Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 563-575.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0563
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on circulation classification and atmospheric pollution mechanisms in Gansu based on machine learning
LIU Zongrui1( ), WAN Ziyue1, ZHAO Yuhan1, LIU Weiping2, WANG Ruoan3, MA Yuxia1(
), WAN Ziyue1, ZHAO Yuhan1, LIU Weiping2, WANG Ruoan3, MA Yuxia1( )
)
- 1. College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
2. Lanzhou Regional Climate Center, Lanzhou 730020, China
3. Pingliang Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Pingliang 744000, Gansu, China
-
Received:2025-03-20Revised:2025-05-08Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-08
基于机器学习的环流分型与甘肃大气污染机制研究
刘宗瑞1( ), 万紫悦1, 赵宇瀚1, 刘卫平2, 王若安3, 马玉霞1(
), 万紫悦1, 赵宇瀚1, 刘卫平2, 王若安3, 马玉霞1( )
)
- 1.兰州大学大气科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730000
2.兰州区域气候中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
3.甘肃省平凉市气象局,甘肃 平凉 744000
-
通讯作者:马玉霞 -
作者简介:刘宗瑞(2000—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为极端天气及其影响。E-mail: liuzr2023@lzu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(4235177);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(23JRRA1079)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Zongrui, WAN Ziyue, ZHAO Yuhan, LIU Weiping, WANG Ruoan, MA Yuxia. Research on circulation classification and atmospheric pollution mechanisms in Gansu based on machine learning[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(4): 563-575.
刘宗瑞, 万紫悦, 赵宇瀚, 刘卫平, 王若安, 马玉霞. 基于机器学习的环流分型与甘肃大气污染机制研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 563-575.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0563
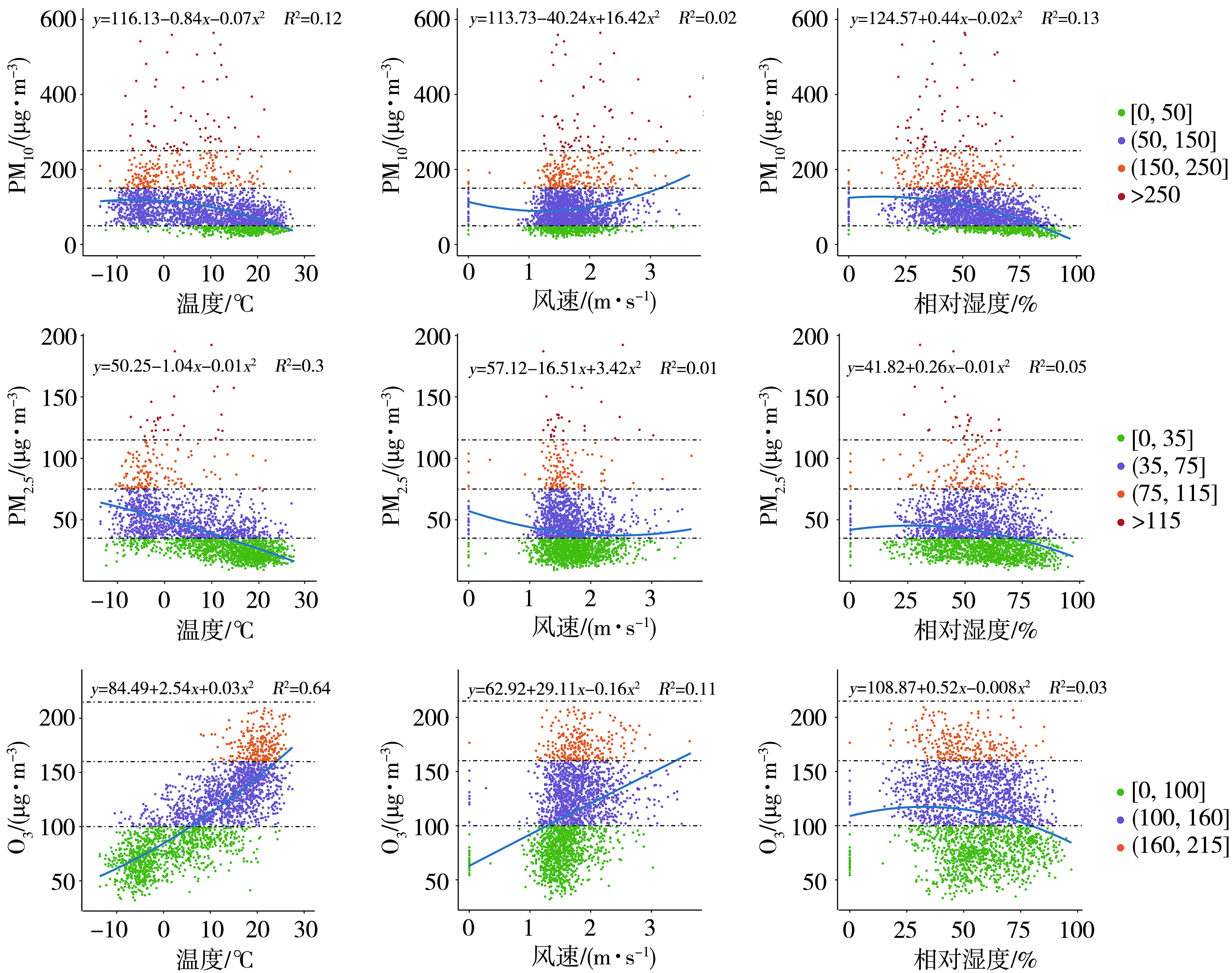
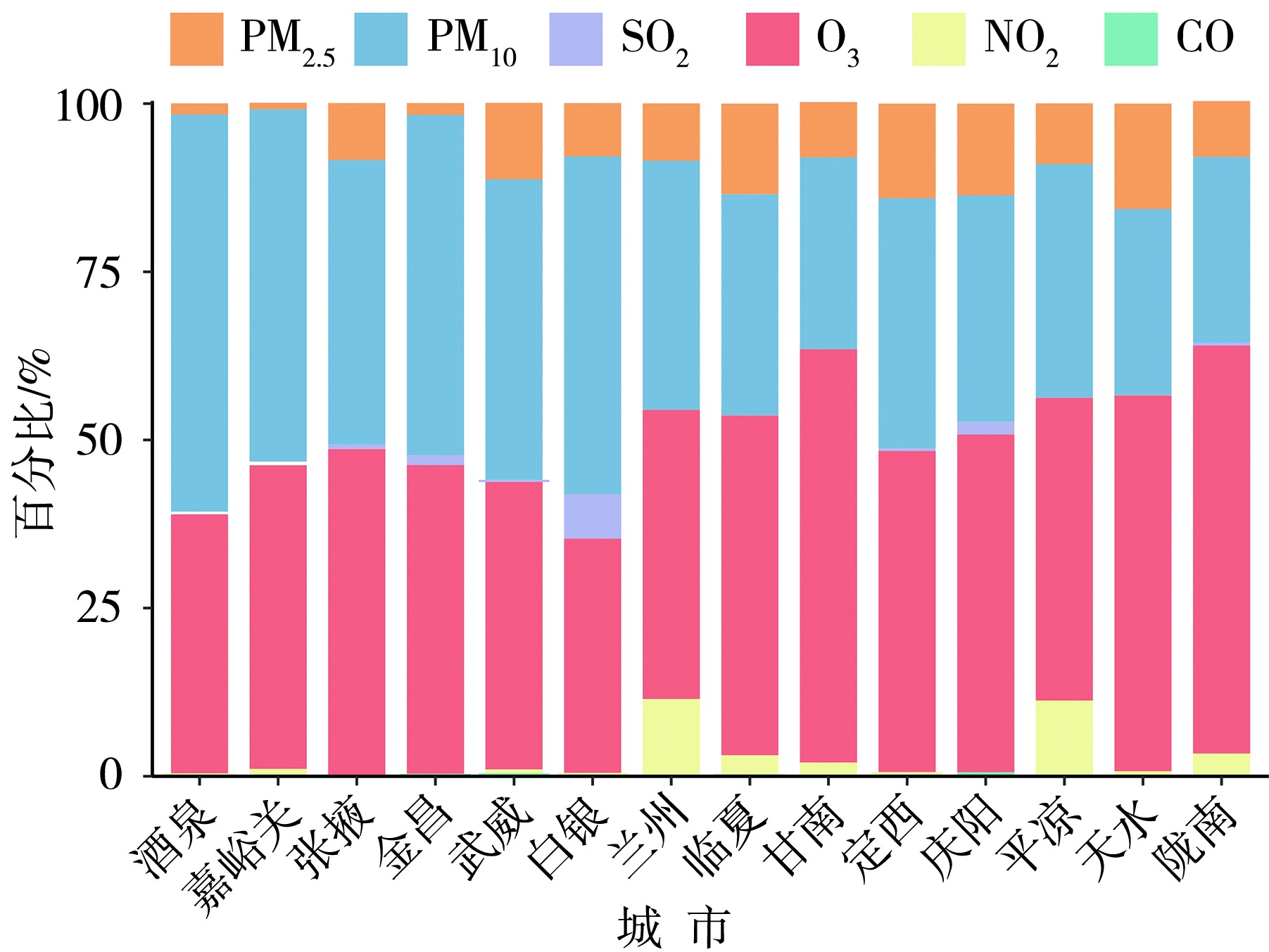
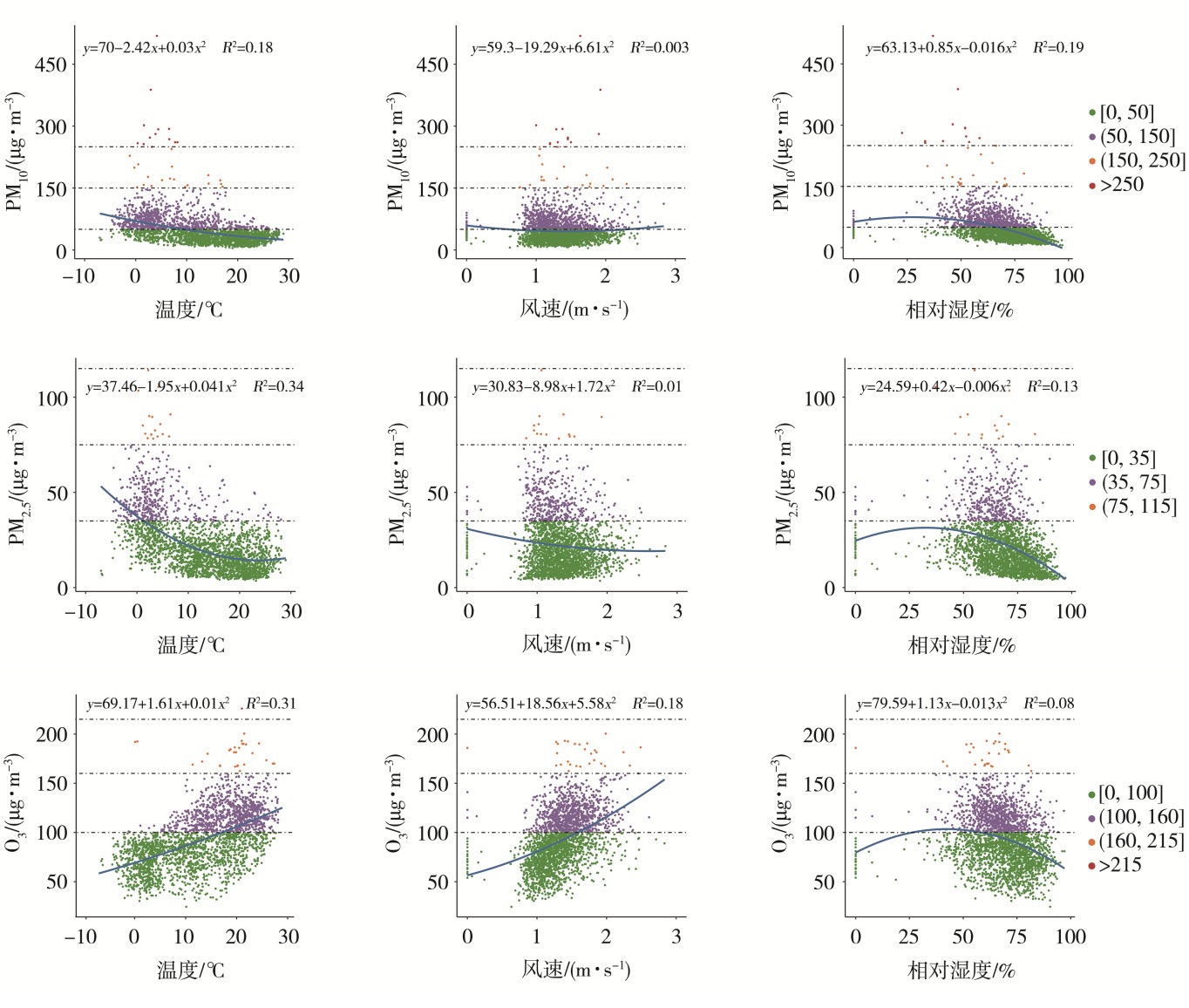
Fig.2 The fitting relationship between meteorological elements in Lanzhou and the mass concentrations of PM10, PM2.5 and O3 (The circle colors represent the mass concentration ranges of PM10, PM2.5 and O3 at different IAQI levels,the same as below)
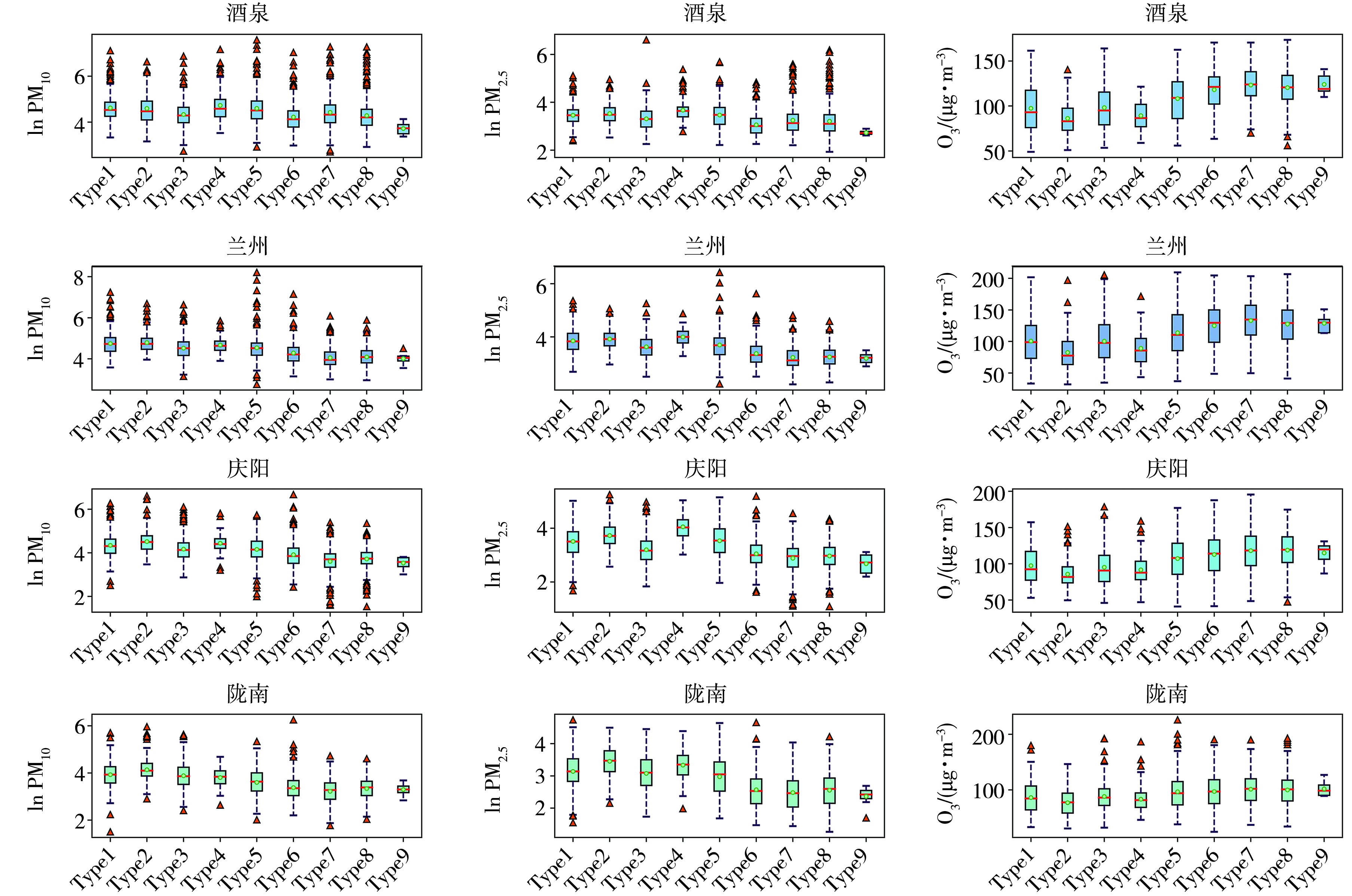
Fig.8 Box plots of the mass concentrations of three pollutants under nine circulation patterns in typical cities (The dots represent the mean values, the red lines denote the median, the upper line of the box indicates the upper quartile, the lower line of the box signifies the lower quartile, the upper edge represents the maximum value, the lower edge corresponds to the minimum value, and the triangles denote outliers)
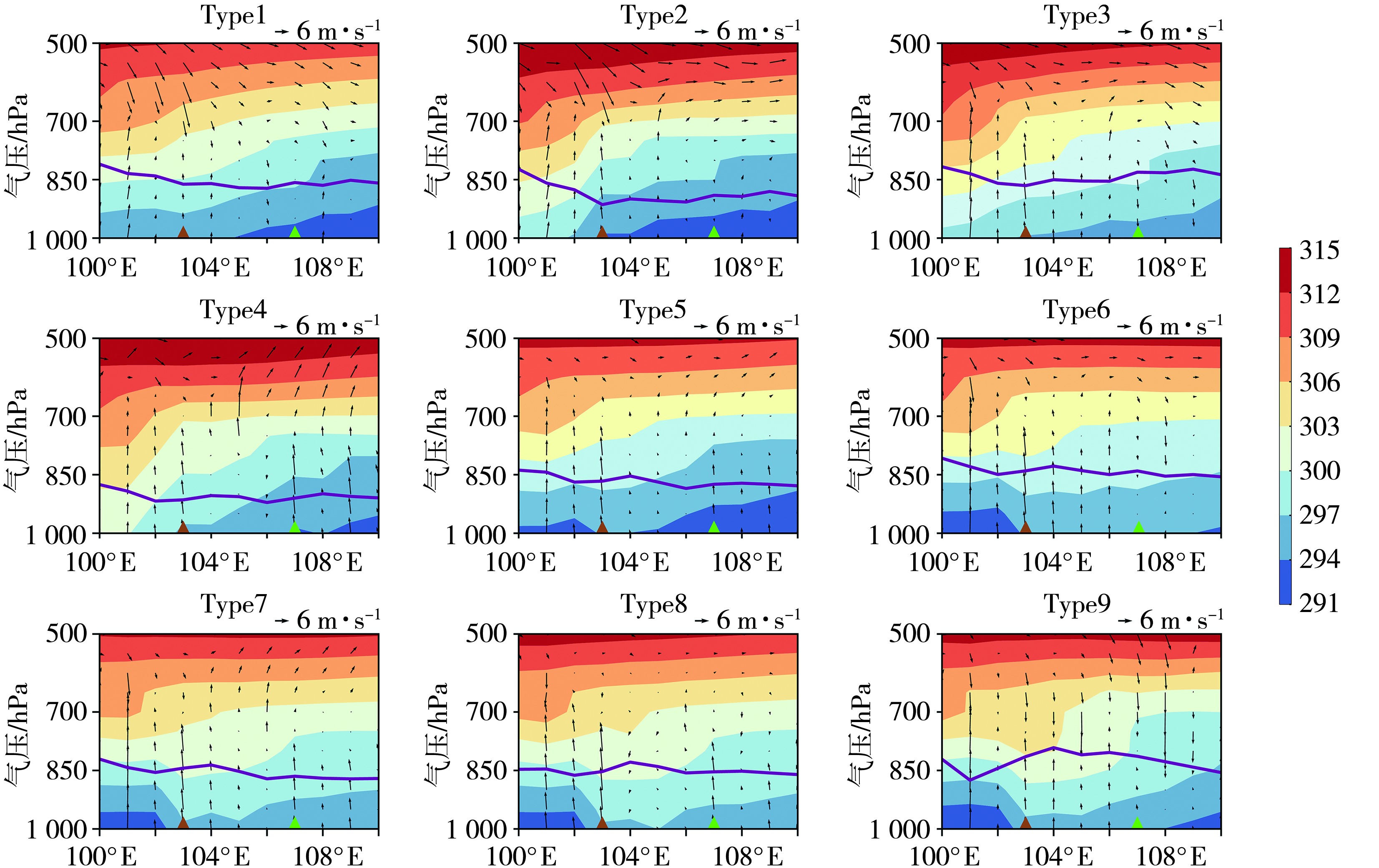
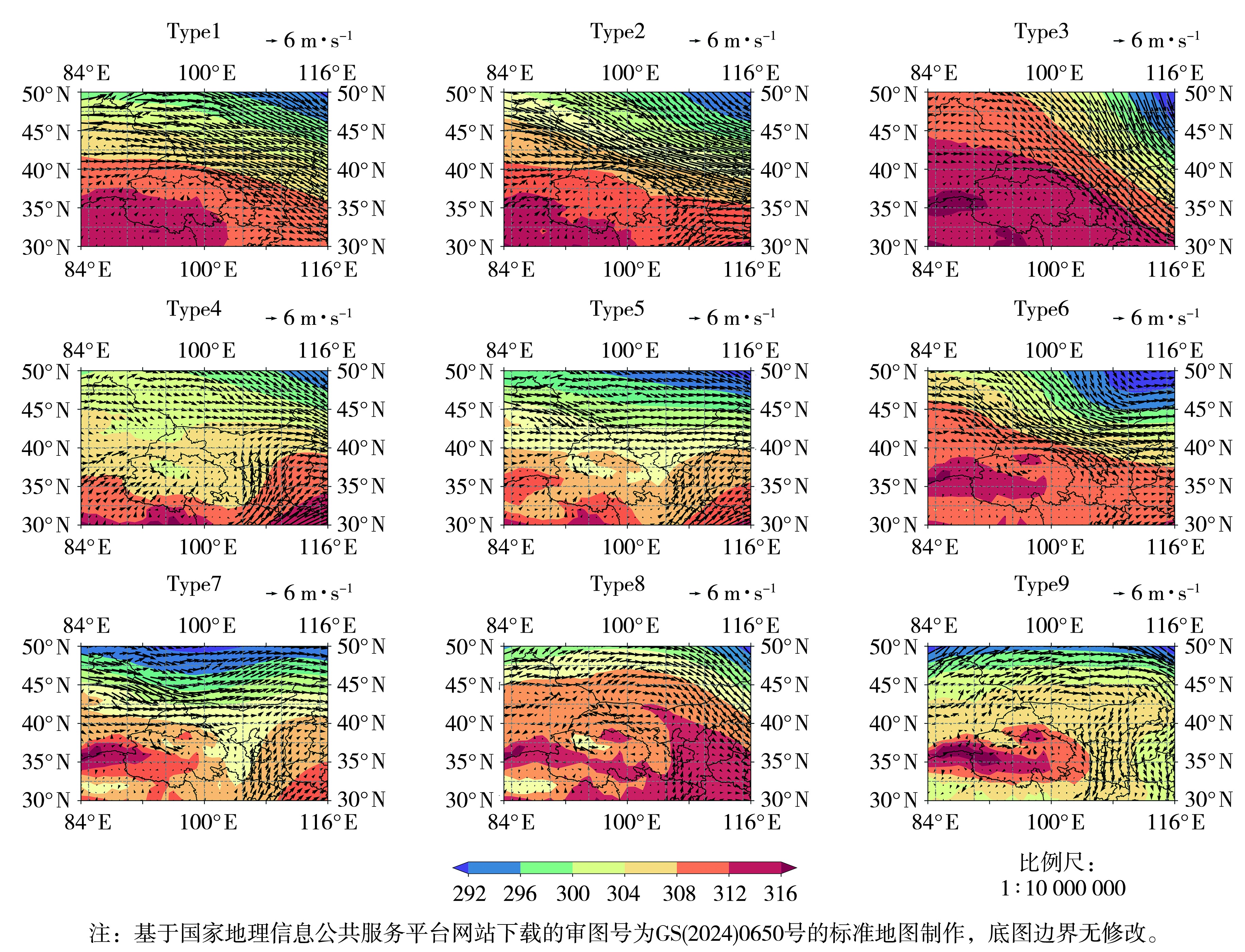
Fig.9 The vertical cross-sections of potential temperature (the color shaded, Unit: K) and wind (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) under different circulation patterns over Lanzhou and Qingyang (The purple lines represent the boundary layer height, the same as below; the brown and green triangles indicate the longitudes of Lanzhou and Qingyang, respectively)
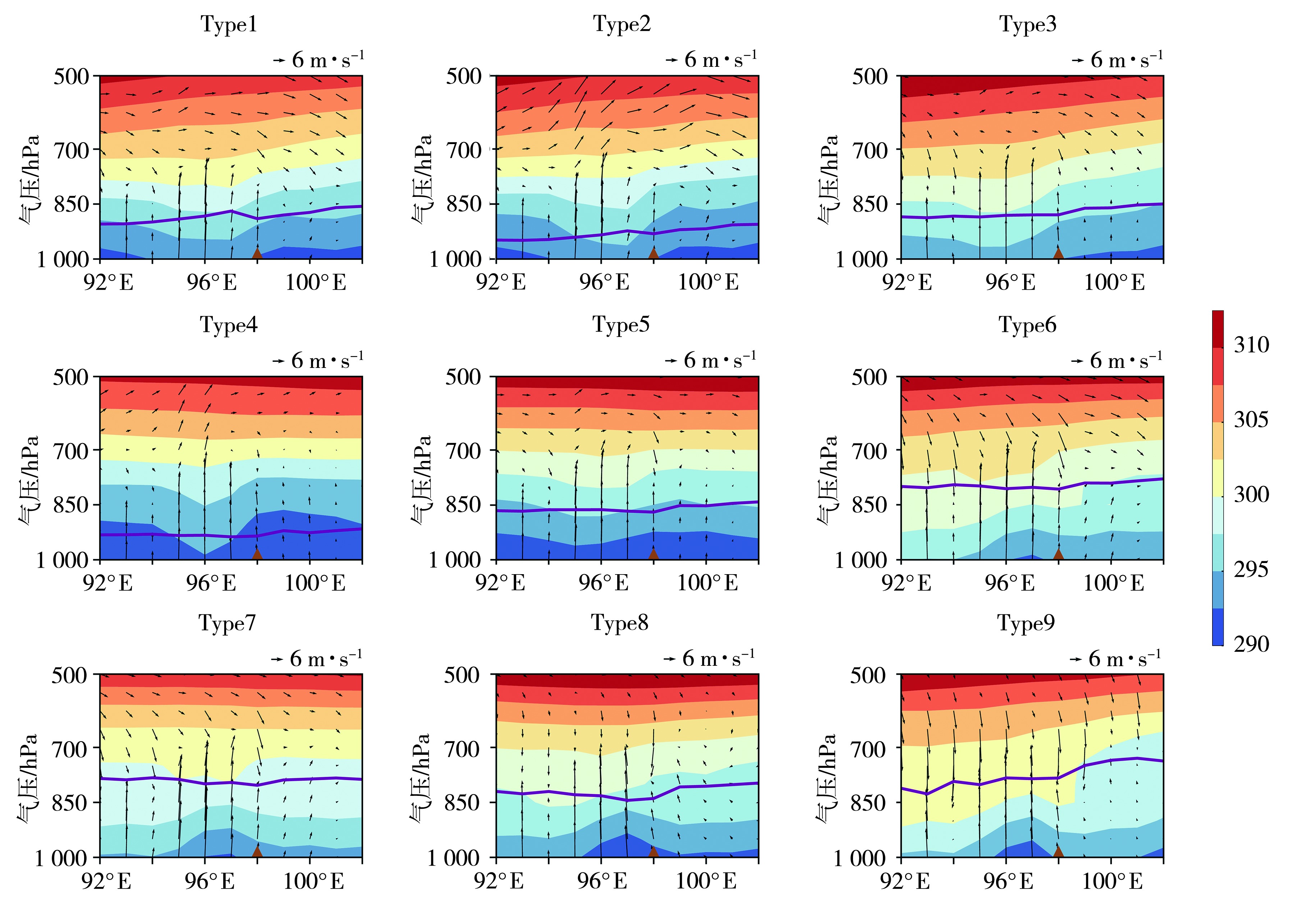
Fig.10 The vertical cross-sections of potential temperature (the color shaded, Unit: K) and wind (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) under various circulation patterns over Jiuquan (The brown triangle indicates the longitude of Jiuquan)
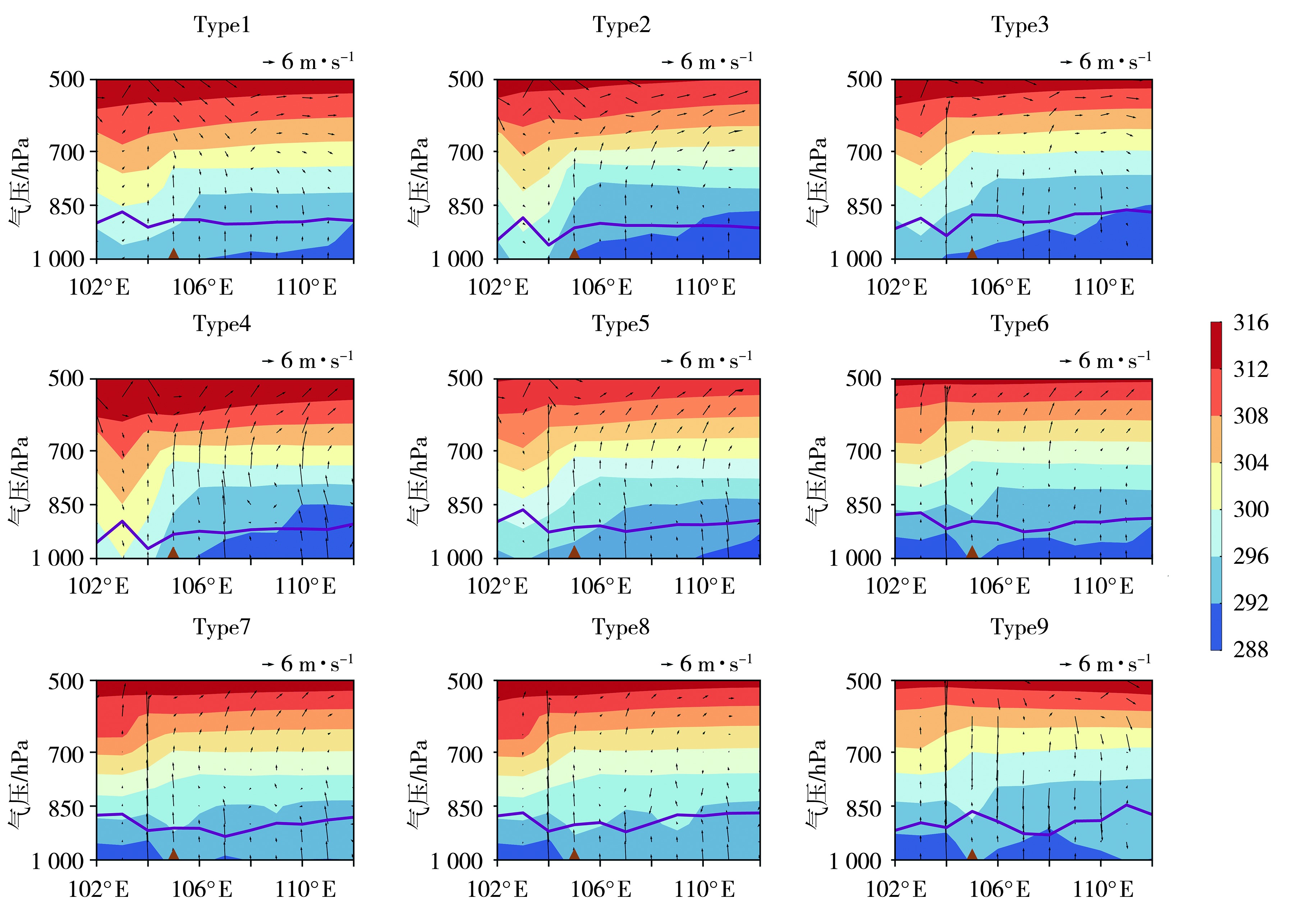
Fig.11 The vertical cross-sections of potential temperature (the color shaded, Unit: K) and wind (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) under various circulation patterns over Longnan (The brown triangle indicates the longitude of Longnan)
| [1] | 陈锦超, 2017. 合肥近地面臭氧浓度分布特征及影响因素[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学. |
| [2] | 胡春梅, 陈道劲, 周国兵, 等, 2020. 基于自组织神经网络算法的重庆秋冬季空气污染与天气分型的关系[J]. 气象, 46(9):1222-1 234. |
| [3] | 国家环境保护部, 2012a. 环境空气质量标准(GB3095—2012)[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| [4] | 国家环境保护部, 2012b. 环境空气质量指数(AQI)技术规定(试行)(HJ633—2012)[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| [5] | 黄瑶, 陶丽, 刘新超, 等, 2021. 大渡河上游强降水的环流分型及时空分布特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(4):58-67. |
| [6] | 吉莉, 刘晓冉, 2023. 重庆中心城区气象因子对大气污染影响的研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(2):113-119. |
| [7] | 李顺姬, 李红, 陈妙, 等, 2018. 气象因素对西安市西南城区大气中臭氧及其前体物的影响[J]. 气象与环境学报, 34(4):59-67. |
| [8] |
马敏劲, 陈然, 曹译丹, 等, 2024. 卷积神经网络研究进展及其在大气科学中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 42(5):719-733.
DOI |
| [9] | 王翠连, 张军, 郑瑶, 等, 2019. 郑州城区PM10、PM2.5质量浓度变化特征及其对气象因子的响应[J]. 环境保护科学, 45(6):76-83. |
| [10] | 吴进, 李琛, 马志强, 等, 2020. 基于天气分型的上甸子大气本底站臭氧污染气象条件[J]. 环境科学, 41(11):4864-4 873. |
| [11] | 杨雅涵, 翟盘茂, 周佰铨, 2024. 基于SOM的长江流域持续性强降水过程典型环流的客观分型[J]. 气象学报, 82(5):632-644. |
| [12] | 张宸赫, 赵天良, 陆忠艳, 等, 2020. 2014—2019年沈阳市大气污染物变化及气象因素影响分析[C]// 中国环境科学学会科学技术年会论文集(第一卷). 北京: 中国环境科学学会. |
| [13] | 张淑平, 韩立建, 周伟奇, 等, 2016. 冬季PM2.5的气象影响因素解析[J]. 生态学报, 36(24): 7 897-7 907. |
| [14] | 张莹, 2016. 我国典型城市空气污染特征及其健康影响和预报研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [15] | 赵熠琳, 李子, 沈劲, 等, 2024. 气象要素与前体物排放对中国区域性臭氧污染的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 46(6):876-881. |
| [16] | 赵天良, 张郁青, 宁贵财, 等, 2024. 四川盆地臭氧污染时空变化及平流层入侵影响研究进展[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(4):11-20. |
| [17] | AGATHOKLEOUS E, FENG Z Z, OKSANEN E, et al, 2020. Ozone affects plant, insect, and soil microbial communities: A threat to terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity[J]. Science Advances, 6(33): eabc1176. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc1176. |
| [18] | APTE J S, BRAUER M, COHEN A J, et al, 2018. Ambient PM2.5 reduces global and regional life expectancy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 5(9): 546-551. DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00360. |
| [19] | BEI N F, LI X P, TIE X X, et al, 2020. Impact of synoptic patterns and meteorological elements on the wintertime haze in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China from 2013 to 2017[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 704: 135210. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135210. |
| [20] | CHAMBERS S D, PODSTAWCZYŃSKA A, 2019. Improved method for characterising temporal variability in urban air quality part II: Particulate matter and precursors in central Poland[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 219:117040. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.117040. |
| [21] | CHEN Z Y, XIE X M, CAI J, et al, 2018. Understanding meteorological influences on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A temporal and spatial perspective[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(8): 5 343-5 358. DOI: 10.5194/acp-18-5343-2018. |
| [22] | CHENG B W, MA Y X, ZHAO Y H, et al, 2024. Influence of topography and synoptic weather patterns on air quality in a valley basin city of Northwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 934: 173362. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173362. |
| [23] | GAO Z Q, DO K, LI Z R, et al, 2024. Predicting PM2.5 levels and exceedance days using machine learning methods[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 323: 120396. DOI:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2024.120396. |
| [24] | GONG S L, LIU Y L, HE J J, et al, 2022. Multi-scale analysis of the impacts of meteorology and emissions on PM2.5 and O3 trends at various regions in China from 2013 to 2020 1: Synoptic circulation patterns and pollution[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 815:152770.DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152770. |
| [25] |
GUAN Q Y, LI F C, YANG L Q, et al, 2018. Spatial-temporal variations and mineral dust fractions in particulate matter mass concentrations in an urban area of northwestern China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 222: 95-103. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.064.
PMID |
| [26] | HU F, XIE P H, XU J, et al, 2025. Impacts of synoptic weather patterns on Hefei’s ozone in warm season and analysis of transport pathways during extreme pollution events[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 156: 371-384. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2024.06.032. |
| [27] | HU X M, HU J, GAO L, et al, 2021. Multisensor and multimodel monitoring and investigation of a wintertime air pollution event ahead of a cold front over Eastern China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 126(10): e2020JD033538. DOI: 10.1029/2020JD033538. |
| [28] | HUANG J, PAN X, GUO X, et al, 2018. Health impact of China’s Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan: An analysis of national air quality monitoring and mortality data[J]. The Lancet Planetary Health, 2(7): e313-e323. DOI: 10.1016/S2542-5196(18)30141-4. |
| [29] | JIN X P, CAI X H, HUANG Q Q, et al, 2021. Atmospheric boundary layer-free troposphere air exchange in the North China plain and its impact on PM2.5 pollution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 126(9): e2021JD0 34641. DOI: 10.1029/2021JD034641. |
| [30] | JUN M J, GU Y, 2023. Effects of transboundary PM2.5 transported from China on the regional PM2.5 concentrations in South Korea: A spatial panel-data analysis[J]. PLoS One, 18(4): e0281988. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281988. |
| [31] | KANG H Q, ZHU B, LIU X H, et al, 2021. Three-dimensional distribution of PM2.5 over the Yangtze River Delta as cold fronts moving through[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 126(8): e2020JD034035. DOI: 10.1029/2020JD034035. |
| [32] |
LI J D, LIAO H, HU J L, et al, 2019. Severe particulate pollution days in China during 2013-2018 and the associated typical weather patterns in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the Yangtze River Delta regions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 248: 74-81. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.124.
PMID |
| [33] | LI M G, WANG L L, LIU J D, et al, 2020. Exploring the regional pollution characteristics and meteorological formation mechanism of PM2.5 in North China during 2013-2017[J]. Environment International, 134: 105283. DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105283. |
| [34] | LIU Y L, SHI G M, ZHAN Y, et al, 2021. Characteristics of PM2.5 spatial distribution and influencing meteorological conditions in Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 253: 118364. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118364. |
| [35] | MA S M, XIAO Z M, ZHANG Y F, et al, 2020. Assessment of meteorological impact and emergency plan for a heavy haze pollution episode in a core city of the North China plain[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 20(1): 26-42. DOI: 10.4209/aaqr.2019.08.0392. |
| [36] | MO J Y, GONG S L, ZHANG L, et al, 2021. Impacts of long-range transports from Central and South Asia on winter surface PM2.5 concentrations in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 777: 146243. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146243. |
| [37] | RUPAKHETI D, YIN X F, RUPAKHETI M, et al, 2021. Spatio-temporal characteristics of air pollutants over Xinjiang, Northwestern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 268: 115907. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115907. |
| [38] | SUN Z B, ZHAO X J, LI Z M, et al, 2021. Boundary layer structure characteristics under objective classification of persistent pollution weather types in the Beijing area[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 21(11): 8 863-8 882. |
| [39] | WANG T H, DU H D, ZHAO Z Z, et al, 2022. Impact of meteorological conditions and human activities on air quality during the COVID-19 lockdown in Northeast China[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10: 877268. DOI: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.877268. |
| [40] | WU K, ZHU S P, MAC KINNON M, et al, 2023. Unexpected deterioration of O3 pollution in the south coast air basin of California: The role of meteorology and emissions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 330: 121728. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121728. |
| [41] | YOO J W, PARK S Y, JO H Y, et al, 2024. Assessing the role of cold front passage and synoptic patterns on air pollution in the Korean Peninsula[J]. Environmental Pollution, 348: 123803. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123803. |
| [42] | YOO J W, PARK S Y, LEE K, et al, 2022. Impacts of plateau-induced lee troughs on regional PM2.5 over the Korean Peninsula[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 13(7): 101459. DOI: 10.1016/j.apr.2022.101459. |
| [43] | YOU T, WU R G, HUANG G, 2018. Differences in meteorological conditions between days with persistent and non-persistent pollution in Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 32(1): 81-98. |
| [44] | ZHANG H, YUAN H O, LIU X H, et al, 2018. Impact of synoptic weather patterns on 24 h-average PM2.5 concentrations in the North China plain during 2013-2017[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 627: 200-210. |
| [45] | ZHOU C, WEI G, ZHENG H, et al, 2019. Effects of potential recirculation on air quality in coastal cities in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 651: 12-23. |
| [1] | SHEN Jiaojiao, HAO Sujuan, JIN Lina, ZHANG Yabin, FAN Dandan, GUO Qi. Impact of urbanization on the climate environment in Xi’an over the past 60 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 403-412. |
| [2] | CHEN Min, CHEN Yuying, CHEN Rong, CHEN Yuxi, YANG Yuanyuan. Classification and meteorological element evolution of rainstorm in the eastern Helan Mountain foothills [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 413-423. |
| [3] | WANG Yajun, LUO Juying, CHENG Liehai, LI Wei. Construction and validation of summer drought prediction model in Hubei Province based on machine learning algorithms [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 661-670. |
| [4] | WANG Yuetong, HE Dongpo, LI Zhongyan, WANG Shuo, CHEN Zaoyang. Analysis of two meteorological drought events in Guizhou Province and establishment of drought prediction model based on machine learning [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 671-682. |
| [5] | SU Hongmei, ZHANG Nan, RAN Xinmin, KANG Chao. Machine learning flood early warning model for small and medium watersheds in arid and semi-arid regions and its application [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 683-693. |
| [6] | PAN Liujie, LIANG Mian, QI Chunjuan, LI Peirong, ZHU Qingliang. Characteristics of meteorological elements and objective forecast verification at the key venues of “the 14th National Games” [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 491-502. |
| [7] | CHEN Rong, WANG Jianying, YANG Wenjun, CHEN Min, WANG Qian, LI Kun. Influence factors of atmospheric boundary layer inversion in Yinchuan City and the relation with PM2.5 in winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 123-131. |
| [8] | FENG Liangmin, ZHOU Qiuxue, CAO Pingping, WANG Jiajin. Study of 2 m temperature variation correction during transitional processes of temperature in Sichuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 164-172. |
| [9] | PEI Kunning, WANG Yan, YAN Shiming, JIANG Yunsheng, GUO Wei. Influence of topography and weather situation on air pollution in Linfen City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 879-887. |
| [10] | XU Lina, LI Zhong, HU Yanan, GU Xinbo. Analysis on Meteorological Conditions About Frequent Air Pollution in Hohhot in Winter of 2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 112-118. |
| [11] | MA Minjin, SU Yumeng, DING Fan, YANG Yi, HUANG Wanlong, TAN Changrong. Similarities and Differences of Air Pollution Between Lanzhou and Its Satellite City and Meteorological Influence Factors [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 834-846. |
| [12] | QI Yajie, CHEN Min, ZHONG Jiqin, FAN Shuiyong, LIU Ruiting, GUO Chunwei. Effect Evaluation of Short-term Forecast of Surface Meteorological Elements by Using RMAPS-ST Coupled Urban Canopy Model in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 859-868. |
| [13] | WU Zhanping, BAI Hui, CHEN Zaoyang, WANG Yuetong, WU Zhehong. Analysis of Meteorological Conditions of Two Air Pollution Processes in Guiyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 827-835. |
| [14] | TAN Changrong1, GUO Xiaoning, CHEN Qi, LI Jinhai,YOU Sangjie, MA Xuelian, MA Yuancang, QI Caihong. Study on Surface Ozone Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors in Xining [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 31-39. |
| [15] | SHANG Ziwei, NING Guicai, WANG Jiexin, CHENG Yifan, WANG Shigong. Relationship Between Air Pollution Index and Visibility,Relative Humidity in Ten Representative Cities of China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 590-597. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||