干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 91-102.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0091
不同边界层参数化方案对台风“烟花”北上阶段暴雨模拟的影响试验
邢蕊1,2( ), 杨健博1,3(
), 杨健博1,3( ), 田梦1,3, 邱晓滨1,3, 庄庭4, 朱晓晶2
), 田梦1,3, 邱晓滨1,3, 庄庭4, 朱晓晶2
- 1.天津市海洋气象重点实验室,天津 300074
2.天津市滨海新区气象局,天津 300457
3.天津市气象科学研究所,天津 300074
4.天津市气象探测中心,天津 300061
-
收稿日期:2022-05-10修回日期:2022-10-25出版日期:2023-02-28发布日期:2023-02-28 -
通讯作者:杨健博(1989—),男,博士,高级工程师,主要从事大气边界层数值模拟及相关研究。E-mail: iamyjb.happy@163.com。
-
作者简介:邢蕊(1985—),女,博士,高级工程师,主要从事台风和灾害性天气高分辨率数值模拟的研究。E-mail:nuistxr@163.com。 -
基金资助:天津市海洋气象重点实验室开放基金项目(2022TKLOM05);天津市自然科学基金项目(20JCYBJC00780);环渤海区域科技协同创新基金项目(QYXM202112);天津市气象局科研项目(202114zdxm01);天津市气象局科研项目(202115dgxm04);天津市气象局科研项目(202226dgxm05)
Effect of different boundary layer parameterization schemes on simulation of the heavy rainfall during Typhoon In-Fa(2106) moving northward period
XING Rui1,2( ), YANG Jianbo1,3(
), YANG Jianbo1,3( ), TIAN Meng1,3, QIU Xiaobin1,3, ZHUANG Ting4, ZHU Xiaojing2
), TIAN Meng1,3, QIU Xiaobin1,3, ZHUANG Ting4, ZHU Xiaojing2
- 1. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Oceanic Meteorology, Tianjin 300074, China
2. Tianjin Binhai New Area Meteorological Service, Tianjin 300457, China
3. Tianjin Institute of Meteorological Science, Tianjin 300074, China
4. Tianjin Meteorological Observation Centre, Tianjin 300061, China
-
Received:2022-05-10Revised:2022-10-25Online:2023-02-28Published:2023-02-28
摘要:
边界层参数化方案是造成数值模式预报误差的重要来源之一,筛选适用于环渤海地区台风暴雨模拟的边界层参数化方案,可为该地后续业务应用及科研工作提供参考依据。应用WRFV4.3模式中的8种边界层参数化方案(ACM2、BouLac、GBM、MYJ、MYNN、QNSE、UW、YSU),对2021年第6号台风“烟花”北上阶段造成的暴雨过程进行数值模拟试验,对比分析不同边界层参数化方案对暴雨模拟结果的影响,并基于ERA5资料进行边界层热动力结构的模拟效果检验。结果表明:(1)各方案对台风北上阶段的降水(24 h累积降水量、累积降水极值和位置、降水ETS评分、小时最大降水量以及逐小时10.0、20.0 mm降水的落区分布)模拟结果表现出明显差异,对路径的模拟差异主要体现在模拟时段的中后期。(2)局地闭合的BouLac方案对于10.0 mm以上量级24 h累积降水量的ETS评分表现最优,而非局地ACM2方案所模拟的24 h累积降水量在25.0、50.0、100.0 mm以上量级降水的ETS评分均为最优,且累积降水极值、区域平均24 h累积降水量以及小时最大降水量均值等也与ERA5资料较为接近,在环渤海地区海陆共存的下垫面背景下,ACM2方案是最适合台风“烟花”暴雨过程模拟的参数化方案。(3)与其他方案相比,ACM2方案对于边界层高度、位温和水汽混合比垂直廓线的模拟与实况最接近,这是ACM2方案对大雨以上量级预报较为准确的原因。(4)各方案模拟的700 hPa垂直速度基本决定了小时最大降水量的变化趋势以及区域平均24 h累积降水量的相对大小。
中图分类号:
引用本文
邢蕊, 杨健博, 田梦, 邱晓滨, 庄庭, 朱晓晶. 不同边界层参数化方案对台风“烟花”北上阶段暴雨模拟的影响试验[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 91-102.
XING Rui, YANG Jianbo, TIAN Meng, QIU Xiaobin, ZHUANG Ting, ZHU Xiaojing. Effect of different boundary layer parameterization schemes on simulation of the heavy rainfall during Typhoon In-Fa(2106) moving northward period[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 91-102.
| 试验名称 | 边界层参数化方案 | 地面层参数化方案 |
|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | 非局地向上混合与局地向下混合的ACM2方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| BouLac | Bougeault 和 Lacarrere (BouLac)湍流动能方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| GBM | GBM TKE-type 方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| MYJ | Mellor-Yamada-Janjic (Eta)湍流动能方案 | Monin-Obukhov (Janjic Eta)方案 |
| MYNN | MYNN 2.5阶湍流动能方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| QNSE | 准正态尺度消除方案QNSE | 准正态尺度消除方案QNSE |
| UW | Bretherton-Park/UW 湍流动能方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| YSU | Yonsei University参数化方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
表1 数值试验方案设计
Tab.1 Designs for numerical experiments
| 试验名称 | 边界层参数化方案 | 地面层参数化方案 |
|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | 非局地向上混合与局地向下混合的ACM2方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| BouLac | Bougeault 和 Lacarrere (BouLac)湍流动能方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| GBM | GBM TKE-type 方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| MYJ | Mellor-Yamada-Janjic (Eta)湍流动能方案 | Monin-Obukhov (Janjic Eta)方案 |
| MYNN | MYNN 2.5阶湍流动能方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| QNSE | 准正态尺度消除方案QNSE | 准正态尺度消除方案QNSE |
| UW | Bretherton-Park/UW 湍流动能方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
| YSU | Yonsei University参数化方案 | Revised MM5 Monin-Obukhov方案 |
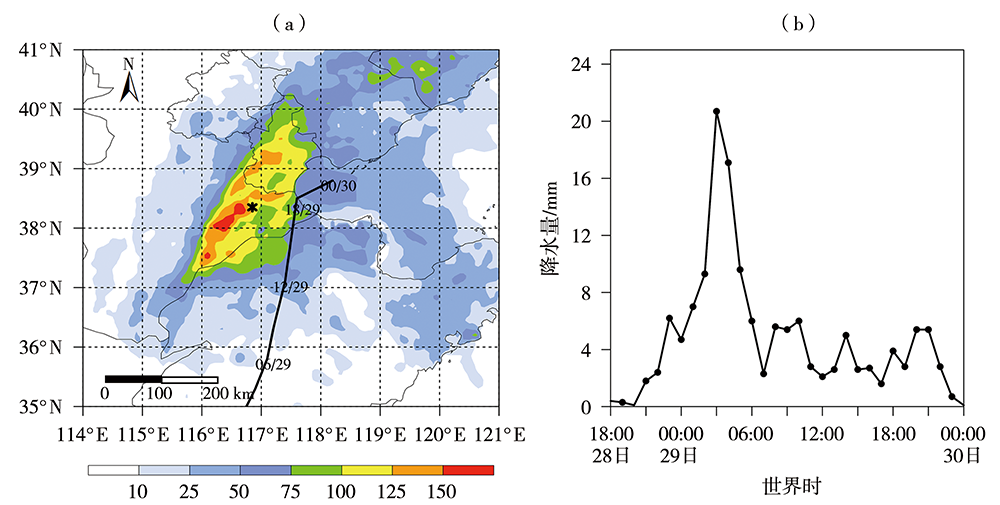
图1 2021年7月29日00:00至30日00:00实况24 h累积降水量(填色,单位:mm)分布及台风“烟花”北上路径(黑色实线)(a)与28日18:00至30日00:00沧州站逐小时降水演变(b) [图1(a)中星号代表沧州站,数字06/29代表29日06:00,余类推。下同]
Fig.1 The distribution of observed 24 h accumulated rainfall (the color shaded, Unit: mm) and the typhoon track (the black solid line) during its northward period from 00:00 July 29 to 00:00 July 30, 2021 (a) and hourly rainfall evolution at Cangzhou weather station from 18:00 July 28 to 00:00 July 30, 2021 (b) (The asterisk in fig.1a denotes Cangzhou weather station, and the number 06/29 in fig.1a indicates 06:00 July 29, others are in a similar fashion. the same as below)
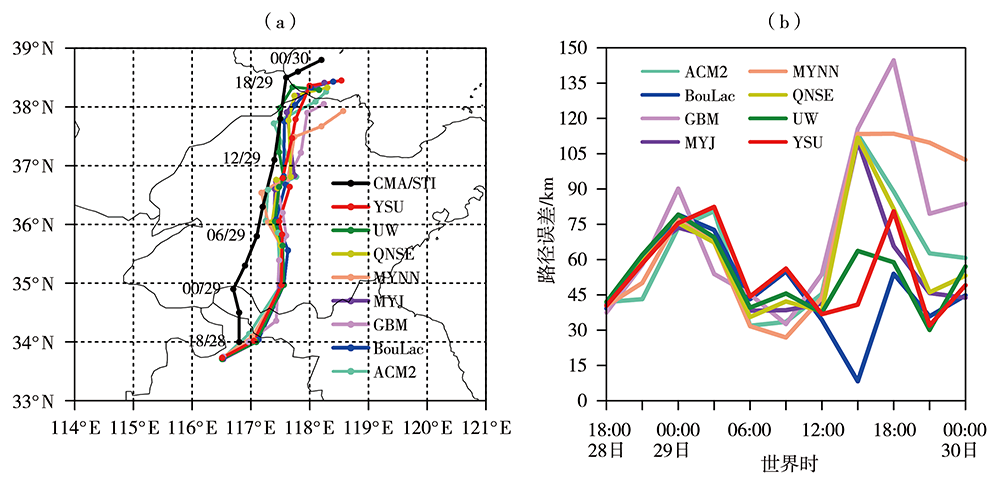
图2 2021年7月28日18:00至30日00:00观测与8组试验模拟的台风路径(a)和路径误差(b)
Fig.2 The typhoon tracks observed and simulated by 8 sets of test schemes (a) and track errors (b)from 18:00 July 28 to 00:00 July 30, 2021

图3 2021年7月29日00:00至30日00:00实况及8组试验模拟的D01区域24 h累积降水量分布(单位:mm) [左上角括号中数字为24 h最大累积降水量,黑色十字代表最大降水量出现位置,黑色方框(115.5°E—118°E,37.2°N—40.2°N)为主要降水区]
Fig.3 The 24 h accumulated precipitation observed and simulated by 8 sets of test schemes from 00:00 July 29 to 00:00 July 30, 2021 in the D01 region (Unit: mm) (The number on the upper left brackets denotes the maximum 24 h accumulated precipitation, the black cross denotes the location of maximum rainfall, and the black rectangle (115.5°E—118°E, 37.2°N—40.2°N) denotes the main precipitation area)
| 试验 | 区域平均24 h 降水量/mm | 最大降水量 /mm | 模拟与实况最大降水量区域间 距离/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | 54.7 | 151.1 | 99.9 |
| BouLac | 51.1 | 131.2 | 56.3 |
| GBM | 46.3 | 121.4 | 56.3 |
| MYJ | 52.0 | 141.2 | 76.7 |
| MYNN | 53.0 | 143.7 | 76.7 |
| QNSE | 54.9 | 143.1 | 159.0 |
| UW | 55.0 | 173.4 | 36.1 |
| YSU | 48.2 | 140.2 | 36.1 |
表2 8组试验方案模拟的主要降水区域平均24 h累积降水量、最大降水量及模拟与实况最大降水量区域间距离
Tab.2 The main rainfall area averaged 24 h accumulated precipitation and maximum rainfall simulated by 8 sets of test schemes and the range between the locations of simulated and observed maximum precipitation
| 试验 | 区域平均24 h 降水量/mm | 最大降水量 /mm | 模拟与实况最大降水量区域间 距离/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | 54.7 | 151.1 | 99.9 |
