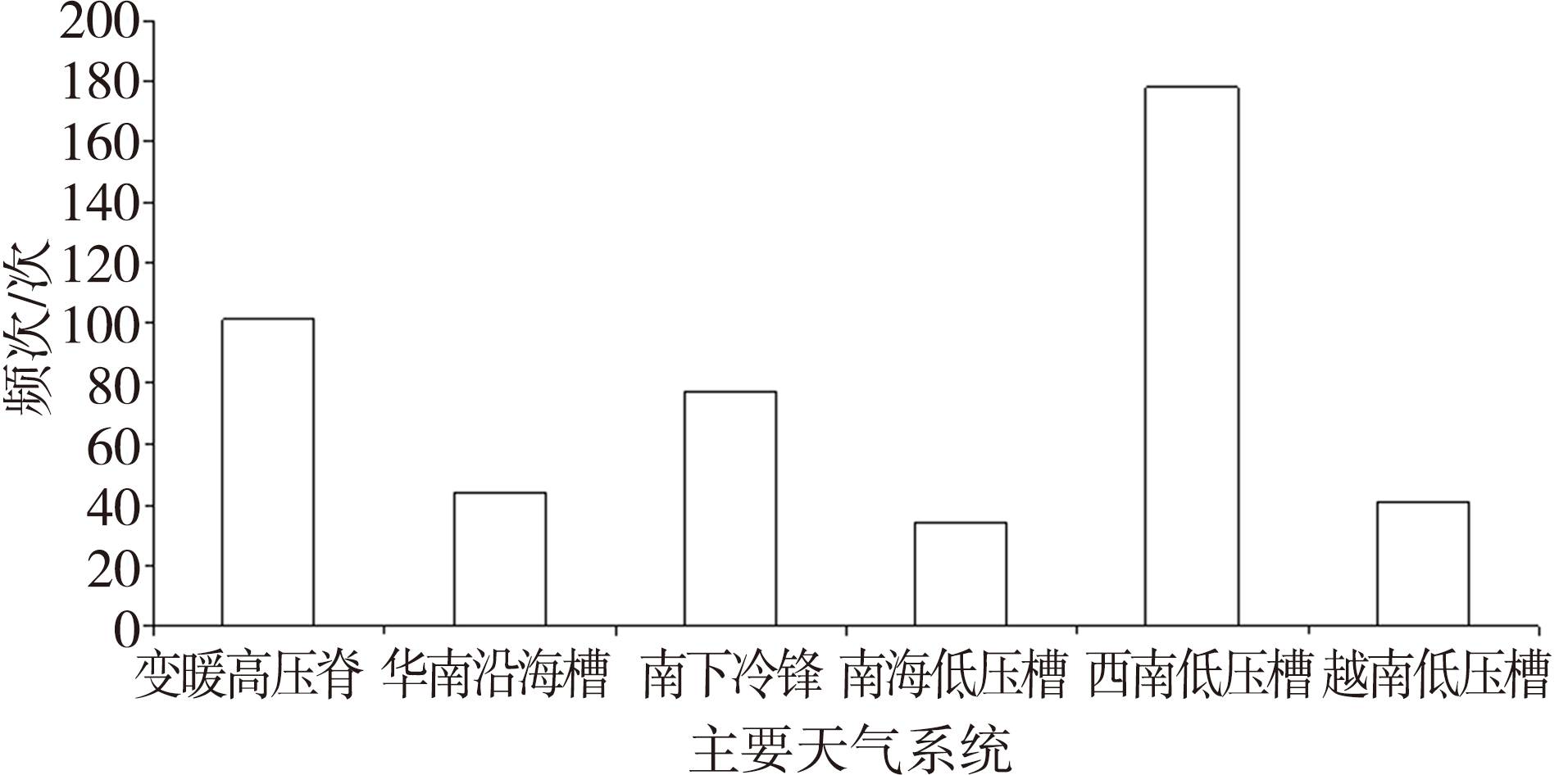
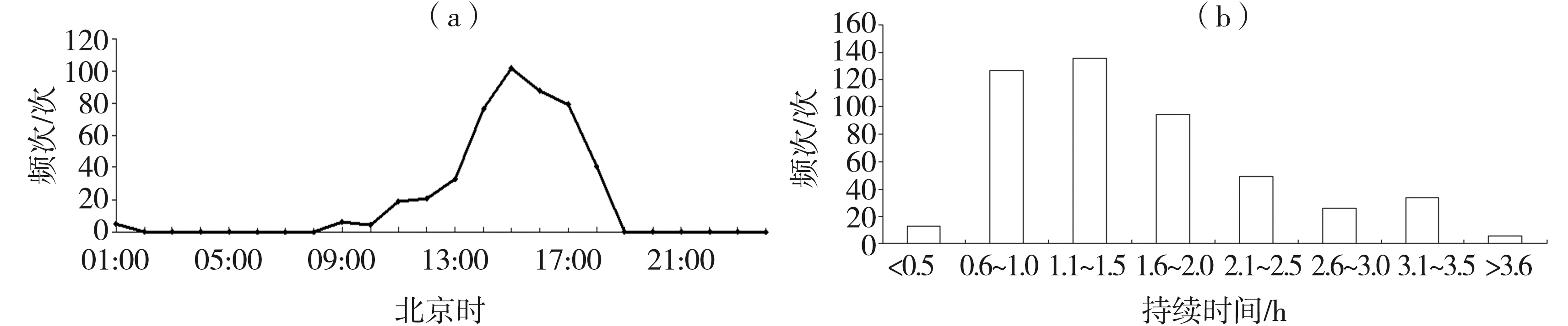
| [1] |
符晓虹, 郑育群, 羊清雯, 2015. 天气系统与海南降水的关系研究[J]. 气象研究与应用, 36(1): 10-19.
|
| [2] |
郭飞燕, 刁秀广, 褚颖佳, 等, 2023. 两次极端强降水风暴双偏振参量特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 103-113.
DOI
|
| [3] |
何娜, 丁青兰, 俞小鼎, 等, 2020. 北京及周边地区雷暴阵风锋特征统计分析[J]. 气象学报, 78(2): 250-259.
|
| [4] |
黄钰, 阮征, 罗秀明, 等, 2015. 垂直探测雷达的降水云分类方法在北京地区的应用[J]. 高原气象, 34(3): 815-824.
DOI
|
| [5] |
赖晨, 支树林, 李婕, 等, 2020. SC型双偏振雷达在江南南部一次对流性天气过程中的应用分析[J]. 气象, 46(11): 1 427-1 439.
|
| [6] |
李宏江, 曹洁, 李勋, 等, 2021. 基于有限区域风场分解的海南岛一次飑线过程演变特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 30(2): 24-35.
|
| [7] |
林文, 张深寿, 罗昌荣, 等, 2020. 不同强度强对流云系S波段双偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象, 46(1): 63-72.
|
| [8] |
潘佳文, 魏鸣, 郭丽君, 等, 2020. 闽南地区大冰雹超级单体演变的双偏振特征分析[J]. 气象, 46(12): 1 608-1 620.
|
| [9] |
申高航, 高安春, 李君, 2021. 雨滴谱及双偏振雷达等资料在一次强降水过程中的应用[J]. 气象, 47(6): 737-745.
|
| [10] |
王春乙, 吴慧, 邢旭煌, 等, 2014. 海南气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [11] |
王凌梓, 苗峻峰, 管玉平, 2020. 多云天气下海南岛地形对局地海风环流结构影响的数值模拟[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(2): 322-335.
|
| [12] |
万明波, 孟宪贵, 刁秀广, 等, 2015. 山东极端强降雨风暴传播类型及流场结构特征[J]. 高原气象, 34(6): 1 741-1 750.
|
| [13] |
王莎, 沙勇, 宋金妹, 等, 2019. 冀东地区冰雹云多普勒雷达参数特征分析[J]. 气象, 45(5): 713-722.
