干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 596-604.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-04-0596
线状MCSs强降水特征及形成条件
- 1. 河北省气象与生态环境重点实验室,河北 石家庄 050021
2. 河北省廊坊市气象局,河北 廊坊 065000
3. 河北省永清县气象局,河北 永清 065600
Formation conditions and characteristics of heavy precipitation with quasi-linear MCSs
XU Min1,2( ), SHEN Fang2, LIU Qiqi2, LI Na2, WANG Jie3
), SHEN Fang2, LIU Qiqi2, LI Na2, WANG Jie3
- 1. Key Laboratory of Meteorology and Ecological Environment of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang 050021, China
2. Langfang Meteorological Bureau of Hebei Province, Langfang 065000, Hebei,China
3. Yongqing County Meteorological Bureau of Hebei Province , Yongqing 065600, Hebei,China
摘要:
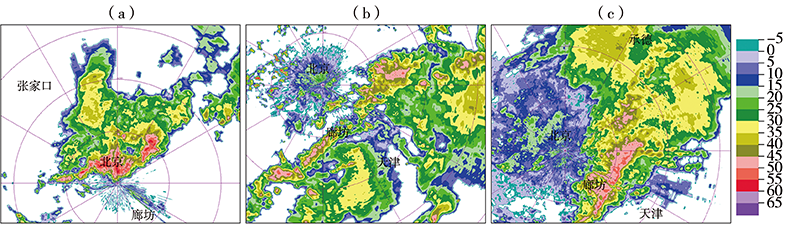
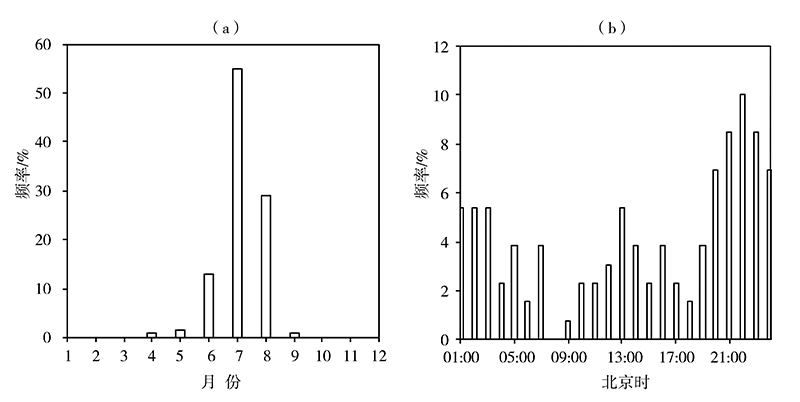
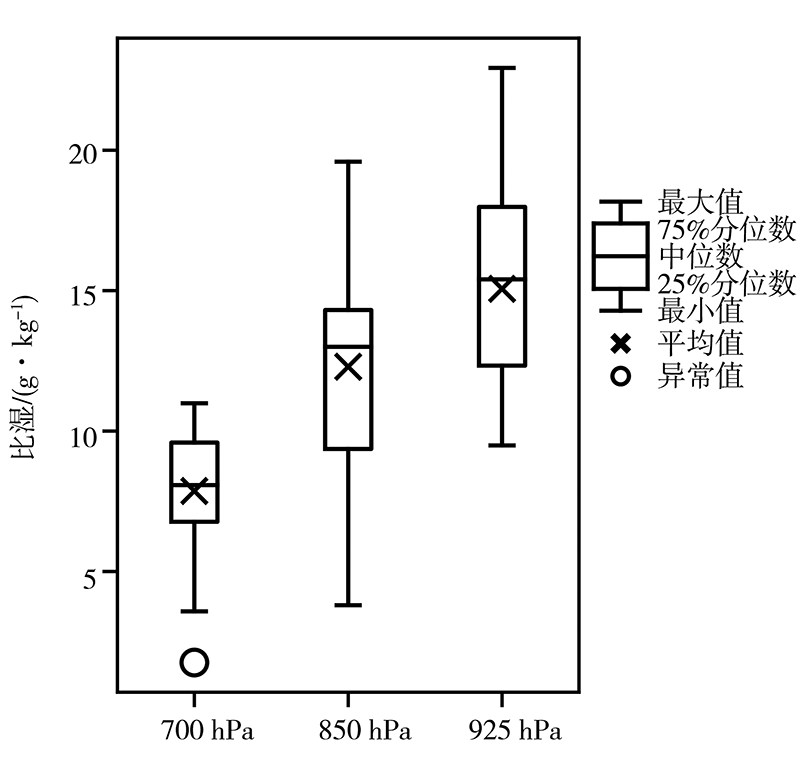
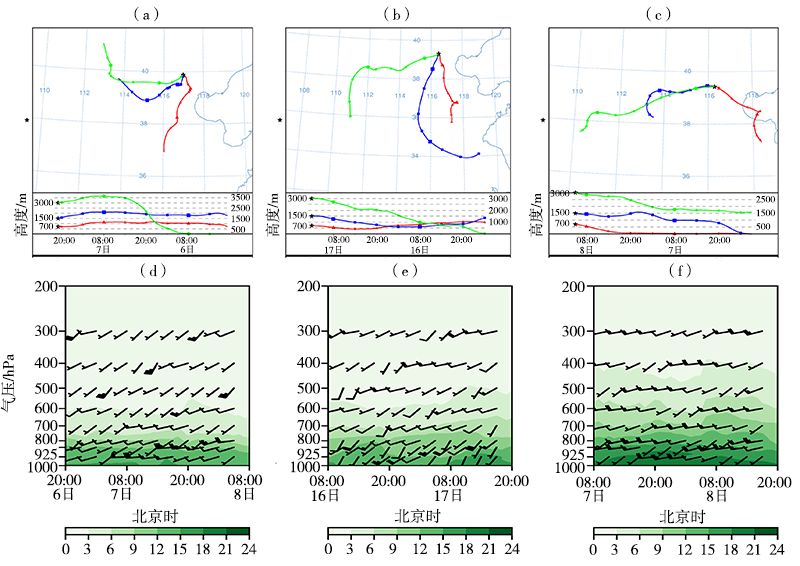
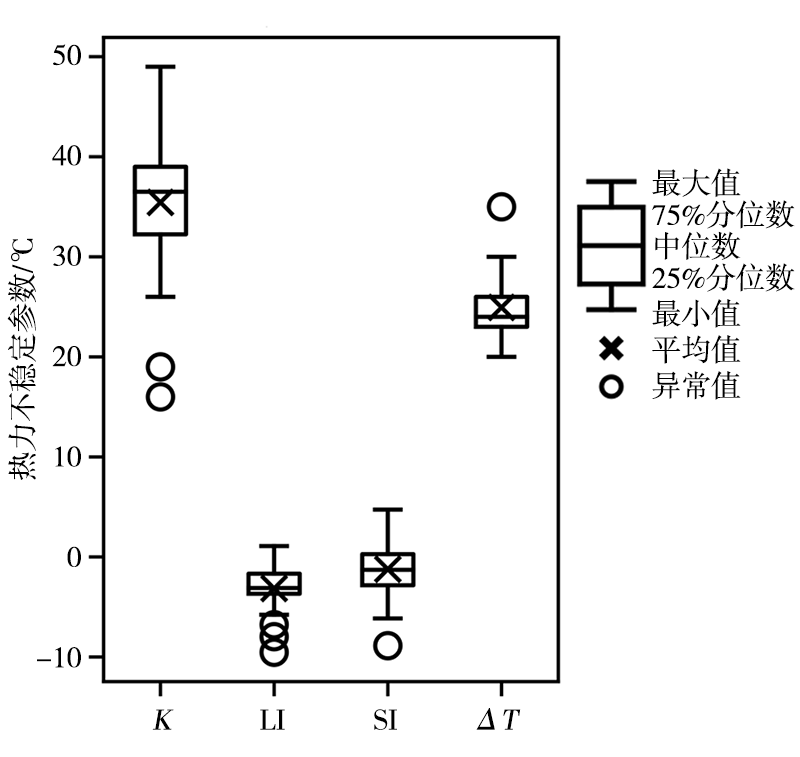
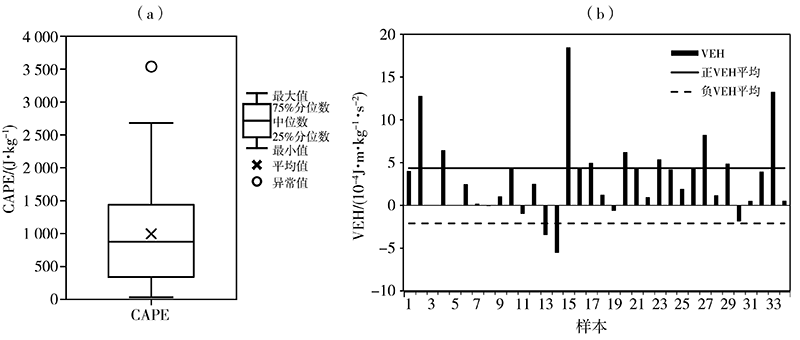
基于2010—2019年国家气象站观测资料和多普勒雷达资料,以及美国国家环境预报中心(National Centers for Environmental Prediction,NCEP)再分析资料和欧洲中期天气预报中心(European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts,ECMWF)第5代全球大气再分析产品——ERA5,对冀中廊坊线状MCSs强降水雷达回波、气候特征,以及降水过程中物理量变化进行定性和定量分析。结果表明:(1)线状MCSs强降水的雷达反射率因子回波形态有3类,即层状云后置(trailing stratiform,TS)型,层状云前置(leading stratiform,LS)型和层状云平行(parallel stratiform,PS)型,其中TS型出现频率最高,LS型和PS型出现频率相对较少,线状MCSs强降水发生具有明显的月际变化和日变化特征,高发于一年中的7月和一日中的前半夜;(2)线状MCSs强降水形成于4种天气尺度环流形势下,即低槽型、横槽型、低涡型和西风环流型,以低槽型最为普遍;(3)700 hPa偏西方向来的相对干冷空气与低空西南气流共同作用,加剧了大气的层结不稳定性,提高了降水效率,850 hPa偏南水汽分量越大,越有利于形成雨区相对较小、但雨强较大的强降雨天气,925 hPa东南风的配合明显扩大了强降雨落区;(4)线状MCSs生成于强的热力环境背景下,对流有效位能(convective available potential energy, CAPE)在316.7~1545.7 J·kg-1,垂直能量螺旋度(vertical energy helicity,VEH)为正值且明显大于2×10-4 J·m·kg-1·s-2是其形成的有利能量条件。PS型MCSs强降水过程中,高空水平辐散加强了抽吸作用,使大的上升速率得以维持,优越的动力条件是强降雨持续时间更长的重要原因之一。
中图分类号: