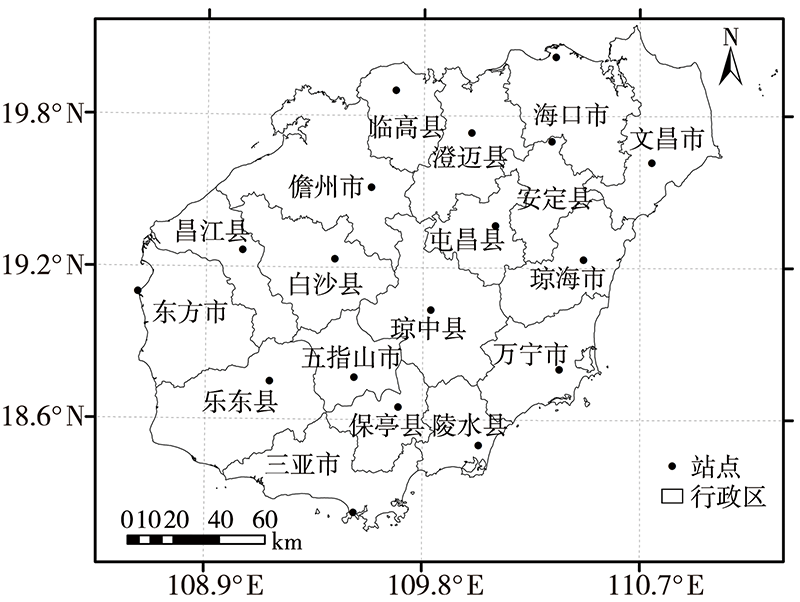
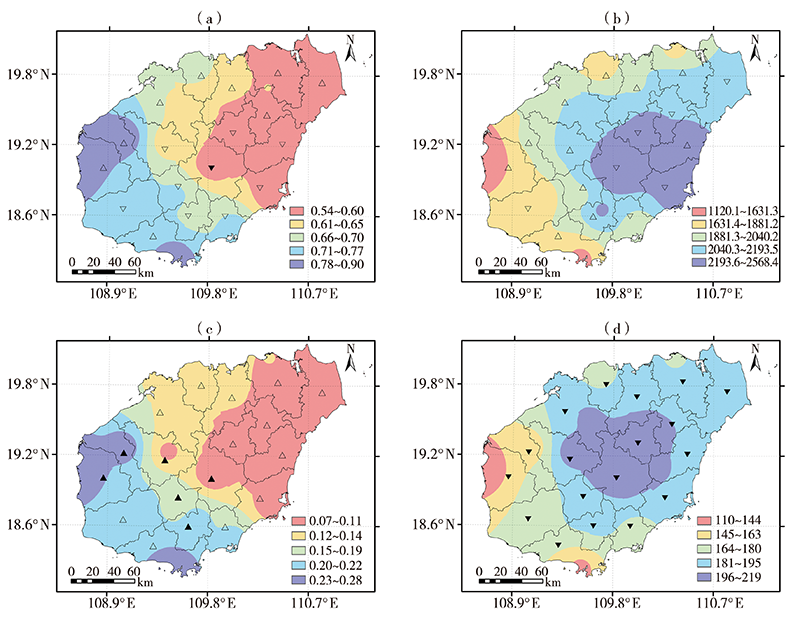
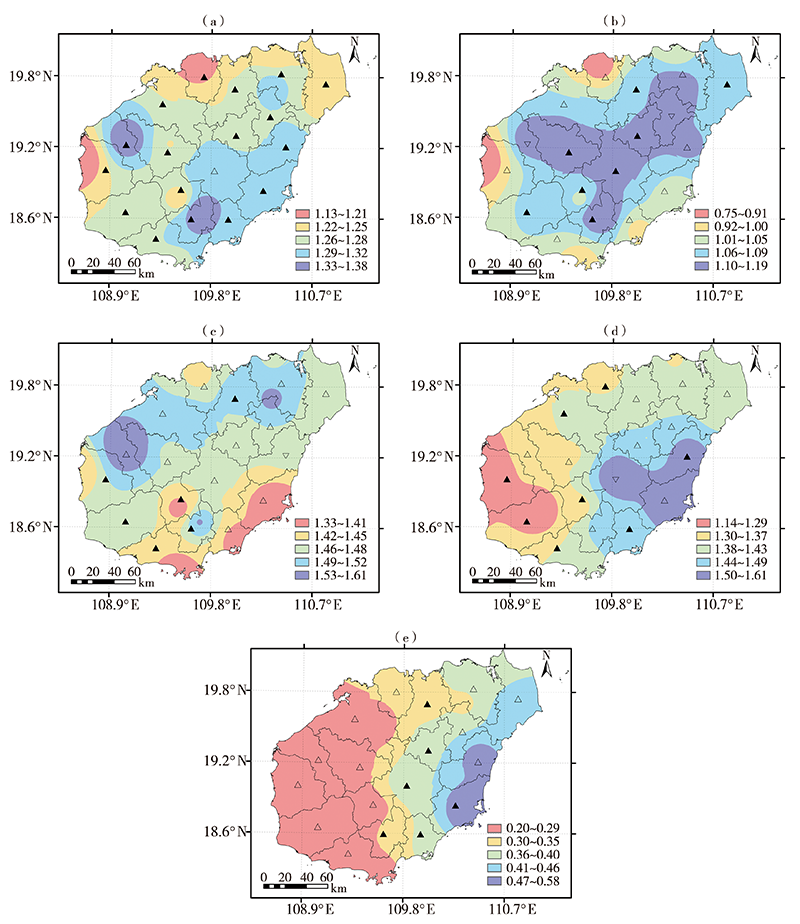
| [1] |
任国玉, 战云健, 任玉玉, 等. 中国大陆降水时空变异规律——Ⅰ. 气候学特征[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(3): 299-310.
