干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 238-250.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0238
CLDAS陆面资料对区域数值预报系统气温预报的改进研究
- 浙江省气象科学研究所,浙江 杭州 310008
-
收稿日期:2023-05-04修回日期:2023-09-05出版日期:2024-04-30发布日期:2024-05-12 -
通讯作者:陈锋(1982—),男,博士,正高级工程师,主要从事数值模式及资料同化研究。E-mail:fchen_zj@163.com 。 -
作者简介:邱金晶(1988—),女,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事数值预报技术研究和应用。E-mail: jinjing_qiu@163.com。 -
基金资助:浙江省基础公益研究计划项目(LGF20D050001);中国气象局复盘总结专项(FPZJ2024-053);浙江省气象科技计划项目(2019 ZD11);浙江省气象科技计划项目(2021YYZX06)
Research on improvement of temperature forecasts of the regional numerical prediction system using CLDAS land data
QIU Jinjing( ), CHEN Feng(
), CHEN Feng( ), DONG Meiying, FAN Yuemin, YU Zhenshou
), DONG Meiying, FAN Yuemin, YU Zhenshou
- Institute of Meteorological Sciences of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310008, China
-
Received:2023-05-04Revised:2023-09-05Online:2024-04-30Published:2024-05-12
摘要:
为提升区域数值预报系统2 m气温预报性能,利用土壤温度和土壤湿度站点观测资料,对中国气象局陆面数据同化系统(CMA Land Data Assimilation System,CLDAS)陆面资料在浙江地区的精度进行评估,并将其融合应用于浙江省数值预报业务系统。结果表明:CLDAS土壤温度、土壤湿度产品相对于美国全球预报系统(Global Forecast System,GFS)分析场,与观测相比具有更小的均方根误差和更高的相关系数,在浙江省有较好的适用性。