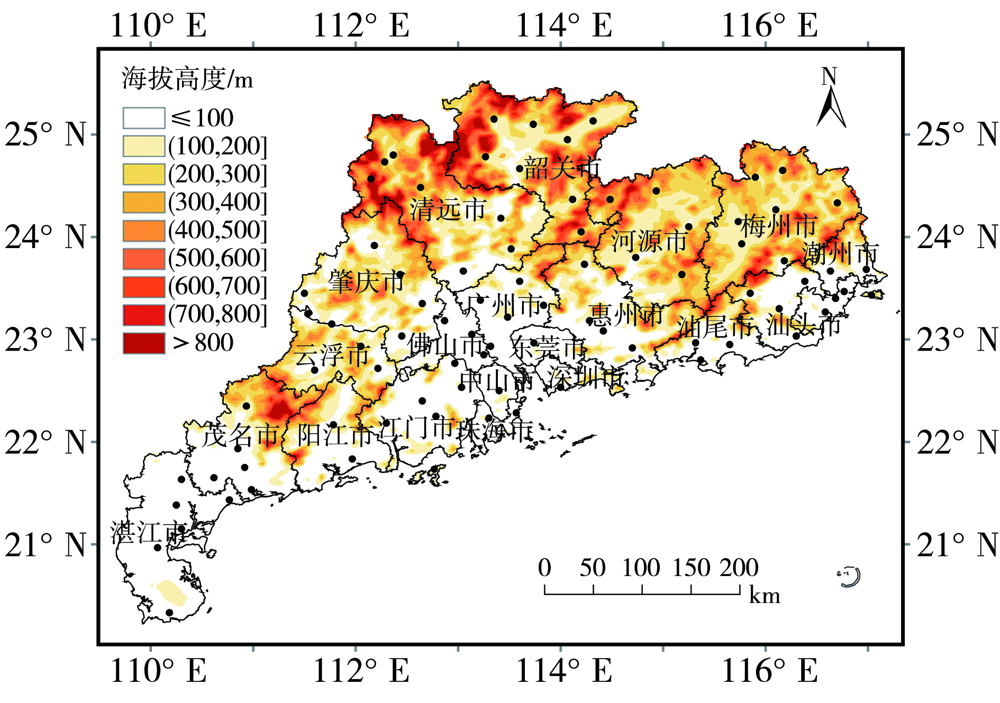
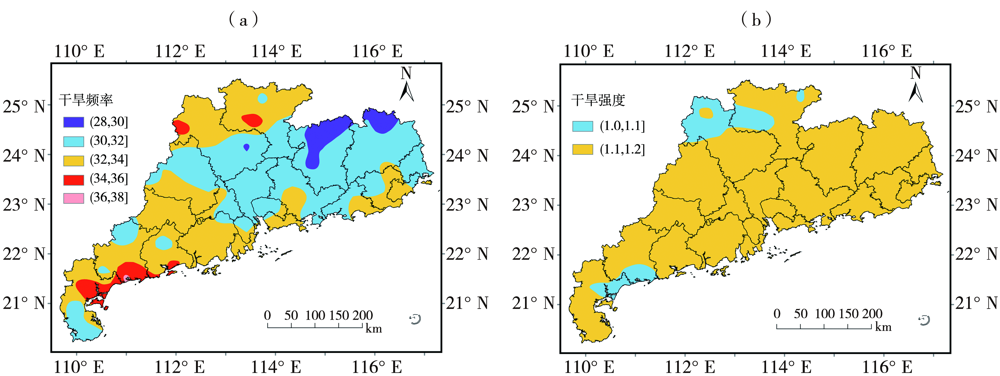
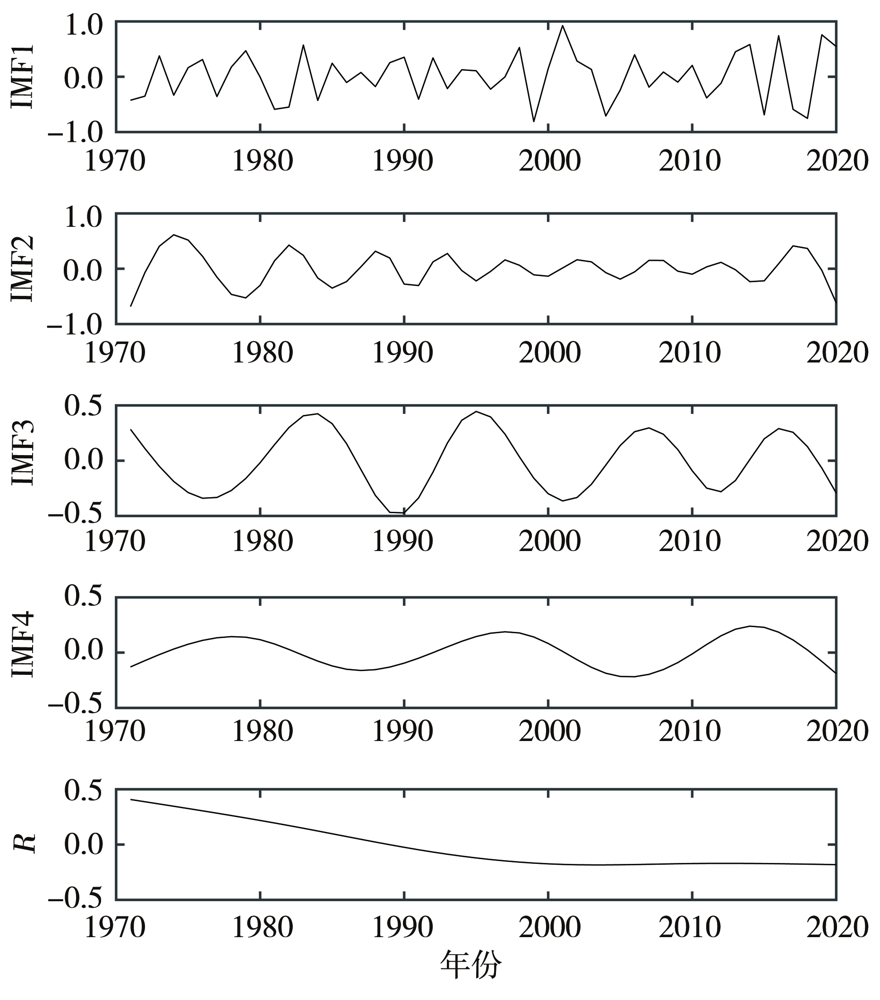
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 1051-1058.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-1051
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatial-temporal characteristics of drought in recent 50 years in Guangdong Province based on SPEI
YU Xingzhan1( ), PU Yiliang2, KANG Boqian3
), PU Yiliang2, KANG Boqian3
- 1. Taishan Meteorological Bureau of Guangdong Province, Taishan 529200, Guangdong, China
2. Jiangmen Meteorological Bureau of Guangdong Province, Jiangmen 529000, Guangdong, China
3. Heshan Meteorological Bureau of Guangdong Province, Heshan 529700, Guangdong, China
-
Received:2022-01-21Revised:2022-04-28Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-10
基于SPEI的广东省近50 a干旱时空特征
- 1.广东省台山市气象局,广东 台山 529200
2.广东省江门市气象局,广东 江门 529000
3.广东省鹤山市气象局,广东 鹤山 529700
-
作者简介:余兴湛(1991—),男,工程师,主要从事天气预报及气象服务.E-mail:526996271@qq.com。 -
基金资助:广东省江门市气象局科技项目(202105)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Xingzhan, PU Yiliang, KANG Boqian. Spatial-temporal characteristics of drought in recent 50 years in Guangdong Province based on SPEI[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 1051-1058.
余兴湛, 蒲义良, 康伯乾. 基于SPEI的广东省近50 a干旱时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1051-1058.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-06-1051
| SPEI | 干旱等级 |
|---|---|
| -1.0 | 轻旱 |
| -1.5 | 中旱 |
| -2.0 | 重旱 |
| SPEI≤-2.0 | 特旱 |
Tab.1 Drought grades classification based on SPEI
| SPEI | 干旱等级 |
|---|---|
| -1.0 | 轻旱 |
| -1.5 | 中旱 |
| -2.0 | 重旱 |
| SPEI≤-2.0 | 特旱 |
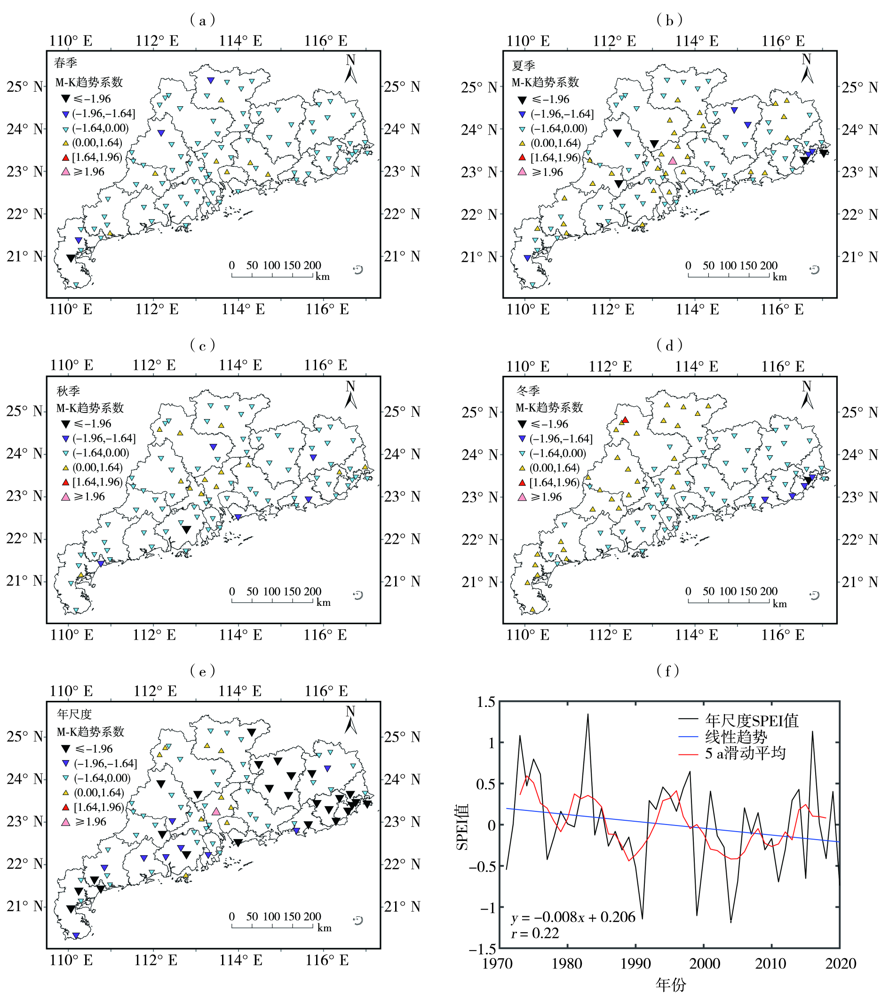
Fig.2 Mann-Kendall trend coefficients of SPEI at different time scales (a, b, c, d, e) and inter-annual variation of annual scale SPEI (f) in Guangdong Province during 1971-2020
| 模态 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% |
|---|---|---|
| EOF1 | 51.62 | 51.62 |
| EOF2 | 11.49 | 63.11 |
| EOF3 | 6.40 | 69.51 |
| EOF4 | 4.36 | 73.87 |
| EOF5 | 2.50 | 76.37 |
Tab.2 Contribution rates of the first five modes of EOF decomposition of annual scale SPEI in Guangdong Province during 1971-2020
| 模态 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% |
|---|---|---|
| EOF1 | 51.62 | 51.62 |
| EOF2 | 11.49 | 63.11 |
| EOF3 | 6.40 | 69.51 |
| EOF4 | 4.36 | 73.87 |
| EOF5 | 2.50 | 76.37 |
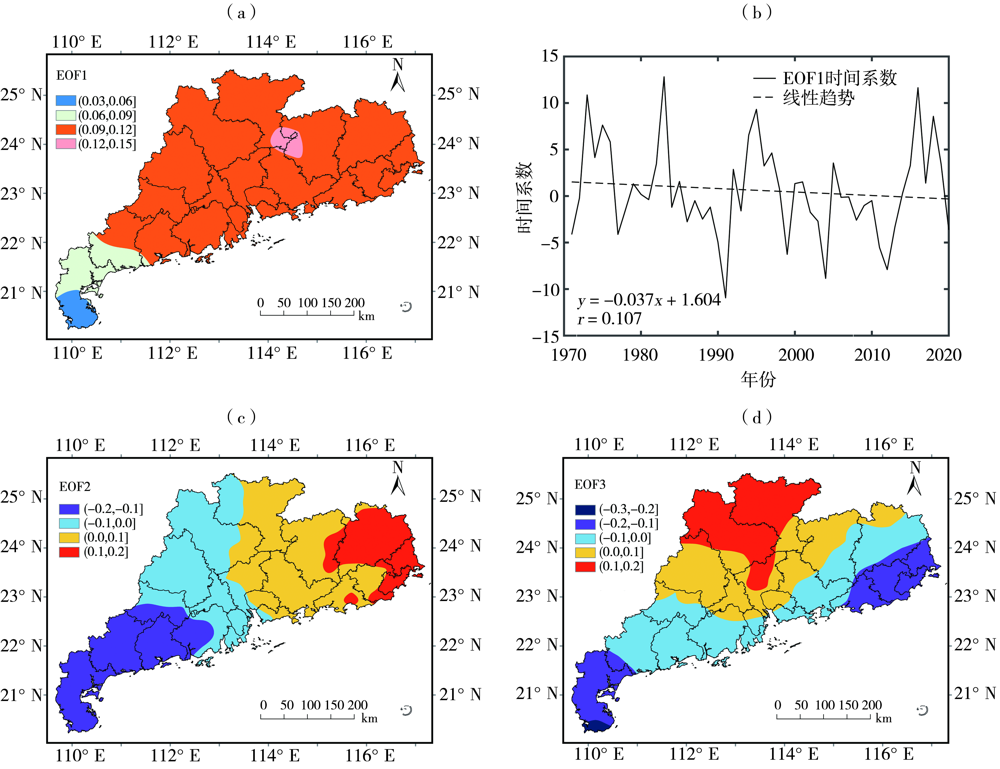
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of the first three modes (a, c, d) and the time coefficient of the first mode (b) of EOF decomposition of annual scale SPEI in Guangdong Province during 1971-2020
| 时间系数 | 厄尔尼诺强度指标 | 西太平洋副热带高压指标 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niño 1+2区 | Niño 3区 | Niño 4区 | Niño 3.4区 | 面积 | 强度 | 脊线位置 | 西伸 脊点 | |
| PC1 | 0.33** | 0.24** | 0.02 | 0.18** | 0.05 | 0.06 | -0.04 | -0.04 |
| PC2 | 0.09* | 0.03 | -0.03 | -0.01 | 0.13** | 0.12** | 0.04 | 0.11** |
Tab.3 The correlation between time coefficients of EOF1, EOF2 and El Ni?o strength indexes, western Pacific subtropical high (WPSH) indexes
| 时间系数 | 厄尔尼诺强度指标 | 西太平洋副热带高压指标 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niño 1+2区 | Niño 3区 | Niño 4区 | Niño 3.4区 | 面积 | 强度 | 脊线位置 | 西伸 脊点 | |
| PC1 | 0.33** | 0.24** | 0.02 | 0.18** | 0.05 | 0.06 | -0.04 | -0.04 |
| PC2 | 0.09* | 0.03 | -0.03 | -0.01 | 0.13** | 0.12** | 0.04 | 0.11** |
| 模态分量 | 周期/a | 方差贡献率/% |
|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 3.1 | 47.33 |
| IMF2 | 7.1 | 20.04 |
| IMF3 | 12.5 | 18.07 |
| IMF4 | 16.7 | 4.61 |
| 趋势余量R | 无 | 9.95 |
Tab.4 The period and variance contribution rate of each modal component of ESMD decomposition of annual scale SPEI in Guangdong Province during 1971-2020
| 模态分量 | 周期/a | 方差贡献率/% |
|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 3.1 | 47.33 |
| IMF2 | 7.1 | 20.04 |
| IMF3 | 12.5 | 18.07 |
| IMF4 | 16.7 | 4.61 |
| 趋势余量R | 无 | 9.95 |
| [1] |
LOBELL D B, ROBERTS M J, SCHLENKER W S, et al. Greater sensitivity to drought accompanies maize yield increase in the U. S. Midwest[J]. Science, 2014, 344(6183): 516-519.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HALLEGATTE S, GREEN C, NICHOLLS R J, et al. Future flood losses in major coastal cities[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2013, 3(9): 802-806.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 王劲松, 李耀辉, 王润元, 等. 我国气象干旱研究进展评述[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(4): 497-508. |
| [4] | 顾颖, 刘静楠, 林锦. 近60年来我国干旱灾害特点和情势分析[J]. 水利水电技术, 2010, 41(1): 71-74. |
| [5] | 刘晓云, 李栋梁, 王劲松. 1961—2009年中国区域干旱状况的时空变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(2): 473-483. |
| [6] |
TSAKIRIS G, PANGALOU D, VANGELIS H. Regional drought assessment based on the reconnaissance drought index (RDI)[J]. Water Resources Management, 2007, 21(5): 821-833.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 王劲松, 郭江勇, 倾继祖. 一种K干旱指数在西北地区春旱分析中的应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 2007, 22(5): 709-717. |
| [8] | 王劲松, 郭江勇, 周跃武, 等. 干旱指标研究的进展与展望[J]. 干旱区地理, 2007, 30(1): 60-65. |
| [9] | 张强, 张良, 崔显成, 等. 干旱监测与评价技术的发展及其科学挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(7): 763-778. |
| [10] | 刘业伟, 张秀平, 谢国栋, 等. 基于标准化降水指数与Z指数的萍乡市干旱特征分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2020, 38(6): 8-12. |
| [11] |
程航, 孙国武, 冯呈呈, 等. 亚非地区近百年干旱时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(2): 196-202.
DOI |
| [12] | 高睿娜, 王素艳, 高娜, 等. CI和MCI干旱指数在宁夏的适应性对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 185-192. |
| [13] |
李忆平, 李耀辉. 气象干旱指数在中国的适应性研究进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(5): 709-723.
DOI |
| [14] |
