Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 553-562.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0553
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature characteristics of summer high temperature anomaly in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River
CHEN Xiaoxiao1,2( ), HUANG Zhiyong1(
), HUANG Zhiyong1( ), QIN Pengcheng3, XIA Zhihong3, YAO Yao1, TANG Xingzhi1, WANG Yingqiong1
), QIN Pengcheng3, XIA Zhihong3, YAO Yao1, TANG Xingzhi1, WANG Yingqiong1
- 1. Hubei Branch of China Meteorological Administration Training Center, Wuhan 430074, China
2. Hubei Key Laboratory for Heavy Rain Monitoring and Warning Research, Institute of Heavy Rain, China Meteorological Administration, Wuhan 430205, China
3. Wuhan Regional Climate Center, Wuhan 430074, China
-
Received:2023-06-27Revised:2023-09-12Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-13
长江中游夏季高温异常的大气环流和海温特征
陈笑笑1,2( ), 黄治勇1(
), 黄治勇1( ), 秦鹏程3, 夏智宏3, 姚瑶1, 汤兴芝1, 汪应琼1
), 秦鹏程3, 夏智宏3, 姚瑶1, 汤兴芝1, 汪应琼1
- 1.中国气象局气象干部培训学院湖北分院,湖北 武汉 430074
2.中国气象局武汉暴雨研究所/暴雨监测预警湖北省重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430205
3.武汉区域气候中心,湖北 武汉 430074
-
通讯作者:黄治勇(1969—),男,湖北武汉人,研究员,主要从事暴雨和高温机理研究工作。E-mail:hzyqxj@126.com 。 -
作者简介:陈笑笑(1995—),女,湖北武汉人,工程师,主要从事气候变化与数值模拟研究工作。E-mail: 1823392134@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41971026);中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2023J051);干部学院科技发展基金项目(2023CMATCQN13)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Xiaoxiao, HUANG Zhiyong, QIN Pengcheng, XIA Zhihong, YAO Yao, TANG Xingzhi, WANG Yingqiong. Atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature characteristics of summer high temperature anomaly in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 553-562.
陈笑笑, 黄治勇, 秦鹏程, 夏智宏, 姚瑶, 汤兴芝, 汪应琼. 长江中游夏季高温异常的大气环流和海温特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 553-562.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0553
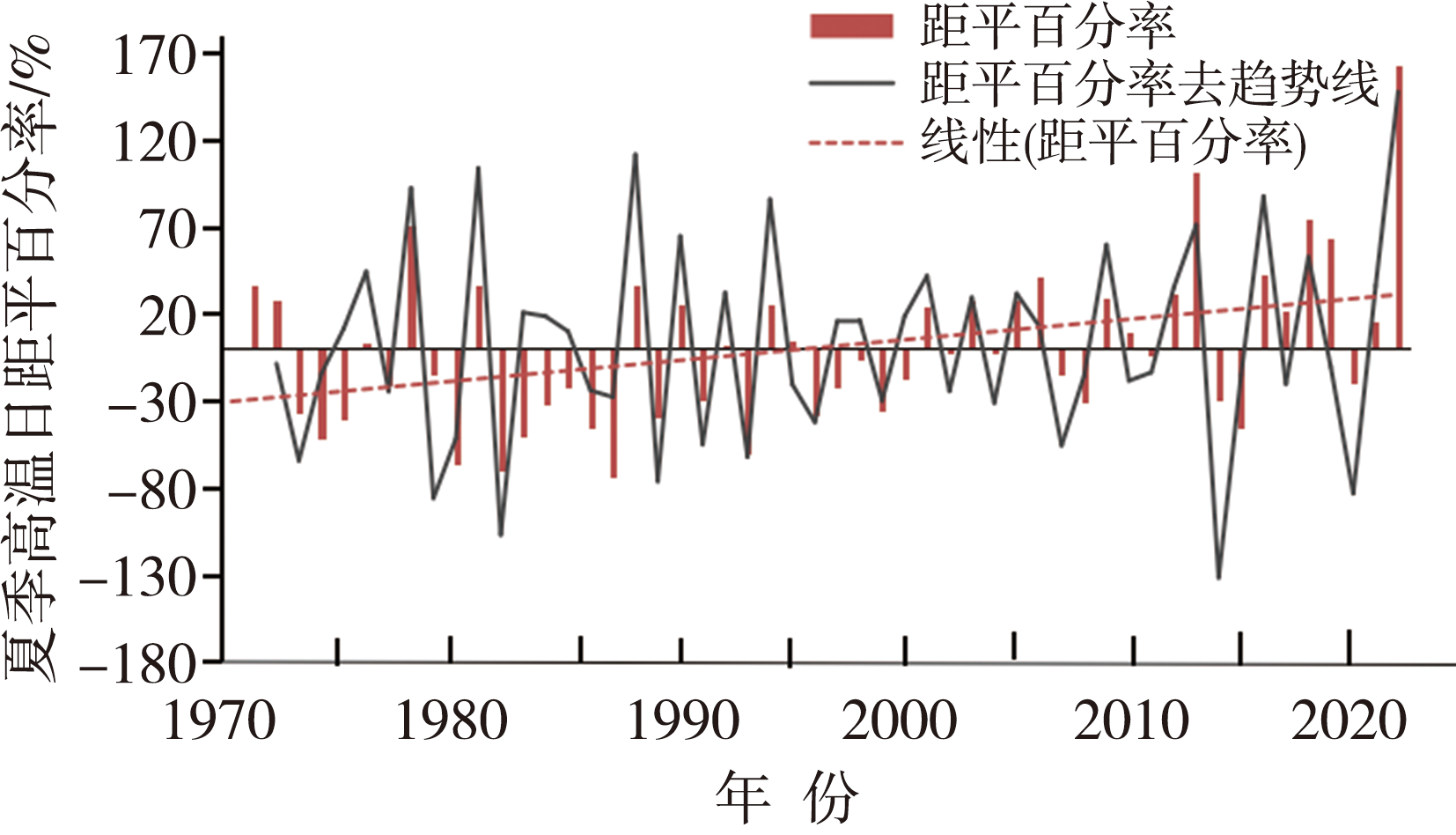
Fig.1 The anomaly percentage and its detrended series of summer high temperature days in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River from 1971 to 2022 (The climatological state is the average of 1991-2020)

Fig.2 Distribution of differences of 200 hPa height field (the color shaded, Unit: gpm), zonal wind field (isolines, Unit: m·s-1) (a), 500 hPa height field (the color shaded, Unit: gpm), horizontal wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) between abnormally more and less years for high temperature days in summer in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River from 1971 to 2022 (The red box is the research area, the dotted areas pass the significance test at α=0.05, the same as below)