个例分析表明区域数值模式2 m气温预报对陆面资料变化较敏感,融合CLDAS地表温度、土壤温湿度实时分析产品的初始场,可持续影响到模式预报后期,主要通过地表感热、潜热通量直接影响气温变化。从均方根误差来看,与基于GFS分析场作为陆面初始场的区域模式预报相比,应用了CLDAS陆面资料的模式预报改进了13.6%。2021年7月阶段性应用结果显示,模式初始场融合CLDAS陆面资料后有效提高了浙江省2 m气温预报水平,融合后的预报改进效果夜间较白天明显,且晴热高温天气背景下较梅雨期、台风期改进更佳。高温天气预报评估进一步表明,CLDAS陆面资料的应用对浙江省高温事件预报有较好的改进,尤其对金衢盆地等高温区改进明显。
中图分类号:
引用本文
邱金晶, 陈锋, 董美莹, 范悦敏, 余贞寿. CLDAS陆面资料对区域数值预报系统气温预报的改进研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 238-250.
QIU Jinjing, CHEN Feng, DONG Meiying, FAN Yuemin, YU Zhenshou. Research on improvement of temperature forecasts of the regional numerical prediction system using CLDAS land data[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 238-250.
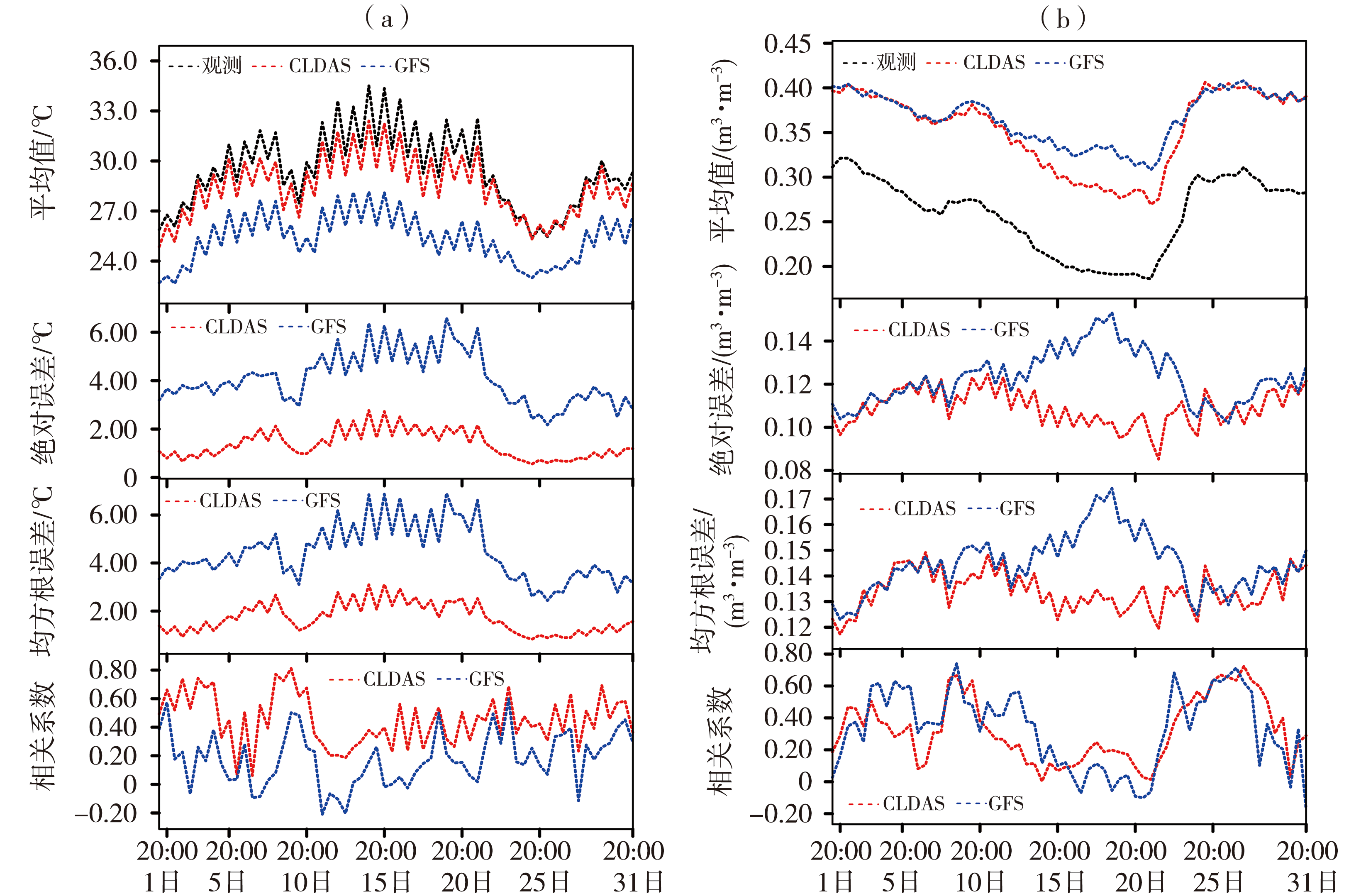
图2 浙江省2021年7月CLDAS和GFS分析场0~10 cm土壤温度(a)和土壤湿度(b)平均值、绝对误差、均方根误差、相关系数的逐12 h演变
Fig.2 The 12-hour variation of averages, absolute errors, root mean square errors and correlation coefficients of 0-10 cm soil temperature (a) and 0-10 cm soil moisture (b) of CLDAS and GFS analysis fields in Zhejiang Province in July 2021

图3 浙江省2021年7月CLDAS(a、c)、GFS分析场(b、d)与观测数据0~10 cm土壤温度(a、b)、土壤湿度(c、d)的时间相关系数空间分布
Fig.3 Spatial distributions of time correlation coefficients between CLDAS (a, c), GFS analysis fields (b, d) and 0-10 cm soil temperature (a, b), 0-10 cm soil moisture (c, d) in July 2021 in Zhejiang Province