|
| [14] |
王子周, 2011. 强对流天气雷达回波特征提取及预报方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学.
|
| [15] |
邢峰华, 黄菲婷, 黄彦彬, 等, 2020. 基于风廓线雷达的降水云分类方法在海南地区的应用[J]. 海南大学学报, 38(1): 76-83.
|
| [16] |
肖现, 陈明轩, 高峰, 等, 2015. 弱天气系统强迫下北京地区对流下山演变的热动力机制[J]. 大气科学, 39(1): 100-124.
|
| [17] |
杨俊梅, 王星星, 封秋娟, 等, 2017. 山西汾阳地区层状云和对流云降水雨滴谱特征[J]. 干旱气象, 35(3): 439-445.
DOI
|
| [18] |
袁野, 冯静夷, 蒋年冲, 等, 2008. 夏季催化对流云雷达回波特征对比分析[J]. 气象, 34(1): 41-48.
|
| [19] |
岳治国, 牛生杰, 2007. 洛川地区孤立对流云雷达回波特征分析[J]. 陕西气象, (5): 1-5.
|
| [20] |
朱士超, 袁野, 吴林林, 等, 2017. 江淮对流云发生规律及其垂直结构分析[J]. 气象, 43(6): 696-704.
|
| [21] |
朱士超, 袁野, 吴月, 等, 2019. 江淮地区孤立对流云统计特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(6): 690-699.
|
| [22] |
BLUESTEIN H B, JAIN M H, 1985. Formation of mesoscale lines of precipitation: severe squall lines in Oklahoma during the spring[J]. Journal Atmospheric Sciences, 42 (16): 1 711-1 732.
|
| [23] |
CARBONE R E, WILSON J W, KEENAN T, et al, 2000. Tropical island convection in the absence of significant topography. Part I: life cycle of diurnally forced convection[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 128:3 459-3 479.
|
| [24] |
FREY W, BORMANN S, FIERLI F, et al, 2014. Tropical deep convective life cycle: Cb-anvil cloud microphysics from high-altitude aircraft observations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14: 13 223-13 240.
|
| [25] |
FUTYAN J M, DEL GENIO A D, 2007. Deep convective system evolution over Africa and the tropical Atlantic[J]. Journal of Climate, 20(20): 5 041-5 060.
|
| [26] |
LOMBARDO K A, COLLE B A, 2010. The spatial and temporal distribution of organized convective structures over the Northeast and their ambient conditions[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 138(12): 4 456-4 474.
|
| [27] |
PARKER P D, JOHNSON R H, 2000. Organizational modes of midlatitude mesoscale convective systems[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 128 (10):3 413-3 436.
|
| [28] |
RAO T N, KIRANKUMAR N Y P, RADHAKRISHNA B, et al, 2008. Classification of tropical precipitating systems using wind profiler spectral moments[J]. Journal Atmospheric Oceanic Technology, 25 (6):884-897.
DOI
URL
|
| [29] |
ROWE A K, RUTLEDGE S A, LANG T J, 2011. Investigation of microphysical processes occurring in isolated convection during NAME[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 139 (2):424-443.
DOI
URL
|
| [30] |
WANG C C, KIRSHBAUM D J, 2015. Thermally forced convection over a mountainous tropical island[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 72(6):2 484-2 506.
|
| [31] |
ZHANG A Q, FU Y F, 2018. Life cycle effects on the vertical structure of precipitation in East China measured by Himawari-8 and GPM DPR[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 146 (7): 2 183-2 199.
|
 ), 黄彦彬1(
), 黄彦彬1( ), 李春鸾3, 黄菲婷2, 李光伟1, 敖杰1
), 李春鸾3, 黄菲婷2, 李光伟1, 敖杰1
 ), HUANG Yanbin1(
), HUANG Yanbin1( ), LI Chunluan3, HUANG Feiting2, LI Guangwei1, AO Jie1
), LI Chunluan3, HUANG Feiting2, LI Guangwei1, AO Jie1