干旱气象 ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (06): 966-973.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-06-0966
甘肃陇南市短时强降水时空分布特征及中尺度分析
苏军锋1( ), 张锋1, 黄玉霞2(
), 张锋1, 黄玉霞2( ), 刘丽1, 张秋瑜1, 魏清霞1, 张燕1
), 刘丽1, 张秋瑜1, 魏清霞1, 张燕1
- 1.甘肃省陇南市气象局,甘肃 武都 746000
2.兰州中心气象台,甘肃 兰州 730020
Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and mesoscale analysis of short-time heavy precipitation in Longnan of Gansu Province
SU Junfeng1( ), ZHANG Feng1, HUANG Yuxia2(
), ZHANG Feng1, HUANG Yuxia2( ), LIU Li1, ZHANG Qiuyu1, WEI Qingxia1, ZHANG Yan1
), LIU Li1, ZHANG Qiuyu1, WEI Qingxia1, ZHANG Yan1
- 1. Longnan Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Wudu 746000, Gansu, China
2. Lanzhou Regional Meteorological Observatory, Lanzhou 730020, China
摘要:
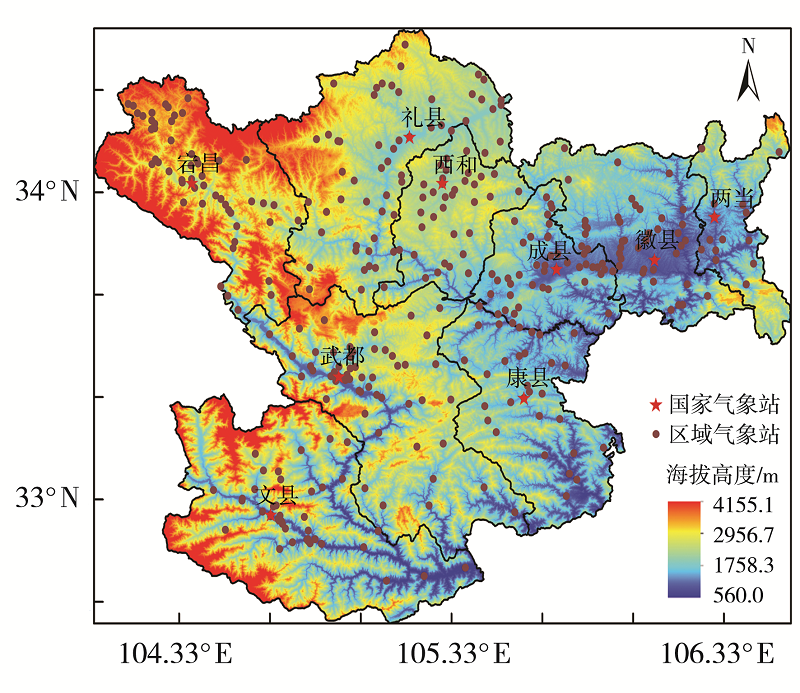
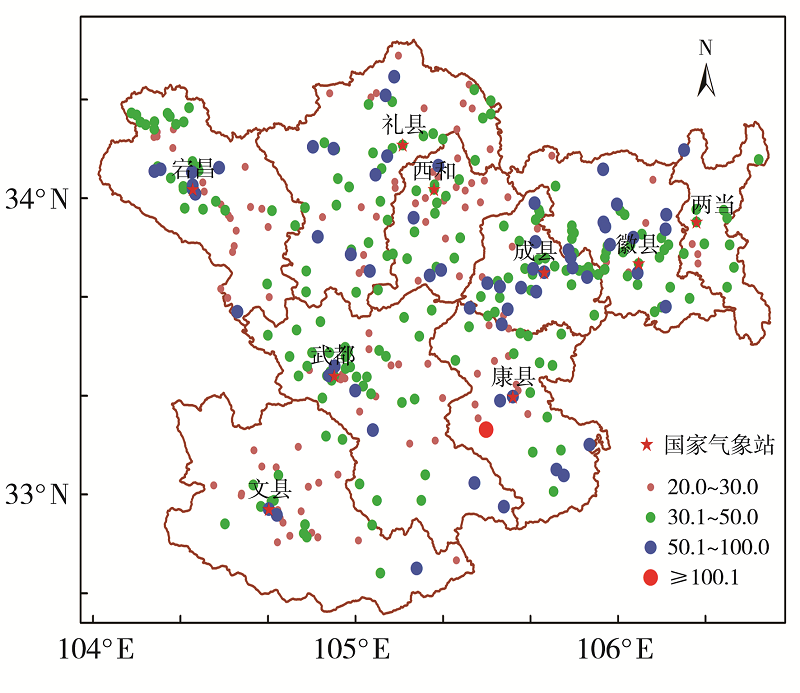
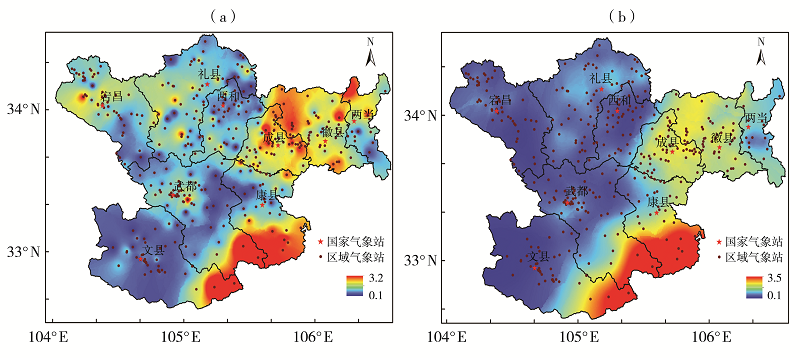
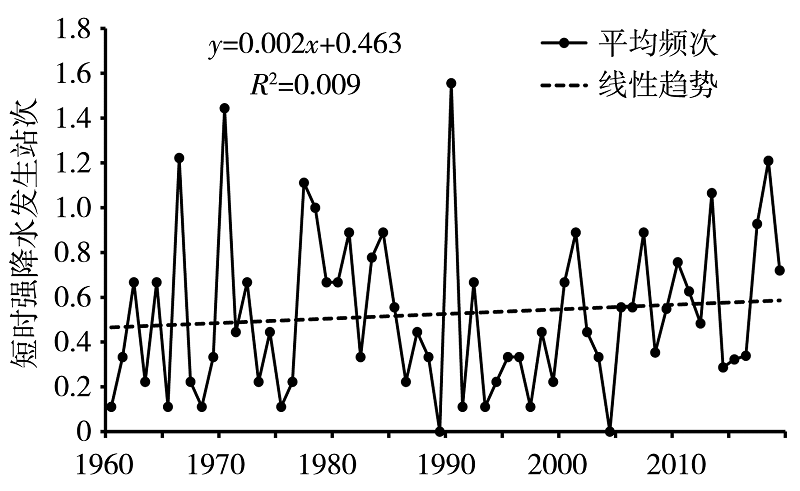
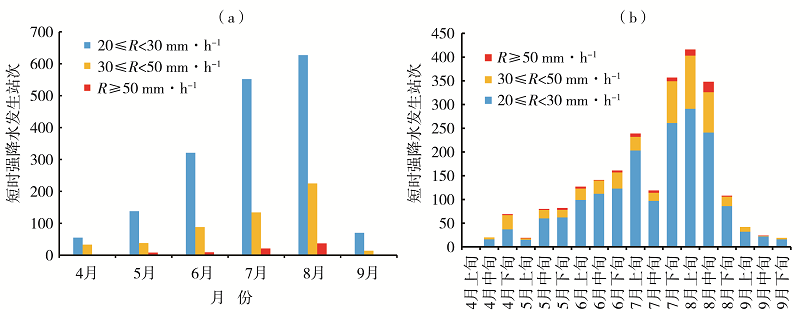
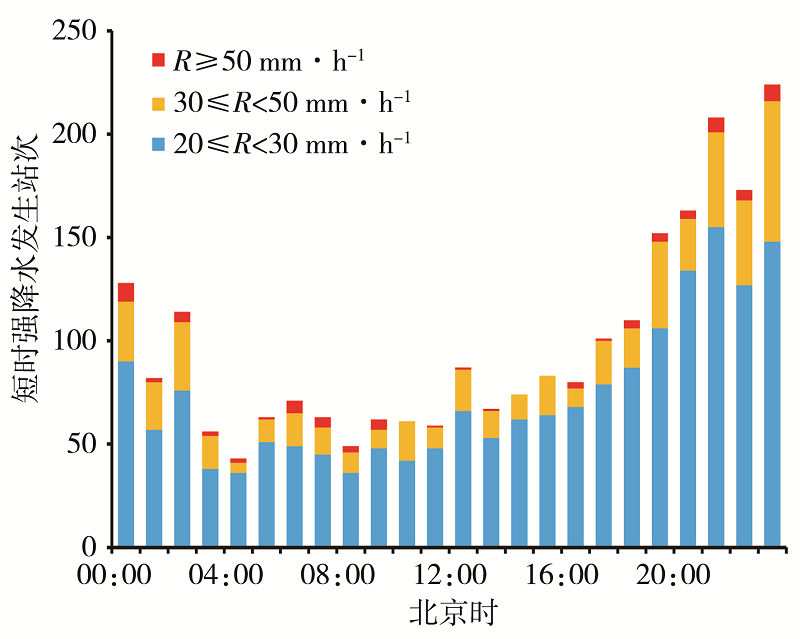
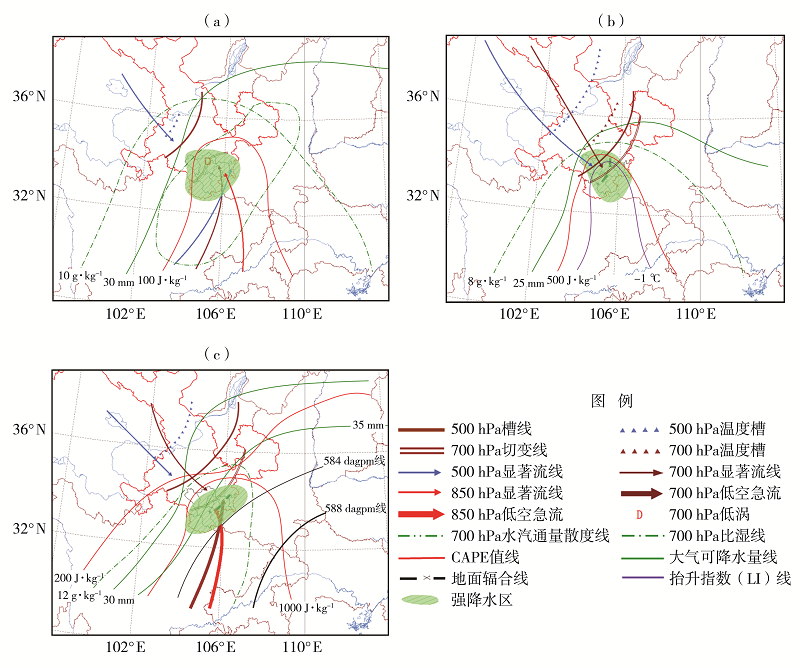
利用1960—2019年陇南市9个国家气象站和2008—2019年逐年建成的400个区域气象站4—9月逐时降水资料,同期NCEP FNL 1°×1°再分析资料和MICAPS资料,对陇南市短时强降水时空分布及中尺度特征进行分析。结果表明:(1)陇南市短时强降水发生频次从西北向东南明显增加,雨强大于50 mm·h-1的短时强降水出现在陇南市东部的成县、徽县和康县。短时强降水与暴雨发生频次东南部偏多,另外陇南市西北山地局部地区短时强降水发生频次较多。(2)1960年以来,陇南市短时强降水发生站次呈缓慢增加趋势,月际变化呈单峰型,8月最多,占短时强降水总站次的37.5%;旬变化呈双峰型,分别出现在7月上旬和8月上旬,且7月下旬至8月中旬最多,占47.2%;日变化具有夜间明显多于白天的特征,存在多个峰值,从15:00开始短时强降水明显增加,集中出现在19:00—23:00,23:00为日峰值,占9.4%。(3)陇南市短时强降水和暴雨有密切联系,对暴雨的贡献率达53.4%。陇南市短时强降水中尺度概念模型主要有低涡切变型、西北气流低槽东移型、副高外围西南气流型。
中图分类号: