干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 444-455.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0444
华北地区一次对流激发重力波的卫星观测和数值模拟研究
殷青青( ), 任璐, 田文寿(
), 任璐, 田文寿( ), 王涛, 杨景怡, 张健恺
), 王涛, 杨景怡, 张健恺
- 兰州大学大气科学学院,半干旱气候变化教育部重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730000
-
收稿日期:2022-03-13修回日期:2022-04-24出版日期:2022-06-30发布日期:2022-06-28 -
通讯作者:田文寿 -
作者简介:殷青青(1997—),女,硕士生,主要从事平流层-对流层相互作用研究. E-mail: yinqq19@lzu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金重点项目“北半球平流层-对流层化学-动力-地表过程耦合对中高纬度极端天气气候事件的影响研究”(42130601)
Satellite observation and numerical simulation of gravity wave excited by a convection over North China
YIN Qingqing( ), REN Lu, TIAN Wenshou(
), REN Lu, TIAN Wenshou( ), WANG Tao, YANG Jingyi, ZHANG Jiankai
), WANG Tao, YANG Jingyi, ZHANG Jiankai
- College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University, Key Laboratory for Semi-AridClimate Change of the Ministry of Education, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2022-03-13Revised:2022-04-24Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-06-28 -
Contact:TIAN Wenshou
摘要:
对流激发的重力波能够向中层大气输送动量和能量,准确获取重力波主要特征对于研究中层大气的动力学和热力学结构非常重要。本文利用COSMIC(constellation observing system for meteorology, ionosphere and climate)资料,结合中尺度数值预报模式WRF(weather research and forecasting),对2010年8月4日发生在华北地区上空的一次对流激发的重力波事件进行分析。结果表明:此次事件激发的重力波在平流层以中低频重力波为主,且在平流层中垂直波长、水平波长分别为9~11 km和650~800 km,约62%的动量聚集在15~25 km高度的低平流层。在对流活动发生期间,低平流层重力波势能密度一直维持较大数值,而上平流层重力波势能密度则在对流减弱后迅速减小,且伴随着下一次对流活动的出现再次迅速增大。平流层不同高度上重力波势能密度对对流活动的响应主要与对流发展高度和背景风场有关,当对流发展较浅时,其激发的重力波在低层西风中易耗散;当对流发展较深到16 km甚至更高时,其激发的重力波接近零风层,并在东风中迅速上传,使得高层重力波势能密度增加较快。
中图分类号:
引用本文
殷青青, 任璐, 田文寿, 王涛, 杨景怡, 张健恺. 华北地区一次对流激发重力波的卫星观测和数值模拟研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 444-455.
YIN Qingqing, REN Lu, TIAN Wenshou, WANG Tao, YANG Jingyi, ZHANG Jiankai. Satellite observation and numerical simulation of gravity wave excited by a convection over North China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 444-455.
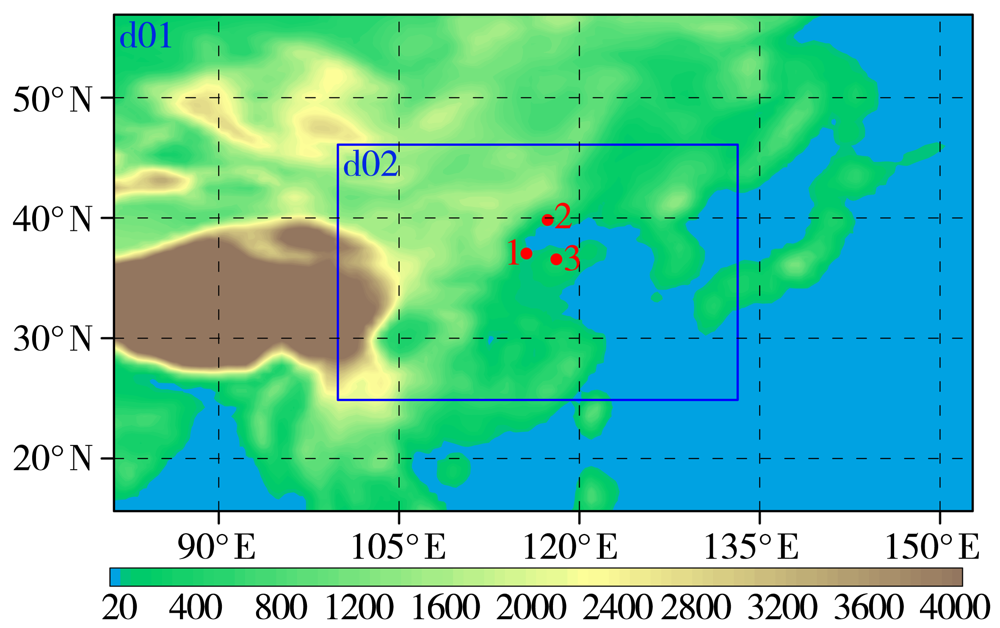
图1 WRF模拟区域的海拔高度(填色区,单位:m)和双重网格嵌套区域(矩形区)以及选取的 COSMIC卫星廓线位置(红色圆点)分布 [红色采样点1(115.60°E,37.04°N)、2(117.36°E,39.83°N)、3(118.08°E,36.56°N)的扫描时间分别为12:19、18:30、12:19(世界时)]
Fig.1 The altitude (color shaded areas, Unit: m) of simulation area by WRF model and double grid domains (rectangle areas), and the location distribution of selected profiles from COSMIC satellite (red dots) (The scanning time of red sampling point 1 (115.60°E, 37.04°N), 2 (117.36°E, 39.83°N) and 3 (118.08°E, 36.56°N) is 12:19 UTC, 18:30 UTC and 12:19 UTC, respectively)
| 参数化方案 | 设 置 |
|---|---|
| 微物理参数化方案 | WSM3方案[ |
| 积云参数化方案 | Grell-Devenyi积云对流方案[ |
| 行星边界层方案 | MYJ方案[ |
| 长波辐射方案 | RRTM方案[ |
| 短波辐射方案 | Dudhia方案[ |
| 近地面层方案 | MYJ Monin-Obukhov方案[ |
| 陆面过程方案 | Noah 方案[ |
表1 WRF模式的参数化方案设置
Tab.1 Parameterized scheme setting of WRF model
| 参数化方案 | 设 置 |
|---|---|
| 微物理参数化方案 | WSM3方案[ |
| 积云参数化方案 | Grell-Devenyi积云对流方案[ |
| 行星边界层方案 | MYJ方案[ |
| 长波辐射方案 | RRTM方案[ |
| 短波辐射方案 | Dudhia方案[ |
| 近地面层方案 | MYJ Monin-Obukhov方案[ |
| 陆面过程方案 | Noah 方案[ |
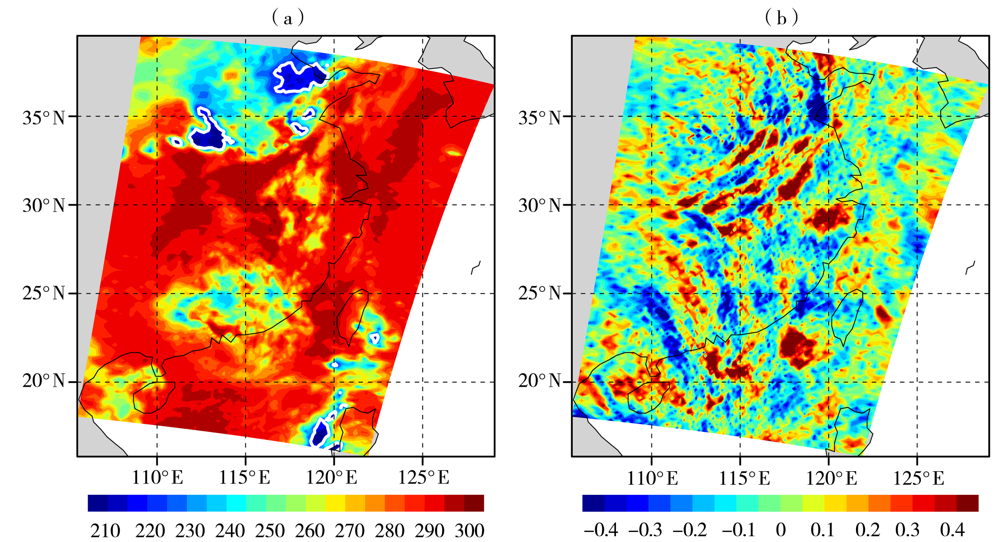
图2 2010年8月4日18:05AIRS卫星观测的8.1 μm亮温(a)和4.3 μm亮温扰动振幅(b)的空间分布(单位:K) (白色实线包围的区域亮温值小于220 K)
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of brightness temperature at 8.1 μm (a) and amplitude of brightness temperature disturbance at 4.3 μm (b) from AIRS at 18:05 UTC on 4 August 2010 (Unit: K ) (The value of brightness temperature in regions enclosed by white solid line is less than 220 K)
