干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 613-623.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0613
基于ISCCP和CMORPH-AWS资料的中国南方地区云与降水关系分析
- 1. 四川省人工影响天气办公室,四川 成都 610072
2. 中国气象局云降水物理与人工影响天气重点开放实验室,北京 100081
3. 中国气象局大气探测重点开放实验室,四川 成都 610103
4. 东华大学环境科学与工程学院,上海 201620
Relationship between the clouds and precipitation over southern China based on ISCCP and CMORPH-AWS data
FAN Sirui1,2,3( ), WANG Weijia1,2(
), WANG Weijia1,2( ), CHEN Yonghang4
), CHEN Yonghang4
- 1. Weather Modification Office of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
2. CMA Cloud-Precipitation Physics and Weather Modification Key Laboratory, Beijing 100081, China
3. Key Laboratory of Atmosphere Sounding of China Meteorological Administration, Chengdu 610103, China
4. College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
摘要:
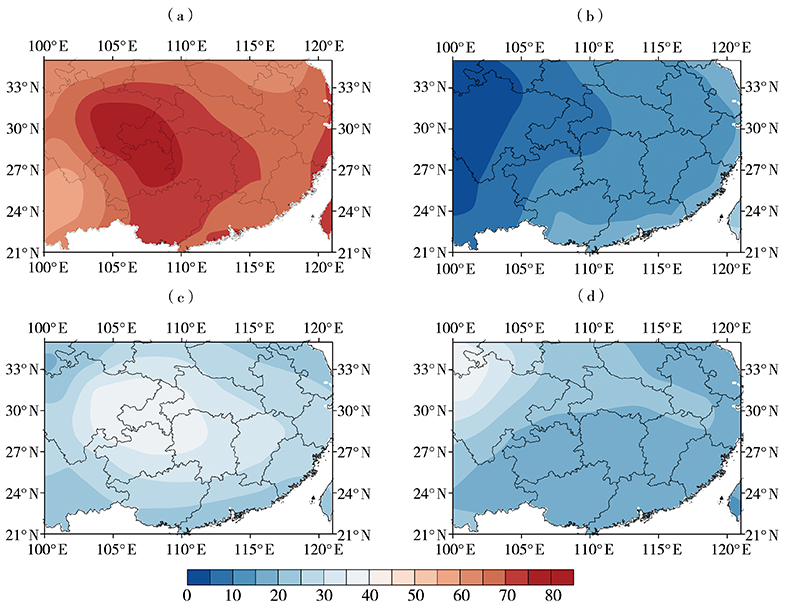
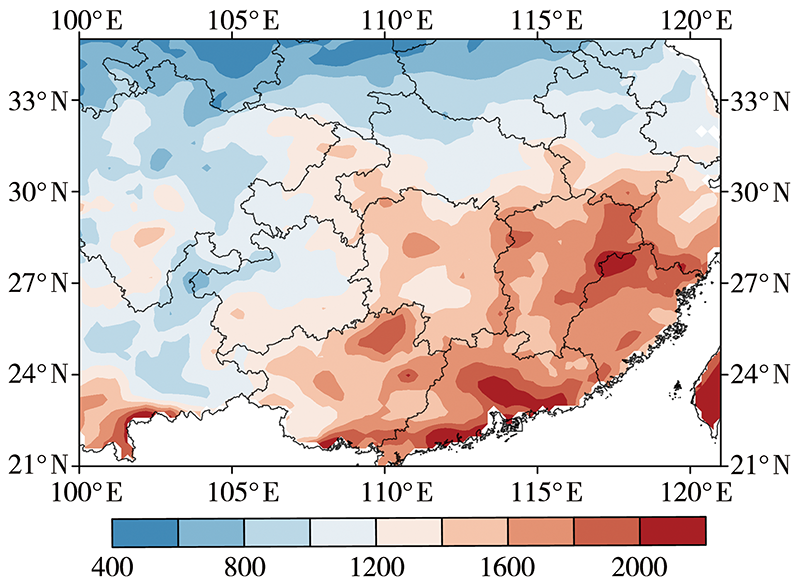
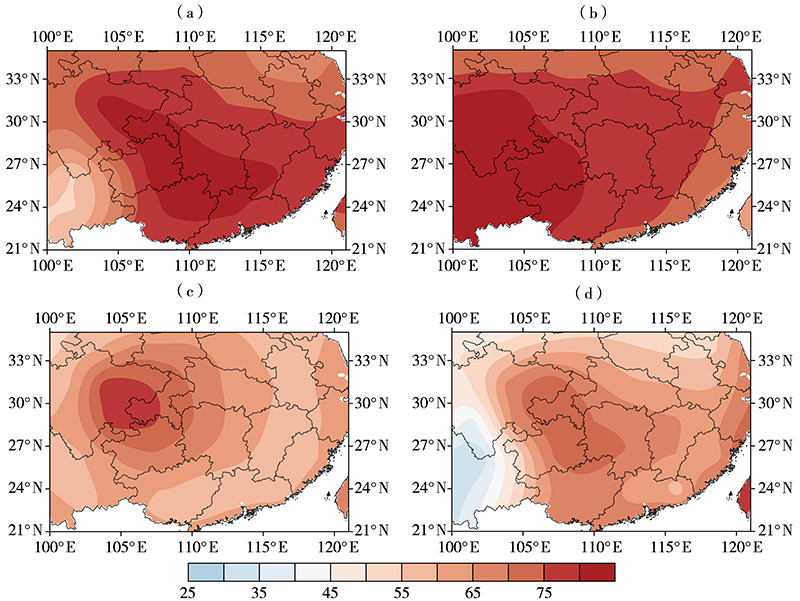
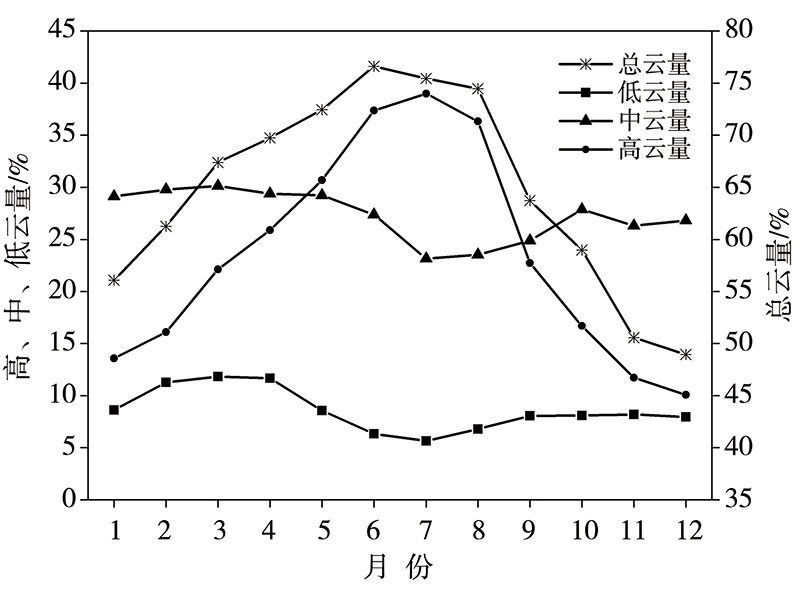
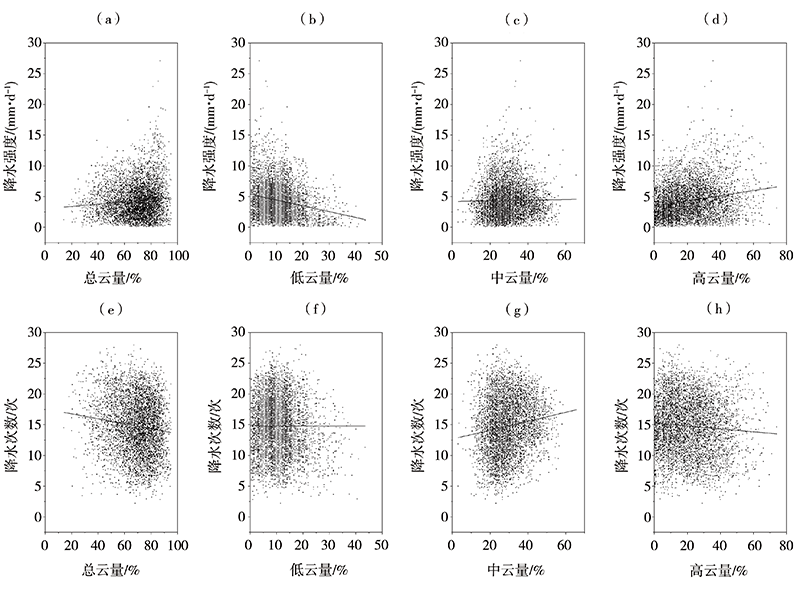
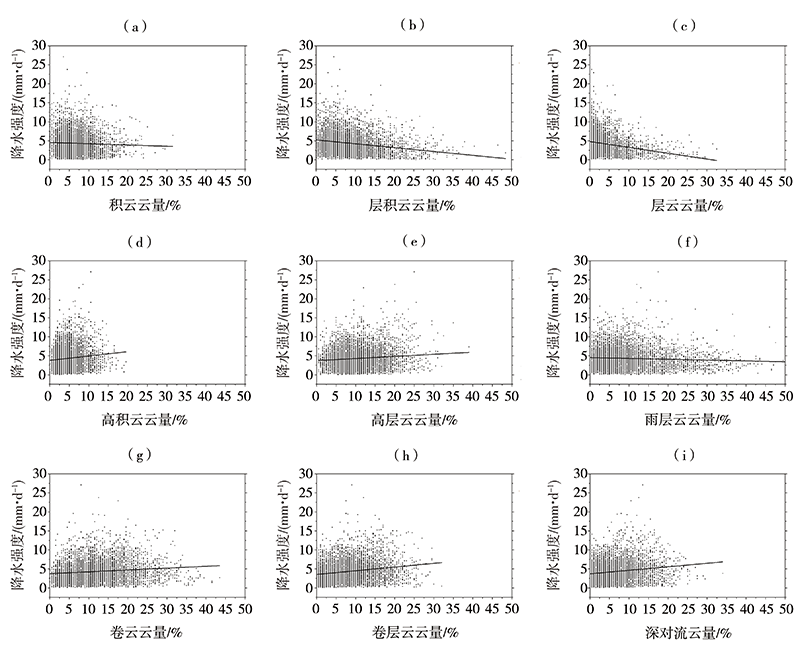
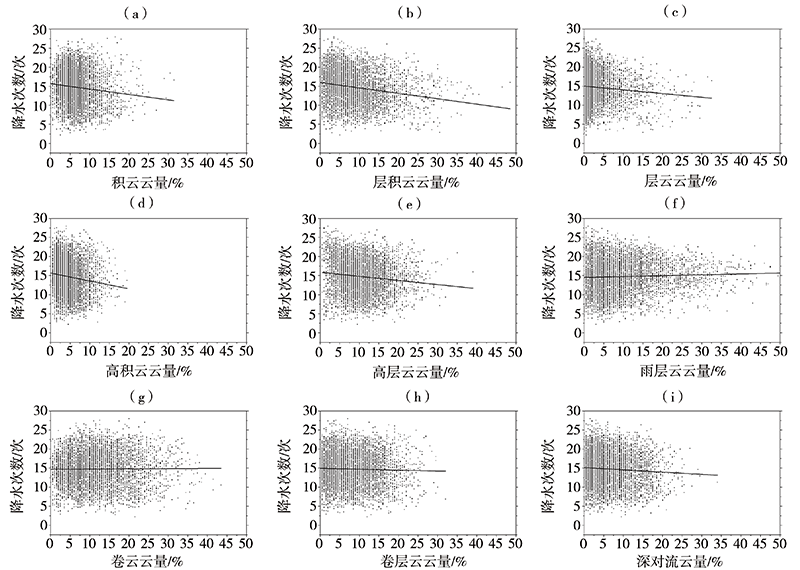
探究中国南方地区不同高度云量的时空变化及其与降水的关系,可了解云在降水中的作用和反馈机制并为空中云水资源开发提供基础和依据。利用国际卫星云气候计划(International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project, ISCCP)中D系列卫星观测云数据集12 a(1998—2009年)资料,详细分析了中国南方地区总云量、低云量、中云量、高云量的时空分布特征,并结合中国自动站(automatic weather station, AWS)降水数据与美国国家海洋和大气管理局(National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, NOAA)气候预测中心(Climate Prediction Center, CPC) MORPHing technique(CMORPH)卫星反演降水产品融合的格点降水产品(CMORPH-AWS)分析了云量与降水强度、降水次数的关系。结果表明:(1)在空间分布上,中国南方地区总云量和中云量空间分布类似,高值中心位于四川盆地、贵州、重庆交接处,低值中心位于云南地区;高云主要分布在南方地区的西部,表现为由西向东逐渐减少的分布特征;低云主要分布在南方地区的东南部,表现为沿海地区向内陆地区逐渐减少的空间分布特征。(2)在季节变化上,总云量和高云量为夏季多、冬季少,总云量高值中心随季节位移,高云量随季节变化,中云量和低云量为冬季多夏季少,季节性变化小。(3)随着总云量和高云量的增多,降水强度增大、月降水次数减小;随着中云量增多,月降水次数增加、降水强度无明显变化。(4)随着层积云、层云云量的增加,降水强度和月降水次数减小;随着高积云、高层云、深对流云云量的增加,降水强度增加但月降水次数减小。总体而言,中国南方地区云量和降水关系密切,特别是总云量和高云量对降水强度和降水次数影响较大,中云量仅对降水次数影响较大,层积云、层云、高积云、高层云、深对流云云量对降水强度和降水次数影响较大,卷云、卷层云云量仅对降水强度影响较大。
中图分类号: