Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 11-20.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0011
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics of summer compound dry hot events in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and their impact on runoff
YANG Bocheng1( ), LI Weiguo1, LIU Xiaoyun2(
), LI Weiguo1, LIU Xiaoyun2( ), DONG Shenghu3, GUI Qiang1, GAN Zeliang1, ZHENG Qiong4
), DONG Shenghu3, GUI Qiang1, GAN Zeliang1, ZHENG Qiong4
- 1. Baiying Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province,Baiying 730090,Gansu,China
2. Lanzhou Institute of Arid Meteorology,CMA,Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province,Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Reducing Disaster,CMA,Lanzhou 730020,China
3. Bureau of Upper Reach Hydrology and Water Resource,YRCC,Lanzhou 730030,China
4. Huining County Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province,Huining 730700,Gansu,China
-
Received:2024-09-05Revised:2024-10-30Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-14
黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件变化特征及其对径流的影响
杨博成1( ), 李维国1, 刘晓云2(
), 李维国1, 刘晓云2( ), 董胜虎3, 贵强1, 甘泽良1, 郑琼4
), 董胜虎3, 贵强1, 甘泽良1, 郑琼4
- 1.甘肃省白银市气象局,甘肃 白银 730090
2.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
3.黄河水利委员会上游水文水资源局,甘肃 兰州 730030
4.甘肃省会宁县气象局,甘肃 会宁 730700
-
通讯作者:刘晓云(1980—),女,陕西宝鸡人,高级工程师,主要从事气候变化研究工作。E-mail:jqliuxy@126.com。 -
作者简介:杨博成(2000—),男,甘肃定西人,主要从事天气气候业务及科研工作。E-mail:Ybc000904@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42375039);国家自然科学基金项目(42230611);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究项目(2019QZKK0105);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(23JRRA1324);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(24JRRA725);中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2022J049)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Bocheng, LI Weiguo, LIU Xiaoyun, DONG Shenghu, GUI Qiang, GAN Zeliang, ZHENG Qiong. Characteristics of summer compound dry hot events in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and their impact on runoff[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 11-20.
杨博成, 李维国, 刘晓云, 董胜虎, 贵强, 甘泽良, 郑琼. 黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件变化特征及其对径流的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 11-20.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0011

Fig.2 The spatial distribution of summer high temperature days (a,Unit: d) and precipitation (b,Unit: mm) in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River averaged from 1961 to 2022
| 模态 | 高温日数 | 降水量 |
|---|---|---|
| EOF1 | 77.18 | 26.73 |
| EOF2 | 5.97 | 9.78 |
| EOF3 | 3.65 | 6.72 |
| EOF4 | 3.09 | 6.18 |
| EOF5 | 1.73 | 5.72 |
| EOF6 | 1.24 | 5.12 |
| EOF7 | 1.13 | 4.81 |
| EOF8 | 0.91 | 4.05 |
| EOF9 | 0.76 | 3.71 |
| EOF10 | 0.67 | 3.37 |
Tab.1
| 模态 | 高温日数 | 降水量 |
|---|---|---|
| EOF1 | 77.18 | 26.73 |
| EOF2 | 5.97 | 9.78 |
| EOF3 | 3.65 | 6.72 |
| EOF4 | 3.09 | 6.18 |
| EOF5 | 1.73 | 5.72 |
| EOF6 | 1.24 | 5.12 |
| EOF7 | 1.13 | 4.81 |
| EOF8 | 0.91 | 4.05 |
| EOF9 | 0.76 | 3.71 |
| EOF10 | 0.67 | 3.37 |
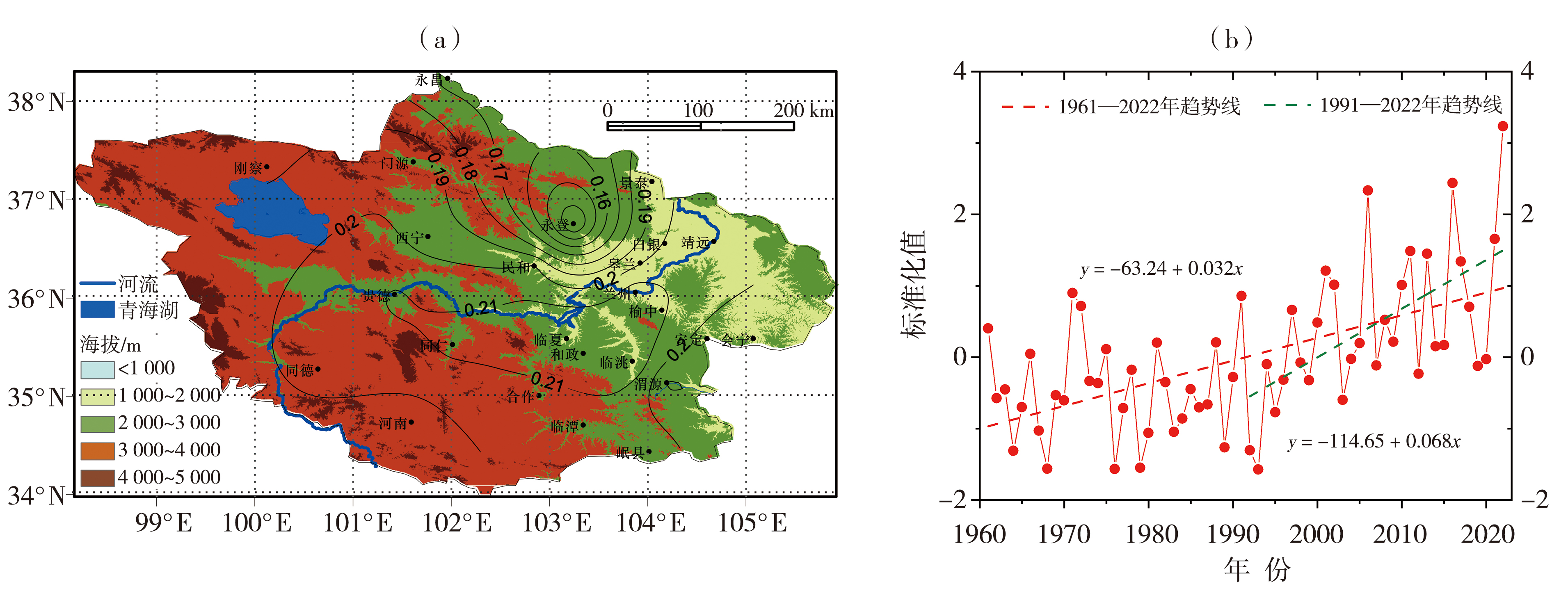
Fig.3 The first model spatial distribution (a) and time coefficient (b) of EOF decomposition of high temperature days in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River in summer from 1961 to 2022
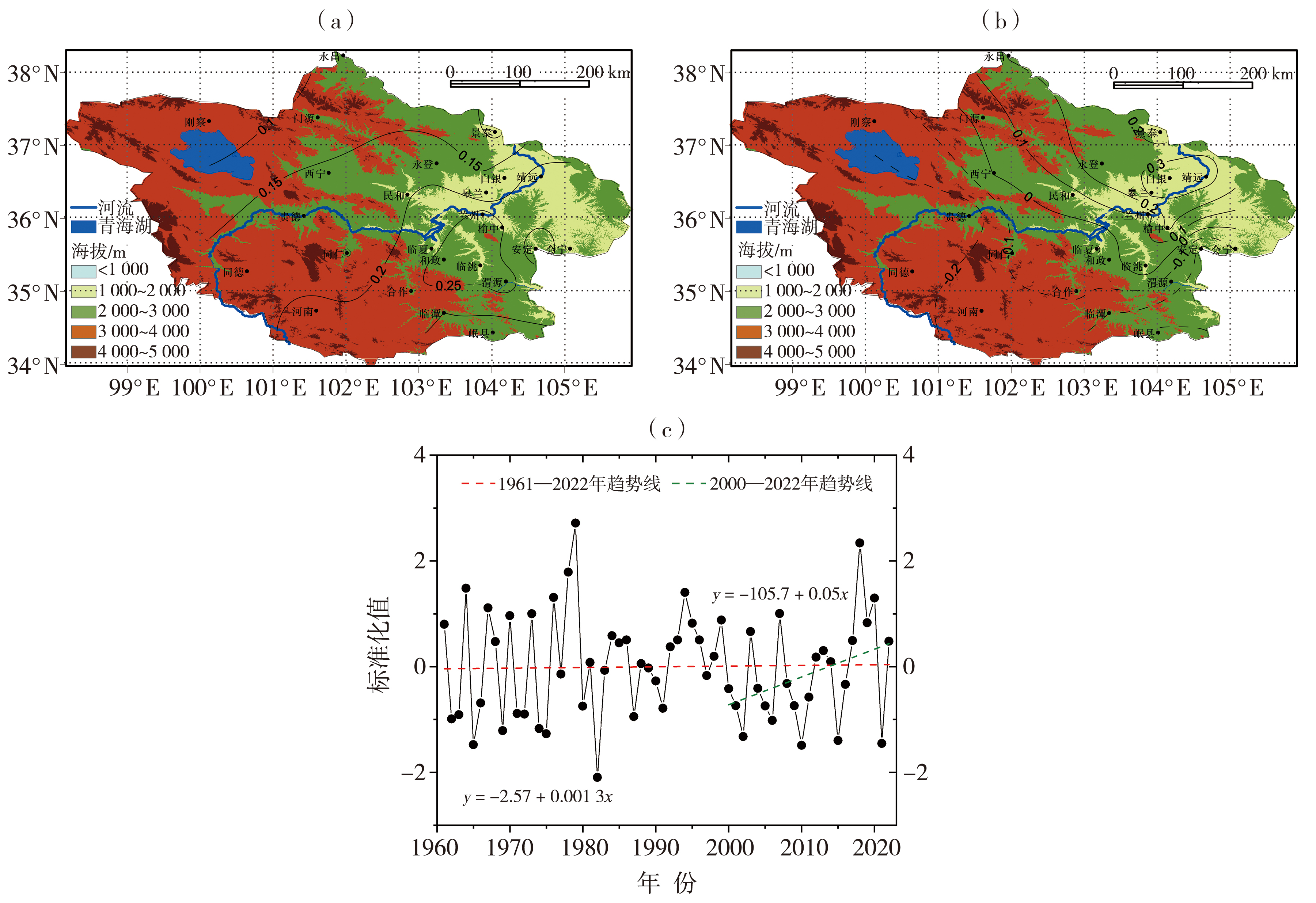
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of the first mode (a),the second mode (b),and the time coefficient of the first mode (c) of EOF decomposition of precipitation in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River in summer from 1961 to 2022
| 排位 | 年份 | 复合干热指数 | 高温日数PC1标准化值 | 降水量PC1标准化值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 顺序1 | 2021 | 8.59 | 1.66 | -1.45 |
| 顺序2 | 2006 | 5.18 | 2.33 | -1.02 |
| 顺序3 | 2010 | 4.72 | 1.01 | -1.49 |
| 顺序4 | 2002 | 4.56 | 1.02 | -1.32 |
| 顺序5 | 1971 | 3.16 | 0.90 | -0.89 |
| 逆序5 | 1995 | -2.47 | -0.78 | 0.82 |
| 逆序4 | 1967 | -4.36 | -1.03 | 1.11 |
| 逆序3 | 1964 | -7.07 | -1.31 | 1.49 |
| 逆序2 | 1976 | -7.10 | -1.57 | 1.31 |
| 逆序1 | 1979 | -9.16 | -1.55 | 2.71 |
Tab.2 The high temperature days and precipitation standardized values of the top 5 corresponding years in the order and reverse order of summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 排位 | 年份 | 复合干热指数 | 高温日数PC1标准化值 | 降水量PC1标准化值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 顺序1 | 2021 | 8.59 | 1.66 | -1.45 |
| 顺序2 | 2006 | 5.18 | 2.33 | -1.02 |
| 顺序3 | 2010 | 4.72 | 1.01 | -1.49 |
| 顺序4 | 2002 | 4.56 | 1.02 | -1.32 |
| 顺序5 | 1971 | 3.16 | 0.90 | -0.89 |
| 逆序5 | 1995 | -2.47 | -0.78 | 0.82 |
| 逆序4 | 1967 | -4.36 | -1.03 | 1.11 |
| 逆序3 | 1964 | -7.07 | -1.31 | 1.49 |
| 逆序2 | 1976 | -7.10 | -1.57 | 1.31 |
| 逆序1 | 1979 | -9.16 | -1.55 | 2.71 |
| 分量 | 贡献率C/% | 周期T/a | 与原序列相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 53.17 | 3.3 | 0.59*** |
| IMF2 | 11.71 | 8.2 | 0.568*** |
| IMF3 | 7.47 | 17.7 | 0.340** |
| IMF4 | 1.22 | 20.7 | 0.212 |
| 趋势项 | 26.43 | 0.395** |
Tab.3 Contribution rates of different time scale components of sumer compound dry-hot index based on EEMD decomposition in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 分量 | 贡献率C/% | 周期T/a | 与原序列相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 53.17 | 3.3 | 0.59*** |
| IMF2 | 11.71 | 8.2 | 0.568*** |
| IMF3 | 7.47 | 17.7 | 0.340** |
| IMF4 | 1.22 | 20.7 | 0.212 |
| 趋势项 | 26.43 | 0.395** |
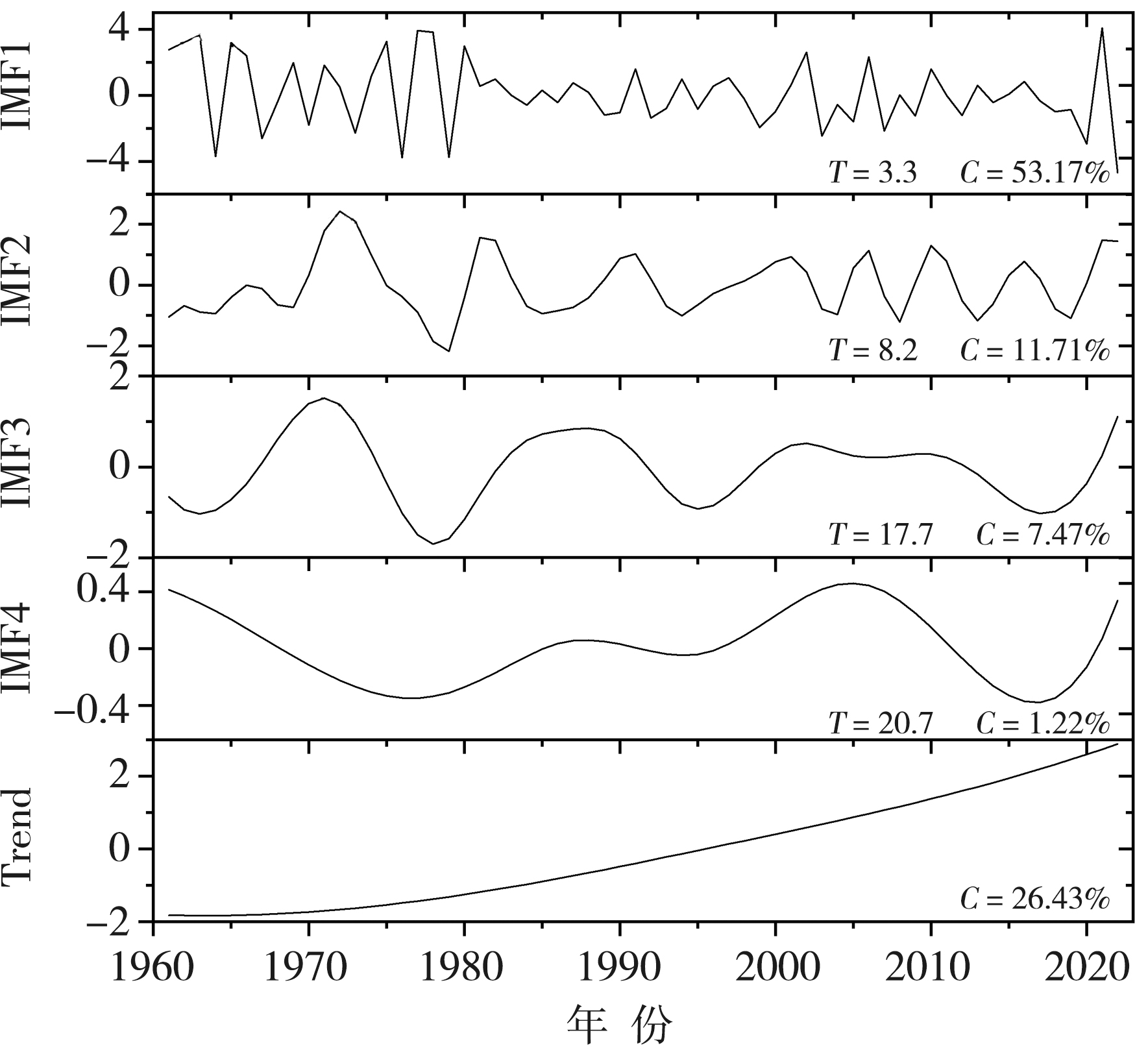
Fig.6 The variation of different time scales components of summer compound dry-hot index based on EEMD decomposition in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 项目 | 时间尺度 | 西风指数 | 东亚夏季风指数 | 南亚夏季风指数 | 高原夏季风指数 | 北风指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEMD分解前 | -0.09 | 0.01 | -0.24* | 0.06 | 0.05 | |
| EEMD分解后 | 年际 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| 年代际 | 0.19 | -0.09 | 0.03 | 0.65*** | 0.09 | |
| 多年代际 | -0.52*** | -0.49*** | -0.88*** | -0.28* | 0.51*** |
Tab.4 Correlation coefficients between summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and circulation indices before and after EEMD decomposition
| 项目 | 时间尺度 | 西风指数 | 东亚夏季风指数 | 南亚夏季风指数 | 高原夏季风指数 | 北风指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEMD分解前 | -0.09 | 0.01 | -0.24* | 0.06 | 0.05 | |
| EEMD分解后 | 年际 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| 年代际 | 0.19 | -0.09 | 0.03 | 0.65*** | 0.09 | |
| 多年代际 | -0.52*** | -0.49*** | -0.88*** | -0.28* | 0.51*** |

Fig.7 The summer climate state of 500 hPa geopotential height field (a),and 500 hPa geopotential height field (b) and its anomaly field (c) in compound dry-hot years (Unit: dagpm) (The black dotted areas passed the significant test at 0.05,the red closed area is the research area,the same as below)
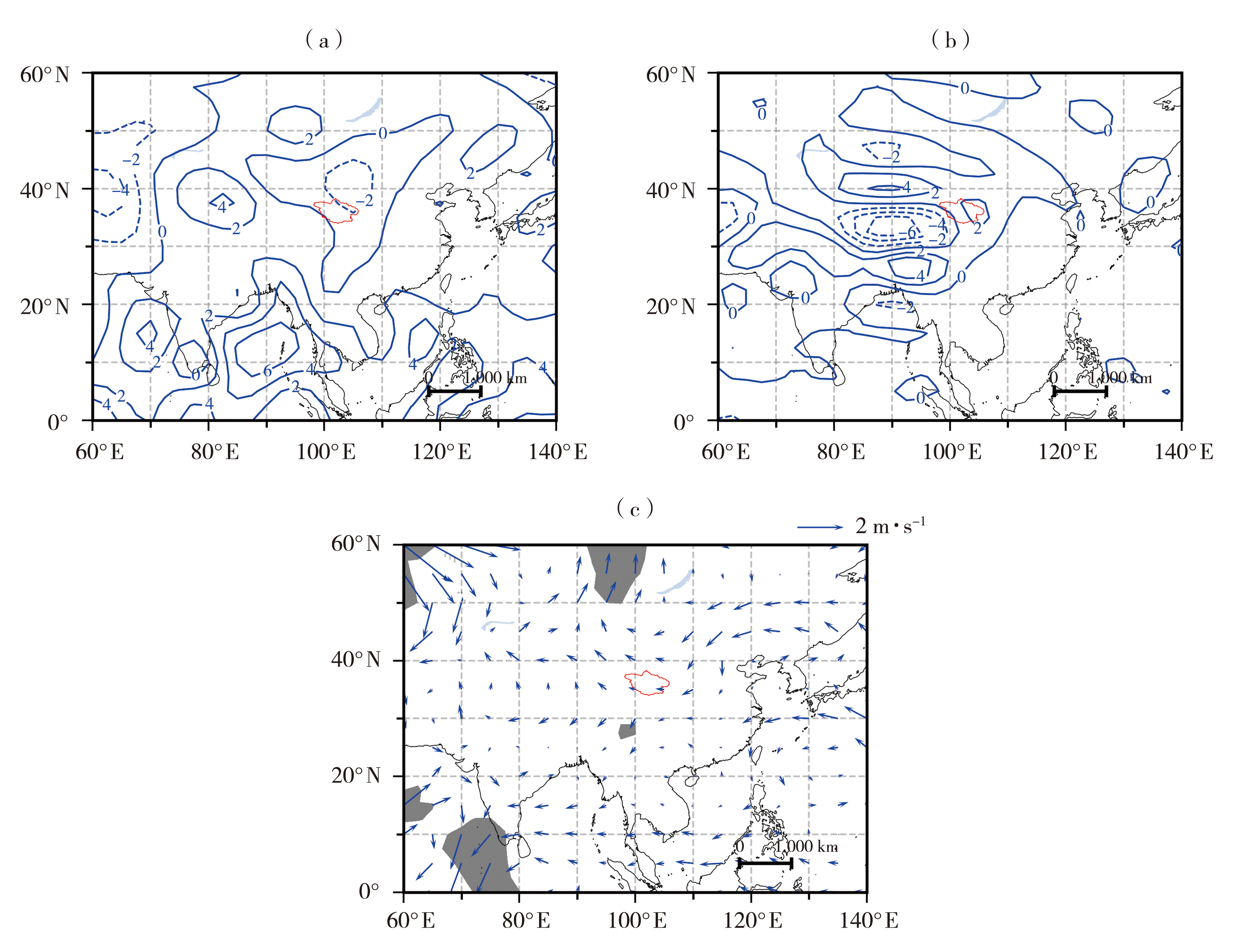
Fig.8 The 200 hPa (a),600 hPa (b) divergence fields (Unit: 10-6s) and 600 hPa anomalous wind fields (c,Unit: m·s-1) in summer compound dry-hot years (The gray shaded areas passed the significant test at 0.05)
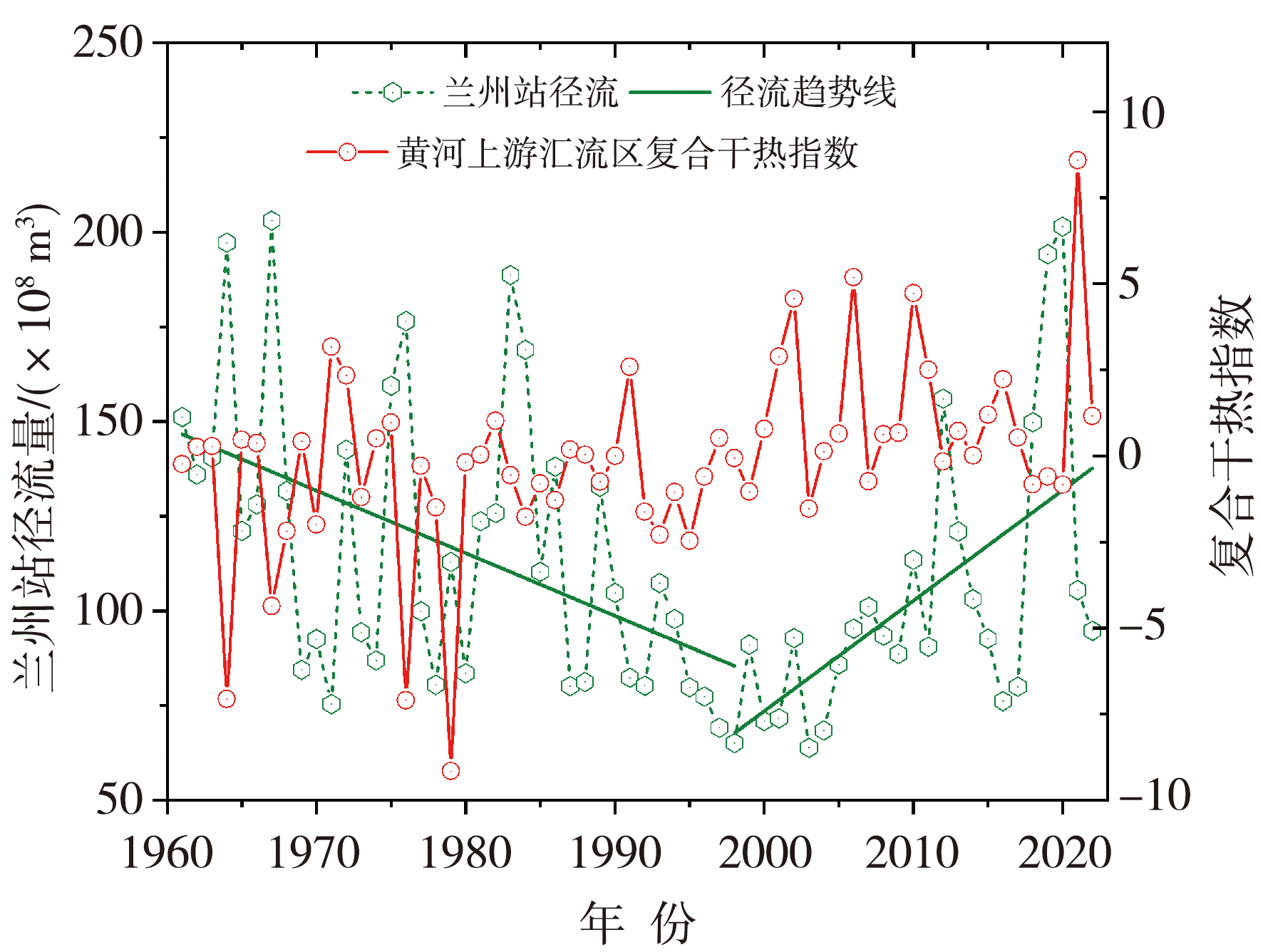
Fig.9 The inter-annual variation of summer runoff in the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River and the summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 时段 | 高温 | 降水 | 复合干热指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1961—1997年 | -0.33* | 0.14 | -0.41** |
| 1998—2022年 | -0.18 | 0.48** | -0.32* |
Tab.5 Correlation coefficients between summer high temperature,precipitation,and compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and summer runoff in the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River during different time periods
| 时段 | 高温 | 降水 | 复合干热指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1961—1997年 | -0.33* | 0.14 | -0.41** |
| 1998—2022年 | -0.18 | 0.48** | -0.32* |
| [1] | 白肇烨, 徐国昌, 1988. 中国西北天气[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [2] | 毕硕本, 孙力, 李兴宇, 等, 2018. 基于EEMD的1470—1911年黄河中下游地区旱涝灾害多时间尺度特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 27(1):137-147. |
| [3] |
陈少勇, 王劲松, 郭俊庭, 等, 2012. 中国西北地区1961—2009年极端高温事件的演变特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 27(5): 832-844.
DOI |
| [4] | 程捷, 张绪教, 田明中, 等, 2006. 黄河源区冰楔假型群的发育及其古气候意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(1):92-98. |
| [5] | 李万莉, 王可丽, 傅慎明, 等, 2008. 区域西风指数对西北地区水汽输送及收支的指示性[J]. 冰川冻土, 30(1):28-34. |
| [6] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 748-763.
DOI |
| [7] | 马浩, 刘昌杰, 钱奇峰, 等, 2020. 2018年5月浙江省极端高温气候特征及环流背景[J]. 干旱气象, 38(6): 909-919. |
| [8] | 梅梅, 高歌, 李莹, 等, 2023. 1961—2022年长江流域高温干旱复合极端事件变化特征[J]. 人民长江, 54(2): 12-20. |
| [9] |
汤懋苍, 沈志宝, 陈有虞, 1979. 高原季风的平均气候特征[J]. 地理学报, 34(1): 33-42.
DOI |
| [10] |
唐懿, 蔡雯悦, 翟建青, 等, 2022. 2021年夏季中国气候异常特征及主要气象灾害[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 179-186.
DOI |
| [11] | 王可丽, 江灏, 吴虹, 2001. 南亚夏季风年际变化特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 20(3): 318-324. |
| [12] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [13] | 魏明华, 2021. 中国北方季风边缘区1960—2010年夏季气候干湿变化的时空特征及影响因素[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [14] | 武新英, 郝增超, 张璇, 等, 2021. 中国夏季复合高温干旱分布及变异趋势[J]. 水利水电技术:中英文, 52(12): 90-98. |
| [15] | 杨金虎, 张强, 杨博成, 等, 2023. 黄河上游暖湿化的多时间尺度特征及对生态植被的影响[J]. 高原气象, 42(4): 1 018-1 030. |
| [16] | 余荣, 翟盘茂, 2021. 关于复合型极端事件的新认识和启示[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(5): 645-649. |
| [17] | 郑本兴, 王苏民, 1996. 黄河源区的古冰川与古环境探讨[J]. 冰川冻土, 18(3): 210-218. |
| [18] | HAO Z C, 2022. Compound events and associated impacts in China[J]. iScience, 25(8): 104689. DOI:10.1016/j.isci.2022.104689. |
| [19] | HUANG N E, SHEN S P, 2005. Hibert-Huang transform and its applications[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd: 56-62. |
| [20] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [21] | LYU X M, ZHOU G S, ZHOU M Z, et al, 2019. Projection of heat injury to single-cropping rice in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China under future global warming scenarios[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 33(2): 363-374. |
| [22] | MUKHERJEE S, ASHFAQ M, MISHRA A K, 2020. Compound drought and heatwaves at a global scale: The role of natural climate variability‐associated synoptic patterns and land‐surface energy budget anomalies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125(11): e2019JD031943.DOI:10.1029/2019JD031943. |
| [23] | WANG B, FAN Z, 1999. Choice of south Asian summer monsoon indices[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 80: 629-638. |
| [24] | WU Z H, HUANG N E, 2009. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 1(1): 1-41. |
| [25] | XUN X Y, HU Z Y, MA Y M, 2012. The dynamic plateau monsoon index and its association with general circulation anomalies[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 29(6): 1 249-1 263. DOI:10.1007/s00376-012-1125-9. |
| [26] | YANG J H, ZHANG Q, YUE P, et al, 2023. Characteristics of warming and humidification in the Yellow River's upper reaches and their impact on surface water resources[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 43: 7 667-7 681. |
| [27] | YANG J H, ZHANG Q, LU G Y, et al, 2021. Climate transition from warm-dry to warm-wet in eastern northwest China[J]. Atmosphere, 12(5): 548.DOI:10.3390/atmos12050548. |
| [28] | YU R, ZHAI P M, 2020a. More frequent and widespread persistent compound drought and heat event observed in China[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 14576.DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-71312-3. |
| [29] | YU R, ZHAI P M, 2020b. Changes in compound drought and hot extreme events in summer over populated Eastern China[J]. Weather and Climate Extremes, 30: 100295. DOI:10.1016/j.wace.2020.100295. |
| [30] | ZHANG Q, YANG J H, DUAN X Y, et al, 2022. The eastward expansion of the climate humidification trend in northwest China and the synergistic influences on the circulation mechanism[J]. Climate Dynamics, 59(7): 2 481-2 497. |
| [31] | ZSCHEISCHLER J, WESTRA S, VAN DEN HURK B J J M, et al, 2018. Future climate risk from compound events[J]. Nature Climate Change, 8(6): 469-477. |
| [1] |
HE Hang, YANG Zesu, WU Yuyan.
Characterization of multi-land surface factor-atmosphere coupling in different ecosystems in the climate transition zones
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 207-220.
|
| [2] |
XIE Na , YE Bangping , YANG Kangquan, , CHEN Jun , KANG Lan, , FAN Jianglin , XU Yang.
Simulation of runoff and analysis of disaster causes of flash floods in small watersheds with complex terrain in the western Sichuan Basin
#br#
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 231-241.
|
| [3] |
LI Meng, , ZHU Li, , ZHANG Yuehan.
Evolution and cause analysis of an extreme rainstorm process in the Sichuan Basin
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 242-253.
|
| [4] | LIU Jiahuimin, LI Ming, OUYANG Yu, JI Qing, WANG Qingxia, LI Wenyao, LI Hanyu. Characteristics of low-level wind during typical sudden precipitation processes at the northern foot of Qinling Mountains in midsummer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 41-53. |
| [5] | GAO Ruina, ZHU Xiaowei, WANG Fan, ZHAI Yingjia, GOU Xiaohui, ZHOU Jiqiang. Evolution of urban heat island effect in Yinchuan and evaluation of cooling effect of lake wetland [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 97-103. |
| [6] | WANG Yajun, LUO Juying, CHENG Liehai, LI Wei. Construction and validation of summer drought prediction model in Hubei Province based on machine learning algorithms [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 661-670. |
| [7] | YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping, ZENG Dingwen, WANG Lijuan, ZHANG Jinyu, LU Xiaojuan, YUE Ping, JIN Jie. Characteristics of regional high temperature and drought in China from April to June 2024 and their influence factors [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 507-518. |
| [8] | XIAO Ying, GAO Yaqi, DU Liangmin, REN Yongjian. Analysis on the characteristics and causes of intraseasonal differences of the continuous rainfall in Hanjiang River Basin during the summer and autumn in 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 563-575. |
| [9] | ZHU Zhanyun, ZHANG Luxuan, LI Fugang, ZHANG Jue, ZHANG Weiwei, LI Qiang. Study on the characteristics of meteorological and hydrological droughts in Xin’an River Basin and their relationship [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 157-165. |
| [10] | HAO Lisheng, HE Liye, MA Ning, HAO Yuqian. Relationship between interannual variability of El Niño events and summer droughts in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 829-840. |
| [11] | XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922. |
| [12] | ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Qiang, WANG Runyuan, YUE Ping, WANG Sheng, ZENG Jian, YANG Zesu, LI Hongyu, QIAO Liang, WANG Wenyu, ZHANG Hongli, YANG Siqi, ZHAO Funian. New progresses in the study of land-atmosphere interaction in summer monsoon transition zone in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 519-530. |
| [13] | HAN Yaojie, PENG Jiyong, ZHANG Xihe, LI Shuyan. Spatial and temporal variations of heat resources utilization efficiency of summer maize in growth season under climate change in Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 639-647. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yuchen, TIAN Hongwei. Analysis of spatial-temporal variation of urban heat island and driving mechanism in Zhengzhou in recent 17 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 403-412. |
| [15] | ZHANG Cunhou, CUI Wei, YUE Kun, ZHAO Xinghua, WU Yingjie, SEN Di. Fluctuating response of soil moisture to precipitation in arid and semi-arid areas: a case study of Damao County in desert steppe [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 260-267. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

