Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 263-273.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0263
• Test and Correction of New Meteorological Data • Previous Articles Next Articles
Suitability assessment of CMA multi-source precipitation analysis products for short-term heavy rainfall monitoring in Shaanxi
LIU Juju1,2( ), ZHAO Qiang1(
), ZHAO Qiang1( ), JING Yu1, ZHANG Weiran1, DAI Changming1
), JING Yu1, ZHANG Weiran1, DAI Changming1
- 1. Shaanxi Meteorological Observatory, Xi'an 710014, China
2. Key Laboratory of Ecological and Environmental Meteorology of Qinling and Loess Plateau, Shaanxi Meteorological Bureau, Xi'an 710016, China
-
Received:2023-02-09Revised:2023-11-25Online:2024-04-30Published:2024-05-12
CMPAS融合产品在陕西短时强降水监测中的适用性评估
刘菊菊1,2( ), 赵强1(
), 赵强1( ), 井宇1, 张蔚然1, 戴昌明1
), 井宇1, 张蔚然1, 戴昌明1
- 1.陕西省气象台,陕西 西安 710014
2.陕西省气象局秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室,陕西 西安 710016
-
通讯作者:赵强(1981—),男,硕士,正高级工程师,主要从事天气预报研究。E-mail:zhaoq66@sina.com 。 -
作者简介:刘菊菊(1991—),女,硕士,工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报研究。E-mail: wwqxjljj@163.com。 -
基金资助:陕西省自然科学基础研究计划项目(2023-JC-QN-0367);中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2021Z009);秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室面上项目(2022G-15)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Juju, ZHAO Qiang, JING Yu, ZHANG Weiran, DAI Changming. Suitability assessment of CMA multi-source precipitation analysis products for short-term heavy rainfall monitoring in Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 263-273.
