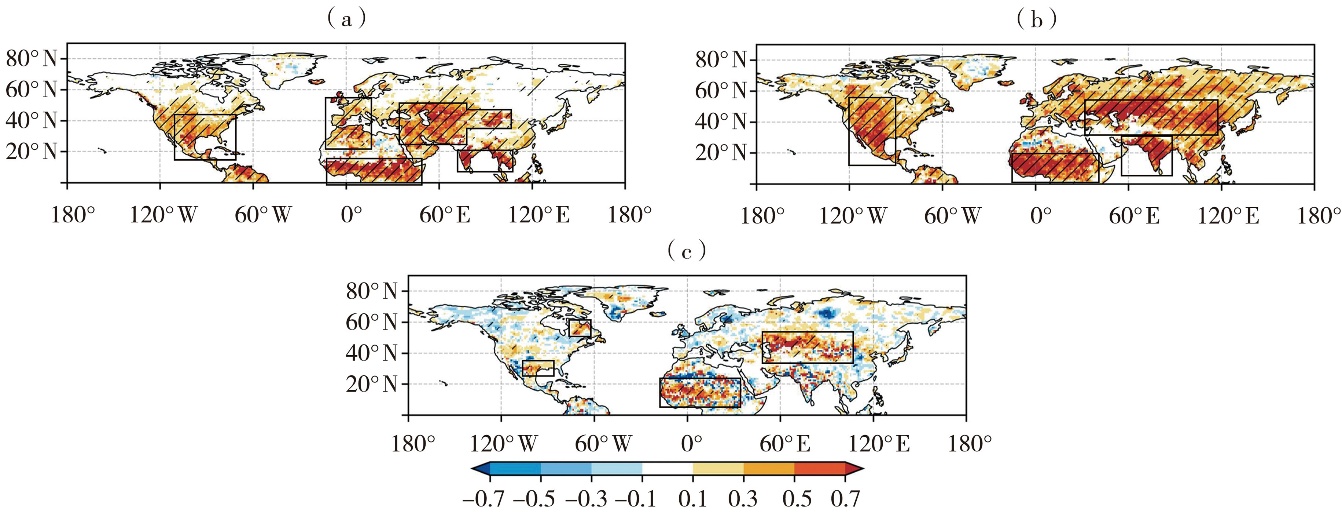
Fig.1 Spatial distribution of the land-atmosphere coupling index λ over the Northern Hemisphere during the period of 1950-2020(a) spring, (b) summer, (c) cross-seasonal (spring to summer) (The diagonal area passes the significance test at 0.05, the black box area represents the key area of land-atmosphere coupling)
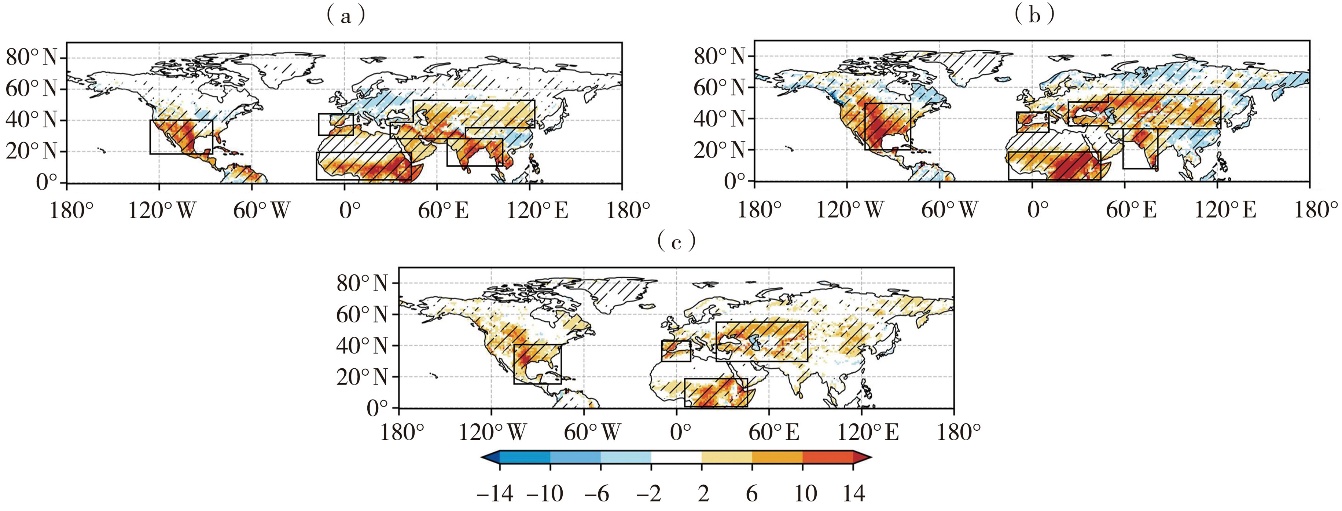
Fig.2 Spatial distribution of the land-atmosphere coupling index ISM-LH over the Northern Hemisphere during the period of 1950-2020 (Unit: W·m-2)(a) spring, (b) summer, (c) cross-seasonal (spring to summer)
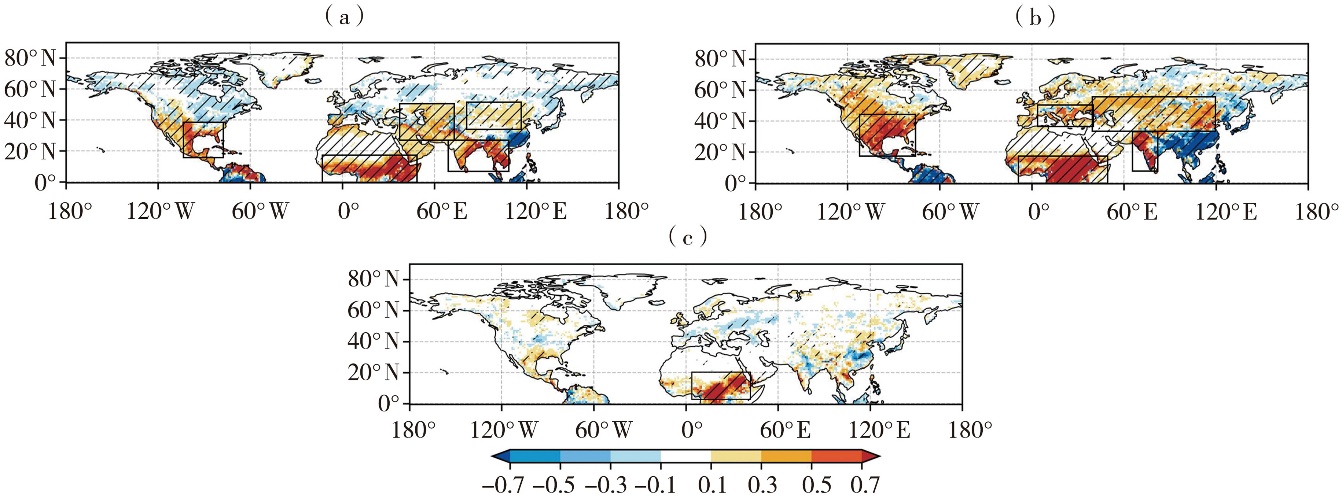
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of the land-atmosphere coupling index ILH-Pr over the Northern Hemisphere during the period of 1950-2020 (Unit: mm/mon)(a) spring, (b) summer, (c) cross-seasonal (spring to summer)

Fig.4 The locations of key regions of land-atmosphere coupling over the Northern Hemisphere in spring and summer (a) and during spring to summer (b) from 1950 to 2020, as well as the spatial distribution of drought index climate state from 1991 to 2020 (c)
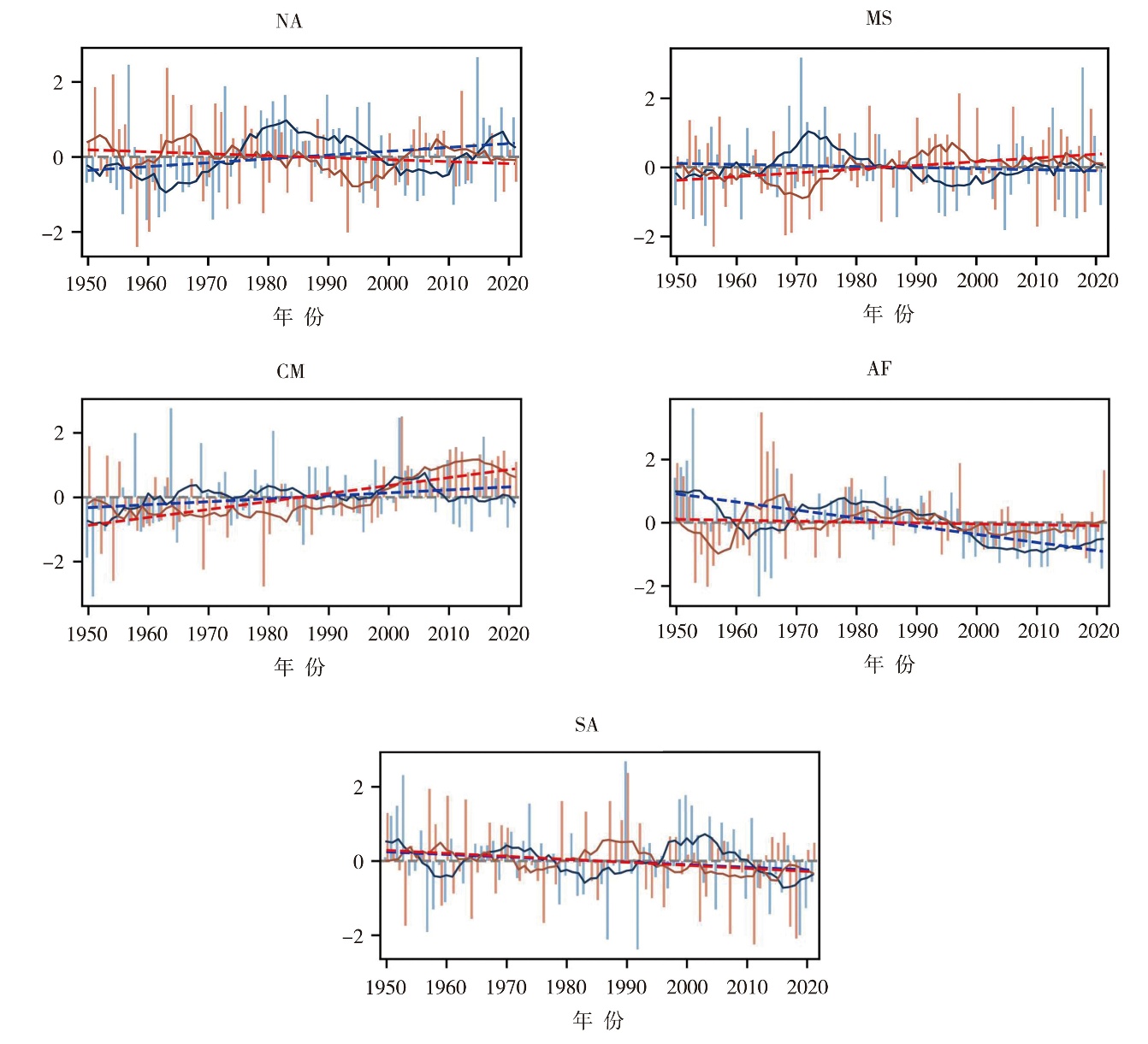
Fig.5 Interannual variation of spring land-atmosphere coupling intensity and precipitation in five land-atmosphere coupling key areas from 1950 to 2020 (The blue (red) histogram is the standardized precipitation (coupling index), the blue (red) dotted line is the linear trend of precipitation (coupling index), and the blue (red) broken line is the 9-year moving average of precipitation (coupling indexes), the same as below)
