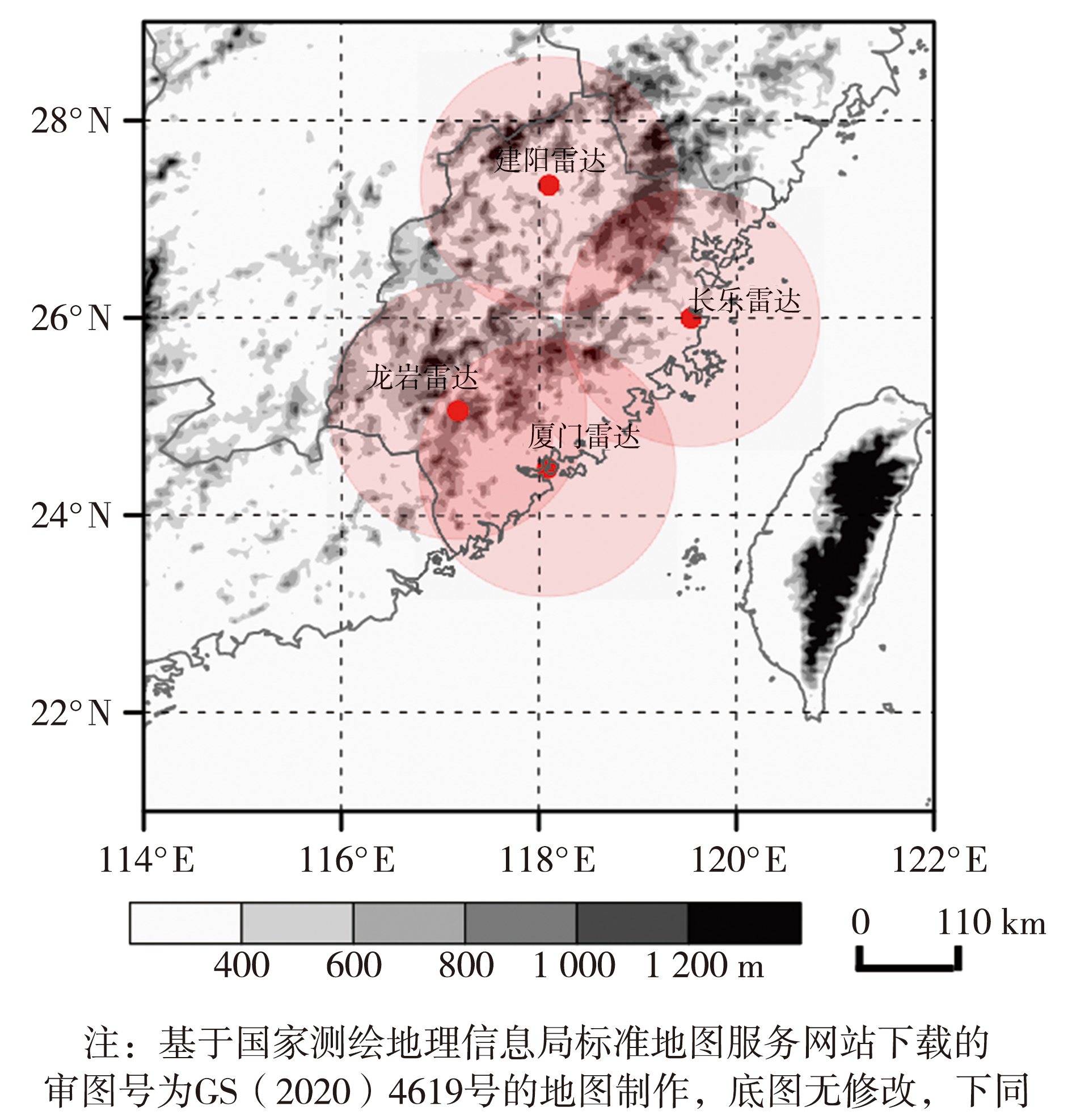
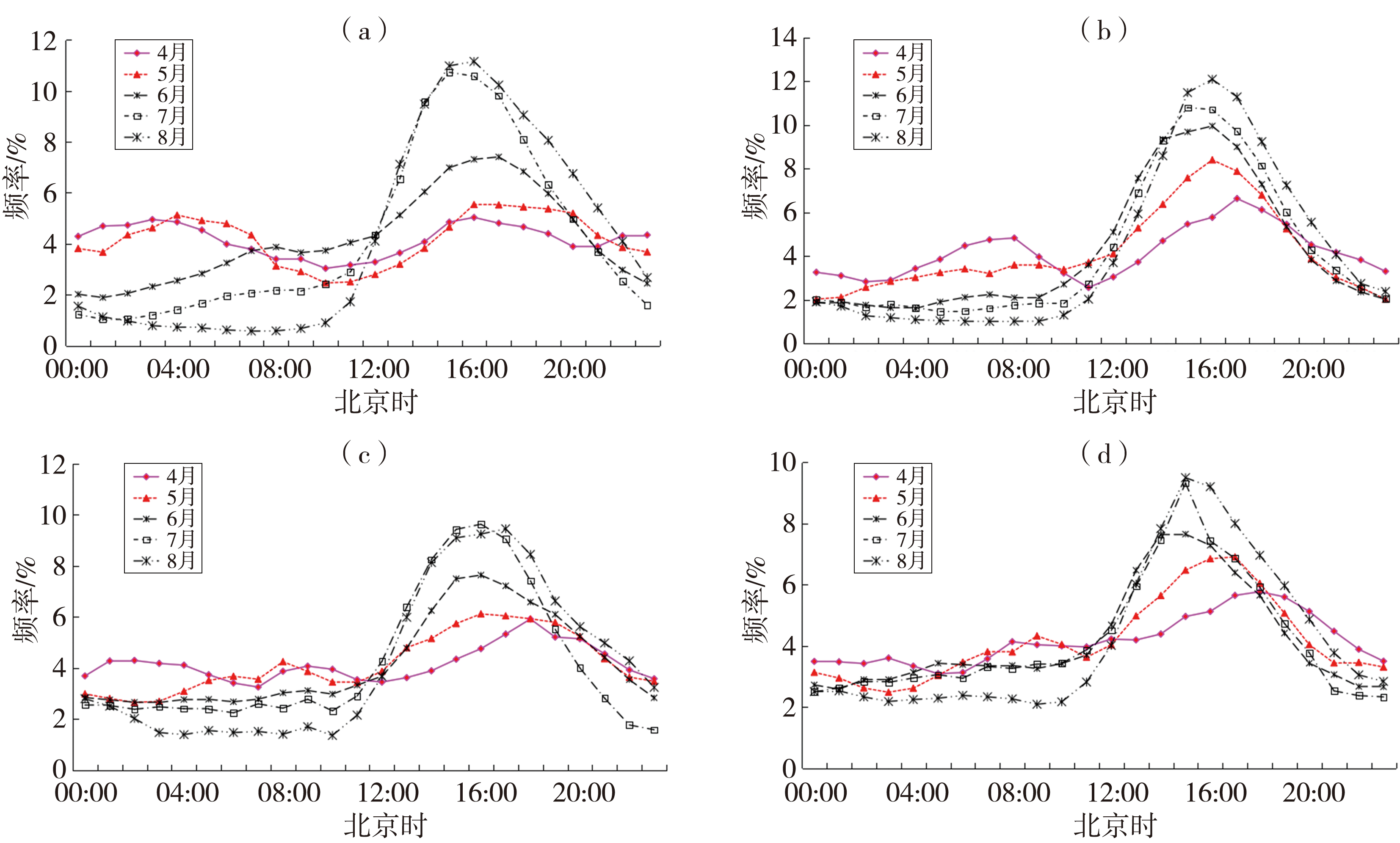
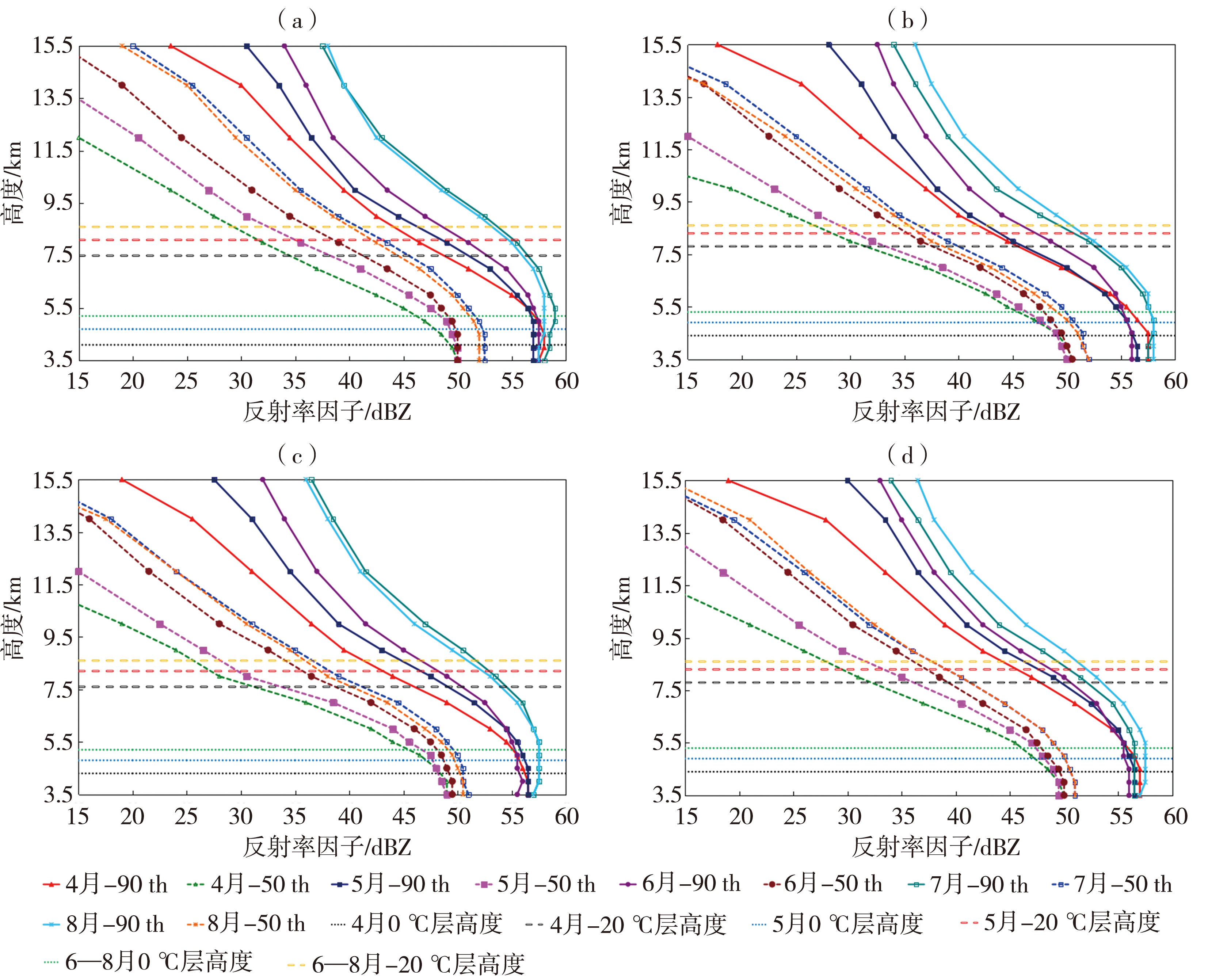
| [1] |
陈炯, 郑永光, 张小玲, 等, 2013. 中国暖季短时强降水分布和日变化特征及其与中尺度对流系统日变化关系分析[J]. 气象学报, 71(3): 367-382.
|
| [2] |
陈明轩, 王迎春, 高峰, 等, 2014. 雷达气候研究进展及其在城市区域强天气临近预报中的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 4(5): 30-41.
|
| [3] |
陈兴超, 2016. 华南暖季对流的雷达气候学特征及其机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学.
|
| [4] |
管理, 戴建华, 赵渊明, 等, 2020. 上海地区暖季午后对流的雷达气候学特征分析[J]. 气象, 46(12): 1 543-1 554
|
| [5] |
韩雷, 俞小鼎, 郑永光, 等, 2009. 京津及邻近地区暖季强对流风暴的气候分布特征[J]. 科学通报, 54(11): 1 585-1 590
|
| [6] |
雷瑜, 黄武斌, 黎倩, 等, 2022. 不同天气分型下甘肃河东地区强冰雹天气多普勒雷达产品特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 234-243.