刘菊菊, 赵强, 井宇, 张蔚然, 戴昌明. CMPAS融合产品在陕西短时强降水监测中的适用性评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 263-273.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0263

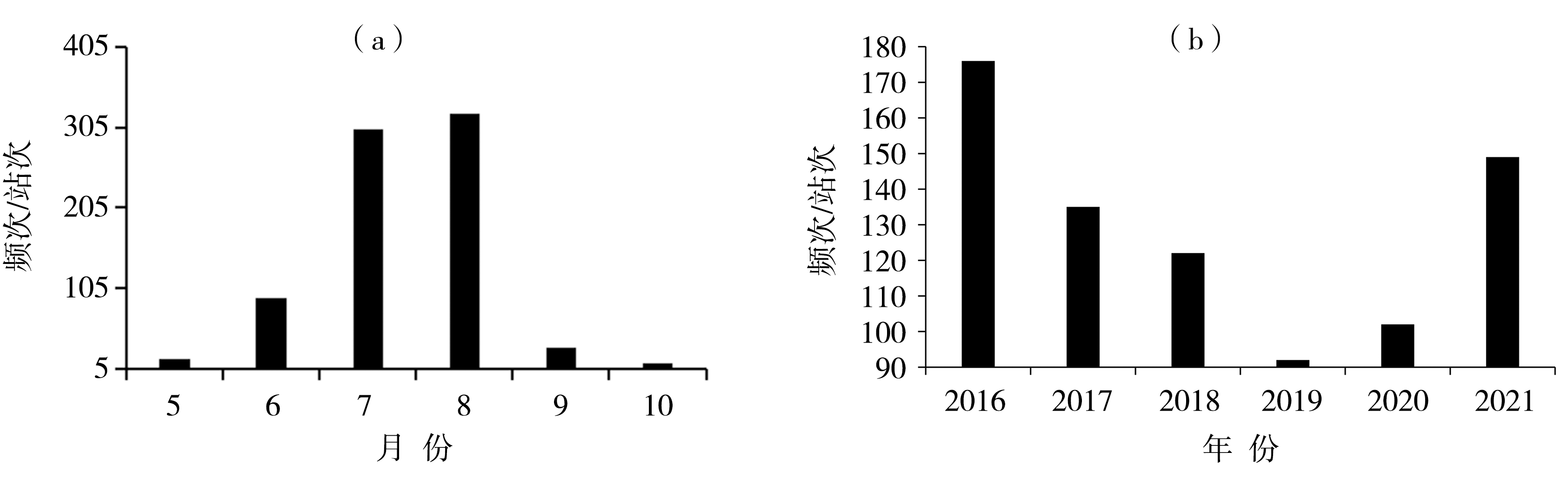
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of the frequency (a, Unit: times) and extreme value (b, Unit: mm) of short-time heavy rainfall in Shaanxi from 2016 to 2021

Fig.4 Mean absolute error distribution of two-source (a) and three-source (b) precipitation products during short-term heavy rainfall processes in Shaanxi from 2018 to 2021 (Unit: mm)

Fig. 5 The spatial distribution of mean error of two-source (a) and three-source (b) precipitation products (Unit: mm) and absolute value of two-source mean error minus absolute value of three-source mean error (c) during short-term heavy rainfall in Shaanxi from 2018 to 2021

Fig.6 Variation of two-source (a) and three-source (b) precipitation products mean absolute error with precipitation intensity and the mean absolute errors corresponding to the two types of products for different precipitation intervals (c) during short-term heavy rainfall processes in Shaanxi from 2018 to 2021
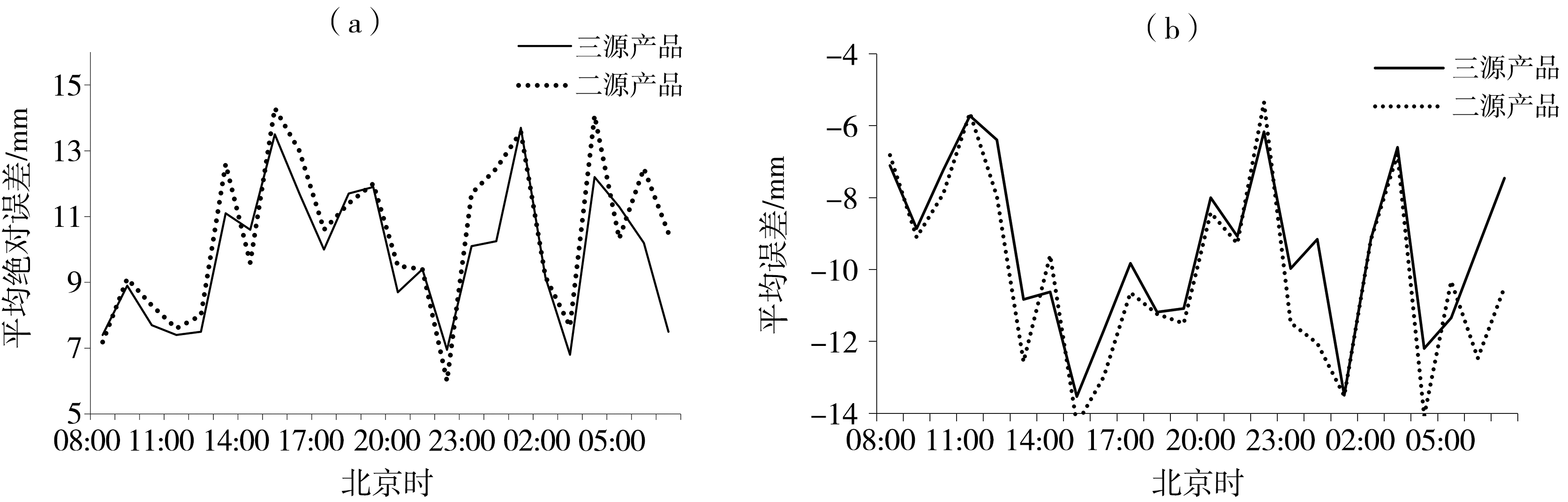
Fig.7 Diurnal variations of multi-source precipitation products mean absolute error (a) and mean error (b) during short-term heavy rainfall processes in Shaanxi from 2018 to 2021
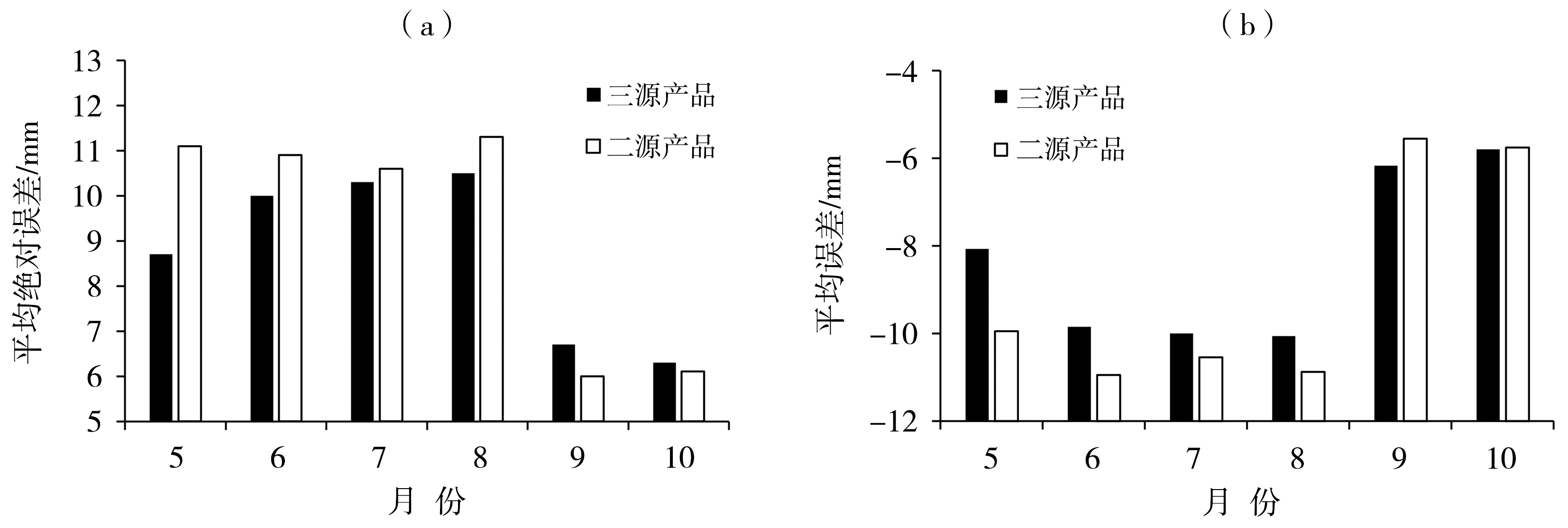
Fig.8 Monthly variations of multi-source precipitation products mean absolute error (a) and mean error (b) during short-time heavy rainfall processes in Shaanxi from 2018 to 2021
| 产品 | 降水阈 值/mm | 准确率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年平均 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 2021年 | ||
| 二源 | 20 | 35 | 18 | 26 | 42 | 50 |
| 15 | 60 | 37 | 62 | 68 | 72 | |
| 10 | 84 | 62 | 88 | 90 | 94 | |
| 三源 | 20 | 36 | 20 | 32 | 45 | 47 |
| 15 | 63 | 43 | 60 | 78 | 72 | |
| 10 | 86 | 74 | 80 | 93 | 94 | |
Tab.1 Average annual accuracy rate of multi-source precipitation products under different short-term heavy rainfall thresholds
| 产品 | 降水阈 值/mm | 准确率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年平均 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 2021年 | ||
| 二源 | 20 | 35 | 18 | 26 | 42 | 50 |
| 15 | 60 | 37 | 62 | 68 | 72 | |
| 10 | 84 | 62 | 88 | 90 | 94 | |
| 三源 | 20 | 36 | 20 | 32 | 45 | 47 |
| 15 | 63 | 43 | 60 | 78 | 72 | |
| 10 | 86 | 74 | 80 | 93 | 94 | |
| 产品 | 降水阈值/mm | 准确率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5月 | 6月 | 7月 | 8月 | 9月 | 10月 | ||
| 二源 | 20 | 33 | 26 | 29 | 38 | 56 | 50 |
| 15 | 44 | 53 | 56 | 61 | 78 | 90 | |
| 10 | 78 | 77 | 84 | 84 | 93 | 100 | |
| 三源 | 20 | 44 | 30 | 32 | 38 | 44 | 60 |
| 15 | 56 | 59 | 58 | 64 | 81 | 90 | |
| 10 | 78 | 82 | 83 | 88 | 89 | 100 | |
Tab.2 Monthly grade accuracy rate of multi-source precipitation products under different short-term heavy rainfall thresholds