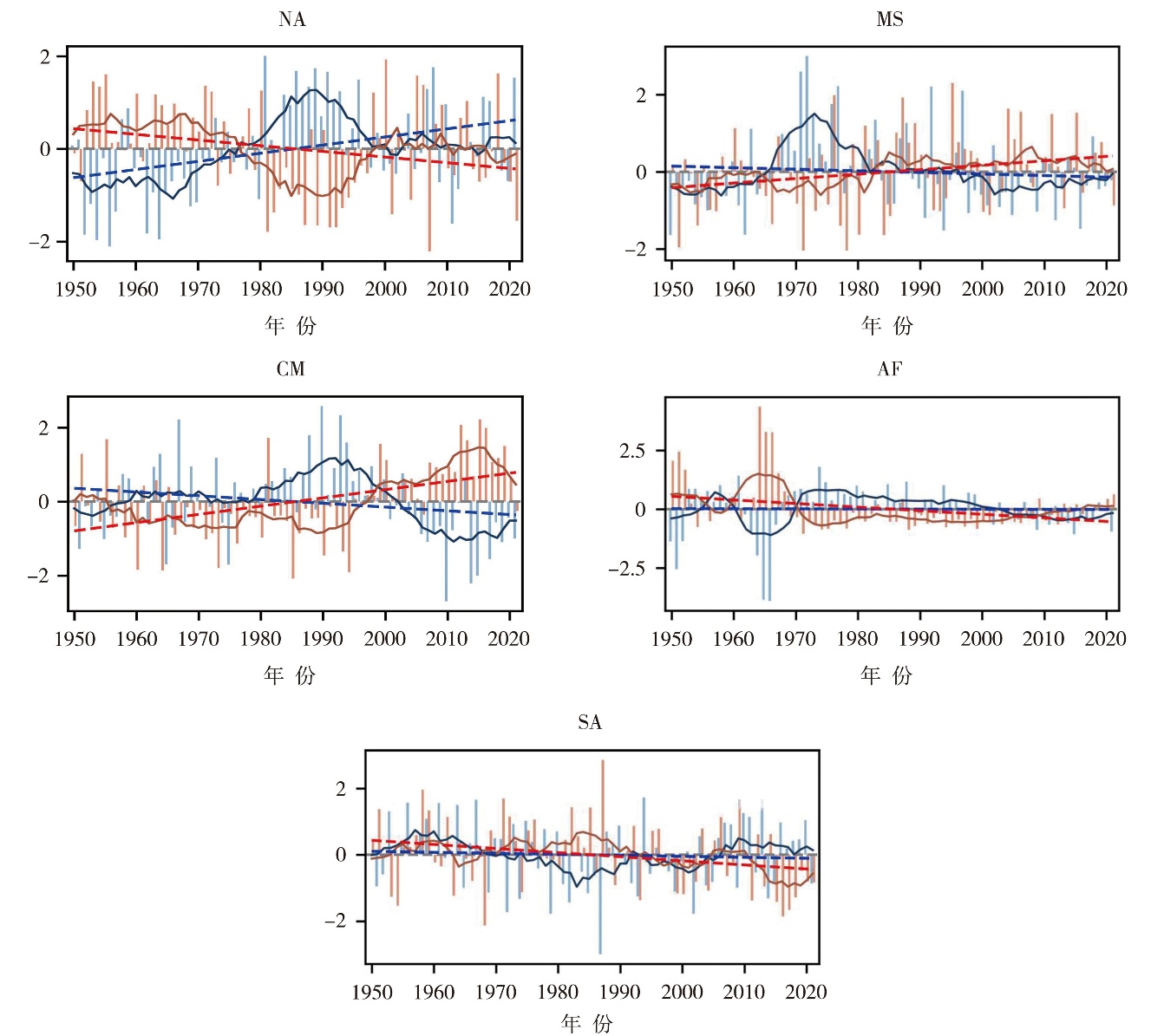
Fig.6 Interannual variation of summer land-atmosphere coupling intensity and precipitation in five land-atmosphere coupling key areas from 1950 to 2020
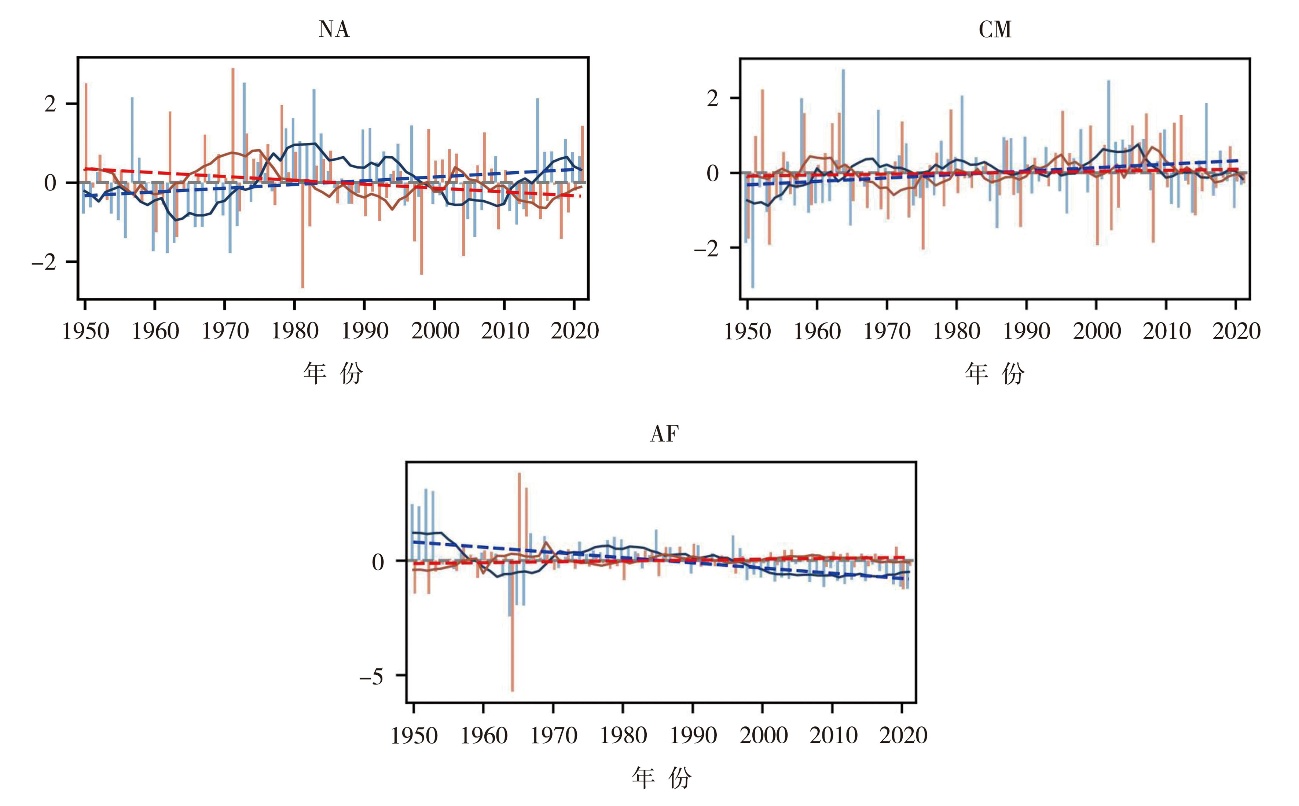
Fig.7 Interannual variation of spring-summer land-atmosphere coupling intensity and summer precipitation in three land-atmosphere coupling key areas from 1950 to 2020
| 时段 | NA | MS | CM | AF | SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | -0.350** | -0.469** | -0.211* | -0.164 | -0.335** |
| 夏季 | -0.580** | 0.071 | -0.301** | -0.821** | -0.217* |
| 春夏之间 | -0.156 | 0.044 | -0.167 |
Tab.1 Correlation coefficients between the land-atmosphere coupling intensity and precipitation in the Northern Hemisphere
| 时段 | NA | MS | CM | AF | SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | -0.350** | -0.469** | -0.211* | -0.164 | -0.335** |
| 夏季 | -0.580** | 0.071 | -0.301** | -0.821** | -0.217* |
| 春夏之间 | -0.156 | 0.044 | -0.167 |
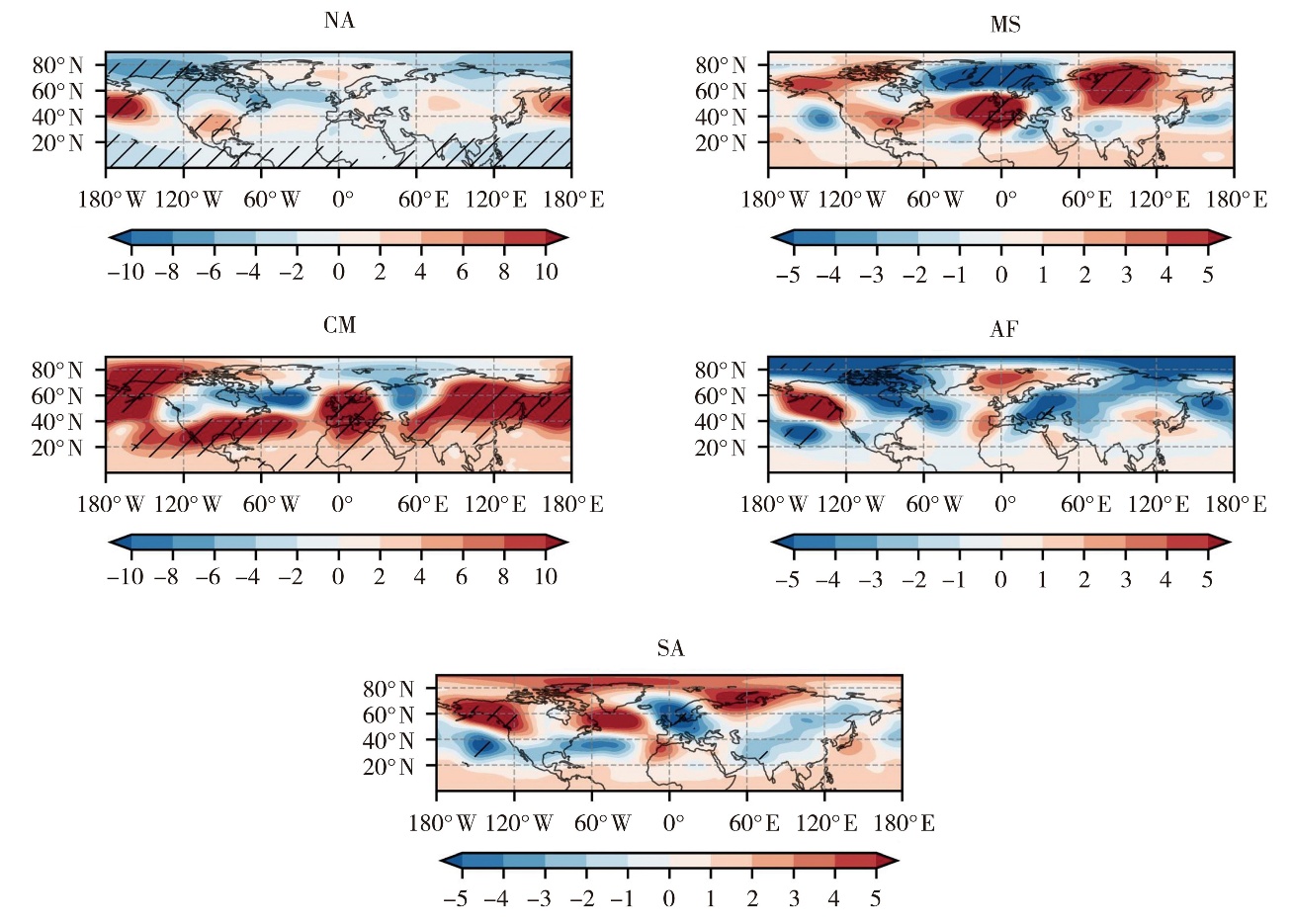
Fig.8 The 500 hPa geopotential height regressed by the index of land-atmosphere coupling strength over the Northern Hemisphere in spring during 1950-2020 (Unit: gpm) (the diagonal area passing the significance test at 0.05,the same as below)
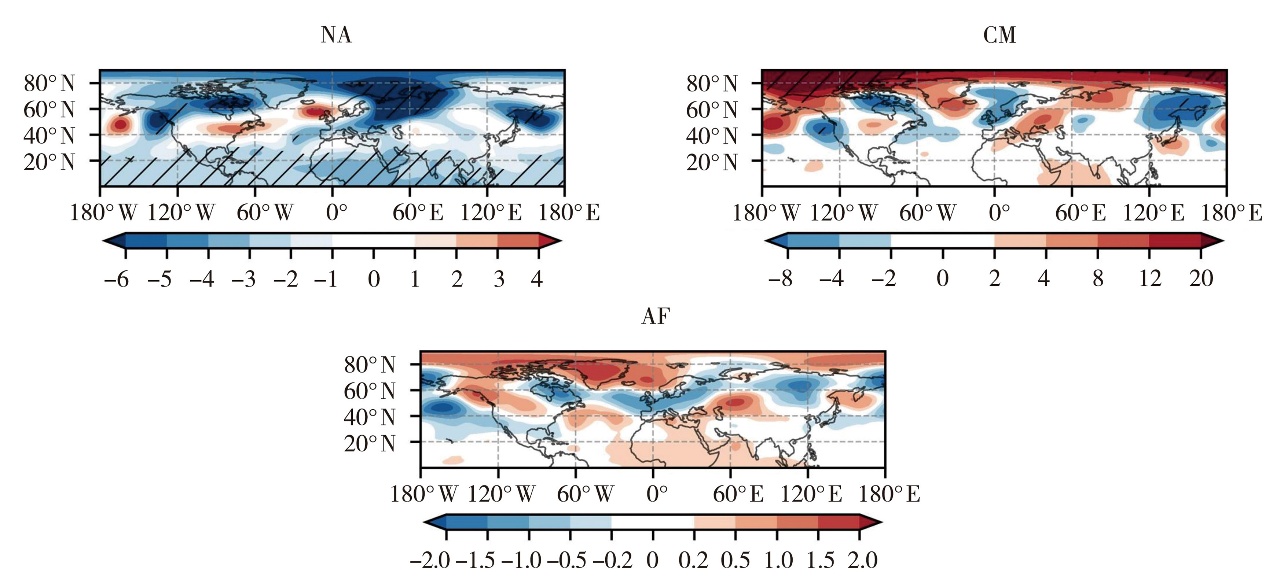
Fig.10 The 500 hPa geopotential height regressed by the index of land-atmosphere coupling strength between spring and summer over the Northern Hemisphere during 1950-2020 (Unit: gpm)
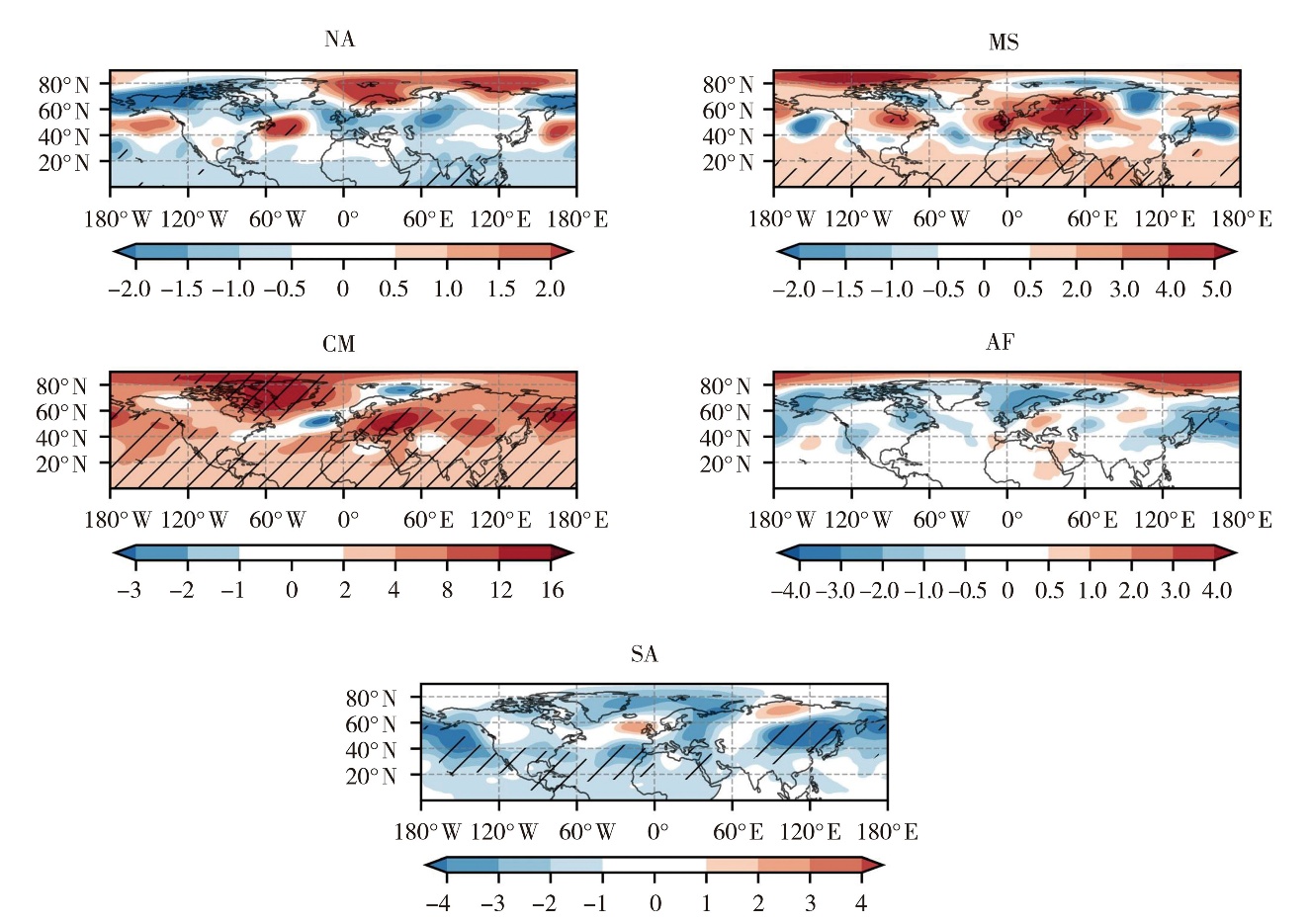
Fig.9 The 500 hPa geopotential height regressed by the index of land-atmosphere coupling strength over the Northern Hemisphere in summer during 1950-2020 (Unit: gpm)
| [1] | 陈泠羽, 陈海山, 齐雅静, 2025. 陆-气耦合对中国东部夏季高温事件影响的区域性差异及其可能机制[J]. 大气科学, 49(1):107-122. |
| [2] | 黄荣辉, 陈际龙, 刘永, 2011. 我国东部夏季降水异常主模态的年代际变化及其与东亚水汽输送的关系[J]. 大气科学, 35(4): 589-606. |
| [3] |
蒋靖海, 王澄海, 2020. 北半球季节性冻融区与北半球夏季降水关系的研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 42(1): 53-61.
DOI |
| [4] |
李登宣, 王澄海, 2016. 青藏高原春季土壤湿度与中国东部夏季降水之间的关系[J]. 冰川冻土, 38(1): 89-99.
DOI |
| [5] | 李课臣, 2022. 北半球陆气相互作用关键区及其与大气环流关系的研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [6] | 李若麟, 保鸿燕, 李课臣, 等, 2016. 全球土壤湿度的记忆性及其气候效应[J]. 冰川冻土, 38(6): 1 470-1 481. |
| [7] | 李忠贤, 陈海山, 倪东鸿, 等, 2012. 土壤湿度对东亚夏季气候潜在可预报性影响的数值模拟[J]. 大气科学学报, 35(4): 423-430. |
| [8] | 林朝晖, 杨晓松, 郭裕福, 2001. 陆面过程模式对土壤含水量初值的敏感性研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 6(2): 240-248. |
| [9] | 马柱国, 魏和林, 符淙斌, 2000. 中国东部区域土壤湿度的变化及其与气候变率的关系[J]. 气象学报, 58(3): 278-287. |
| [10] | 史一丛, 陈海山, 高楚杰, 2015. 土壤湿度初始异常对东亚区域气候模拟影响的敏感性试验[J]. 气象科学, 35(4): 379-388. |
| [11] | 孙丞虎, 李维京, 张祖强, 等, 2005. 淮河流域土壤湿度异常的时空分布特征及其与气候异常关系的初步研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 16(2): 129-138. |
| [12] | 孙莉娟, 陈海山, 潘敖大, 等, 2015. 土壤湿度年际异常对中国春、夏季气候模拟的影响[J]. 气象科学, 35(5): 521-533. |
| [13] | 佟华, 刘辉志, 陈起英, 等, 2007. 土壤湿度初值对边界层物理量预报影响的分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(4): 546-552. |
| [14] | 王澄海, 尚大成, 2007. 藏北高原土壤温、湿度变化在高原干湿季转换中的作用[J]. 高原气象, 26(4): 677-685. |
| [15] | 杨扬, 杨启东, 王芝兰, 等, 2021. 中国区域陆气耦合强度的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 374-385. |
| [16] | 张强, 岳平, 张良, 等, 2019. 夏季风过渡区的陆-气相互作用:述评与展望[J]. 气象学报, 77(4):758-773. |
| [17] | 张文君, 周天军, 智海, 2012. 土壤湿度影响中国夏季气候的数值试验[J]. 气象学报, 70(1): 78-90. |
| [18] | 曾毓金, 谢正辉, 2015. 基于CMIP5模拟的中国区域陆气耦合强度评估及未来情景预估[J]. 气候与环境研究, 20(3):337-346. |
| [19] | ALFIERI L, CLAPS P, D’ODORICO P, et al, 2008. An analysis of the soil moisture feedback on convective and stratiform precipitation[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 9(2): 280-291. |
| [20] | CHEN H S, 2022. Key regions where land surface processes shape the East Asian climate[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 15(3): 100209. DOI: 10.1016/j.aosl.2022.100209. |
| [21] | CHOW K C, CHAN J C L, SHI X L, et al, 2008. Time-lagged effects of spring Tibetan Plateau soil moisture on the monsoon over China in early summer[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 28(1): 55-67. |
| [22] | DIRMEYER P A, 2006. The hydrologic feedback pathway for land-climate coupling[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 7(5): 857-867. |
| [23] | DIRMEYER P A, 2011. The terrestrial segment of soil moisture-climate coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(16): 136. DOI: 10.1029/2011GL048268. |
| [24] | GAO C J, CHEN H S, SUN S L, et al, 2018. Regional features and seasonality of land-atmosphere coupling over Eastern China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 35(6): 689-701. |
| [25] | GUO Z C, DIRMEYER P A, KOSTER R D, et al, 2006. GLACE: The global land-atmosphere coupling experiment. Part II: Analysis[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 7(4): 611-625. |
| [26] | KOSTER R D, SUÁREZ M J, 1995. Relative contributions of land and ocean processes to precipitation variability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 100(D7): 13 775-13 790. |
| [27] | KOSTER R D, CHANG Y H, SCHUBERT S D, 2014. A mechanism for land-atmosphere feedback involving planetary wave structures[J]. Journal of Climate, 27(24): 9 290-9 301. |
| [28] | KOSTER R D, CHANG Y H, WANG H L, et al, 2016. Impacts of local soil moisture anomalies on the atmospheric circulation and on remote surface meteorological fields during boreal summer: A comprehensive analysis over North America[J]. Journal of Climate, 29(20): 7 345-7 364. |
| [29] | KOSTER R D, DIRMEYER P A, GUO Z C, et al, 2004. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation[J]. Science, 305(5687): 1 138-1 140. |
| [30] | KOSTER R D, SUÁREZ M J, HEISER M, 2000. Variance and predictability of precipitation at seasonal-to-interannual timescales[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 1(1): 26-46. |
| [31] | LI K C, ZHANG F M, YANG K, et al, 2022. Improvement of summer precipitation simulation by correcting biases of spring soil moisture in the seasonal frozen-thawing zone over the Northern Hemisphere[J]. Climate Dynamics, 58(9): 2 767-2 780. |
| [32] | MENG L, LONG D, QUIRING S M, et al, 2014. Statistical analysis of the relationship between spring soil moisture and summer precipitation in East China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 34(5): 1 511-1 523. |
| [33] | MUÑOZ SABATER J, 2019. ERA5-Land hourly data from 1950 to present[J]. Copernicus Climate Change Service Climate Data Store. DOI:10.24381/cds.e2161bac. |
| [34] | PITMAN A J, 2003. The evolution of, and revolution in, land surface schemes designed for climate models[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 23(5): 479-510. |
| [35] | PLEIM J E, XIU A J, 2003. Development of a land surface model. Part II: Data assimilation[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 42(12): 1 811-1 822. |