|
| [2] |
李鑫鑫, 桑燕芳, 谢平, 等. 基于信息熵的我国日降水量随机性和时空差异性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(4): 1071-1078.
|
| [3] |
丁一汇, 王绍武, 郑景云, 等. 中国气候[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 327-391.
|
| [4] |
潘根兴, 高民, 胡国华, 等. 气候变化对中国农业生产的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(9): 1698-1706.
|
| [5] |
翟盘茂, 邹旭恺. 1951—2003年中国气温和降水变化及其对干旱的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2005, 1(1): 16-18.
|
| [6] |
任国玉, 任玉玉, 战云健, 等. 中国大陆降水时空变异规律——Ⅱ. 现代变化趋势[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(4): 451-465.
|
| [7] |
李峰平, 章光新, 董李勤. 气候变化对水循环与水资源的影响研究综述[J]. 地理科学, 2013, 33(4): 457-464.
|
| [8] |
王春乙. 海南气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2014: 4, 18-26, 151-153, 164-165.
|
| [9] |
董闯, 粟晓玲. 基于信息熵的石羊河流域降雨时空变异性研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(1): 222-228.
|
| [10] |
黄颖, 毛文茜, 王潇雅, 等. 近39 a祁连山及其周边地区降水量时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 527-534.
|
| [11] |
GEMMER M, BECKER S, JIANG T. Observed monthly precipitation trends in China 1951-2002[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2004, 77(1/2): 39-45.
|
| [12] |
FEIZI V, MOLLASHAHI M, FRAJZADEH M, et al. Spatial and temporal trend analysis of temperature and precipitation in Iran[J]. Ecopersia, 2014, 2(4): 727-742.
|
| [13] |
张婧婷, 冯利平, 潘志华. 黑龙江省未来41年气候变化趋势与突变分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2014, 37(3):60-66.
|
| [14] |
ANCTIL F, COULIBALY P. Wavelet analysis of the interannual variability in southern Québec streamflow[J]. Journal of Climate, 2004, 17(1): 163-173.
|
| [15] |
吴慧, 陈小丽. 海南省四十年来气候变化的多时间尺度分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2003, 19(2): 213-218.
|
| [16] |
潘攀. 1961—2012年河南省夏季降水时空及环流特征[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2014, 37(3):27-33.
|
| [17] |
徐利岗, 周宏飞, 梁川, 等. 中国北方荒漠区降水多时间尺度变异性研究[J]. 水利学报, 2009, 40(8): 1002-1011.
|
| [18] |
张玮玮, 张眉, 吴杨, 等. 复杂地形下浙江夏季气候要素空间插值方法评价[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 674-682.
|
| [19] |
YOU Y J, JIA X J. Interannual variations and prediction of spring precipitation over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31(2): 655-670.
|
| [20] |
MISHRA A K, ÖZGER M, SINGH V P. An entropy-based investigation into the variability of precipitation[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 370: 139-154.
|
| [21] |
赵传成, 姚淑霞, 刘君, 等. 基于信息熵的天山山区降水时空变化特征[J]. 草业科学, 2016, 33(4): 645-654.
|
| [22] |
黄家俊, 张强, 张生, 等. 基于信息熵的新疆降水时空变异特征研究[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(13): 4444-4455.
|
| [23] |
SINGH V P. The use of entropy in hydrology and water resources[J]. Hydrological Processes, 1997, 11(6): 587-626.
|
| [24] |
王枭轩, 左小清, 杨泽楠, 等. 基于Mann-Kendall检验和信息熵的成都市1980—2016年降水时空变化[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2019, 17(4): 26-33.
|
| [25] |
郑泳杰, 张强, 张生, 等. 基于信息熵的淮河流域降水时空变异特征研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2016, 34(1): 1-5.
|
| [26] |
许格希, 郭泉水, 牛树奎, 等. 近50 a来海南岛不同气候区气候变化特征研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2013, 28(5): 799-810.
|
| [27] |
SHANNON C E. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27: 379-423.
|
| [28] |
吴岩峻. 中国气象灾害大典:海南卷[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2008: 98-101.
|
| [29] |
MANN H B. Non-parametric test against trend[J]. Econometrica, 1945, 13(3): 245-259.
|
| [30] |
KENDALL M G. Rank correlation methods[M]. London: Charles Griffin, 1975: 202.
|
| [31] |
张莉莉, 陶忠良, 张京红. 基于GIS海南岛气象要素空间插值法比较分析[J]. 热带农业科学, 2012, 32(4): 57-61, 66.
|
| [32] |
白蕤, 李宁, 陈汇林, 等. 海南岛农业洪涝灾害监测指标修订与灾害时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(6): 1012-1020.
|
 ), 张京红1,2, 陈小敏1,2, 李伟光1,2, 白蕤1,2, 吕润1,2
), 张京红1,2, 陈小敏1,2, 李伟光1,2, 白蕤1,2, 吕润1,2
 ), ZHANG Jinghong1,2, CHEN Xiaomin1,2, LI Weiguang1,2, BAI Rui1,2, LÜ Run1,2
), ZHANG Jinghong1,2, CHEN Xiaomin1,2, LI Weiguang1,2, BAI Rui1,2, LÜ Run1,2