| BouLac | 51.1 | 131.2 | 56.3 |
| GBM | 46.3 | 121.4 | 56.3 |
| MYJ | 52.0 | 141.2 | 76.7 |
| MYNN | 53.0 | 143.7 | 76.7 |
| QNSE | 54.9 | 143.1 | 159.0 |
| UW | 55.0 | 173.4 | 36.1 |
| YSU | 48.2 | 140.2 | 36.1 |
| 降水量级 | 试验 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | BouLac | GBM | MYJ | MYNN | QNSE | UW | YSU | |
| 大于等于10.0 mm | 0.590 3 | 0.650 2* | 0.616 6 | 0.557 3 | 0.544 4 | 0.616 6 | 0.574 3 | 0.382 0 |
| 大于等于25.0 mm | 0.634 2* | 0.559 4 | 0.409 2 | 0.616 0 | 0.592 4 | 0.592 4 | 0.587 7 | 0.545 9 |
| 大于等于50.0 mm | 0.564 6* | 0.488 7 | 0.253 9 | 0.447 4 | 0.463 6 | 0.430 3 | 0.481 2 | 0.499 1 |
| 大于等于100.0 mm | 0.136 6* | 0.059 9 | -0.009 2 | 0.051 9 | -0.012 9 | 0.023 8 | -0.010 2 | 0.047 6 |
表3 8组试验模拟的不同量级24 h累积降水量的ETS评分
Tab.3 Equitable threat scores of 24 h accumulated rainfall with different levels simulated by 8 sets of test schemes
| 降水量级 | 试验 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | BouLac | GBM | MYJ | MYNN | QNSE | UW | YSU | |
| 大于等于10.0 mm | 0.590 3 | 0.650 2* | 0.616 6 | 0.557 3 | 0.544 4 | 0.616 6 | 0.574 3 | 0.382 0 |
| 大于等于25.0 mm | 0.634 2* | 0.559 4 | 0.409 2 | 0.616 0 | 0.592 4 | 0.592 4 | 0.587 7 | 0.545 9 |
| 大于等于50.0 mm | 0.564 6* | 0.488 7 | 0.253 9 | 0.447 4 | 0.463 6 | 0.430 3 | 0.481 2 | 0.499 1 |
| 大于等于100.0 mm | 0.136 6* | 0.059 9 | -0.009 2 | 0.051 9 | -0.012 9 | 0.023 8 | -0.010 2 | 0.047 6 |
| 降水量级 | 试验 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | BouLac | GBM | MYJ | MYNN | QNSE | UW | YSU | |
| 大于等于10.0 mm | 0.937 2 | 0.941 7 | 0.955 2 | 0.950 7 | 0.923 8 | 0.955 2 | 0.932 7 | 0.843 0 |
| 大于等于25.0 mm | 1.018 0 | 1.053 9 | 1.185 6 | 1.059 9 | 1.059 9 | 1.059 9 | 1.018 0 | 1.006 0 |