| 产品 | 降水阈值/mm | 准确率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5月 | 6月 | 7月 | 8月 | 9月 | 10月 | ||
| 二源 | 20 | 33 | 26 | 29 | 38 | 56 | 50 |
| 15 | 44 | 53 | 56 | 61 | 78 | 90 | |
| 10 | 78 | 77 | 84 | 84 | 93 | 100 | |
| 三源 | 20 | 44 | 30 | 32 | 38 | 44 | 60 |
| 15 | 56 | 59 | 58 | 64 | 81 | 90 | |
| 10 | 78 | 82 | 83 | 88 | 89 | 100 | |
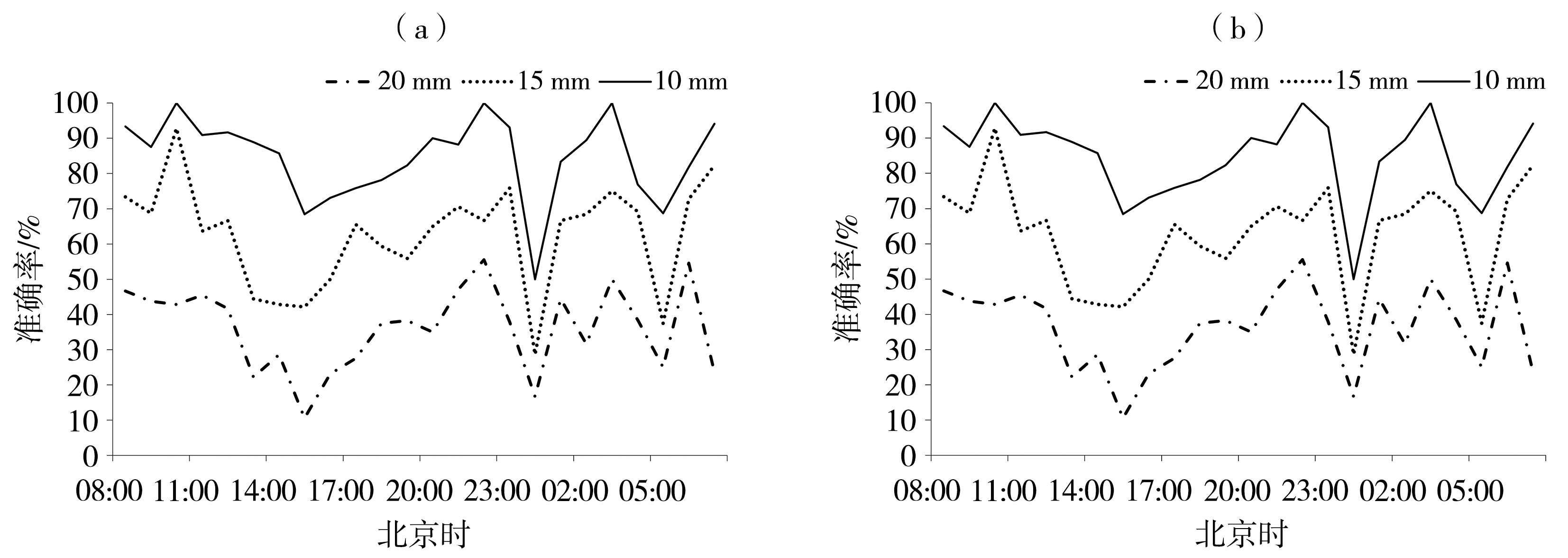
Fig.9 Diurnal variation of two-source (a) and three-source (b) precipitation products accuracy rate under different short-term heavy rainfall thresholds in Shaanxi from 2018 to 2021

Fig.11 Spatial distribution of two-source product (a, d, g), three-source product (b, e, h) and observed precipitation (c, f, i) in Shaanxi during three short-term heavy rainfall processes at 16:00 on August 21, 2018 (a, b, c), 00:00 on August 21, 2021 (d, e, f) and 12:00 on October 3, 2021 (g, h, i) (Unit: mm)

Fig.12 The topographic height of Guanzhong (a, Unit: m; the black dots indicate the stations where the error values of both types of multi-source precipitations are less than -5 during short-term heavy rainfall processes, the triangle indicates the location of the radar station in Xi'an) and the detection range diagram of 0.5° elevation of the C-band radar station in Xi'an combined with the topographic height map (b, the black indicates the part obscured by the terrain)
| [1] | 黄勤, 龙亚星, 李亚丽, 2021. 多源融合降水产品在陕西的适用性评估[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 38(4): 108-111. |
| [2] | 孔玉寿, 章东华, 2000. 现代天气预报技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [3] | 李超, 唐千红, 陈宇, 等, 2017. 多源数据融合系统LAPS的研究进展及其在实况数据服务中的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 7(2): 32-38. |
| [4] | 李显风, 周自江, 李志鹏, 等, 2017. 基于江西省水文资料对中国融合降水产品的质量评估[J]. 气象, 43(12): 1 534-1 546. |
| [5] | 李超, 李华宏, 杨素雨, 等, 2021. 国家级多源融合降水产品在云南的适用性评估[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 41(3): 108-114. |
| [6] | 刘菊菊, 陈小婷, 肖贻青, 等, 2022. 降水融合格点产品在陕西2019年暴雨过程中的检验[J]. 陕西气象(2): 1-9. |
| [7] | 刘晓阳, 杨洪平, 李建通, 等, 2010. 新一代天气雷达定量降水估测集成系统[J]. 气象, 36(4): 90-95. |
| [8] | 李萍云, 赵强, 王楠, 等, 2019. 2005—2018年陕西短时强降水时空分布特征[J]. 陕西气象, (5): 34-39. |
| [9] | 潘旸, 谷军霞, 徐宾, 等, 2018a. 多源降水数据融合研究及应用进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 8(1): 143-152. |
| [10] | 潘旸, 沈艳, 宇婧婧, 等, 2012. 基于最优插值方法分析的中国区域地面观测与卫星反演逐时降水融合试验[J]. 气象学报, 70(6): 1 381-1 389. |
| [11] | 潘旸, 谷军霞, 宇婧婧, 等, 2018b. 中国区域高分辨率多源降水观测产品的融合方法试验[J]. 气象学报, 76(5): 755-766. |
| [12] | 任芝花, 赵平, 张强, 等, 2010. 适用于全国自动站小时降水资料的质量控制方法[J]. 气象, 36(7): 123-132. |
| [13] | 宋雯雯, 龙柯吉, 黄晓龙, 等, 2022. 融合格点降水产品在四川盆地西部一次极端暴雨过程中的评估分析[J]. 中低纬山地气象, 46(3): 9-15. |
| [14] |
孙靖, 程光光, 黄小玉, 2021. 中国地面气象要素格点融合业务产品检验[J]. 高原气象, 40(1): 178-188.
DOI |
| [15] |
沈晓燕, 申燕玲, 权晨, 等, 2022. 不同方法对青海2020年强降水模式产品预报性能的检验对比[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 333-343.
DOI |
| [16] | 吴薇, 黄晓龙, 徐晓莉, 等, 2021. 融合降水实况分析产品在四川地区的适用性评估[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(4): 1-8. |
| [17] |
吴薇, 黄晓龙, 徐晓莉, 等, 2023. 四川省降水实况分析产品影响因素综合评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 143-151.