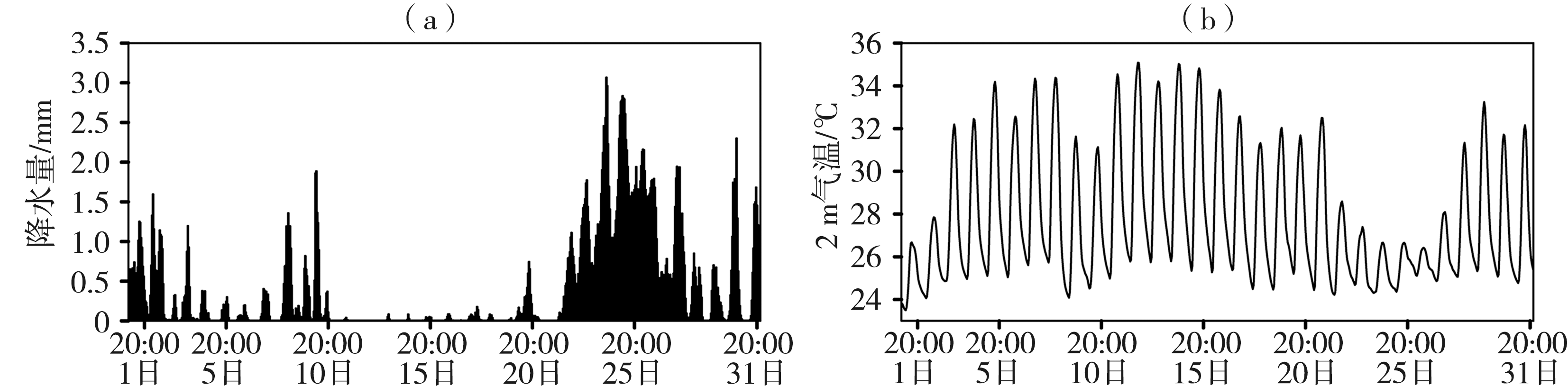
图4 TCLDAS试验和TGFS试验2021年7月13日20:00预报的1~72 h浙江省平均2 m气温误差(a)、绝对误差(b)、均方根误差(c)和相关系数(d)
Fig.4 The errors (a), absolute errors (b), root mean square errors (c) and correlation coefficients (d) of average 2 m temperature predicted by TCLDAS and TGFS for 1-72 h validity period starting at 20:00 on 13 July 2021 in Zhejiang Province

图5 TCLDAS和TGFS试验2021年7月13日20:00预报的1~72 h平均、第18、第42、第66小时浙江省2 m气温误差空间分布(单位:℃) (黑色四边形为后文重点关注区域)
Fig.5 Spatial distributions of errors of 2 m temperature of 1-72 h average and the 18th hour, the 42th hour and the 66th hour in Zhejiang Province predicted by TCLDAS and TGFS starting at 20:00 on 13 July 2021 (Unit: °C) (Black quadrilateral is the focus area for the following part)
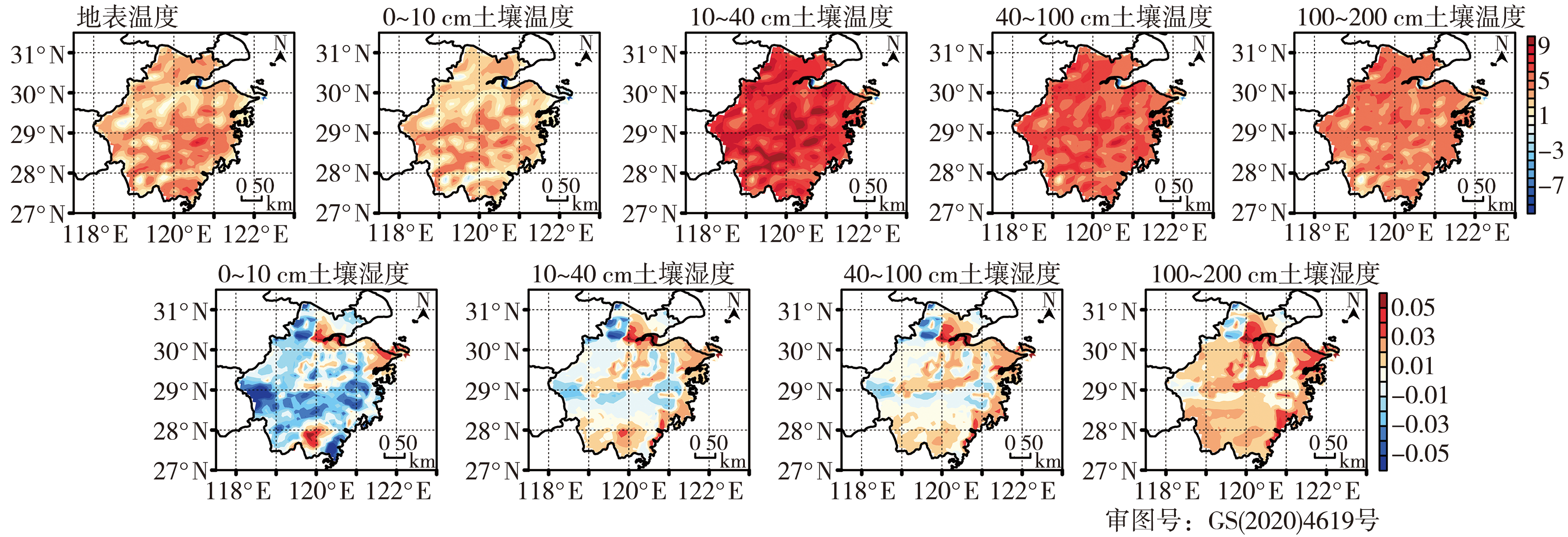
图6 2021年7月13日20:00 CLDAS和GFS分析场地表温度、不同层次土壤温度(单位:℃)及不同层次土壤湿度(单位:m3·m-3)差值分布
Fig.6 Difference distributions between CLDAS and GFS surface temperature, soil temperature (Unit: ℃) for different layers and soil moisture (Unit: m3·m-3) for different layers at 20:00 on 13 July 2021
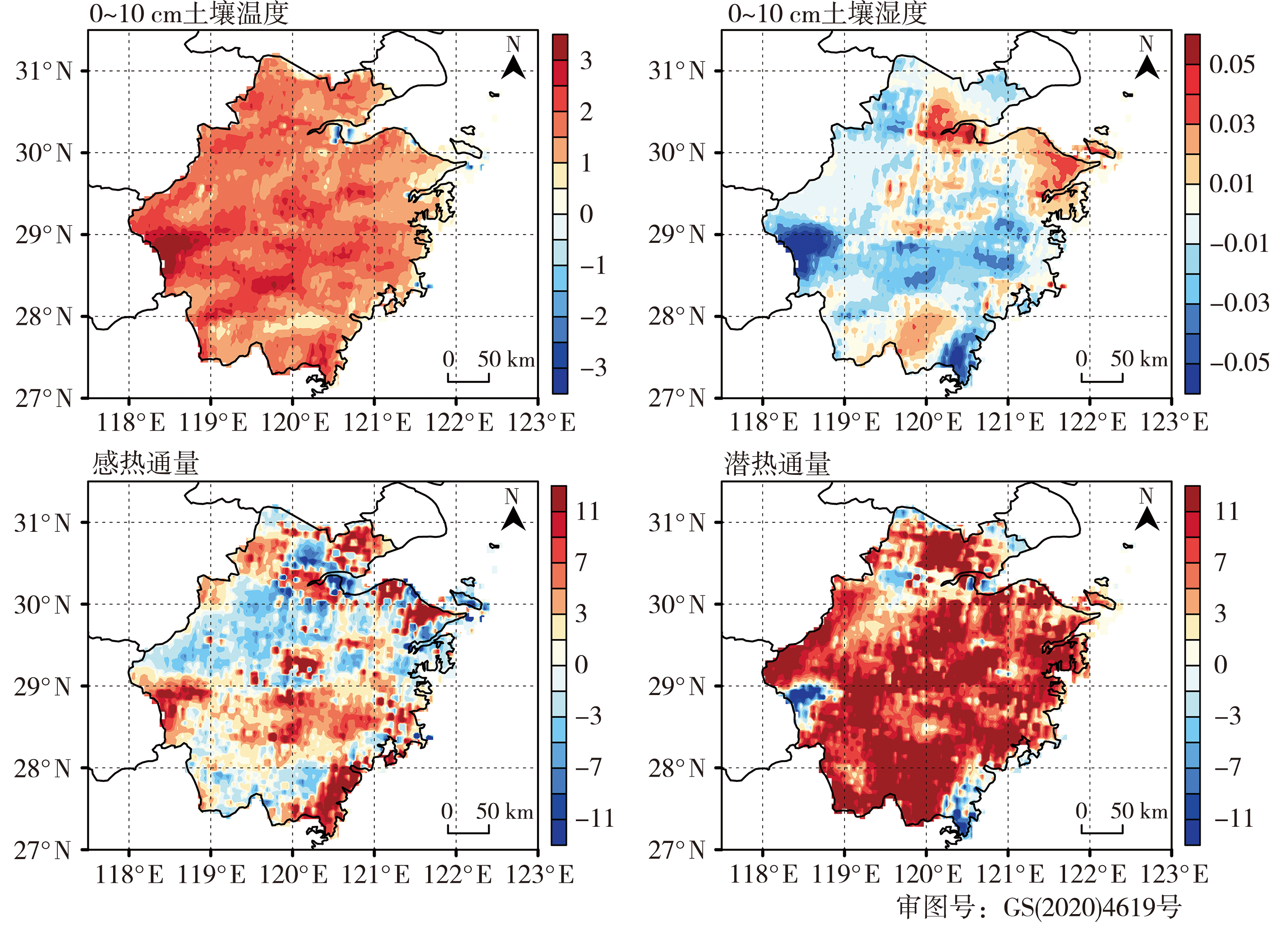
图7 TCLDAS和TGFS试验2021年7月13日20:00预报1~72 h平均0~10 cm土壤温度(单位:℃)、0~10 cm土壤湿度(单位:m3·m-3)、感热通量(单位:W·m-2)、潜热通量(单位:W·m-2)的差值分布
Fig.7 Difference distributions of 0-10 cm soil temperature (Unit: ℃), 0-10 cm soil moisture (Unit: m3·m-3), sensible heat flux (Unit: W·m-2) and latent heat flux (Unit: W·m-2) for 1-72 h average predicted by TCLDAS and TGFS starting at 20:00 on 13 July 2021

图8 TCLDAS和TGFS试验2021年7月13日20:00预报的区域平均1~72 h 2 m气温(a)及其差值(b)、0~10 cm土壤温度(c)及其差值(d)、0~10 cm土壤湿度(e)及其差值(f)、感热通量(g)及其差值(h)、潜热通量(i)及其差值(j)的时间演变
Fig.8 The 1-72 h regional averages of 2 m temperature (a) and their difference (b), 0-10 cm soil temperature (c) and their difference (d), 0-10 cm soil moisture (e) and their difference (f), sensible heat flux (g) and their difference (h), latent heat flux (i) and their difference (j) predicted by TCLDAS and TGFS starting at 20:00 on 13 July 2021
| 时 段 | 试验名称 | 误差/℃ | 绝对误差/℃ | 均方根误差/℃ | 相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—10日 | TCLDAS | -0.75 | 1.82 | 2.22 | 0.55 |
| TGFS | -1.10 | 1.92 | 2.32 | 0.54 | |
| 11—19日 | TCLDAS | -1.30 | 1.89 | 2.31 | 0.67 |
| TGFS | -1.77 | 2.18 | 2.61 | 0.65 | |
| 20—31日 | TCLDAS | -0.23 | 1.55 | 1.94 | 0.63 |
| TGFS | -0.60 | 1.66 | 2.05 | 0.62 |
表1 2021年7月不同天气背景下TCLDAS和TGFS试验预报浙江省2 m气温评估结果