| 大于等于50.0 mm | 0.992 4 | 1.083 3 | 0.947 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.030 3 | 1.030 3 | 1.015 2 | 1.000 0 |
| 大于等于100.0 mm | 0.696 4 | 0.410 7 | 0.125 0 | 0.517 9 | 0.392 9 | 0.660 7 | 0.625 0 | 0.321 4 |
表4 8组试验模拟的不同量级24 h累积降水量的BS评分
Tab.4 Bias scores of 24 h accumulated rainfall with different levels simulated by 8 sets of test schemes
| 降水量级 | 试验 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM2 | BouLac | GBM | MYJ | MYNN | QNSE | UW | YSU | |
| 大于等于10.0 mm | 0.937 2 | 0.941 7 | 0.955 2 | 0.950 7 | 0.923 8 | 0.955 2 | 0.932 7 | 0.843 0 |
| 大于等于25.0 mm | 1.018 0 | 1.053 9 | 1.185 6 | 1.059 9 | 1.059 9 | 1.059 9 | 1.018 0 | 1.006 0 |
| 大于等于50.0 mm | 0.992 4 | 1.083 3 | 0.947 0 | 1.000 0 | 1.030 3 | 1.030 3 | 1.015 2 | 1.000 0 |
| 大于等于100.0 mm | 0.696 4 | 0.410 7 | 0.125 0 | 0.517 9 | 0.392 9 | 0.660 7 | 0.625 0 | 0.321 4 |
| 台风路径排名 | 不同降水量级ETS评分排名 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大于等于10.0 mm | 大于等于25.0 mm | 大于等于50.0 mm | 大于等于100.0 mm | ||
| 1 | BouLac | BouLac | ACM2 | ACM2 | ACM2 |
| 2 | UW | GBM | MYJ | YSU | BouLac |
| 3 | YSU | QNSE | MYNN | BouLac | MYJ |
| 4 | MYJ | ACM2 | QNSE | UW | YSU |
| 5 | QNSE | UW | UW | MYNN | QNSE |
| 6 | ACM2 | MYJ | BouLac | MYJ | GBM |
| 7 | MYNN | MYNN | YSU | QNSE | UW |
| 8 | GBM | YSU | GBM | GBM | MYNN |
表5 8组试验模拟的台风路径和不同量级24 h累积降水量的ETS评分排名
Tab.5 Rankings of typhoon track and equitable threat score of 24 h accumulated precipitation with different levels simulated by 8 sets of test schemes
| 台风路径排名 | 不同降水量级ETS评分排名 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大于等于10.0 mm | 大于等于25.0 mm | 大于等于50.0 mm | 大于等于100.0 mm | ||
| 1 | BouLac | BouLac | ACM2 | ACM2 | ACM2 |
| 2 | UW | GBM | MYJ | YSU | BouLac |
| 3 | YSU | QNSE | MYNN | BouLac | MYJ |
| 4 | MYJ | ACM2 | QNSE | UW | YSU |
| 5 | QNSE | UW | UW | MYNN | QNSE |
| 6 | ACM2 | MYJ | BouLac | MYJ | GBM |
| 7 | MYNN | MYNN | YSU | QNSE | UW |
| 8 | GBM | YSU | GBM | GBM | MYNN |
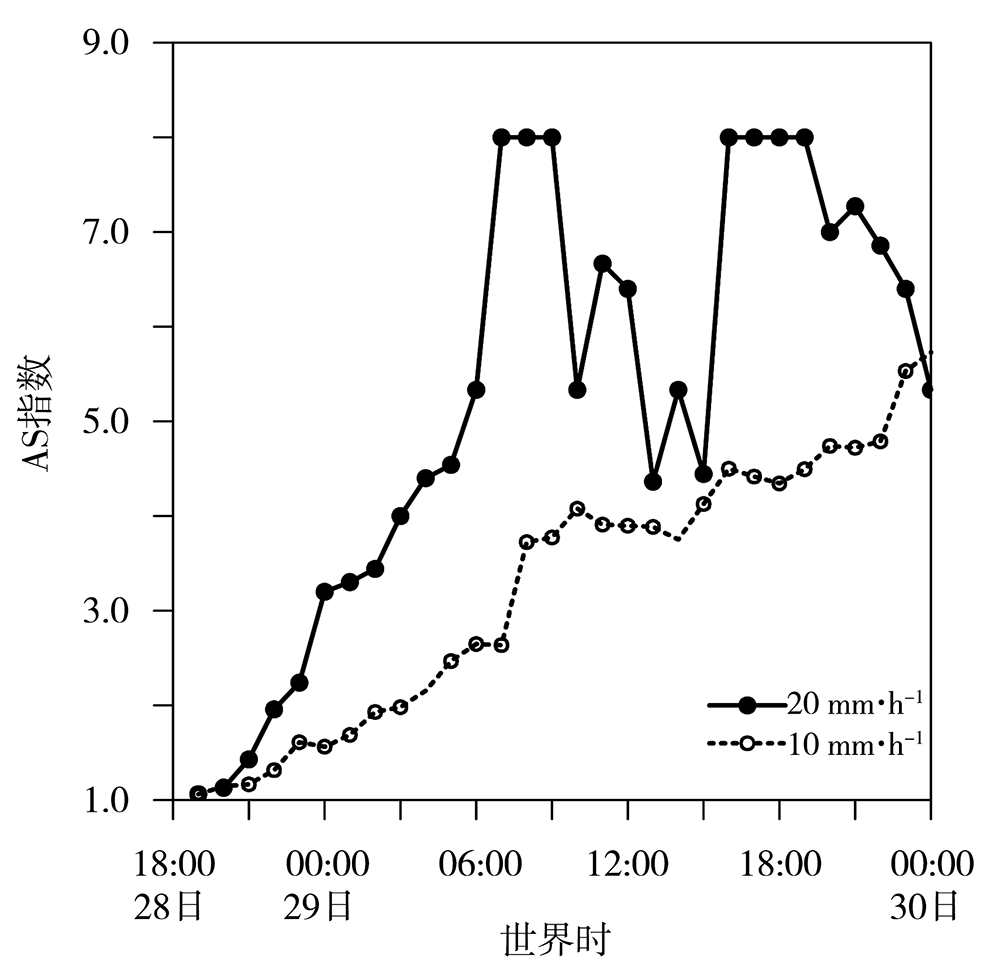
图4 2021年7月28日18:00 至30日00:00 8组试验模拟的10.0、20.0 mm·h-1雨强时的AS指数变化
Fig.4 The variation of AS index for 10.0 and 20.0 mm·h-1 rainfall intensity simulated by 8 sets of test schemes from 18:00 July 28 to 00:00 July 30, 2021
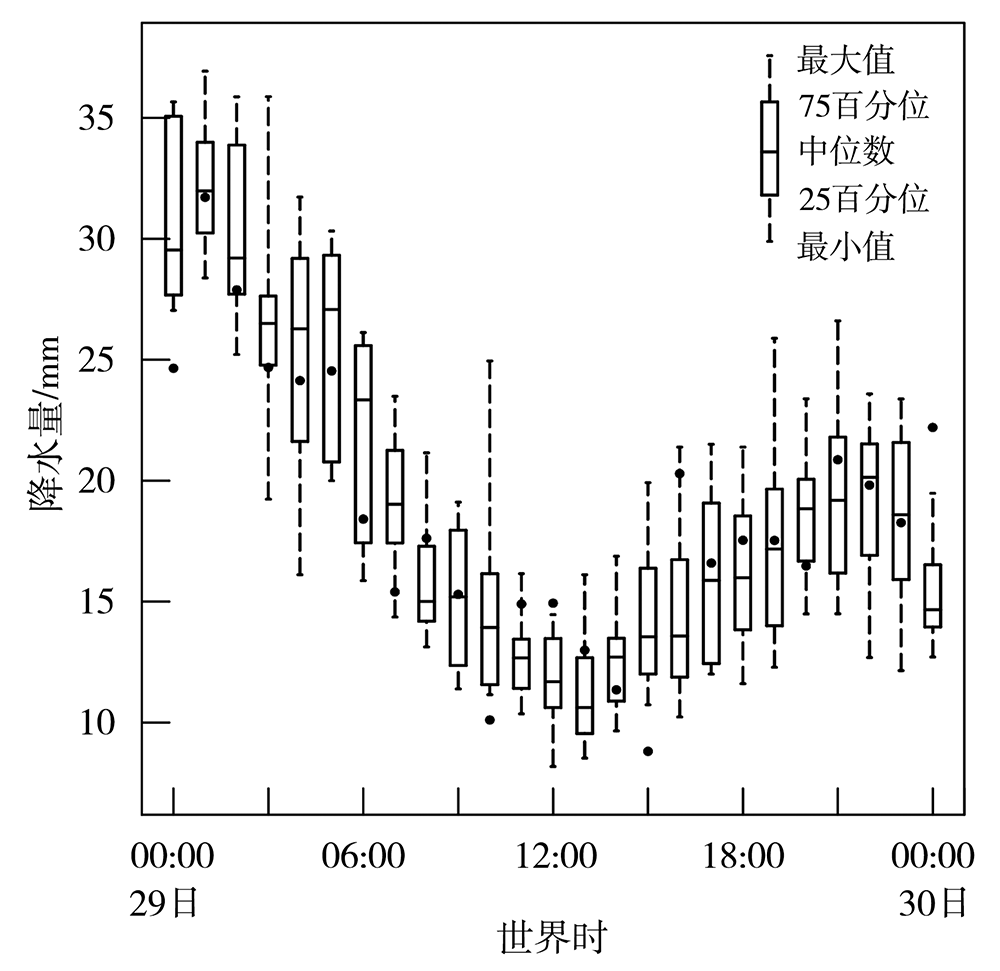
图5 2021年7月29日00:00至30日00:00 8组试验模拟的小时最大降水量随时间变化箱线图 (黑色圆点为实况)
Fig.5 The box plots for hourly maximum precipitation varying with time simulated by 8 sets of test schemes from 00:00 July 29 to 00:00 July 30, 2021 (The black dots denote the hourly maximum precipitation from CMPAS data)
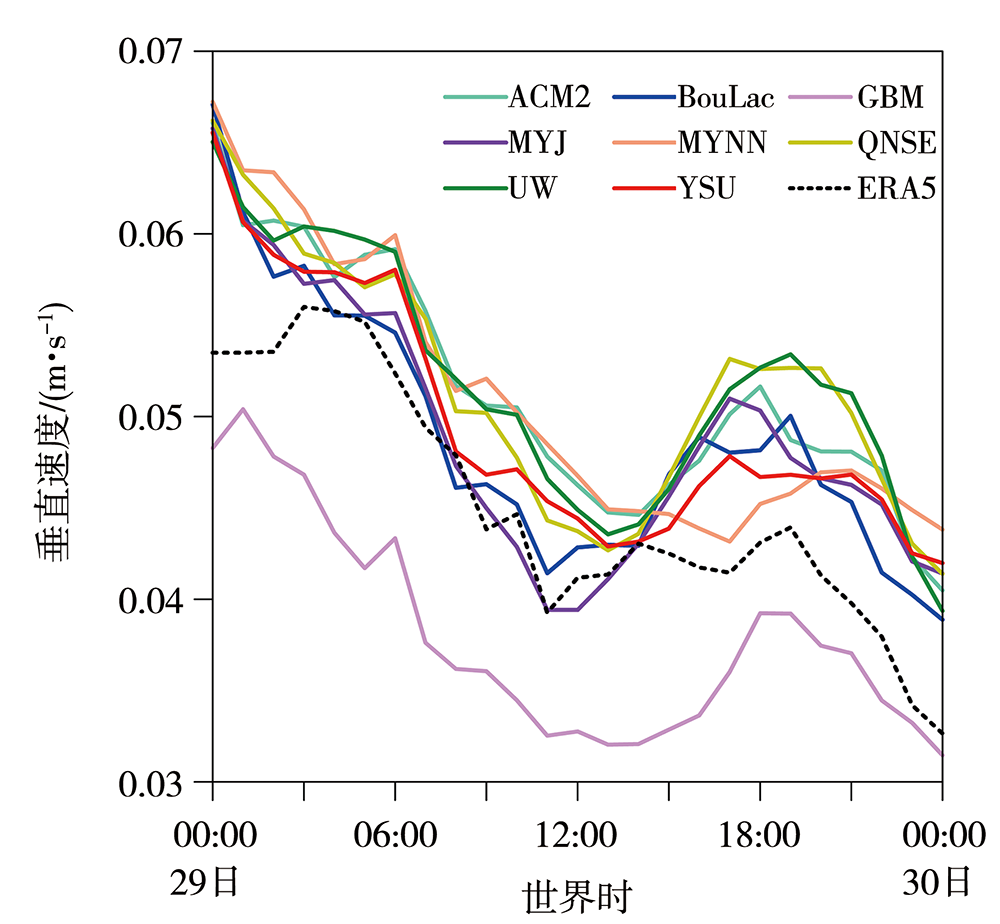
图6 2021年7月29日00:00至30日00:00 8组试验模拟和ERA5资料的区域平均700 hPa正垂直速度时间序列 (平均区域为8组试验模拟及实况台风中心所在纬度以北400 km半径的半圆区域)
Fig.6 Time series of area mean 700 hPa positive vertical velocity from simulated data of 8 sets of test schemes and ERA5 data from 00:00 July 29 to 00:00 July 30, 2021 (The region selected to calculate the mean value is the 400 km radius north of the latitude of typhoon center in real data and simulation results)
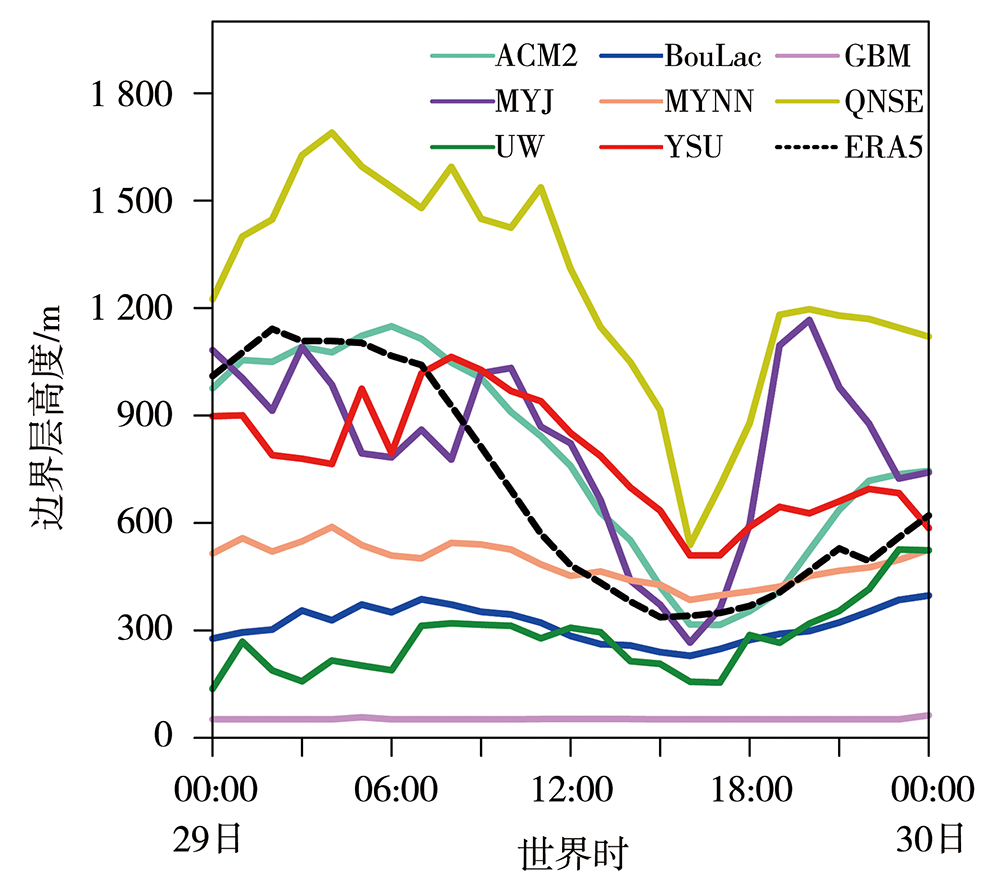
图7 2021年7月29日00:00至30日00:00 ERA5资料及8组试验模拟的区域(117.0°E—117.4°E,38.0°N—38.4°N)平均边界层高度的时间序列
Fig.7 The time series of mean planetary boundary layer height from ERA5 data and simulated data of 8 sets of test schemes averaged on the region of 117.0°E-117.4°E, 38.0°N-38.4°N from 00:00 July 29 to 00:00 July 30, 2021
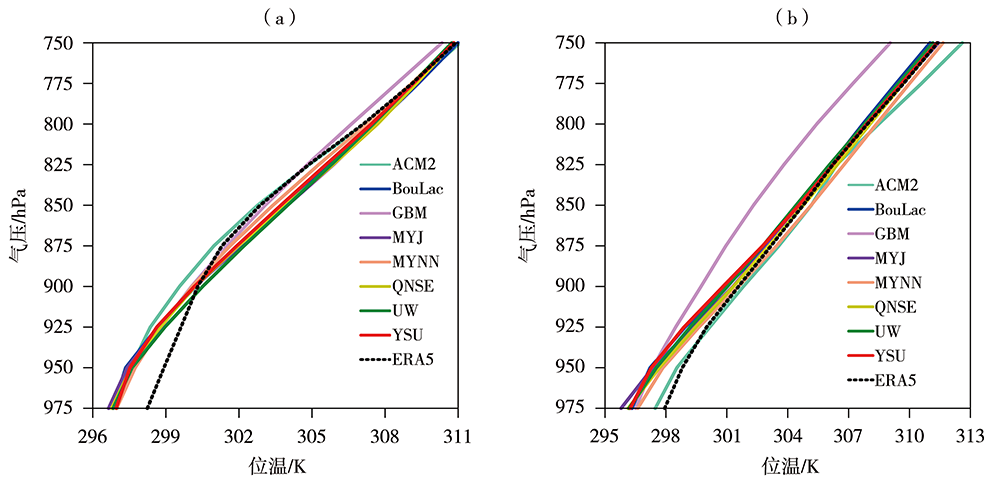
图8 2021年7月29日06:00(a)和18:00(b)ERA5资料和8组试验模拟的区域(117.0°E—117.4°E,38.0°N—38.4°N)平均位温垂直廓线