DOI |
| [18] | 许冠宇, 李琳琳, 田刚, 等, 2020. 国家级降水融合产品在长江流域的适用性评估[J]. 暴雨灾害, 39(4): 400-408. |
| [19] | 俞剑蔚, 李聪, 蔡凝昊, 等, 2019. 国家级格点实况分析产品在江苏地区的适用性评估分析[J]. 气象, 45(9): 1 288-1 298. |
| [20] | 宇婧婧, 沈艳, 潘旸, 等, 2013. 概率密度匹配法对中国区域卫星降水资料的改进[J]. 应用气象学报, 24(5): 544-553. |
| [21] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等, 2000. 天气学原理和方法: 第4版[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 341-342. |
| [22] | 赵强, 王建鹏, 王楠, 等, 2017. 2012年夏季秦巴山区暴雨过程的地形作用诊断[J]. 气象科技, 45(1): 139-147. |
| [23] | JACOBS C M J, MOORS E J, TER MAAT H W, et al, 2008. Evaluation of European Land Data Assimilation System (ELDAS) products using in situ observations[J]. Tellus Series A: Dynamic Meteorology & Oceanography, 60(5): 1 023-1 037. |
| [24] | JOYCE R J, JANOWIAK J E, ARKIN P A, et al, 2004. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 5(3): 487-503. |
| [1] | SUN Linhai, ZHU Xiaying, LI Xiang, AI Wanxiu, YANG Mingzhu. Assessment of monthly climate prediction in China from 1971 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 794-803. |
| [2] | JING Yu, CHEN Chuang, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Juju. Spatial-temporal distribution and meteorological conditions of thunderstorm gales in Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 576-587. |
| [3] | LONG Keji, YANG Kangquan, KANG Lan. Performance verification of multi-model heavy rainfall processes prediction in the Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 473-483. |
| [4] | LIU Wenying, SUN Suqin, ZHU Xingqiu, OUYANG Xinxin. Analysis and assessment of regional high temperature and drought processes in Jiangxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 187-196. |
| [5] | MA Zhimin, WANG Jiang, LIAN Yu, ZHANG Wancheng, NIU Fabao, YANG Suyu. Analysis on synoptic causes of a severe convective rainstorm in Yunnan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 629-638. |
| [6] | CAI Yiheng, LI Shuai, ZHANG Qiang, DENG Biao, LUO Yu, SUN Rui. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 241-250. |
| [7] | MA Lei, ZHAO Wei, YANG Liu, WANG Jianying, YONG Jia, HAN Lulu. Assessment of climate resource suitability to “starry sky tourism” in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 309-317. |
| [8] | ZHANG Hongfang, ZHANG Xi, LIANG Jia, GUO Qi, WANG Jingzhong. Characteristics and influence factors of low visibility along Shaanxi section of the Lian-Huo expressway [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 82-90. |
| [9] | WU Wei, HUANG Xiaolong, XU Xiaoli, LI Shiying, DU Bing, JIANG Yuhe. Comprehensive assessment of influencing factors of precipitation real-time analysis products in Sichuan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 143-151. |
| [10] | YANG Lijie, CAO Yanchao, LIU Weicheng, XU Lili, ZHANG Hongfen, SUN Zizhu. Research on spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of short-term heavy rainfall and terrain influence in the Loess Plateau arid region of eastern Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 945-953. |
| [11] | CHEN Xiaoting, ZHAO Qiang, LIU Hui, PENG Li. Analysis of water vapor characteristics of two different types of rainstorms over the Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 968-980. |
| [12] | LAN Mingcai, ZHOU Li, JIANG Shuai, YIN Yiwen, XU Lin. Causes of a short-term heavy rainfall under the control of the western Pacific subtropical high in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 656-666. |
| [13] | LE Zhangyan, SHI Minghua, LI De, HUO Zhiguo, DU Zixuan, TAN Yanjing. Risk assessment of low temperature disaster in winter for facility agriculture in Henan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 667-676. |
| [14] | PENG Shuangzi, LIU Xinmiao, CHEN Tao, YANG Min, XU Di, KUANG Yufei, XIAO Meiying. Discussion on drought monitoring and evaluation technology in the Heng-Shao drought corridor [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 894-899. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xiaopei, FAN Zhichao. Research on Safety Risk Assessment Method of Ground Weather Modification Operation Based on SCA-LEC Model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 1037-1042. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||