| 时段 | 东亚夏季西风急流位置指数 | 相关系数 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 偏多年 | 偏少年 | ||
| 夏季 | 3.401 | -1.660 | 0.517* |
| 6月 | 0.679 | -2.320 | 0.053 |
| 7月 | 6.822 | -1.310 | -1.838 |
| 8月 | 2.559 | -1.838 | 0.374* |
Tab.1 Location index of East Asian Summer Westerly Jet and its correlation coefficients with abnormally more and less years for high temperature days in summer in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River
| 时段 | 东亚夏季西风急流位置指数 | 相关系数 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 偏多年 | 偏少年 | ||
| 夏季 | 3.401 | -1.660 | 0.517* |
| 6月 | 0.679 | -2.320 | 0.053 |
| 7月 | 6.822 | -1.310 | -1.838 |
| 8月 | 2.559 | -1.838 | 0.374* |
| 时段 | 西太副高指数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/km2 | 强度/(gpm·km2) | 脊线/°N | 西伸脊点/°E | |
| 夏季 | 25.21* | 76.63 | 2.77* | -12.93* |
| 6月 | 38.20 | 108.66 | 0.78 | -7.42 |
| 7月 | 12.46 | 5.89 | 3.54* | -12.66* |
| 8月 | 29.76* | 113.52* | 3.80* | -17.75* |
Tab.2 The differences between Western Pacific Subtropical High indexes in abnormally more and less years for high temperature days in summer in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River
| 时段 | 西太副高指数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/km2 | 强度/(gpm·km2) | 脊线/°N | 西伸脊点/°E | |
| 夏季 | 25.21* | 76.63 | 2.77* | -12.93* |
| 6月 | 38.20 | 108.66 | 0.78 | -7.42 |
| 7月 | 12.46 | 5.89 | 3.54* | -12.66* |
| 8月 | 29.76* | 113.52* | 3.80* | -17.75* |

Fig.3 Distribution of differences of 850 hPa vertical velocity (a, Unit: hPa·s-1) and OLR (b, Unit: W·m-2) between abnormally more and less years for high temperature days in summer in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River

Fig. 4 The distribution of correlation coefficient between high temperature days in summer in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and sea surface temperature in previous winter (a), spring (b) and summer (c) from 1971 to 2022

Fig.5 Distribution of differences of sea surface temperatures in previous winter (a), spring (b), and summer (c) between abnormally more and less years for high temperature days in summer in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River (Unit: ℃)
| [1] | 陈丽华, 周率, 党建涛, 等, 2010. 2006年盛夏川渝地区高温干旱气候形成的物理机制研究[J]. 气象, 36 (5): 85-91. |
| [2] | 邓振镛, 文小航, 黄涛, 等, 2009. 干旱与高温热浪的区别与联系[J]. 高原气象, 28 (3): 702-709. |
| [3] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 2022. 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 721-732.
DOI |
| [4] | 胡菊芳, 占龙飞, 谢远玉, 2022. 江西省近60年极端高温变化特征及其对水稻的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 61(9): 27-32. |
| [5] | 贾子康, 郑志海, 封国林, 2020. 中国南方地区盛夏高温类型及其对应的大尺度环流和海温异常[J]. 气象学报, 78(6): 928-944. |
| [6] | 姜雨彤, 郝增超, 冯思芳, 等, 2022. 长江与黄河流域复合高温干旱事件时空演变特征[J]. 水资源保护, 39(2): 70-77. |
| [7] | 李晓萌, 孙永华, 孟丹, 等, 2013. 近10年北京极端高温天气条件下的地表温度变化及其对城市化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 33(20): 6 694-6 703. |
| [8] | 林佳, 2022. 极端高温袭来:“热穹顶”之下的北美洲[J]. 中国减灾(4): 42-45. |
| [9] | 刘诗梦, 张杰, 于涵, 2018. 近30年江淮流域夏季年代际干旱特征及其与欧亚西风环流异常的关系[J]. 高原气象, 37(5): 1 254-1 263. |
| [10] | 刘芸芸, 李维京, 艾孑兑秀, 等, 2012. 月尺度西太平洋副热带高压指数的重建及应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 23(4): 414-423. |
| [11] | 罗伯良, 李易芝, 2015. 湖南高温日时空分布特征及高温日数气候预测[J]. 气象科技, 43(6): 1 110-1 115. |
| [12] | 彭京备, 张庆云, 布和朝鲁, 2007. 2006年川渝地区高温干旱特征及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(3): 464-474. |
| [13] | 孙建奇, 2014. 2013年北大西洋破纪录高海温与我国江淮-江南地区极端高温的关系[J]. 科学通报, 59(27): 2 714-2 719 |
| [14] | 孙建奇, 王会军, 袁薇, 2011. 我国极端高温事件的年代际变化及其与大气环流的联系[J]. 气候与环境研究, 16(2): 199-208. |
| [15] | 孙亚卿, 李春, 石剑, 2022. 长江流域夏季极端高温的年代际变化特征及其与大西洋多年代际振荡的关系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 52(2): 13-22. |
| [16] | 谈建国, 郑有飞, 彭丽, 等, 2008. 城市热岛对上海夏季高温热浪的影响[J]. 高原气象, 27(B12): 144-149. |
| [17] | 王慧美, 刘舸, 彭京备, 等, 2021. 热带大西洋海温异常季节内演变对中国江南地区夏季持续性高温事件影响的初步研究[J]. 大气科学, 45(2): 300-314. |
| [18] | 王文, 许金萍, 蔡晓军, 等, 2017. 2013年夏季长江中下游地区高温干旱的大气环流特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(6): 1 595-1 607. |
| [19] | 吴志文, 秦正坤, 林朝晖, 2022. 中西亚极端干早特征及其与热带海温的联系[J]. 高原气象, 41(5): 1 141-1 152. |
| [20] | 肖艳林, 秦育婧, 张润琼, 2013. 春季Hadley环流强度与我国东部地区夏季降水的联系[J]. 贵州气象, 37(6): 25-29. |
| [21] | 许金萍, 王文, 蔡晓军, 等, 2017. 长江中下游地区2011年冬春连旱及2013年夏季高温干旱环流特征及其与Rossby波活动的联系对比分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 33(6): 992-999. |
| [22] | 宣守丽, 2011. 东亚高空西风急流多时间尺度变化机理及其对我国夏季降水的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| [23] | 杨辉, 李崇银, 2005. 2003年夏季中国江南异常高温的分析研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 10(1): 80-85. |
| [24] | 袁媛, 丁婷, 高辉, 等, 2018. 我国南方盛夏气温主模态特征及其与海温异常的联系[J]. 大气科学, 42(6): 1 245-1 262. |
| [25] |
张剑明, 廖玉芳, 吴浩, 等, 2018. 湖南夏秋干旱及环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(3): 353-364.
DOI |
| [26] | 张强, 谢五三, 陈鲜艳, 等, 2021. 1961—2019年长江中下游区域性干旱过程及其变化[J]. 气象学报, 79(4): 570-581. |
| [27] | 张志薇, 王式功, 尚可政, 等, 2011. 华中地区近50年高温事件及大气环流成因分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 47(2): 50-55. |
| [28] | 赵昶昱, 陈海山, 孙善磊, 2019. 我国中部地区夏委于旱的多时间尺度特征及其环流、海温异常[J]. 气象科学, 39(3): 386-395. |
| [29] | 周晓, 黄菲, 2015. 中国极端高温事件的年代际突变及其与海温的关系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 45(5): 19-27. |
| [30] | DOLE R, HOERLING M, PERLWITZ J, et al, 2011. Was there a basis for anticipating the 2010 Russian heat wave?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(6), L06702. Doi: 10:1029/2010GL046582. |
| [31] | DONG S, SUN Y, AGUILAR E, et al, 2017. Observed changes in temperature extremes over Asia and their attribution[J]. Climate Dynamics, 51(3): 1-15. |
| [32] | FENG S, HAO Z, ZHANG X, et al, 2019. Probabilistic evaluation of the impact of compound dry-hot events on global maize yields[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 689: 1 228-1 234. |
| [33] | HONG C C, CHANG T C, HSU H H, 2014. Enhanced relationship between the tropical Atlantic SST and the summertime western North Pacific subtropical high after the early 1980s[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 119(7): 3 715-3 722. |
| [34] | HU K M, HUANG G, HUANG R H, 2011. The impact of tropical Indian Ocean variability on summer surface air temperature in China[J]. Journal of Climate, 24(20): 5 365-5 377. |
| [35] | IPCC, 2021. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis[R]//Masson-Delmotte V, ZHAI P, PIRANI A, et al. Contribution of Working Group Ⅰ to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [1] |
WANG Yuetong , HE Dongpo , LI Zhongyan , WANG Shuo , CHEN Zaoyang.
Analysis of two meteorological drought events in Guizhou Province and establishment of drought prediction model based on machine learning
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 671-682.
|
| [2] | JIANG Zhongbao, WANG Yukun, YANG Xueyan, LI Shangfeng, YU Xiujing, PAN Chunxiao, QIU Yixuan. Characteristics of climate comfort period in Changbai Mountain region from 1961 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 620-628. |
| [3] | WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [4] | XIE Ao, LUO Boliang, DENG Jianbo, GAO Xiaxia. Characteristics and cause analysis of extreme and persistent drought in summer, autumn and winter in 2022/2023 in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 910-922. |
| [5] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [6] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia. Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [7] | XU Weiping, MENG Xiangxin, GU Weizong, BO Zhongkai. Relationship between extremely low temperature in spring in Shandong Province and North Atlantic SST in preceding winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 202-211. |
| [8] | WANG Jianjiang, MA Hao, YU Liping, GONG Liqing, WANG Chen. Analysis of Atmospheric Circulation Characteristics Associated with Autumn Drought over Zhejiang Province in 2019 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 1-7. |
| [9] | MA Youxuan, LI Wanzhi, WANG Lixia, BAI Wenrong, WANG Ziwen. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Atmospheric Circulation Diagnosis of Spring Drought Based on SPI in Qinghai Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 362-370. |
| [10] | LIU Xiaoran, HU Zuheng, LI Yonghua, TANG Hongyu. Variation Characteristics and Formation Cause of Cold and Warm Winter in Chongqing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 404-410. |
| [11] | LUO Liansheng, XU Min, HE Dongyan. Interdecadal Characteristics of Summer Precipitation over Huaihe River Basinand the Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies Since 2000 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 540-549. |
| [12] | Lü Xingyue, RONG Yanshu, SHI Dandan. Reanalysis on the Causes of Continuous Drought from Autumn 2010 to Spring 2011 in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 198-208. |
| [13] | CAI Xinling, LI Yu, LI Qian, HU Shulan. Climatic Characteristics of Autumn Rain in Shaanxi and Their Relationship with Atmospheric Circulation and SST During 1961-2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 226-232. |
| [14] | HU Chunli1, LI Rongping1, WANG Ting1, LI Fei2, LI Linlin1. Forecast Model of Rice Harvest in Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 501-. |
| [15] | QUE Zhiping, WU Fan, ZHOU Junhui. Rainfall Anomaly and Its Causes in Jiangxi Province in November 2015 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(2): 263-271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||