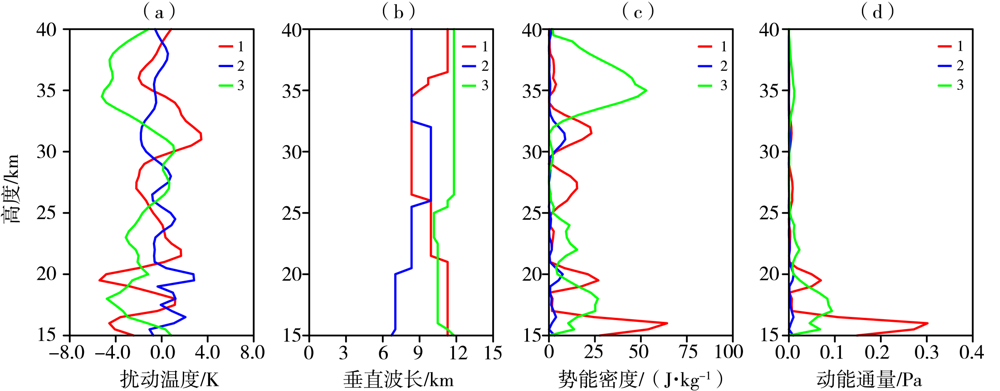
图3 2010年8月4日COSMIC卫星探测的不同采样点扰动温度(a)、垂直波长(b)、势能密度(c)和动量通量(d)廓线 (数字1、2、3为图1上的采样点。下同)
Fig.3 The profiles of disturbance temperature (a), vertical wavelength (b), potential energy per unit mass (c) and momentum flux (d) at different sampling points from COSMIC satellite on 4 August 2010 (The number 1, 2, 3 represent the sampling points in Fig. 1. the same as below)
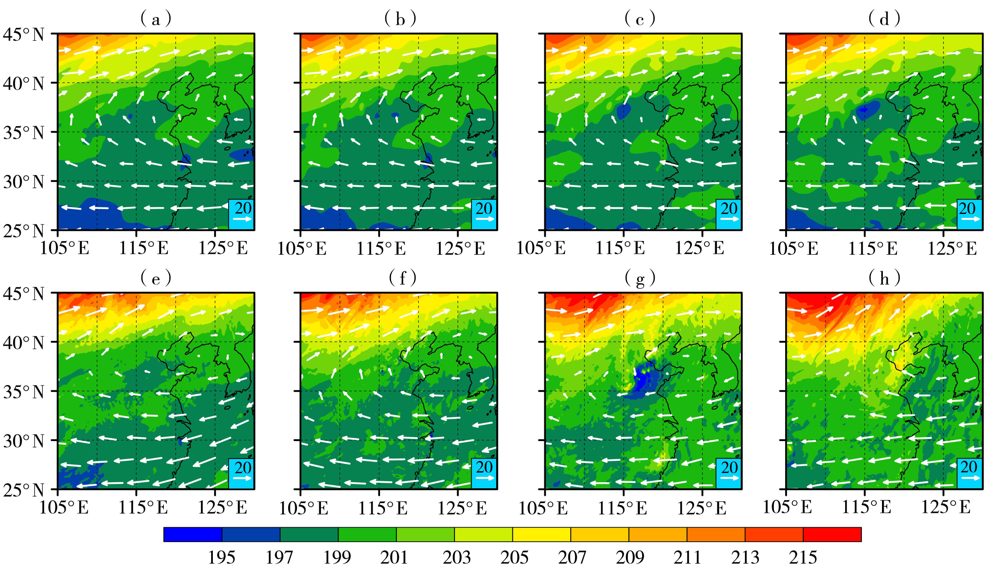
图4 2010年8月4日00:00—18:00 30 hPa高度上ERA5再分析资料(a、b、c、d)和WRF模式输出(e、f、g、h)的温度场(填色区,单位:K)和水平风场(白色箭头,单位:m·s-1)对比(a、e)00:00,(b、f)06:00,(c、g)12:00,(d、h)18:00
Fig.4 The comparison of temperature field (color shaded areas, Unit: K) and horizontal wind field (white arrows, Unit: m·s-1) from ERA5 reanalysis data (a, b, c, d) and WRF simulation (e, f, g, h) at 30 hPa from 00:00 UTC to 18:00 UTC on 4 August 2010(a, e) 00:00 UTC, (b, f) 06:00 UTC, (c, g) 12:00 UTC, (d, h) 18:00 UTC

图5 2010年8月4日06:00—21:00 FY-2E卫星探测的TBB(a、b、c、d、e、f)和WRF模式模拟的CTT(g、h、i、j、k、l)对比(单位:K)(a、g)06:00,(b、h)09:00,(c、i)12:00,(d、j)15:00,(e、k)18:00,(f、l)21:00
Fig.5 The comparison of observed TBB from FY-2E satellite (a, b, c, d, e, f) with simulated CTT by WRF model(g, h, i, j, k, l) from 06:00 UTC to 21:00 UTC on 4 August 2010 (Unit: K) (a, g) 06:00 UTC, (b, h) 09:00 UTC, (c, i) 12:00 UTC, (d, j) 15:00 UTC, (e, k) 18:00 UTC, (f, l) 21:00 UTC
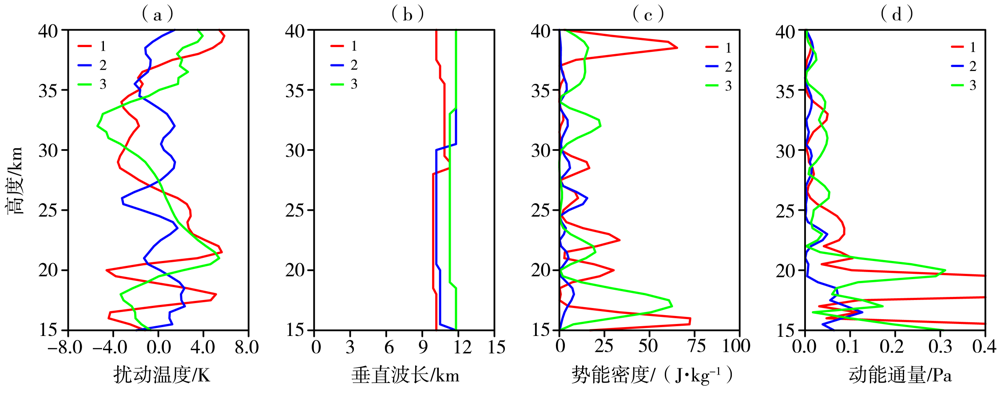
图6 2010年8月4日WRF模式模拟的不同采样点扰动温度(a)、垂直波长(b)、势能密度(c)和动量通量(d)廓线
Fig.6 The profiles of disturbance temperature (a), vertical wavelength (b), potential energy per unit mass (c)and momentum flux (d) simulated by WRF model at different sampling points on 4 August 2010

图7 2010年8月4日06:00—21:00 WRF模式输出的30 hPa垂直速度分布(单位:m·s-1)(a)06:00,(b)09:00,(c)12:00,(d)15:00,(e)18:00,(f)21: 00
Fig.7 The distribution of vertical velocity from WRF model at 30 hPa from 06:00 UTC to 21:00 UT C on 4 August 2010 (Unit: m·s-1) (a) 06:00 UTC, (b) 09:00 UTC, (c) 12:00 UTC, (d)15:00 UTC, (e) 18:00 UTC, (f) 21:00 UTC
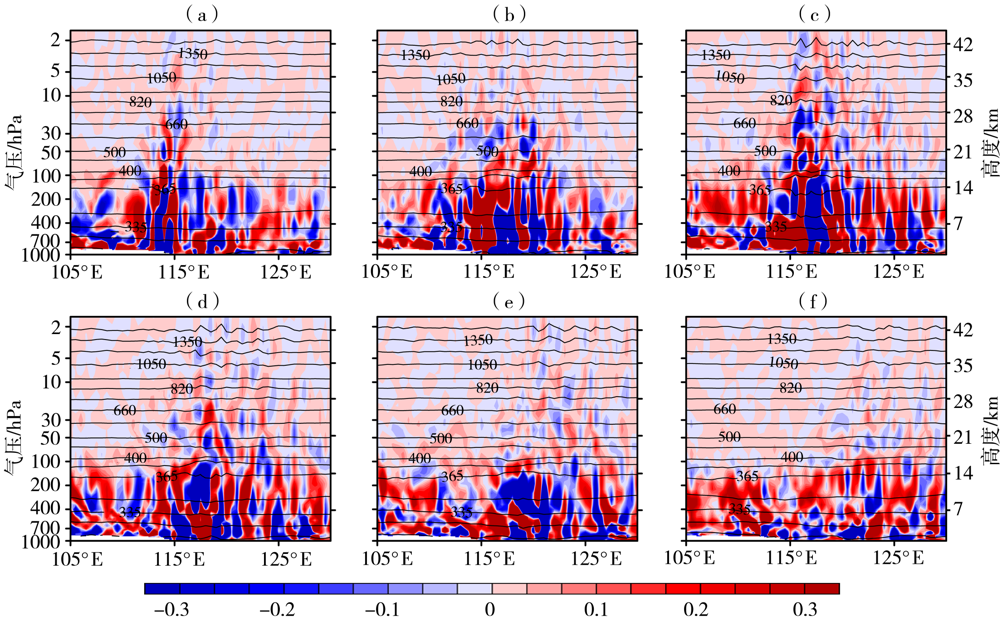
图8 2010年8月4日06: 00—21:00 WRF模式输出的垂直速度(填色区,单位:m·s-1)和位温(黑色实线,单位:K)沿38°N的经度-高度分布(a)06:00,(b)09:00,(c)12:00,(d)15:00,(e)18:00,(f)21:00
Fig.8 The longitude-height distribution of vertical velocity (color shaded areas, Unit: m·s-1) and potential temperature(black solid lines, Unit: K) from WRF model along 38°N from 06:00 UTC to 21:00 UTC on 4 August 2010 (a) 06:00 UTC, (b) 09:00 UTC, (c) 12:00 UTC, (d) 15:00 UTC, (e) 18:00 UTC, (f) 21:00 UTC
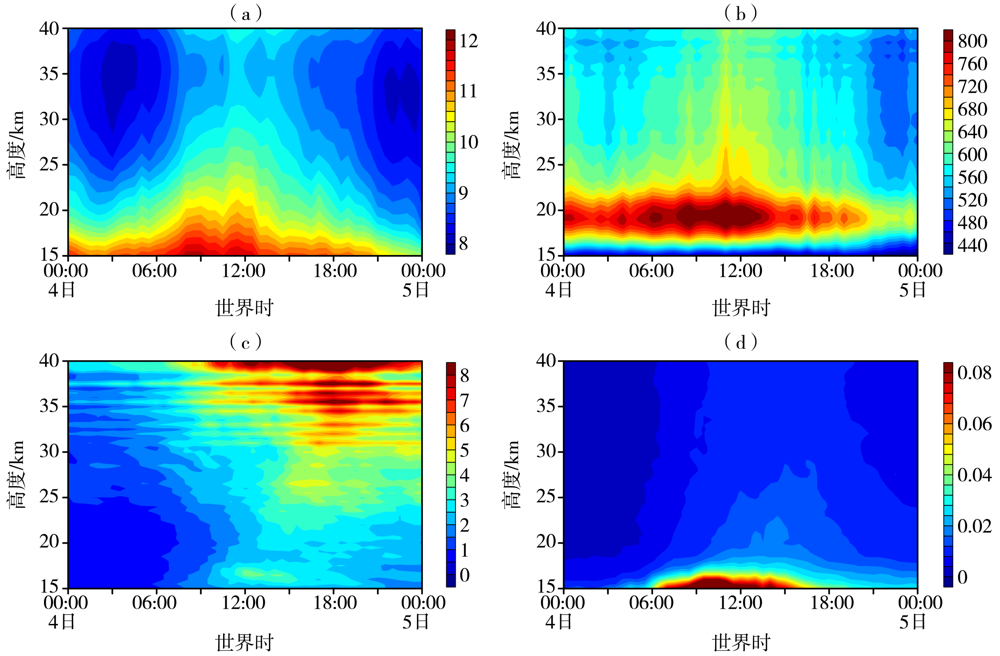
图9 2010年8月4日00:00至5日00:00 WRF模式输出的重力波垂直波长(a,单位:km)、水平波长(b,单位:km)、 势能密度(c,单位:J·kg-1)和动量通量(d,单位:Pa)随高度-时间变化
Fig.9 The change of vertical wavelength (a, Unit: km), horizontal wavelength (b, Unit: km), potential energy per unit mass (c, Unit: J·kg-1) and momentum flux (d, Unit: Pa) simulated by WRF model with height and time from 00:00 UTC on 4 to 00:00 UTC on 5 August 2010

图10 WRF模式输出的不同高度上平均势能密度(a)和对流强度(b)随时间变化 (虚线指示不同高度平均势能密度达到峰值的时间,红色三角形对应对流最强时刻)
Fig.10 The change of average potential energy per unit mass (a) and convective intensity (b) with time simulated by WRF model at different heights (The dotted lines are the corresponding time with the peak value of average potential energy per unit mass at different heights, and the red triangle marks the moment for strongest convection)
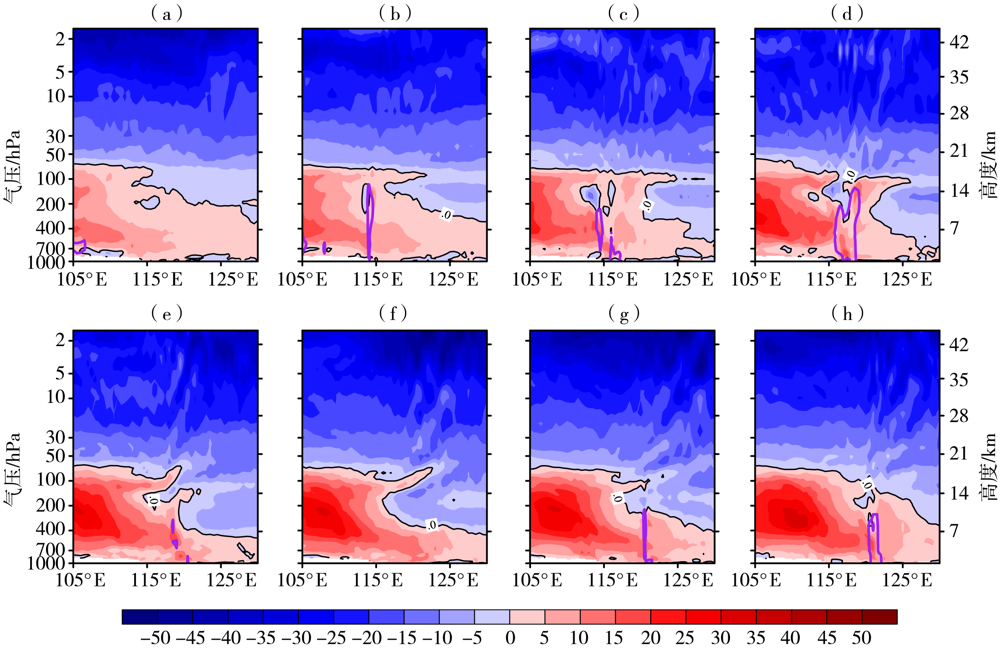
图11 2010年8月4日02:00至5日06:00 WRF模式输出的u风分量沿38°N的经度-高度剖面(单位:m·s-1) (a)4日02:00,(b)4日06:00,(c)4日10:00,(d)4日14:00,(e)4日18:00,(f)4日22:00,(g)5日02:00,(h)5日06:00 (黑色实线的风速为0 m·s-1,紫色实线包围区域的雷达反射率因子大于等于20 dBZ)
Fig.11 The longtitude-height section of u component of wind simulated by WRF model along 38°N from 02:00 UTC on 4 to 06:00 UTC on 5 August 2010 (a) 02:00 UTC 4, (b) 06:00 UTC 4, (c) 10:00 UTC 4, (d) 14:00 UTC 4, (e) 18:00 UTC 4,(f) 22: 00 UTC 4, (g) 02:00 UTC 5, (h) 06:00 UTC 5 (The wind speed for black solid line is equal to 0 m·s-1, and the radar reflectivity factor in area enclosed by purple solid line is greater than or equal to 20 dBZ)
| [1] |
FRITTS D C. Gravity wave saturation in the middle atmosphere: a review of theory and observations[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 1984, 22(3): 275-308.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
MAYR H G, MENGEL J G, REDDY C A, et al. Variability of the equatorial oscillations induced by gravity wave filtering[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25(14): 2629-2632.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LINDZEN R S. Wave-mean flow interactions in the upper atmosphere[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1973, 4(1): 327-343.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LUBKEN F J, FRICKE K H, LANGER M. Noctilucent clouds and the thermal structure near the Arctic mesopause in summer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1996, 101(D5): 9489-9508.
DOI URL |
| [5] | FRITTS D C, ALEXANDER M J. Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2003, 41(1):1-64. |