VICENTE-SERRANO S M, BEGUERÍA S, LÓPEZ-MORENO J I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index[J]. Journal of Climate, 2010, 23(7): 1696-1718.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 韦潇宇, 胡琦, 马雪晴, 等. 基于SPEI的华北平原夏玉米生长季干旱时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(4): 554-560+577. |
| [16] | 周惜荫, 李谢辉. 1978—2017年西南地区干湿时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 357-365. |
| [17] |
郁凌华, 谢五三, 熊世为, 等. 基于SPEI的安徽滁州市旱涝特征及其对小麦产量的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 742-749.
DOI |
| [18] |
WANG F, WANG Z, YANG H, et al. Study of the temporal and spatial patterns of drought in the Yellow River basin based on SPEI[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2018, 61(8): 1098-1111.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 陈燕丽, 蒙良莉, 黄肖寒, 等. 基于SPEI的广西喀斯特地区1971—2017年干旱时空演变[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3): 353-362. |
| [20] | 刘占明, 陈子燊, 黄强, 等. 7种干旱评估指标在广东北江流域应用中的对比分析[J]. 资源科学, 2013, 35(5): 1007-1015. |
| [21] | 李伟光, 侯美亭, 陈汇林, 等. 基于标准化降水蒸散指数的华南干旱趋势研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2012, 21(4): 84-90. |
| [22] | 温克刚, 宋丽莉. 中国气象灾害大典:广东卷[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2006: 204-250. |
| [23] | 林良勋, 冯业荣, 黄忠, 等. 广东省天气预报技术手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2006: 86-93. |
| [24] | 王春林, 邹菊香, 麦北坚, 等. 近50年华南气象干旱时空特征及其变化趋势[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(3): 595-602. |
| [25] | 麦雪湖, 梁华玲, 麦文强, 等. 基于DI指数的佛山市气象干旱变化趋势分析[J]. 中低纬山地气象, 2019, 43(3): 75-77. |
| [26] |
王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等. 几种干旱指标对西南和华南区域月尺度干旱监测的适用性评价[J]. 高原气象, 2015, 34(6): 1616-1624.
DOI |
| [27] |
TRAJKOVIC S. Temperature-based approaches for estimating reference evapotranspiration[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2005, 131(4): 316-323.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局、 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 气象干旱等级: GB/T20481—2017[S]. 2017. http://www.doc88.com/p-9062564148848.html. |
| [29] | 李翔宇, 李曌, 包艳英, 等. 基于反距离加权插值法评价海域水质类别空间分布[J]. 中国环境监测, 2019, 35(6): 70-77. |
| [30] |
史本林, 朱新玉, 胡云川, 等. 基于SPEI指数的近53年河南省干旱时空变化特征[J]. 地理研究, 2015, 34(8): 1547-1558.
DOI |
| [31] | 黄晚华, 杨晓光, 李茂松, 等. 基于标准化降水指数的中国南方季节性干旱近58 a演变特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(7): 50-59. |
| [32] | 魏凤英. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007: 41-65. |
| [33] |
MONAHAN A H, FYFE J C, AMBAUM M H P, et al. Empirical orthogonal functions: the medium is the message[J]. Journal of Climate, 2009, 22(24): 6501-6514.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
NORTH G R, BELL T L, CAHALAN R F, et al. Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1982, 110(7): 699-706.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 朱静思, 张治倩, 陈宏, 等. 基于EOF和REOF方法的海河流域近61 a夏季降水时空演变规律分析[J]. 海河水利, 2017(6): 1-6+67. |
| [36] | 王金良, 李宗军. 极点对称模态分解方法:数据分析与科学探索的新途径[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015:43-87. |
| [37] | 王勇, 于腾丽, 刘严萍, 等. 基于FFT与小波变换的SOI与GNSS ZTD的周期变化影响研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2021, 41(3): 254-261. |
| [1] | HAO Lisheng, HE Liye, MA Ning, HAO Yuqian. Relationship between interannual variability of El Niño events and summer droughts in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 829-840. |
| [2] | DENG Xingchen, YU Tong, SHEN Jiayi , ZHAO Xin, WANG Lin, ZHENG Fei. Impact of the 2023/2024 El Niño event on drought in the Panama Canal region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 841-848. |
| [3] | LUO Xiaoling, YANG Mei, ZHAO Huihua, LI Yanying, JIANG Jufang, FU Fenqi. Influence analysis of El Niño event on temperature, precipitation and meteorological drought in Wuwei, Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 849-859. |
| [4] | MA Siyuan, JIN Yan, ZHANG Si, WANG Chuqin, MA Zhimin. Different impacts of El Niño/Southern Oscillation events on autumn meteorological drought in Yunnan Province#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 860-872. |
| [5] | HE Huigen, ZHANG Chi, WU Yao, LI Yonghua, YANG Qin, MU Yujiao. Characteristics of high temperature and drought during summer in Chongqing and its response to La Niña event [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 873-883. |
| [6] | WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [7] |
XU Dan, LONG Li, ZHANG Donghai, REN Manlin, CHEN Juan.
Drought and disaster variation characteristics in Guizhou based on Meteorological Drought Composite Index
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 897-909.
|
| [8] |
XIE Ao, LUO Boliang DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia.
Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922.
|
| [9] | ZHU Li, LYU Xiaoyu, GUO Hao, MENG Xiangchen, TIAN Yunfei. Suitability study of ERA5-Land precipitation product for drought monitoring in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 677-687. |
| [10] | ZHAO Huizhen, HE Tao, GUO Ruixia, WANG Chengfu, ZHANG Yanrong, LI Qi. Meteorological drought variation characteristics in the Gannan Plateau based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 688-696. |
| [11] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [12] | YANG Yang, ZHAO Weiming, HU Yingbing, SHENG Dong, WEI Yongqiang, SHEN Zhigao, TAN Jun. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of drought in the “Heng-Shao-Lou drought corridor” [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 550-559. |
| [13] | ZHAO Hong, CAI Dihua, WANG Heling, YANG Yang, WANG Runyuan, ZHANG Kai, QI Yue, ZHAO Funian, CHEN Fei, YUE Ping, WANG Xing, YAO Yubi, LEI Jun, WEI Xingxing. Progress and prospect on impact of drought disaster on food security and its countermeasures [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 187-206. |
| [14] | JIANG Peng, QIN Meiou, CAI Fu, WEN Rihong, MENG Ying, YANG Feiyun, SUN Pei, FENG Ailin, FANG Yuan. Impacts of drought-rewetting on spring maize's physiological parameters and yield in the northeast China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 207-214. |
| [15] | QI Yue, ZHANG Qiang, HU Shujuan, WANG Runyuan, YANG Yang, LEI Jun, WANG Heling, ZHAO Hong, CHU Chao, JIN Rong. Response of photosynthetic parameters to leaf temperature of spring maize under drought stress [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 215-222. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||