Fig.8 The profiles of potential temperature averaged on the region of 117.0°E-117.4°E, 38.0°N-38.4°N from ERA5 data and simulated data of 8 sets of test schemes at 06:00 (a) and 18:00 (b) July 29, 2021
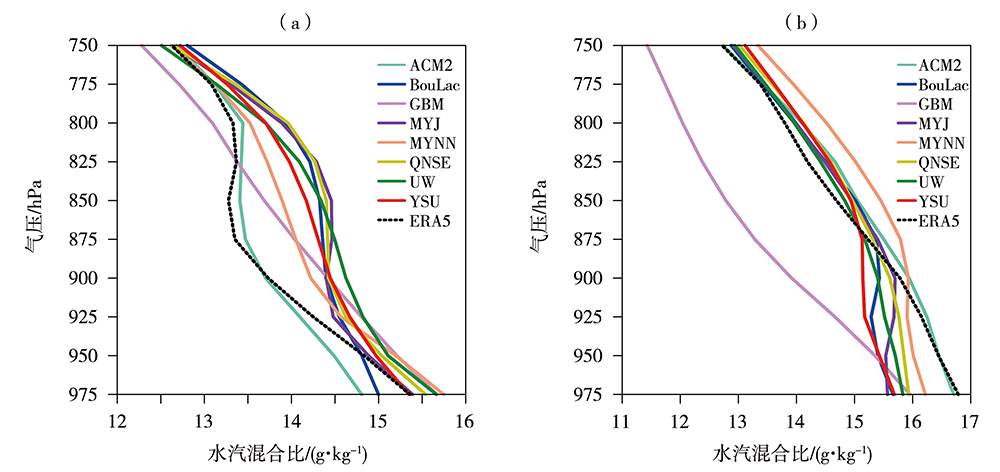
图9 2021年7月29日06:00(a)和18:00(b)ERA5资料和8组试验模拟的区域(117.0°E—117.4°E,38.0°N—38.4°N)平均水汽混合比垂直廓线
Fig.9 The profiles of water vapor mixing ratio averaged on the region of 117.0°E-117.4°E, 38.0°N-38.4°N from ERA5 data and simulated data of 8 sets of test schemes at 06:00 (a) and 18:00 (b) July 29, 2021
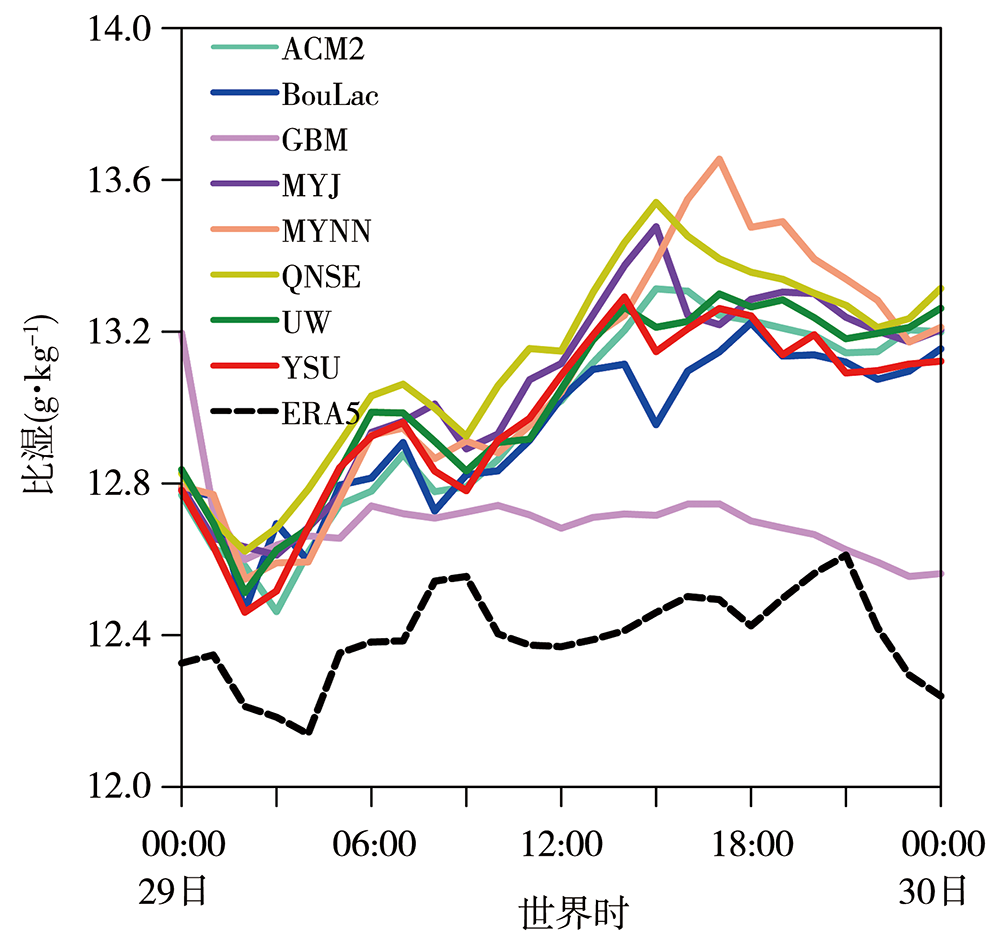
图10 2021年7月29日00:00至30日00:00 8组试验模拟和ERA5资料的区域平均850 hPa比湿时间序列 (平均区域同图6)
Fig.10 Time series of area averaged 850 hPa specific humidity from the simulated data of 8 sets of test schemes and ERA5 data (The selected average region is the same as in fig.6)
| [1] | 陈联寿, 罗哲贤, 李英, 2004. 登陆热带气旋研究的进展[J]. 气象学报, 62(5): 541-549. |
| [2] | 陈联寿, 许映龙, 2017. 中国台风特大暴雨综述[J]. 气象与环境科学, 40(1): 3-10. |
| [3] | 蔡芗宁, 寿绍文, 钟青, 2006. 边界层参数化方案对暴雨数值模拟的影响[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 29(3): 364-370. |
| [4] | 蔡义勇, 党皓飞, 林青, 等, 2019. 福建台风极端强降水的时空分布及环流特征[J]. 海峡科学, 10: 14-21. |
| [5] | 崔驰潇, 包云轩, 袁成松, 等, 2018. 不同边界层参数化方案对江苏地区一次平流雾过程的模拟影响[J]. 大气科学, 42(6): 1 344-1 362. |
| [6] | 邓国, 周玉淑, 李建通, 2005. 台风数值模拟中边界层方案的敏感性试验I: 对台风结构的影响[J]. 大气科学, 29(3): 417-428. |
| [7] | 代昕鹭, 陈葆德, 张旭, 等, 2017. WARMS2.0中边界层参数化方案对一次台风外围降水模拟预报的影响[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 32(5): 513-523. |
| [8] | 丁成慧, 李江南, 赵杨洁, 等, 2018. 边界层参数化方案对南海秋季台风“莎莉嘉”(2016)模拟的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 34(5): 657-673. |
| [9] | 李英, 陈联寿, 2005. 湿地边界层通量影响热带气旋登陆维持和降水的数值试验[J]. 气象学报, 63(5): 683-693. |
| [10] | 温晓培, 隆霄, 张述文, 等, 2016. 边界层参数化方案对台风SANBA初生阶段影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 32(3): 346-357. |
| [11] |
王晨稀, 2013. 边界层参数化影响“梅花”台风的敏感性试验[J]. 地球科学进展, 28(2): 197-208.