| [6] | TSUDA T, MURAYAMA Y, WIRYOSUMARTO H, et al. Radiosonde observations of equatorial atmosphere dynamics over Indonesia: 2. characteristics of gravity waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(D5):10 507-10 516. |
| [7] | VINCENT R A, ALEXANDER M J. Gravity waves in the tropical lower stratosphere: an observational study of seasonal and interannual variability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(D14): 17 971-17 982. |
| [8] |
ALEXANDER M J, HOLTON J R. A model study of zonal forcing in the equatorial stratosphere by convectively induced gravity waves[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1997, 54(3): 408-419.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
STEPHAN C, ALEXANDER M J, RICHTER J H. Characteristics of gravity waves from convection and implications for their parameterization in global circulation models[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2016, 73(7): 2729-2742.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GONG J, GELLER M A. Vertical fluctuation energy in United States high vertical resolution radiosonde data as an indicator of convective gravity wave sources[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115: D11110.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WRIGHT C J. Quantifying the global impact of tropical cyclone-associated gravity waves using HIRDLS, MLS, SABER and IBTrACS data[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2019, 145(724): 3023-3039.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG L, GELLER M A. Morphology of gravity-wave energy as observed from 4 years (1998-2001) of high vertical resolution U.S. radiosonde data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(D16), 4489.DOI: 10.1029/2002JD002786.
