Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 34-42.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0034
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
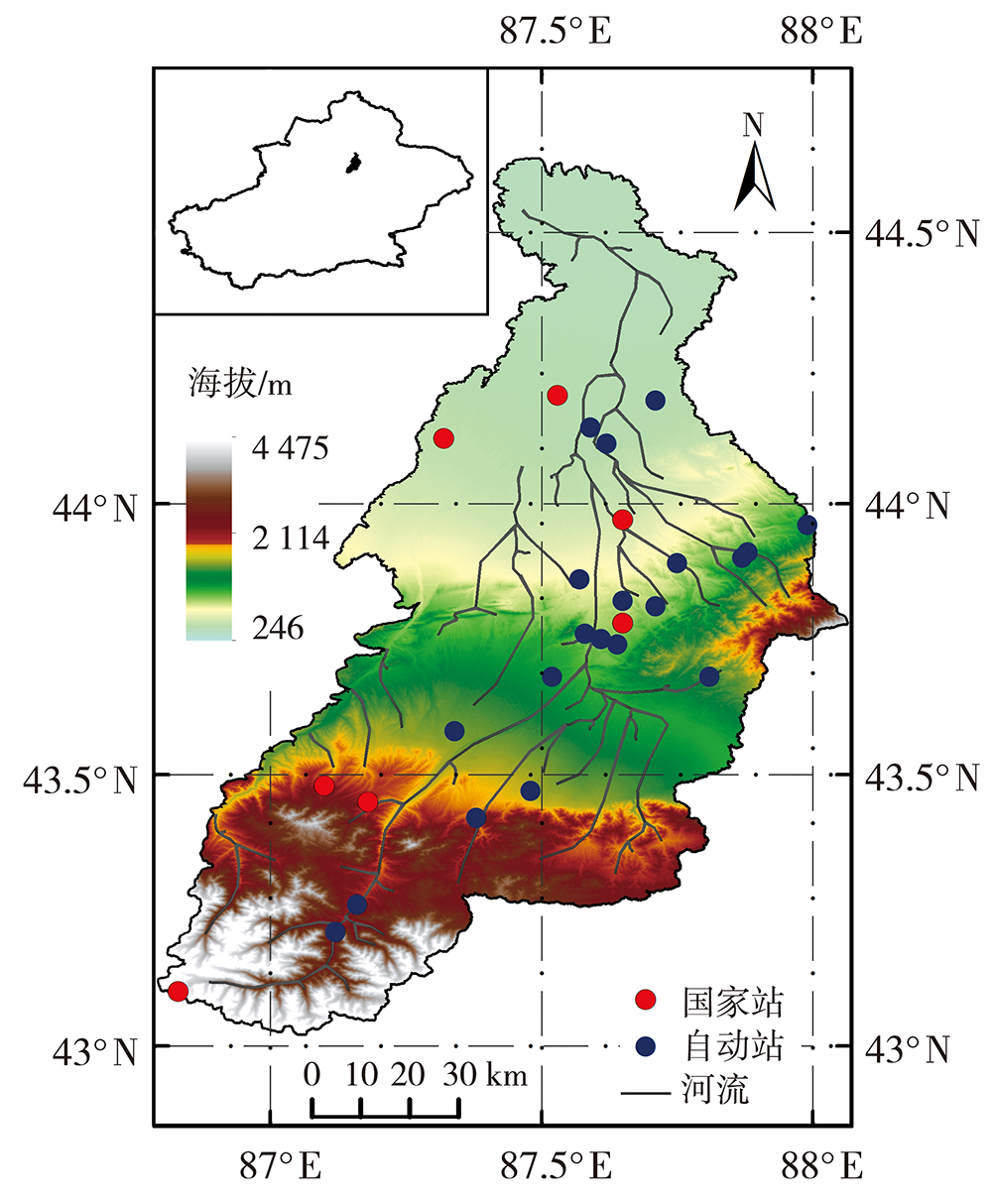
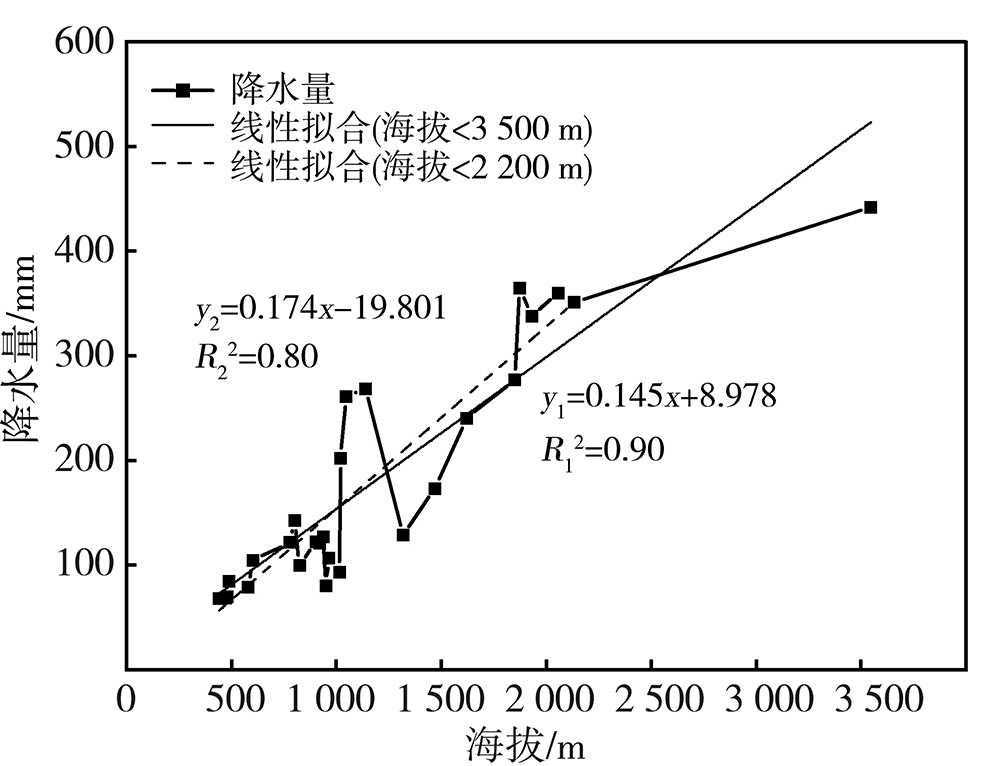
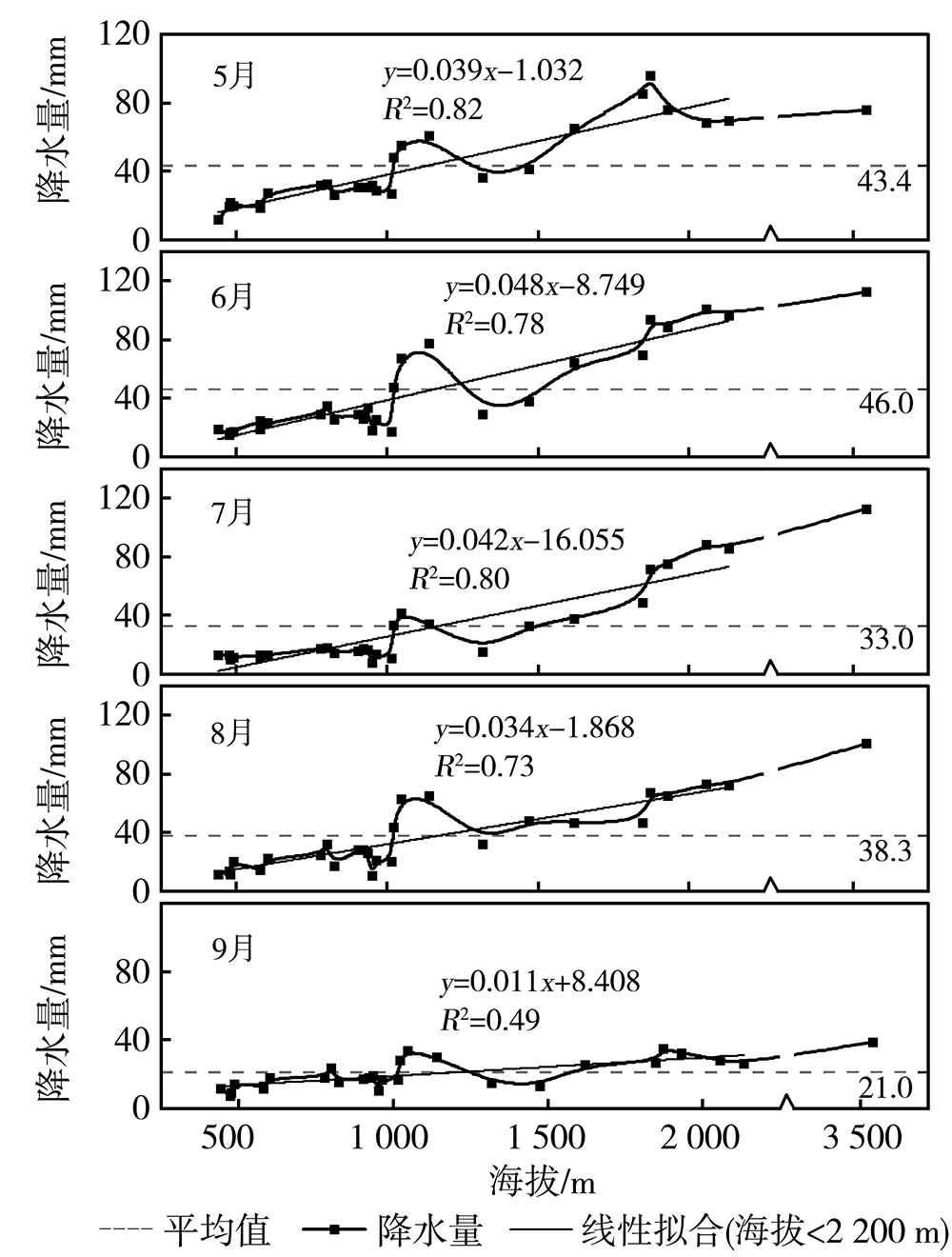
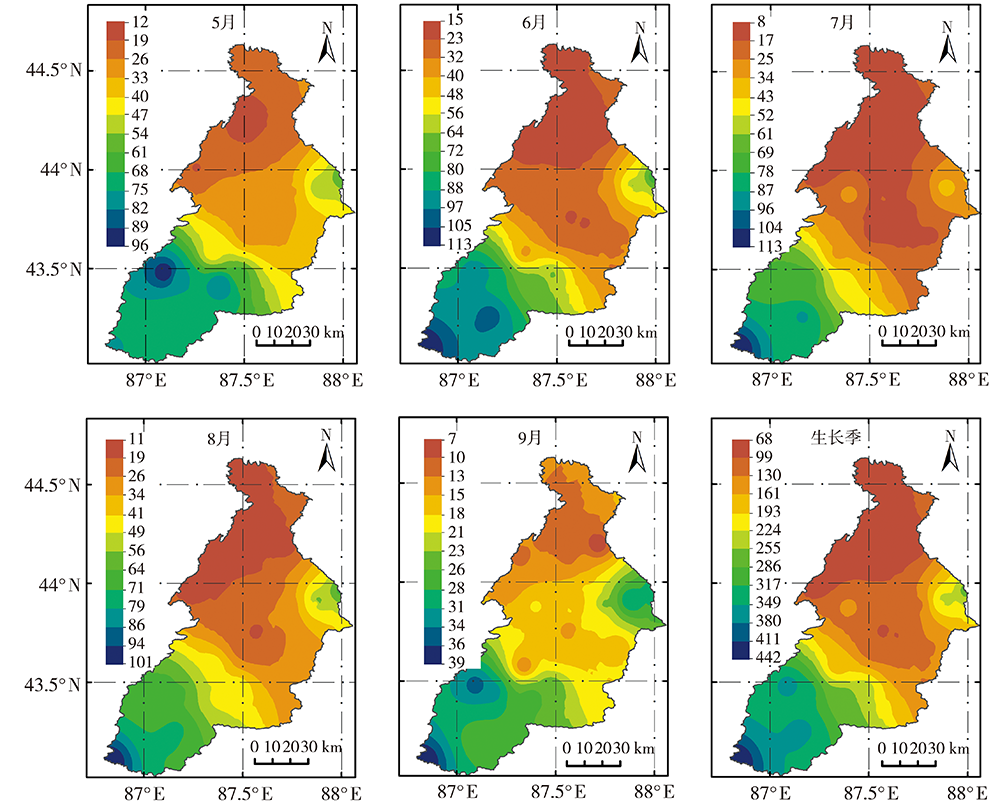
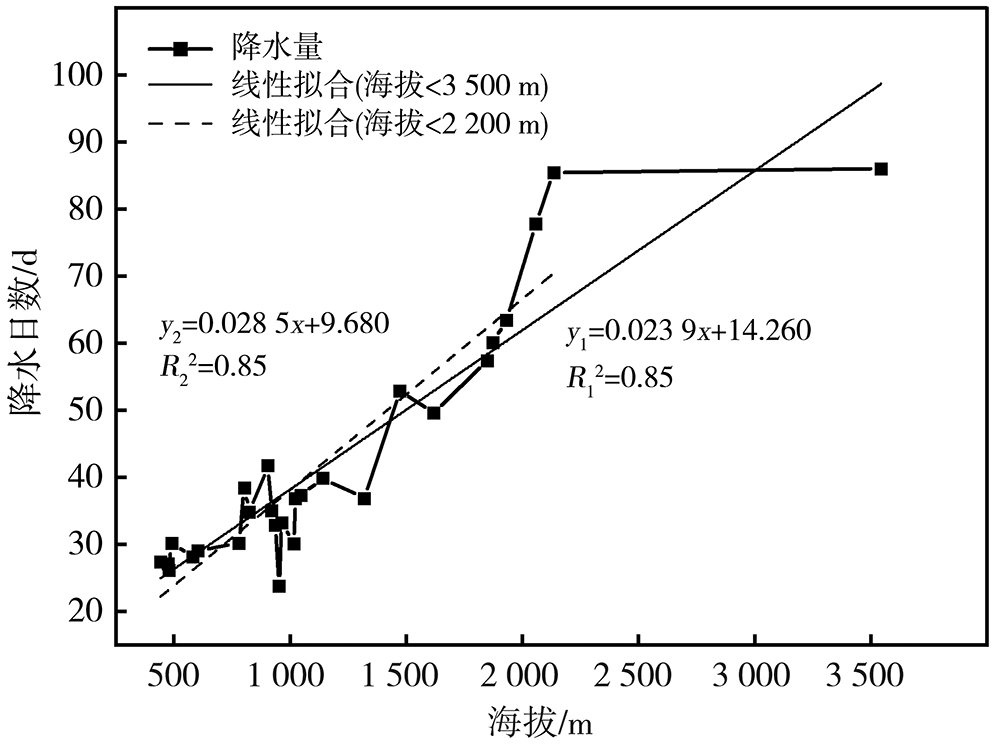
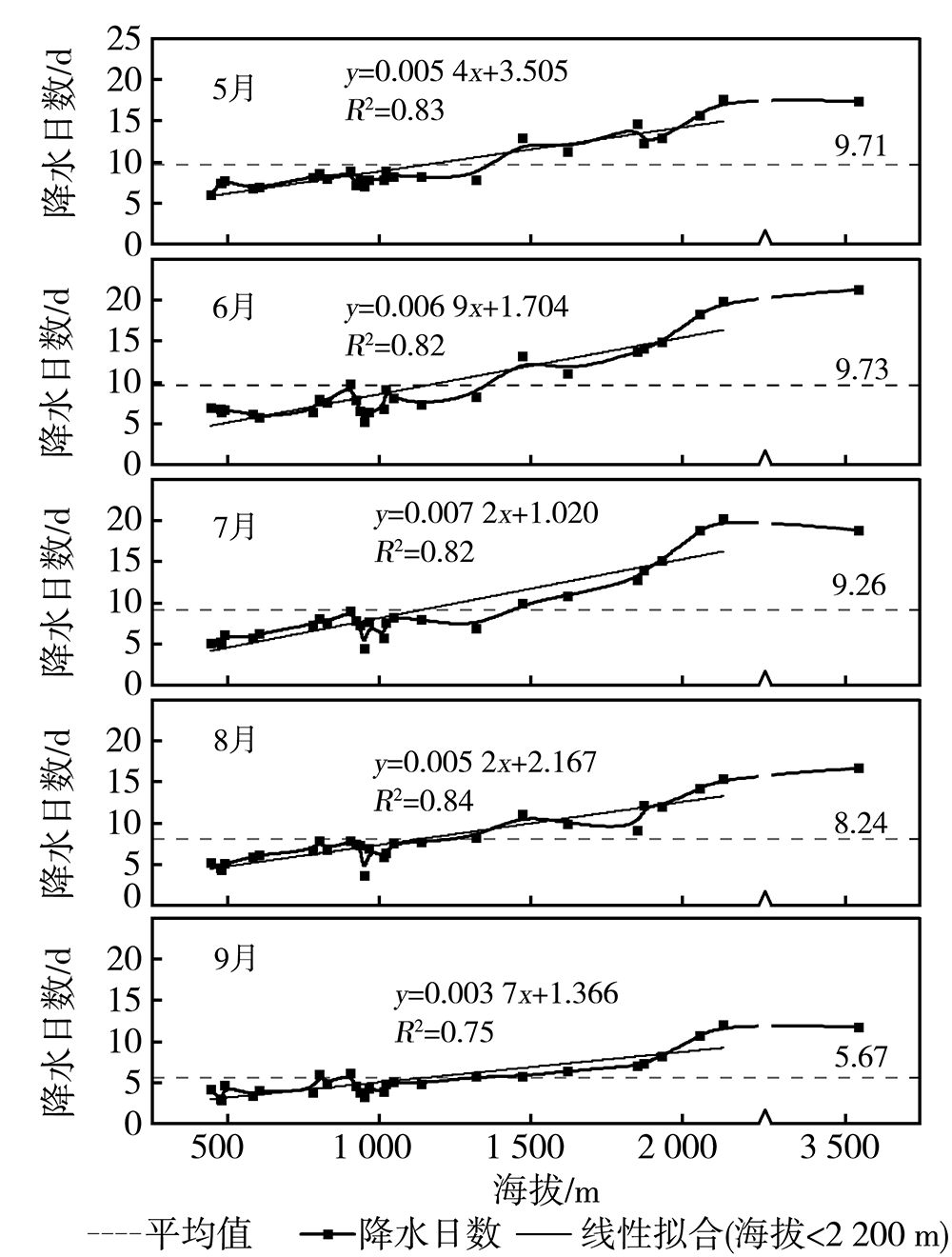
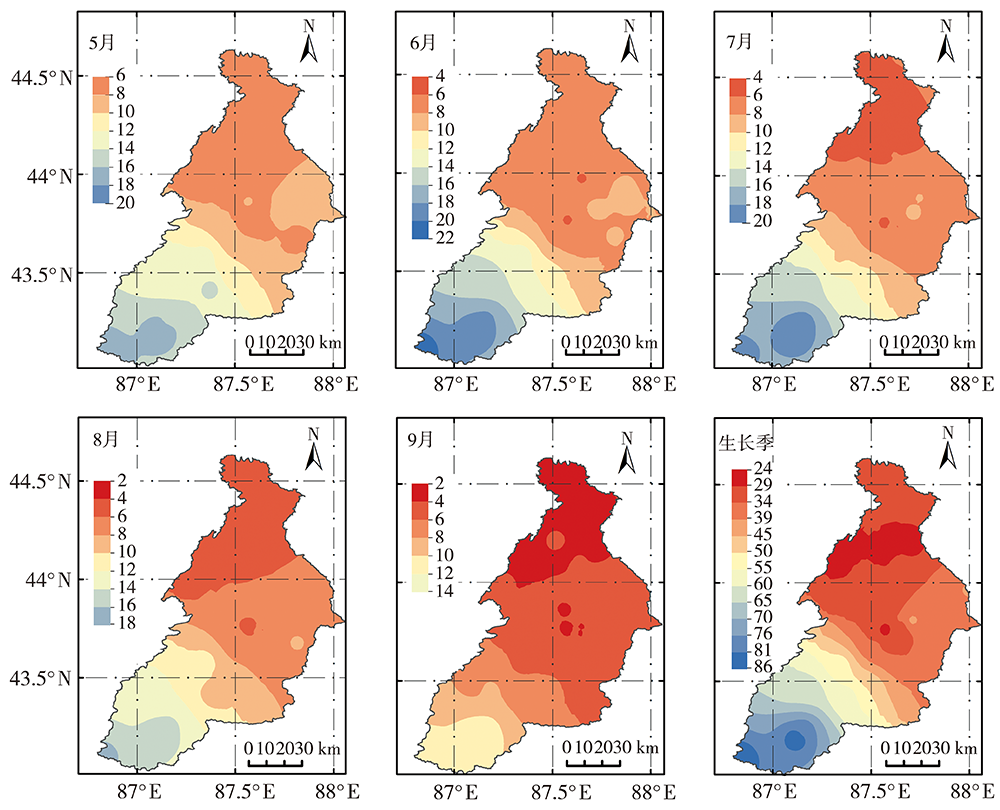
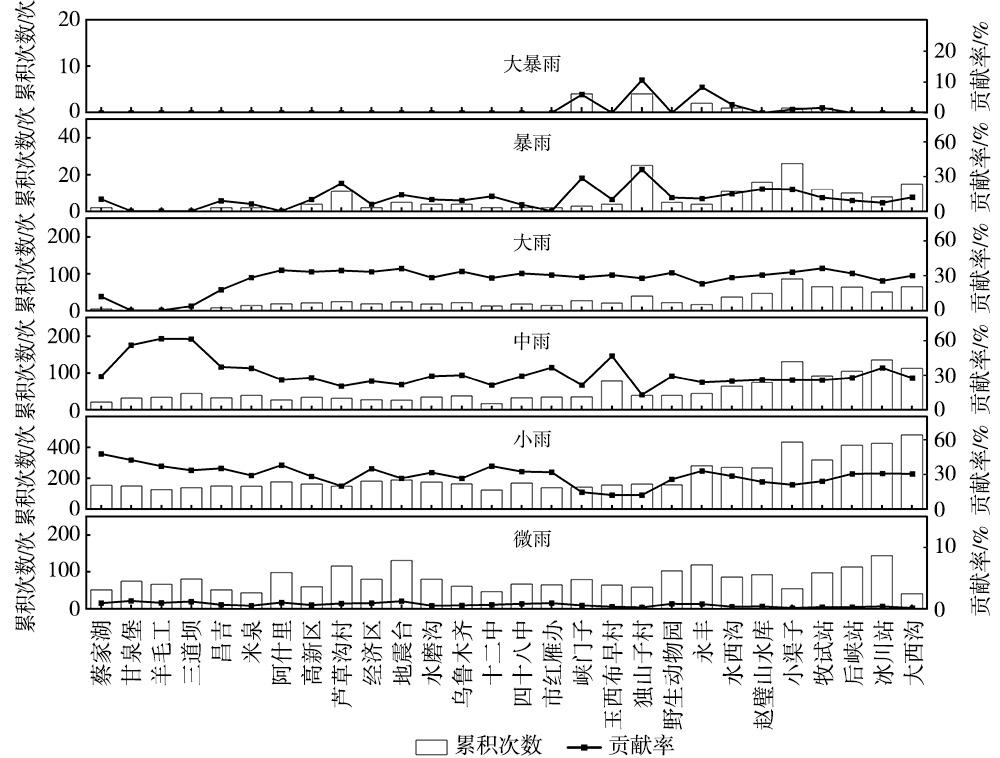
Analysis of precipitation characteristics during the vegetation growth season in the Urumqi River Basin in arid region of northwest China
XING Hongyan1,2( ), HE Qing2,3(
), HE Qing2,3( ), PU Zongchao4, WANG Guosheng1,2, JIN Chen5
), PU Zongchao4, WANG Guosheng1,2, JIN Chen5
- 1. College of Geography Science & Tourism, Xinjiang Normal University, Urumqi 830054, China
2. Institute of Desert Meteorology, China Meteorological Administration, Urumqi 830002, China
3. Field Scientific Experiment Base of Akdala Atmospheric Background, China Meteorological Administration, Altay 836500, Xinjiang, China
4. Urumqi Meteorological Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830002, China
5. College of Geographical Science, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
西北干旱区乌鲁木齐河流域植被生长季降水特征分析
邢红艳1,2( ), 何清2,3(
), 何清2,3( ), 普宗朝4, 王国胜1,2, 金晨5
), 普宗朝4, 王国胜1,2, 金晨5
- 1.新疆师范大学地理科学与旅游学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830054
2.中国气象局乌鲁木齐沙漠气象研究所,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002
3.中国气象局阿克达拉大气本底野外科学试验基地,新疆 阿勒泰 836500
4.新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市气象局,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002
5.新疆大学地理科学学院, 新疆 乌鲁木齐 830046