DOI |
| [12] | 王雨星, 钟中, 孙源, 等, 2017. 两种边界层参数化方案模拟热带气旋Megi(2010)路径差异的机理分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(7): 2 545-2 555. |
| [13] | 王叶红, 赵玉春, 2020. 边界层参数化方案对“莫兰蒂”台风(1614)登陆阶段影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 44(5): 935-959. |
| [14] | 吴志鹏, 李跃清, 李晓岚, 等, 2021. WRF模式边界层参数化方案对川渝盆地西南涡降水模拟的影响[J]. 大气科学, 45(1): 58-72. |
| [15] | 夏丽花, 苏志重, 刘爱鸣, 等, 2014. 台湾地形对1011号台风“凡亚比”影响的数值试验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 33(2): 149-155. |
| [16] | 徐亚钦, 翟国庆, 李国平, 等, 2017. WRF模式对高影响浙江型台风微物理和边界层参数化方案的优化试验[J]. 热带气象学报, 33(2): 201-211. |
| [17] | 许鲁君, 刘辉志, 徐祥德, 等, 2018. WRF模式对青藏高原那曲地区大气边界层模拟适用性研究[J]. 气象学报, 76(6): 955-967. |
| [18] | 赵鸣, 2008. 边界层和陆面过程对中国暴雨影响研究的进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 27(2): 186-190. |
| [19] | 周昊, 朱伟军, 彭世球, 2013. 不同微物理方案和边界层方案对超强台风“鲇鱼”路径和强度模拟的影响分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 28(5): 803-812. |
| [20] | 周彦均, 高志球, 濮梅娟, 等, 2019. 不同的边界层参数化方案对江淮一次暴雨过程数值试验研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 42(4): 591-601. |
| [21] |
BOUGEAULT P, LACARRERE P, 1989. Parameterization of orography-induced turbulence in a mesobeta-scale model[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 117(8): 1 872-1 890.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BRETHERTON C S, PARK S, 2009. A new moist turbulence parameterization in the community atmosphere model[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(12): 3 422-3 448.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GRENIER H, BRETHERTON C S, 2001. A moist PBL parameterization for large-scale models and its application to subtropical cloud-topped marine boundary layers[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 129(3): 357-377.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
HONG S Y, NOH Y, DUDHIA J, 2006. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 134(9): 2 318-2 341.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HU X M, NIELSEN-GAMMON J W, ZHANG F Q, 2010. Evaluation of three planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 49(9): 1 831-1 844.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MELLOR G L, YAMADA T, 1982. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 20(4): 851-875.
DOI URL |
| [27] | NAKANISHI M, NIINO H, 2009. Development of an improved turbulence closure model for the atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 87(5): 895-912. |
| [28] |
PLEIM J E, 2007. A combined local and nonlocal closure model for the atmospheric boundary layer. Part I: Model description and testing[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 46(9): 1 383-1 395.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SCHUMACHER R S, DAVIS C A, 2010. Ensemble-based forecast uncertainty analysis of diverse heavy rainfall events[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 25(4): 1 103-1 122.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
SUKORIANSKY S, GALPERIN B, PEROV V, 2005. Application of a new spectral theory of stably stratified turbulence to the atmospheric boundary layer over sea ice[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 117(2): 231-257.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 傅朝, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 徐丽丽, 沙宏娥, 马莉, 崔宇. 西北干旱区一次极端暴雨局地性增强的对流环境特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 909-921. |
| [2] | 张君霞, 黄武斌, 杨秀梅, 刘维成, 周子涵, 沙宏娥. 陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 922-932. |
| [3] | 沙宏娥, 傅朝, 刘维成, 徐丽丽, 刘娜, 刘新雨, 马绎皓. 西北东部半干旱区一次极端特大暴雨的触发和维持机制[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 933-944. |
| [4] | 陈小婷, 赵强, 刘慧, 彭力. 黄土高原两次不同类型暴雨水汽特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [5] | 彭力, 赵强, 乔丹杨, 张雄, 徐浩天, 倪闻. 有无台风影响下陕西西北涡暴雨特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 981-992. |
| [6] | 焦洋, 张永婧, 尹承美, 褚颖佳. 山东夏季暴雨对青藏高原东南部及邻近区域春季大气热源变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [7] | 马思敏, 穆建华, 舒志亮, 孙艳桥, 邓佩云, 周楠. 六盘山区一次典型暴雨过程的地形敏感性模拟试验[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 457-468. |
| [8] | 杨霞, 许婷婷, 张林梅, 华烨, 周鸿奎. 不同气候背景下南疆暖季暴雨特征和差异[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 222-233. |
| [9] | 沈晓玲, 潘灵杰, 左骏, 桑明慧, 章丽娜. 浙江西部梅汛期两次相似落区暴雨过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 244-255. |
| [10] | 苟阿宁, 吴翠红, 王玉娟, 杜牧云, 刘文婷, 冷亮, 邓红. 基于风廓线雷达的湖北梅雨期暴雨中小尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 84-94. |
| [11] | 庄晓翠, 李博渊, 赵江伟, 李建刚, 张林梅. 天山南坡暖季暴雨过程的水汽来源及输送特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 30-40. |
| [12] | 刘新伟,王澄海,郭润霞,杨晓军,狄潇泓. 1981—2018年甘肃省极端暴雨天气过程的气候与环流特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 750-758. |
| [13] | 杨薇,冯文,曾丽,陈有龙. 海南省冬季暴雨时空分布及环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 759-765. |
| [14] | 师锐, 何光碧, 周春花. 四川一次持续性暴雨过程的水汽特征及多尺度系统影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 415-425. |
| [15] | 冯瑶, 阿依先木·尼牙孜, 热依拉·玉努斯. 新疆哈密“7·31”极端大暴雨过程成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 426-435. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