Tab.1 Evaluation results of 2 m temperature in Zhejiang Province predicted by TCLDAS and TGFS under different weather backgrounds in July 2021
| 时 段 | 试验名称 | 误差/℃ | 绝对误差/℃ | 均方根误差/℃ | 相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—10日 | TCLDAS | -0.75 | 1.82 | 2.22 | 0.55 |
| TGFS | -1.10 | 1.92 | 2.32 | 0.54 | |
| 11—19日 | TCLDAS | -1.30 | 1.89 | 2.31 | 0.67 |
| TGFS | -1.77 | 2.18 | 2.61 | 0.65 | |
| 20—31日 | TCLDAS | -0.23 | 1.55 | 1.94 | 0.63 |
| TGFS | -0.60 | 1.66 | 2.05 | 0.62 |
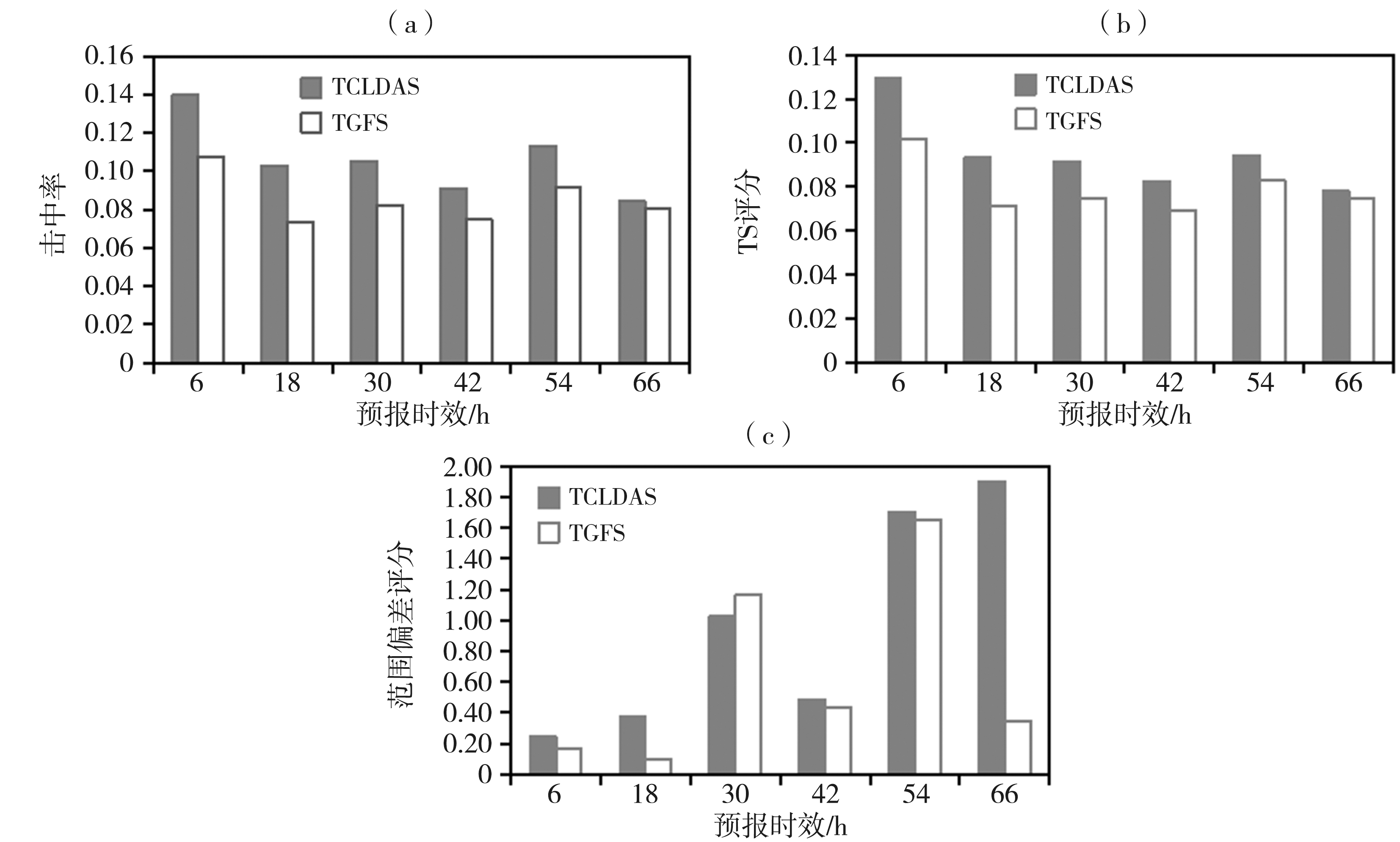
图9 2021年7月TCLDAS和TGFS试验不同提前量下预报逐日14:00 2 m气温(≥35 ℃)评估参数对比 (a)击中率,(b)TS评分,(c)范围偏差评分
Fig.9 Comparison of evaluation parameters of 2 m temperature (≥35 ℃) at 14:00 under different lead time for TCLDAS and TGFS in July 2021 (a) hit rate, (b) threat score, (c) frequency bias

图10 2021年7月逐日14:00平均2 m气温预报及实况空间分布(单位:℃) (a)TCLDAS试验提前6 h预报,(b)TGFS试验提前6 h预报,(c)TCLDAS试验提前18 h预报,(d)TGFS试验提前18 h预报,(e)实况
Fig.10 Spatial distributions of average 2 m temperature at 14:00 in July 2021 (Unit: ℃) (a) forecasted by TCLDAS 6 h in advance, (b) forecasted by TGFS 6 h in advance, (c) forecasted by TCLDAS 18 h in advance, (d) forecasted by TGFS 18 h in advance, (e) observation
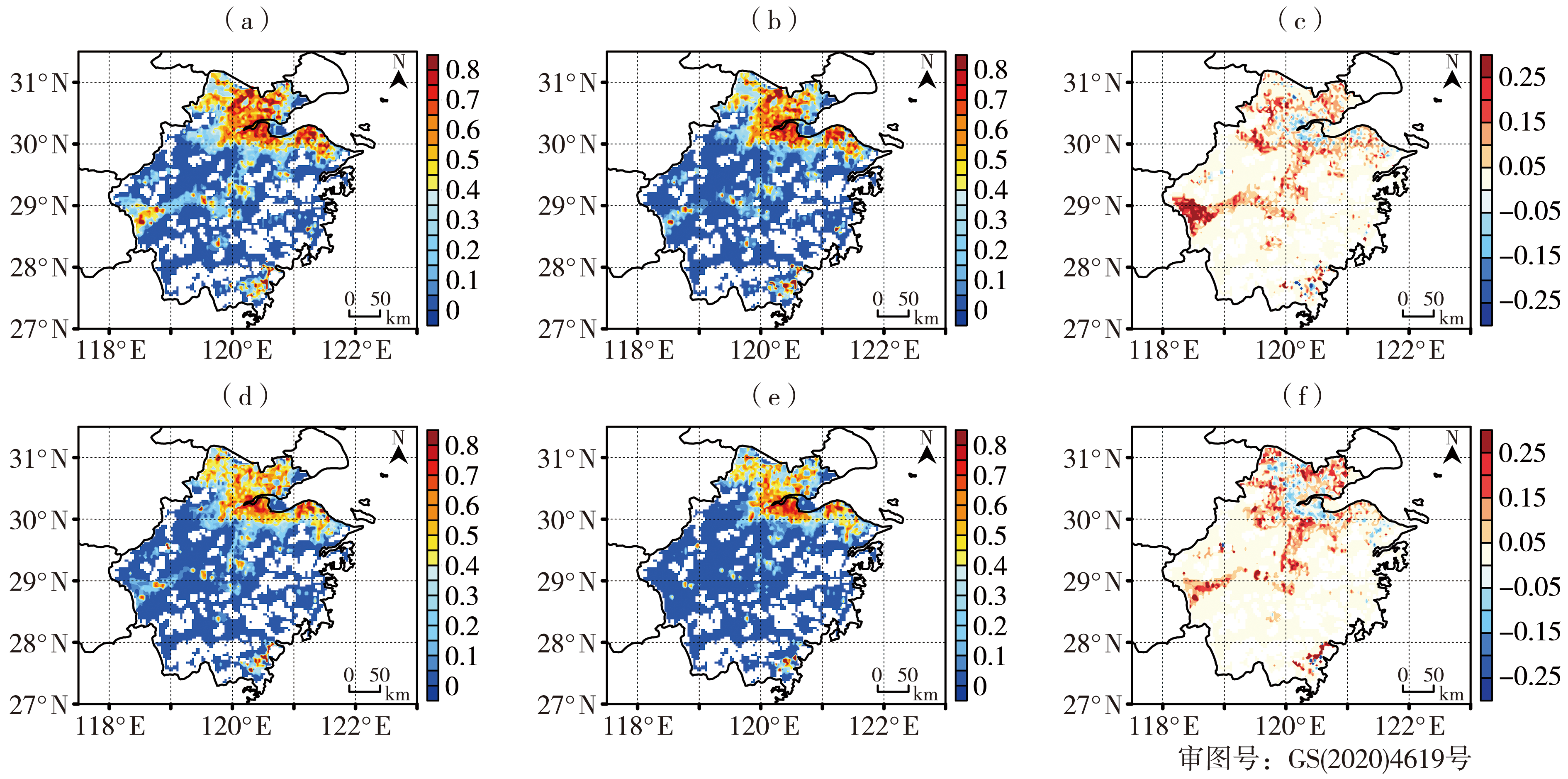
图11 2021年7月TCLDAS和TGFS试验预报逐日14:00 2 m气温(≥35 ℃)TS评分平均值及其差值空间分布 (a)TCLDAS试验提前6 h预报,(b)TGFS试验提前6 h预报,(c)TCLDAS和TGFS试验提前6 h预报差值,(d)TCLDAS试验提前18 h预报,(e)TGFS试验提前18 h预报,(f)TCLDAS和TGFS试验提前18h预报差值
Fig.11 The spatial distributions of averages and differences of threat scores for daily 2 m temperature (≥35 ℃) at 14:00 predicted by TCLDAS and TGFS in July 2021 (a) forecasted by TCLDAS 6 h in advance, (b) forecasted by TGFS 6 h in advance, (c) difference between TCLDAS and TGFS predictions 6 h in advance, (d) forecasted by TCLDAS 18 h in advance, (e) forecasted by TGFS 18 h in advance, (f) difference between TCLDAS and TGFS predictions 18 h in advance
| [1] | 陈锋, 冀春晓, 董美莹, 等, 2012a. 雷达径向风速同化对台风麦莎模拟的影响[J]. 气象, 38(10): 1 170-1 181. |
| [2] | 陈锋, 董美莹, 冀春晓, 等, 2012b. WRF模式对浙江2011年夏季降水和温度预报评估及其湿过程敏感性分析[J]. 浙江气象, 33(3): 3-12. |
| [3] | 陈燕丽, 黄思琦, 莫建飞, 等, 2020. 基于CLDAS数据的甘蔗干旱监测评估标准对比——以2011年广西干旱为例[J]. 干旱气象, 38(2): 188-194. |
| [4] | 崔园园, 张强, 李威, 等, 2020. CLDAS融合土壤相对湿度产品适用性评估及在气象干旱监测中的应用[J]. 海洋气象学报, 40(4): 105-113. |
| [5] | 丁金才, 1995. 天气预报评分方法评述[J]. 大气科学学报, 18(1): 143-150. |
| [6] |
董祝雷, 赵艳丽, 冯晓晶, 等, 2023. CLDAS气温和降水产品在内蒙古地区适用性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5): 811-819.
DOI |
| [7] |
郭阳, 师春香, 徐宾, 等, 2023. CLDAS陆面融合实况数据对天津雾和霾判识的准确性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 657-665.
DOI |
| [8] | 韩帅, 师春香, 林泓锦, 等, 2015. CLDAS土壤湿度业务产品的干旱监测应用[J]. 冰川冻土, 37(2): 446-453. |
| [9] | 刘欢欢, 王飞, 张廷龙, 2018. CLDAS和GLDAS土壤湿度资料在黄土高原的适用性评估[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 36(5): 270-276+294. |
| [10] | 刘佩佩, 宋海清, 鲍炜炜, 等, 2021. CLDAS和GLDAS土壤温度数据在陕西省的适用性评估[J]. 气象科技, 49(4): 604-611. |
| [11] | 马柱国, 魏和林, 符淙斌, 2000. 中国东部区域土壤湿度的变化及其与气候变率的关系[J]. 气象学报, 58(3): 278-287. |
| [12] | 师春香, 姜立鹏, 朱智, 等, 2018. 基于CLDAS2.0驱动数据的中国区域土壤湿度模拟与评估[J]. 江苏农业科学, 46(4): 231-236. |
| [13] | 师春香, 潘旸, 谷军霞, 等, 2019. 多源气象数据融合格点实况产品研制进展[J]. 气象学报, 77(4): 774-783. |
| [14] | 师春香, 谢正辉, 钱辉, 等, 2011. 基于卫星遥感资料的中国区域土壤湿度EnKF数据同化[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 41(3): 375-385. |
| [15] | 王莉莉, 龚建东, 2018. 两种OI陆面同化方法在GRAPES_Meso模式中的初步应用试验[J]. 气象, 44(7): 857-868. |
| [16] | 王万秋, 1991. 土壤温湿异常对短期气候影响的数值模拟试验[J]. 大气科学, 15(5): 115-123. |
| [17] |
温晓培, 吴炜, 李昌义, 等, 2022. 土地利用资料的更新对四川盆地高温天气数值模拟的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 868-878.
DOI |
| [18] | 徐金芳, 邓振镛, 陈敏, 2009. 中国高温热浪危害特征的研究综述[J]. 干旱气象, 27(2): 163-167. |
| [19] | 易翔, 曾新民, 王宁, 等, 2016a. WRF模式中土壤湿度对位势高度模拟影响的敏感性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 34(1): 113-124. |
| [20] | 易翔, 曾新民, 郑益群, 等, 2016b. 高分辨率WRF模式中土壤湿度扰动对短期高温天气模拟影响的个例研究[J]. 大气科学, 40(3): 604-616. |
| [21] | 余贞寿, 冀春晓, 杨程, 等, 2018. 同化风廓线雷达资料对浙江降水预报改进评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 29(1): 97-110. |
| [22] | 曾庆存, 周广庆, 浦一芬, 等, 2008. 地球系统动力学模式及模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 32(4): 653-690. |
| [23] | CHEN F, DUDHIA J, 2001. Coupling an advanced land surface-hydrology model with the Penn State-NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: Model implementation and sensitivity[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 129(4): 569-585. |
| [24] | FAN X G, 2009. Impacts of soil heating condition on precipitation simulations in the weather research and forecasting model[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 137(7): 2 263-2 285. |
| [25] | FERRANTI L, VITERBO P, 2006. The European summer of 2003: Sensitivity to soil water initial conditions[J]. Journal of Climate, 19(15): 3 659-3 680. |
| [26] | GIARD D, BAZILE E, 2010. Implementation of a new assimilation scheme for soil and surface variables in a global NWP model[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 128(4): 997-1 015. |
| [27] | HONG S Y, DUDHIA J, CHEN S H, 2004. A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 132(1): 103-120. |
| [28] | HONG S Y, PAN H L, 1996. Nonlocal boundary layer vertical diffusion in a medium-range forecast model[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 124 (10): 2 322-2 339. |
| [29] | IACONO M J, DELAMERE J S, MLAWER E J, et al, 2008. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Atmospheres), 113(D13), D13103. DOI:10.1029/2008JD009944. |
| [30] | JACOBS C M J, MOORS E J, Ter Maat H W, et al, 2010. Evaluation of European Land Data Assimilation System (ELDAS) products using in situ observations[J]. Tellus A, 60(5): 1 023-1 037. |
| [31] | JIMéNEZ P A, DUDHIA J, GONZáLEZ-ROUCO J F, et al, 2012. A revised scheme for the WRF surface layer formulation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 140(3): 898-918. |
| [32] | LIM Y J, LEE T Y, BYUN K Y, 2008. Korea Land Data Assimilation System (KLDAS) and its application using WRF[C]// In 22nd Conference on Hydrology, 88th American Meteorological Society Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA. |
| [33] | MAHANAMA S P P, KOSTER R D, REICHLE R H, 2008. Impact of subsurface temperature variability on surface air temperature variability: An AGCM study[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 9(4): 804-815. |