| [36] | RODELL M, HOUSER P R, JAMBOR U, et al, 2004. The global land data assimilation system[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 85(3): 381-394. |
| [37] | SANTANELLO J A Jr, PETERS-LIDARD C D, KUMAR S V, et al, 2009. A modeling and observational framework for diagnosing local land-atmosphere coupling on diurnal time scales[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 10(3): 577-599. |
| [38] | SCHULZWEIDA U, 2023. CDO user guide (2.3.0)[M]. Zenodo. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.10020800. |
| [39] | SENEVIRATNE S I, CORTI T, DAVIN E L, et al, 2010. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 99(3/4): 125-161. |
| [40] | WANG C H, CUI Z Q, 2018. Improvement of short-term climate prediction with indirect soil variables assimilation in China[J]. Journal of Climate, 31(4): 1 399-1 412. |
| [41] | WEI J F, DIRMEYER P A, 2012. Dissecting soil moisture-precipitation coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(19): 2012GL053038. DOI: 10.1029/2012gl053038. |
| [42] | YANG K, WANG C H, 2019. Seasonal persistence of soil moisture anomalies related to freeze-thaw over the Tibetan Plateau and prediction signal of summer precipitation in eastern China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 53(3): 2 411-2 424. |
| [43] | YANG K, WANG C H, BAO H Y, 2016. Contribution of soil moisture variability to summer precipitation in the Northern Hemisphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(20): 12 108-12 124. |
| [44] | YANG Z S, ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al, 2025. Water-heat synergy shapes evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling patterns across northern China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 42(6): 1 167-1 178. |
| [45] | ZHANG J Y, WANG W C, LEUNG L R, 2008. Contribution of land-atmosphere coupling to summer climate variability over the contiguous United States[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 113(D22). DOI:10.1029/2008JD010136. |
| [46] | ZHANG J, WU L, DONG W, 2011. Land-atmosphere coupling and summer climate variability over East Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 116: D05117. DOI:10.1029/2010JD014714. |
| [47] | ZHANG Y K, WAGNER N, GOERGEN K, et al, 2024. Summer evapotranspiration-cloud feedbacks in land-atmosphere interactions over Europe[J]. Climate Dynamics, 62(12): 10 767-10 783. |
| [48] | ZOMER R J, XU J C, TRABUCCO A, 2022. Version 3 of the global aridity index and potential evapotranspiration database[J]. Scientific Data, 9(1). DOI: 10.1038/s41597-022-01493-1. |
| [49] | ZUO Z Y, ZHANG R H, 2007. The spring soil moisture and the summer rainfall in Eastern China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(23): 3 310-3 312. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||