DOI |
| [13] | KUMAR K K. VHF radar investigations on the role of mechanical oscillator effect in exciting convectively generated gravity waves[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34: L01803. |
| [14] | ESWARAIAH S, RATNAM M V, MURTHY B V K, et al. Short period gravity wave momentum fluxes observed in the tropical troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2013(105/106): 1-7. |
| [15] |
EHARD B, KAIFLER B, KAIFLER N, et al. Evaluation of methods for gravity wave extraction from middle-atmospheric lidar temperature measurements[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2015, 8(11): 4645-4655.
DOI URL |
| [16] | SCHREINER W, ROCHEN C, SOKOLOVSKIY S, et al. Estimates of the precision of GPS radio occultation from the COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 mission[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34: L04808. |
| [17] |
FABER A, LLAMEDO P, SCHMIDT T, et al. On the determination of gravity wave momentum flux from GPS radio occultation data[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2013, 6(11): 3169-3180.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ALEXANDER P, DE LA TORRE A, SCHMIDT T, et al. Limb sounders tracking topographic gravity wave activity from the stratosphere to the ionosphere around midlatitude Andes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2015, 120(10): 9014-9022.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SCHMIDT T, ALEXANDER P, DE LA TORRE A. Stratospheric gravity wave momentum flux from radio occultations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121(9): 4443-4467.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ALEXANDER M J, BARNET C. Using satellite observations to constrain parameterizations of gravity wave effects for global models[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2007, 64(5): 1652-1665.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 陈丹, 陈泽宇, 吕达仁. 台风重力波的谱结构和动量通量特征分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(5): 874-882. |
| [22] | EVAN S, ALEXANDER M J, DUDHIA J. WRF simulations of convectively generated gravity waves in opposite QBO phases[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117: D12117. |
| [23] |
GHOSH P, RAMKUMAR T K, YESUBABU V, et al. Convection-generated high-frequency gravity waves as observed by MST radar and simulated by WRF model over the Indian tropical station of Gadanki[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2016, 142(701): 3036-3049.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
DU Y, ZHANG F. Banded convective activity associated with mesoscale gravity waves over southern China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2019, 124(4): 1912-1930.
DOI URL |
| [25] | WU D L, ZHANG F Q. A study of mesoscale gravity waves over the North Atlantic with satellite observations and a mesoscale model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2004, 109: D22104. |
| [26] |
BINDU H H, RATNAM M V, YESUBABU V, et al. Medium frequency gravity wave characteristics obtained using Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model simulations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2019, 182: 119-129.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ATHREYAS K N, GUNAWAN E, KIAT T B. Gravity waves generated by thunderstorms: South-East Asia tropical region study[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 63(11): 3436-3451.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
TODD P L, JASON C K. Some effects of model resolution on simulated gravity waves generated by deep, mesoscaleconvection[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2004, 62(9): 3408-3419.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
KALISCH S, CHUN H Y, ERN M, et al. Comparison of simulated and observed convective gravity waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121(22): 13474-13492.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 孙睿, 姚志刚, 韩志刚, 等. 一次暴雨激发平流层重力波的卫星观测与数值模拟[J]. 空间科学学报, 2018, 38(4): 469-481. |
| [31] |
HOFFMANN L, ALEXANDER M J. Occurrence frequency of convective gravity waves during the North American thunderstorm season[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115: D20111.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
HOFFMANN L, XUE X, ALEXANDER M J. A global view of stratospheric gravity wave hotspots located with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013, 118(2): 416-434.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 吴建飞. 热带气旋重力波的激发和传播机制研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2016. |
| [34] |
ALEXANDER M J. Global and seasonal variations in three-dimensional gravity wave momentum flux from satellite limb-sounding temperatures[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(16): 6860-6867.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 王芬, 王文勇, 刘相, 等. FY-2卫星黑体亮温TBB与黔西南短时强降水的关系[J]. 中低纬山地气象, 2021, 45(1): 1-8. |
| [36] |
YAMASHITA C, ENGLAND S L, IMMEL T J, et al. Gravity wave variations during elevated stratopause events using SABER observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013, 118(11): 5287-5303.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
LIU X, YUE J, XU J Y, et al. Variations of global gravity waves derived from 14 years of SABER temperature observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017, 122(12): 6231-6249.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
HONG S Y, DUDHIA J, CHEN S H. A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2004, 132(1): 103-120.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
GRELL G A, DÉVÉNYI D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(14),38.DOI: 10.1029/2002GL015311.
DOI |
| [40] |
MELLOR G L, YAMADA T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 1982, 20(4): 851-875.
DOI URL |
| [41] | MLAWER E J, TAUBMAN S J, BROWN P D, et al. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmosphere: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(D14): 16 663- 16 682. |
| [42] |
DUDHIA J. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1989, 46(20): 3077-3107.
DOI URL |
| [43] | JANJIĆ Z I. Nonsingular implementation of the Mellor-Yamada level 2.5 scheme in the NCEP Meso model[Z]. Maryland,NOAA/NWS/NCEP Office, 2002:1-61. |
| [44] |
CHEN F, DUDHIA J. Coupling an advanced land surface-hydrology model with the Penn State-NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: model implementation and sensitivity[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2001, 129: 569-585.
DOI URL |
| [45] | 卞建春, 陈洪滨, 吕达仁. 用垂直高分辨率探空资料分析北京上空下平流层重力波的统计特性[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2004, 34(8): 748-756. |
| [46] | 邓少格, 钟中, 程胡华. 一次暴雨过程中重力波参数演变特征的模拟结果[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(6): 1831-1843. |
| [47] |
ERN M, PREUSSE P, ALEXANDER M J, et al. Absolute values of gravity wave momentum flux derived from satellite data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2004, 109: D20103.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 姚志刚, 赵增亮, 韩志刚. AIRS观测的东亚夏季平流层重力波特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(4): 1121-1134. |
| [49] |
COSTANTINO L, HEINRICH P, MZÉ N, et al. Convective gravity wave propagation and breaking in the stratosphere: comparison between WRF model simulations and lidar data[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 2015, 33(9): 1155-1171.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
BERES J H, ALEXANDER M J, HOLTON J R. Effects of tropospheric wind shear on the spectrum of convectively generated gravity waves[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2002, 59(11): 1805-1824.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
BERES J H. Gravity wave generation by a three-dimensional thermal forcing[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2004, 61(14): 1805-1815.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 邢峰华, 黄彦彬, 李春鸾, 黄菲婷, 李光伟, 敖 杰. 海南岛热带孤立对流云系特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 442-449. |
| [2] | 褚颖佳, 郭飞燕, 高帆, 胡鹏, 郑丽娜, 刘奕辰, 鲁亓. 冷涡影响下两次不同类型强对流过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 279-289. |
| [3] | 孙明燕, 张述文. 边界层湍流垂直混合强度对局地热对流模拟影响的个例研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 290-300. |
| [4] | 韦惠红, 吴翠红, 魏凡, 鲁易, 孔海妹, 赵欢. 湖北雷暴阵风锋特征及其对流触发作用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 73-81. |
| [5] | 叶茂, 吴钲, 高松, 陈良吕, 游婷. 对流尺度集合预报对川渝地区降水的预报性能分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 152-163. |
| [6] | 傅朝, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 徐丽丽, 沙宏娥, 马莉, 崔宇. 西北干旱区一次极端暴雨局地性增强的对流环境特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 909-921. |
| [7] | 许敏, 沈芳, 刘璇, 刘艳杰, 张湘涵. 京津冀“7·5”强对流天气形成的环境条件及中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 993-1002. |
| [8] | 支树林, 许东蓓, 潘赫拉, 李典南, 包慧濛, 陈娟. 陕西汉中及其周边地区对流活动的雷达气候特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(4): 620-630. |
| [9] | 杨涛, 杨莲梅, 张云惠, 庄晓翠, 黄艳. 新疆短时强降水天气系统环流配置及雷达回波特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(4): 631-640. |
| [10] | 董春卿, 武永利, 郭媛媛, 马丽, 苗青. 山西强对流天气分类指标与判据的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 345-355. |
| [11] | 任丽, 杨艳敏. 东北冷涡底部一次MCC暴雨动力热力特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 65-75. |
| [12] | 邹书平, 黄钰, 曾勇, 李丽丽, 杨哲, 曹水, 柯莉萍. 一次典型强对流单体对的雷达回波相似性特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(06): 974-983. |
| [13] | 董 甫, 张 玲, 张海鹏, 李 佳, 宋柳贤. 基于WRF模式的强天气过程集合预报综述[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 699-708. |
| [14] | 徐娟娟, 郝丽, 刘嘉慧敏, 郭大梅, 赵强. 2018年1月陕西区域性暴雪过程诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(1): 117-125. |
| [15] | 贺哲, 王君, 栗晗, 鲁坦, 崔丽曼, . 河南省一次副高边缘对流性暴雨的多尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(03): 423-432. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