| [34] | PAN H L, MAHRT L, 1987. Interaction between soil hydrology and boundary-layer development[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 38: 185-202. |
| [35] | PETERS-LIDARD C D, BLACKBURN E, LIANG X, et al, 1998. The effect of soil thermal conductivity parameterization on surface energy fluxes and temperatures[J]. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 55(7): 1 209-1 224. |
| [36] | RODELL M, HOUSER P R, JAMBOR U, et al, 2004. The global land data assimilation system[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 85(3): 381-394. |
| [37] | WANG X, PARRISH D, KLEIST D, et al, 2013. GSI 3DVar-based ensemble-variational hybrid data assimilation for NCEP Global Forecast System: Single-resolution experiments[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 141(11): 4 098-4 117. |
| [38] | NIU G Y, YANG Z L, MITCHELL K E, et al, 2011. The community Noah land surface model with multi-parameterization options (Noah-MP):1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Atmospheres), 116, D12109. DOI: 10.1029/2010JD015139. |
| [39] | YANG Z L, NIU G Y, MITCHELL K E, et al, 2011. The community Noah land surface model with multi-parameterization options (Noah-MP):2.Evaluation over global river basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Atmospheres), 116, D12110. DOI: 10.1029/2010JD015140 |
| [40] | ZENG X M, WANG B, ZHANGY, et al, 2014. Sensitivity of high-temperature weather to initial soil moisture: A case study using the WRF model[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14: 9 623-9 639. |
| [41] | ZOU X, QIN Z K, ZHENG Y, 2015. Improved tropical storm forecasts with GOES-13/15 imager radiance assimilation and asymmetric vortex initialization in HWRF[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 143(7): 2 485-2 505. |
| [1] | 环海军, 徐玮平, 刘岩, 葛瑞婷, 丛菁成, 董旭光. 山东高温天气分布及变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 64-75. |
| [2] | 付远, 刘汉华, 周玲丽, 赵军平, 马昊, 陆婷婷, 魏蕾, 宣卓林. 2022年与2013年浙江夏季极端高温特点和成因对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 76-87. |
| [3] | 张玉翠, 谭江红, 闫彩霞. 湖北省区域性高温、干旱及其复合事件变化特征及危险性评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 825-835. |
| [4] | 杨晓玲, 孙旭映, 杨金虎, 吴雯, 赵慧华, 陈静. 石羊河流域复合高温干旱事件的识别及其演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 836-843. |
| [5] | 颜鹏程, 李忆平, 曾鼎文, 王丽娟, 张金玉, 陆晓娟, 岳平, 靳洁. 2024年4—6月我国区域性高温干旱特征及其影响因子[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 507-518. |
| [6] | 陈笑笑, 黄治勇, 秦鹏程, 夏智宏, 姚瑶, 汤兴芝, 汪应琼. 长江中游夏季高温异常的大气环流和海温特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 553-562. |
| [7] | 韩沁哲, 刘海磊, 范嘉智, 吴浩, 陈磊士, 欧小锋, 韩沁真. 湖南省地表高温遥感评估指标构建和特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 367-375. |
| [8] | 刘文英, 孙素琴, 朱星球, 欧阳欣欣. 江西省区域性高温和干旱过程分析与评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 187-196. |
| [9] | 黄瑶, 袁梦, 郭洁, 宋雯雯, 刘新超. 金沙江下游高温天气的环流分型和诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 217-227. |
| [10] | 杨英杰, 曹倩, 税玥. 中亚复合高温干旱事件识别与特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 19-26. |
| [11] | 郭润霞, 刘新伟, 王一丞, 刘娜, 周子涵. CLDAS气温实况融合产品在兰州和武威的检验评估及偏差订正[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 146-155. |
| [12] | 何慧根, 张驰, 吴遥, 李永华, 杨琴, 穆玉娇. 重庆夏季高温干旱特征及其对拉尼娜事件的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 873-883. |
| [13] | 于浩慧, 周长艳, 陈超, 陈永仁. 2021年7—8月四川盆地高温热浪大气环流背景及影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 923-932. |
| [14] | 魏森涛, 王澄海, 张飞民, 杨凯. 基于土壤温、湿度记忆性的土壤湿度预测方法研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 783-791. |
| [15] | 赵兔祥, 李福生, 郭晓雷, 胡悦, 魏建宁, 李小雨. 冬季宁夏贺兰山东麓酿酒葡萄种植区土壤热特性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 648-656. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||