干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 531-539.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0531
对流起沙的研究进展
梁国豪1( ), 毛睿2,3(
), 毛睿2,3( ), SHAO Yaping4, 李晓岚5, 龚道溢6
), SHAO Yaping4, 李晓岚5, 龚道溢6
- 1.北京师范大学环境演变与自然灾害教育部重点实验室,北京 100875
2.北京师范大学国家安全与应急管理学院,北京 100875
3.中国科学院地球环境研究所黄土与第四纪地质国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710061
4.德国科隆大学地球物理与气象研究所,科隆 50923
5.中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所,辽宁 沈阳 110166
6.北京师范大学地表过程与资源生态国家重点实验室,北京 100875
-
收稿日期:2022-10-26修回日期:2022-12-30出版日期:2023-08-31发布日期:2023-08-29 -
通讯作者:毛睿(1980—),男,甘肃兰州人,教授,主要从事气候变化及其影响研究。E-mail: MR@bnu.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:梁国豪(1996—),男,山东枣庄人,硕士生,主要从事大气沙尘气溶胶研究。E-mail:lgh@mail.bnu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:环境演变与自然灾害教育部重点实验室项目(2022-KF-04);黄土与第四纪地质国家重点实验室开放基金项目(SKLLQG-2220)
Research progress of convective turbulent dust emission
LIANG Guohao1( ), MAO Rui2,3(
), MAO Rui2,3( ), SHAO Yaping4, LI Xiaolan5, GONG Daoyi6
), SHAO Yaping4, LI Xiaolan5, GONG Daoyi6
- 1. Key Laboratory of Environmental Change and Natural Disaster of Ministry of Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
2. School of National Safety And Emergency Management, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710061, China
4. Institute for Geophysics and Meteorology, University of Cologne, Cologne 50923, Germany
5. Shenyang Institute of Atmospheric Environment, China Meteorological Administration, Shenyang 110166, China
6. State Key Laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
-
Received:2022-10-26Revised:2022-12-30Online:2023-08-31Published:2023-08-29
摘要:
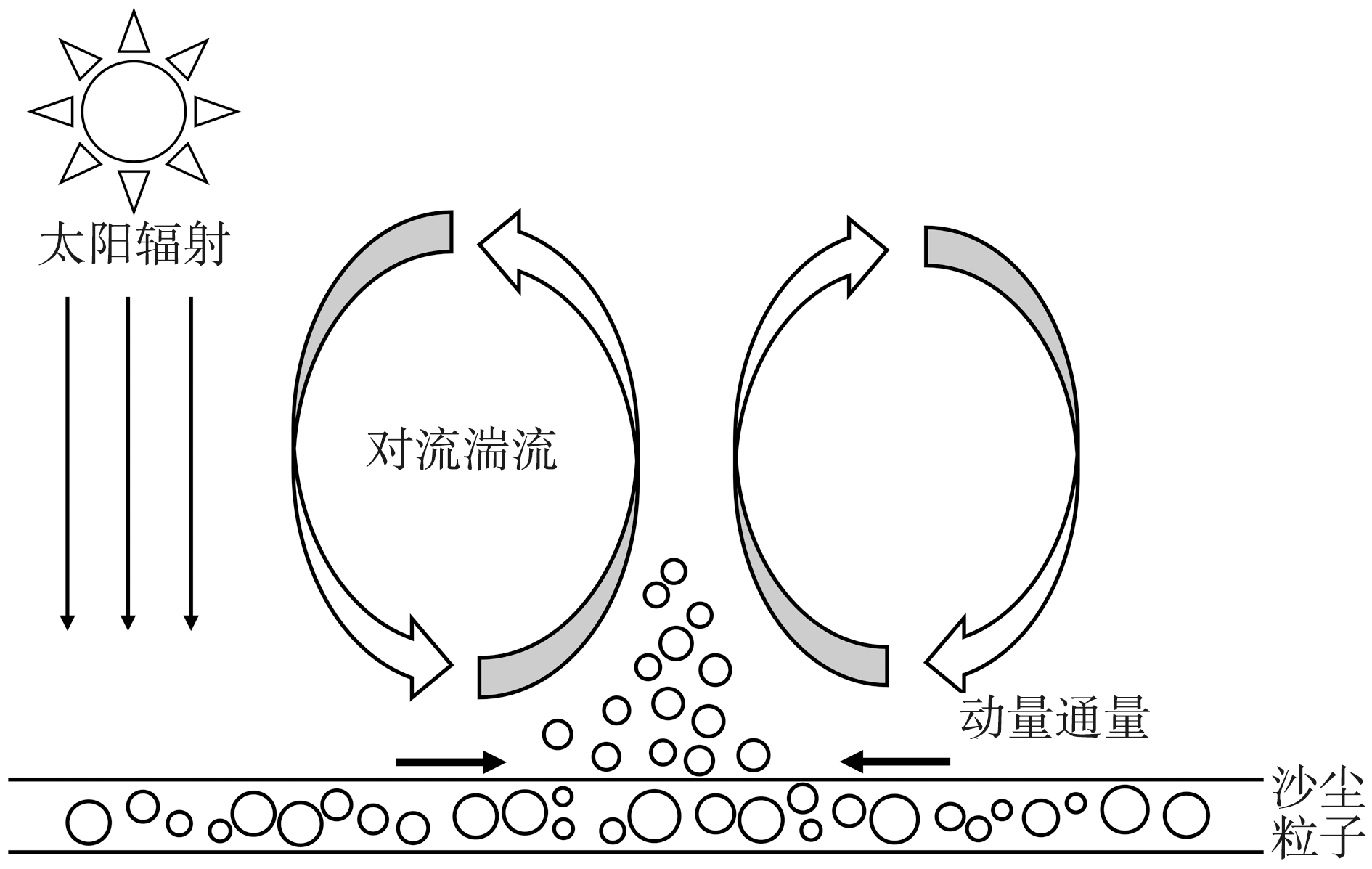
对流起沙是一种由热力对流湍流直接夹卷沙尘进入大气的起沙机制,由于其频繁发生,长期累积的沙尘排放贡献不可忽视。根据国内外研究现状,总结归纳对流起沙的发生机理和影响因素,介绍目前相关的参数化方案,并从发生条件和起沙通量等方面分析对流起沙与跃移起沙、尘卷风的异同。最后,对对流起沙的野外观测和参数化方案改进等方面提出建议:应加强对流起沙潜在活跃区的观测及比较不同沙源地对流起沙的特征,进一步构建土壤湿度、植被覆盖等影响因素的修正函数以提升模式模拟性能。
中图分类号:
引用本文
梁国豪, 毛睿, SHAO Yaping, 李晓岚, 龚道溢. 对流起沙的研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 531-539.
LIANG Guohao, MAO Rui, SHAO Yaping, LI Xiaolan, GONG Daoyi. Research progress of convective turbulent dust emission[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 531-539.
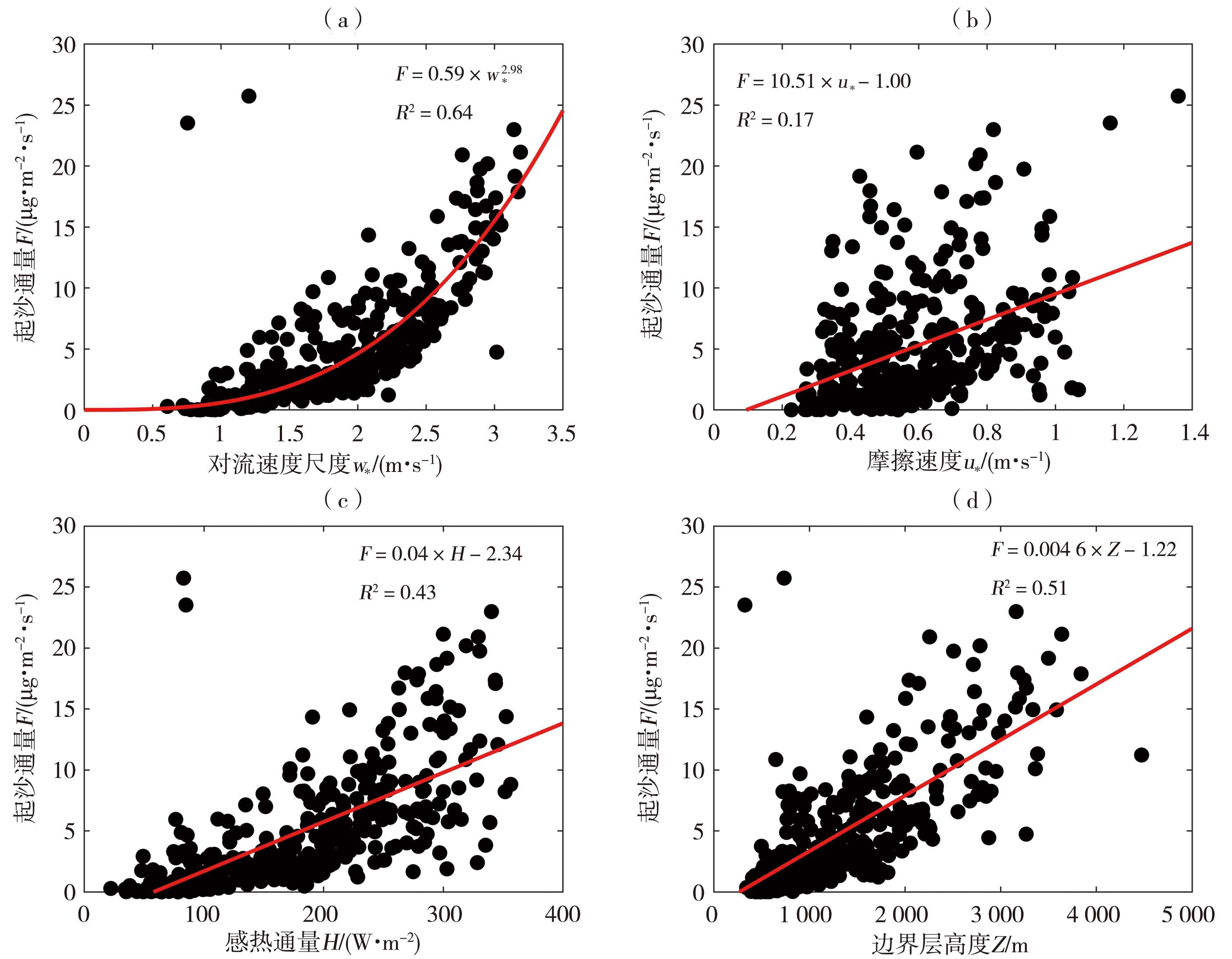
图2 WRF-Chem模式模拟的2016年科尔沁沙地对流起沙通量与对流速度尺度(a)、摩擦速度(b)、感热通量(c)、边界层高度(d)散点图
Fig.2 Scatter plots between dust emission flux and convective velocity scale (a), friction velocity (b), sensible heat flux (c), planetary boundary layer height (d) simulated by WRF-Chem model at Horqin Sandy Land in 2016

图3 WRF-Chem模式模拟的2016年6月1日(a)、2日(b)、3日(c)、4日(d)沙尘柱质量浓度空间分布(单位:mg·m-2) (绿色方框区域为科尔沁沙地)
Fig.3 The spatial distribution of mass concentration of dust column simulated by WRF-Chem model on 1 (a), 2 (b), 3 (c), 4 (d) June 2016 (Unit: mg·m-2) (The green box area represents the Horqin Sandy Land)
| 特征 | 对流起沙 | 跃移起沙 | 尘卷风 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 排放方式 | 热力起沙为主(Klose and Shao, | 动力起沙为主(Shao, | 热力起沙为主(Klose and Shao, |
| 发生条件 | 同时满足 (Li et al., | 同时满足 (韩超信等, | |
| 发生频率 | 高(Li et al., | 较低(李耀辉等, | 高(Balme and Greeley, |
| 主要时段 | 08:00—15:00(Li et al., | 无明显规律 | 12:00—18:00(栾兆鹏等, |
| 单次事件时长 | 大部分小于3 h(Li et al., | 较长(段伯隆等, | 大部分小于30 min(栾兆鹏等, |
| 季节特征 | 夏季>秋季>春季>冬季(Li et al., | 春季最多(元天刚等, | 夏季较多(栾兆鹏等, |
| 水平尺度和 垂直尺度 | 尚不清楚 | 水平范围较大,近地面到对流层中上层(姜学恭等, | 水平范围较小,几米至几千米不等 (Sinclair, |
| 起沙通量 | 0.0~10.0 µg·m-2·s-1 (Li et al., | 27.7~206.0 µg·m-2·s-1 (沈志宝等, | 约0.7×106µg·m-2·s-1 (Han et al., |
| 对总沙尘排放的贡献率 | 27.00%(Ju et al., | 65.17%~76.00%(Ju et al., | 24.00%(刘莹等, |
表1 对流起沙与其他起沙机制的特征比较
Tab.1 Comparison of characteristics between convective turbulent dust emission and other dust emission mechanism
| 特征 | 对流起沙 | 跃移起沙 | 尘卷风 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 排放方式 | 热力起沙为主(Klose and Shao, | 动力起沙为主(Shao, | 热力起沙为主(Klose and Shao, |
| 发生条件 | 同时满足 (Li et al., | 同时满足 (韩超信等, | |
| 发生频率 | 高(Li et al., | 较低(李耀辉等, | 高(Balme and Greeley, |
| 主要时段 | 08:00—15:00(Li et al., | 无明显规律 | 12:00—18:00(栾兆鹏等, |
| 单次事件时长 | 大部分小于3 h(Li et al., | 较长(段伯隆等, | 大部分小于30 min(栾兆鹏等, |
| 季节特征 | 夏季>秋季>春季>冬季(Li et al., | 春季最多(元天刚等, | 夏季较多(栾兆鹏等, |
| 水平尺度和 垂直尺度 | 尚不清楚 | 水平范围较大,近地面到对流层中上层(姜学恭等, | 水平范围较小,几米至几千米不等 (Sinclair, |
| 起沙通量 | 0.0~10.0 µg·m-2·s-1 (Li et al., | 27.7~206.0 µg·m-2·s-1 (沈志宝等, | 约0.7×106µg·m-2·s-1 (Han et al., |
| 对总沙尘排放的贡献率 | 27.00%(Ju et al., | 65.17%~76.00%(Ju et al., | 24.00%(刘莹等, |
| [1] | 曹晓云, 肖建设, 乔斌, 等, 2021. 1961—2019年柴达木盆地沙尘强度时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(1): 46-53. |
| [2] | 段伯隆, 刘新伟, 郭润霞, 等, 2021. “3·15”北方强沙尘暴天气成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(4): 541-553. |
| [3] | 段佳鹏, 韩永翔, 赵天良, 等, 2013. 尘卷风对沙尘气溶胶的贡献及其与太阳辐射的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 33(1): 43-48. |
| [4] | 韩超信, 汤耀国, 韩永翔, 等, 2021. 中国北方地区尘卷风时空分布的数值模拟[J]. 干旱区地理, 44(4): 1 003-1 010. |
| [5] | 韩永翔, 奚晓霞, 宋连春, 等, 2004. 青藏高原沙尘及其可能的气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 24(5): 588-592. |
| [6] | 姜学恭, 陈受钧, 云静波, 2014. 基于CALIPSO资料的沙尘暴过程沙尘垂直结构特征分析[J]. 气象, 40(3): 269-279. |
| [7] | 李耀辉, 张存杰, 高学杰, 2004. 西北地区大风日数的时空分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 24(6): 715-723. |
| [8] | 刘莹, 韩永翔, 杨文清, 等, 2018. 沙尘天气, 尘卷风对沙漠地区起沙量的贡献[J]. 中国沙漠, 38(6): 1 175-1 179. |
| [9] | 栾兆鹏, 赵天良, 韩永翔, 等, 2016. 干旱半干旱地区尘卷风研究进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 10(2): 1-8. |
| [10] |
马明杰, 杨兴华, 何清, 等, 2019. 塔克拉玛干荒漠-绿洲过渡带尘卷风活动特征——以肖塘为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(2): 115-121.
DOI |
| [11] | 沈建国, 孙照渤, 章秋英, 等, 2008. 干旱草原地区起沙通量的初步研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 28(6): 1 045-1 049. |
| [12] | 沈志宝, 申彦波, 杜明远, 等, 2003. 沙尘暴期间戈壁沙地起沙率的观测结果[J]. 高原气象, 22(6):545-550. |
| [13] |
吴焕波, 陈强, 谷新波, 等, 2018. 一次强沙尘天气过程及其对PM10时空分布的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 36(1): 117-123.
DOI |
| [14] | 杨艳, 王杰, 田明中, 等, 2012. 中国沙尘暴分布规律及研究方法分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 32(2): 465-472. |
| [15] |
元天刚, 陈思宇, 康丽泰, 等, 2016. 1961—2010年中国北方沙尘源区沙尘强度时空分布特征及变化趋势[J]. 干旱气象, 34(6): 927-935.
DOI |
| [16] | 张宏升, 朱好, 彭艳, 等, 2007. 沙尘天气过程沙地下垫面沙尘通量的获取与分析研究[J]. 气象学报, 65(5): 744-752. |
| [17] | 张钛仁, 宋振鑫, 王金艳, 等, 2008. 植被参数变化对沙尘起沙影响机理的数值模拟[J]. 高原气象, 27(2): 392-400. |
| [18] | 赵建华, 张强, 隆霄, 2012. 冲击起沙的概念模型[J]. 中国沙漠, 32(2): 323-330. |
| [19] | 赵建华, 张强, 袁铁, 等, 2005. 沙粒启动机制的理论分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 25(6): 853-862. |
| [20] | 赵霞, 张中伟, 2011. 1960—2008年新疆沙雅沙尘天气变化特征及原因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 5(4): 20-25. |
| [21] | 朱好, 张宏升, 2011. 沙尘释放通量外场观测和参数化研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 47(4): 768-776. |
| [22] | 祖拜旦, 依马木, 2015. 巴楚县1961—2010年沙尘天气的变化趋势分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 9(5): 36-40. |
| [23] | ALFARO S C, GOMES L, 2001. Modeling mineral aerosol production by wind erosion: emission intensities and aerosol size distributions in source areas[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 106(D16): 18 075-18 084. |
| [24] |
BALME M, GREELEY R, 2006. Dust devils on Earth and Mars[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 44(3), RG3003. DOI: 10.1029/2005RG000188.
DOI |
| [25] |
BULLARD J E, BADDOCK M, BRADWELL T, et al, 2016. High-latitude dust in the Earth system[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 54(2): 447-485.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
CAKMUR R V, MILLER R L, PERLWITZ J, et al, 2006. Constraining the magnitude of the global dust cycle by minimizing the difference between a model and observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 111(D6), D06207. DOI: 10.1029/2005JD005796.
DOI |
| [27] | CHKHETIANI O G, GLEDZER E B, ARTAMONOVA M S, et al, 2012. Dust resuspension under weak wind conditions: Direct observations and model[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(11): 5 147-5 162. |
| [28] |
HAN Y, WANG K, LIU F, et al, 2016. The contribution of dust devils and dusty plumes to the aerosol budget in western China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 126: 21-27.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
HEINOLD B, TEGEN I, BAUER S, et al, 2011. Regional modelling of Saharan dust and biomass-burning smoke: Part 2: direct radiative forcing and atmospheric dynamic response[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 63(4): 800-813.
DOI URL |
| [30] | HESS G D, SPILLANE K T, 1990. Characteristics of dust devils in Australia[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 29(6): 498-507. |
| [31] | ITO J, TANAKA R, NIINO H, et al, 2010. Large eddy simulation of dust devils in a diurnally-evolving convective mixed layer[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 88(1): 63-77. |
| [32] |
JICKELLS T D, AN Z S, ANDERSEN K K, et al, 2005. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate[J]. Science, 308(5718): 67-71.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
JU T T, LI X L, ZHANG H S, et al, 2018. Parameterization of dust flux emitted by convective turbulent dust emission (CTDE) over the Horqin Sandy Land area[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 187: 62-69.
DOI URL |
| [34] | KLOSE M, SHAO Y, 2012. Stochastic parameterization of dust emission and application to convective atmospheric conditions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(16): 7 309-7 320. |
| [35] |
KLOSE M, SHAO Y, 2013. Large-eddy simulation of turbulent dust emission[J]. Aeolian Research, 8: 49-58.
DOI URL |
| [36] | KLOSE M, 2014. Convective turbulent dust emission: process, parameterization, and relevance in the Earth system[D]. Cologne: University of Cologne. |
| [37] | KLOSE M, SHAO Y, LI X, et al, 2014. Further development of a parameterization for convective turbulent dust emission and evaluation based on field observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(17): 10 441-10 457. |
| [38] |
KLOSE M, SHAO Y, 2016. A numerical study on dust devils with implications to global dust budget estimates[J]. Aeolian Research, 22: 47-58.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
KOCH J, RENNO N O, 2005. The role of convective plumes and vortices on the global aerosol budget[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(18), L18806. DOI: 10.1029/2005GL023420.
DOI |
| [40] |
LAURENT B, MARTICORENA B, BERGAMETTI G, et al, 2006. Modeling mineral dust emissions from Chinese and Mongolian deserts[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 52(1/4): 121-141.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LI X L, KLOSE M, SHAO Y, et al, 2014. Convective turbulent dust emission (CTDE) observed over Horqin Sandy Land area and validation of a CTDE scheme[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 119(16): 9 980-9 992.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
LOOSMORE G A, HUNT J R, 2000. Dust resuspension without saltation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 105(D16): 20 663-20 671.
DOI URL |
| [43] | LU H, SHAO Y, 1999. A new model for dust emission by saltation bombardment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 104(D14): 16 827-16 842. |
| [44] |
MAHOWALD N M, BAKER A R, BERGAMETTI G, et al, 2005. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 19(4), GB4025. DOI: 10.1029/2004GB002402.
DOI |
| [45] | MARTICORENA B, BERGAMETTI G, 1995. Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle. 1. Design of a soil-derived dust emission scheme[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 100(D8): 16 415-16 430. |
| [46] |
PARK S U, CHOE A, LEE E H, et al, 2010. The Asian dust aerosol model 2 (ADAM2) with the use of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) obtained from the Spot4/vegetation data[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 101: 191-208.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
RENNÓ N O, BURKETT M L, LARKIN M P, 1998. A simple thermodynamical theory for dust devils[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 55(21): 3 244-3 252.
DOI URL |
| [48] | SHAO Y, RAUPACH M R, FINDLATER P A, 1993. Effect of saltation bombardment on the entrainment of dust by wind[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 98(D7): 12 719-12 726. |
| [49] |
SHAO Y, 2001. A model for mineral dust emission[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 106(D17): 20 239-20 254.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
SHAO Y, 2004. Simplification of a dust emission scheme and comparison with data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 109(D10), D10202. DOI:10.1029/2003JD004372.
DOI URL |
| [51] | SHAO Y P, 2008. Physics and modelling of wind erosion[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. |
| [52] |
SHAO Y, FINK A H, KLOSE M, 2010. Numerical simulation of a continental-scale Saharan dust event[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 115(D13), D13205. DOI: 10.1029/2009JD012678.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
SHAO Y, ISHIZUKA M, MIKAMI M, et al, 2011. Parameterization of size-resolved dust emission and validation with measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 116(D8), D08203. DOI: 10.1029/2010JD014527.
DOI |
| [54] | SINCLAIR P C, 1969. General characteristics of dust devils[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 8(1): 32-45. |
| [55] |
SINCLAIR P C, 1973. The lower structure of dust devils[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 30(8): 1 599-1 619.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
SOKOLIK I N, TOON O B, 1996. Direct radiative forcing by anthropogenic airborne mineral aerosols[J]. Nature, 381: 681-683.
DOI |
| [57] | ZENDER C S, MILLER R, TEGEN I, 2004. Quantifying mineral dust mass budgets: terminology, constraints, and current estimates[J]. Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 85(48): 509-512. |
| [58] | ZIMON A D, 1982. Adhesion of dust and powder[M]. New York: Consultants Bureau. |
| [1] | 曹晓云, 周秉荣, 周华坤, 乔斌, 颜玉倩, 赵彤, 陈奇, 赵慧芳, 于红妍. 气候变化对青藏高原植被生态系统的影响研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1068-1080. |
| [2] | 陈 炜,李跃清. 对流层重力波的主要研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(5): 717-724. |
| [3] | 尹晗,李耀辉,. 我国西南干旱研究最新进展综述[J]. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(1): 182-193. |
| [4] | 熊亚军,于平,扈海波. 国内高温气候变化事实及其灾害特征研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(1): 194-198. |
| [5] | 薛志磊,张书余. 气温预报方法研究及其应用进展综述[J]. J4, 2012, 30(3): 451-458. |
| [6] | 韩海涛,李仲龙. 地面实时气象数据质量控制方法研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(2): 261-265. |
| [7] | 刘 炜, 周顺武, 杨双艳. 青藏高原大气低频振荡研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(1): 107-113. |
| [8] | 马守存 ,张书余,王宝鉴 ,罗斌. 气象条件对心脑血管疾病的影响研究进展[J]. J4, 2011, 29(3): 350-354. |
| [9] | 孙昭萱, 张 强, 王 胜. 土壤水热耦合模型研究进展[J]. J4, 2009, 27(4): 373-380. |
| [10] | 张强, 赵映东, 张存杰, 李耀辉, 孙国武, 高前兆. 西北干旱区水循环与水资源问题[J]. J4, 2008, 26(2): 1-8. |
| [11] | 张瑞军, 何 清, 孔 丹, 杨兴华. 近几年国内沙尘暴研究的初步评述[J]. J4, 2007, 25(3): 88-94. |
| [12] | 张强. 大气边界层气象学研究综述[J]. J4, 2003, 21(3): 74-78. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||