DOI
|
| [7] |
李慧敏, 安晶晶, 邱学兴, 等, 2023. 安徽暖季对流活动的雷达气候学特征及影响因素[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(5): 554-562.
|
| [8] |
龙美希, 陈桂琴, 张勇, 等, 2023. 雷达估测降水与风暴尺度模式预报降水检验及分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(3): 127-133.
|
| [9] |
潘赫拉, 许东蓓, 陈明轩, 等, 2020. 天气雷达气候学研究新进展[J]. 干旱气象, 38(6): 887-894.
|
| [10] |
孙康远, 郑媛媛, 慕瑞琪, 等, 2017. 南京及周边地区雷达气候学分析[J]. 气象学报, 75(1): 178-192.
|
| [11] |
肖玮, 刘维成, 傅朝, 等, 2023. 甘肃东南部暖季对流活动的雷达气候学特征[J]. 高原气象, 42(6): 1 536-1 547
|
| [12] |
邢峰华, 黄彦彬, 李春鸾, 等, 2023. 海南岛热带孤立对流云系特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 442-449.
DOI
|
| [13] |
朱海斌, 杨婧, 纪晓玲, 等, 2023. 宁夏北部暖季对流风暴雷达气候学特征分析[J]. 气象, 49(9): 1 085-1 096
|
| [14] |
支树林, 许东蓓, 潘赫拉, 等, 2021. 陕西汉中及其周边地区对流活动的雷达气候特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(4): 620-630.
|
| [15] |
郑永光, 陈炯, 朱佩君, 2008. 中国及周边地区夏季中尺度对流系统分布及其日变化特征[J]. 科学通报, 53(4): 471-481.
|
| [16] |
AHIJEVYCH D A, CARBONE R E, DAVIS C A, 2003. Regional-scale aspects of the diurnal precipitation cycle[C]// In 31st International Conference on Radar Meteorology, Seattle, WA, US: American Meteorology Society.
|
| [17] |
BLACKADAR A K, 1957. Boundary layer wind maxima and their significance for the growth of nocturnal inversions[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 38(5): 283-290.
|
| [18] |
CARBONE R E, TUTTLE J D, AHIJEVYCH D A, et al, 2002. Inferences of predictability associated with warm season precipitation episodes[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 59(13): 2 033-2 056
|
| [19] |
CHEN M, WANG Y, GAO F, et al, 2012. Diurnal variations in convective storm activity over contiguous North China during the warm season based on radar mosaic climatology[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 117: D20115. DOI: 10.1029/2012JD018158.
|
| [20] |
DIXON M, WIENER G, 1993. TITAN: Thunderstorm identification, tracking, analysis, and nowcasting-A radar-based methodology[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technologgy, 10(6): 785-797.
|
| [21] |
DONALDSON R J, 1961. Radar reflectivity profiles in thunderstorms[J]. Journal of Meteorology, 18(3): 292-305.
|
| [22] |
STEINER M, HOUZE R A, YUTER S E, 1995. Climatological characterization of three-dimensional storm structure from operational radar and rain gauge data[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 34(9): 1 978-2 007
|
| [23] |
WALLACE J M, 1975. Diurnal variations in precipitation and thunderstorm frequency over the conterminous United States[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 103(5): 406-419.
|
| [24] |
XU W X, ZIPSER E J, 2012. Properties of deep convection in tropical continental, monsoon, and oceanic rainfall regimes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(7): L07802. DOI: 10.1029/2012GL051242.
|
 ), LAI Qiaozhen1, CAI Jing1(
), LAI Qiaozhen1, CAI Jing1( )
)