干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 103-113.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0103
两次极端强降水风暴双偏振参量特征对比分析
郭飞燕1( ), 刁秀广2(
), 刁秀广2( ), 褚颖佳3, 李欣1, 陆雪1, 张少博1
), 褚颖佳3, 李欣1, 陆雪1, 张少博1
- 1.山东省青岛市气象灾害防御工程技术研究中心/青岛市气象局,山东 青岛 266003
2.山东省气象台,山东 济南 250031
3.山东省济南市气象局,山东 济南 250102
Contrast analysis of dual-polarization signatures for the two extreme rainfall storms
GUO Feiyan1( ), DIAO Xiuguang2(
), DIAO Xiuguang2( ), CHU Yingjia3, LI Xin1, LU Xue1, ZHANG Shaobo1
), CHU Yingjia3, LI Xin1, LU Xue1, ZHANG Shaobo1
- 1. Qingdao Engineering Technology Research Center for Meteorological Disaster Prevention/Qingdao Meteorology Bureau, Qingdao 266003, China
2. Shandong Meteorological Observatory, Ji'nan 250031, China
3. Ji'nan Meteorology Bureau of Shandong, Ji'nan 250102, China
摘要:
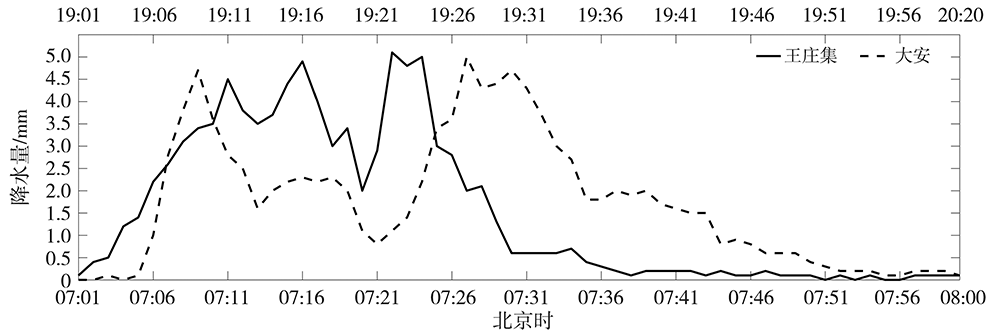
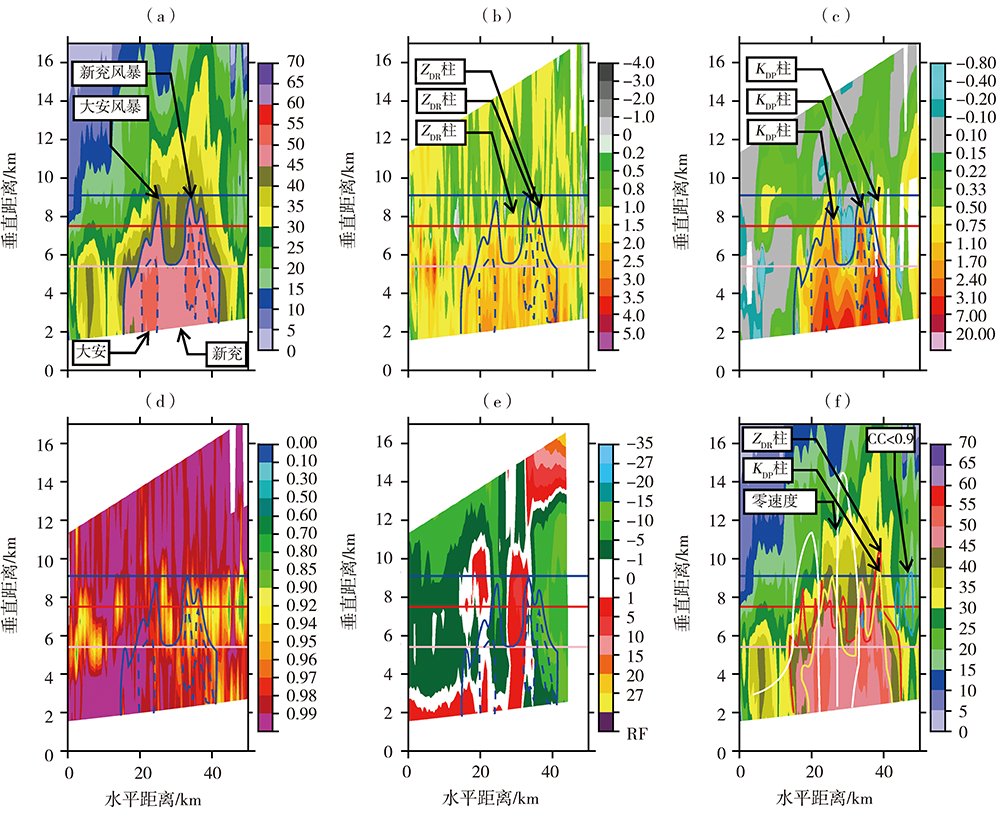
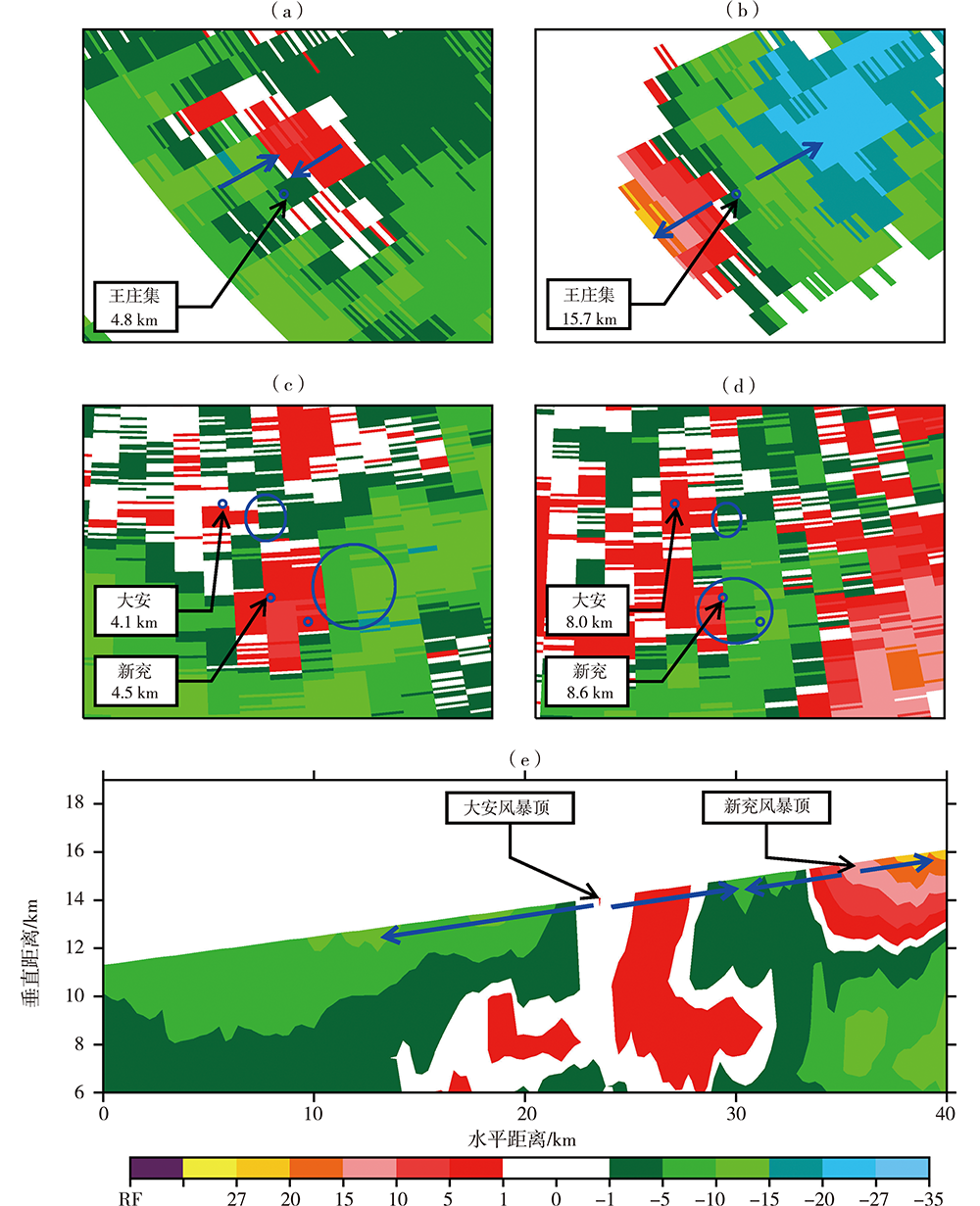
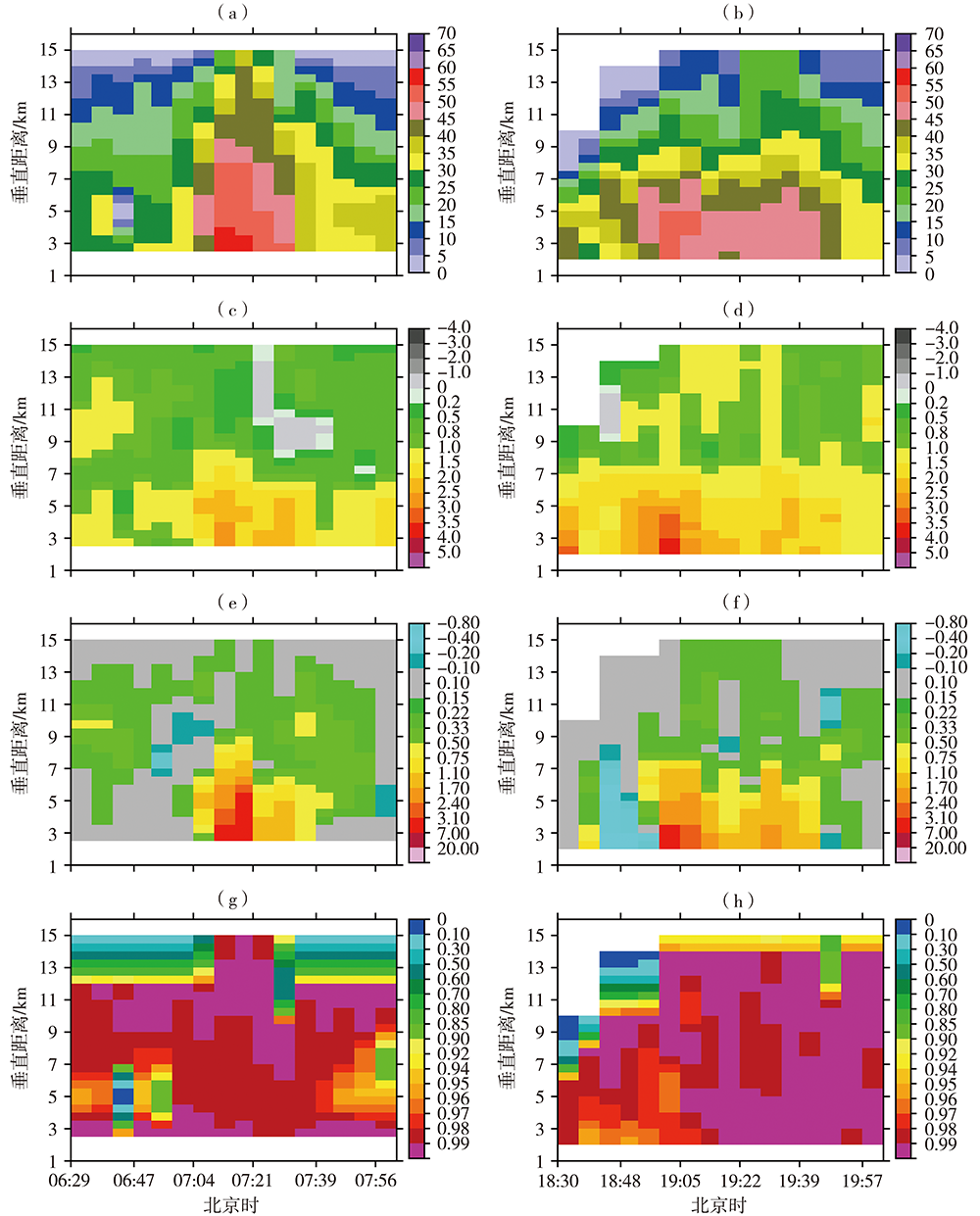
基于济南S波段双偏振多普勒天气雷达(CINRAD/SA-D)探测资料,并结合区域自动气象站以及常规观测资料,对2020年8月5日和6日山东两次极端强降水风暴环境条件进行对比分析,并重点分析莘县王庄集和兖州大安风暴的双偏振参量特征。结果表明:两次极端强降水天气均具有较高的K指数和较大的对流有效位能(Convective Available Potential Energy,CAPE),湿层厚,垂直风切变中等偏弱,但6日强降水低层垂直风切变和相对风暴螺旋度明显偏强。风暴气流结构有明显差异:王庄集和大安风暴分别表现为倾斜上升和气旋性旋转气流结构,前者风暴顶辐散强而后者较弱,从而导致前者风暴顶高度及差分相移率(KDP)柱高度较高。不同高度微物理结构有差异:-10 ℃层高度之上,两者以固态粒子为主,而王庄集风暴含有更加深厚、丰富的霰粒子,-20~-10 ℃层还有一定浓度较小的液态粒子;-10 ℃层高度以下,两者以浓度较高的液态粒子为主,而王庄集风暴含有一定数量的冰相粒子。风暴低层测站周围差分反射率(ZDR)、KDP和相关系数(Correlation Coefficient, CC)大致相当,ZDR适中,粒子大小适中,KDP和CC较大,风暴降水主体液态雨滴浓度较高,含水量丰富,从而产生高强度降水。
中图分类号: