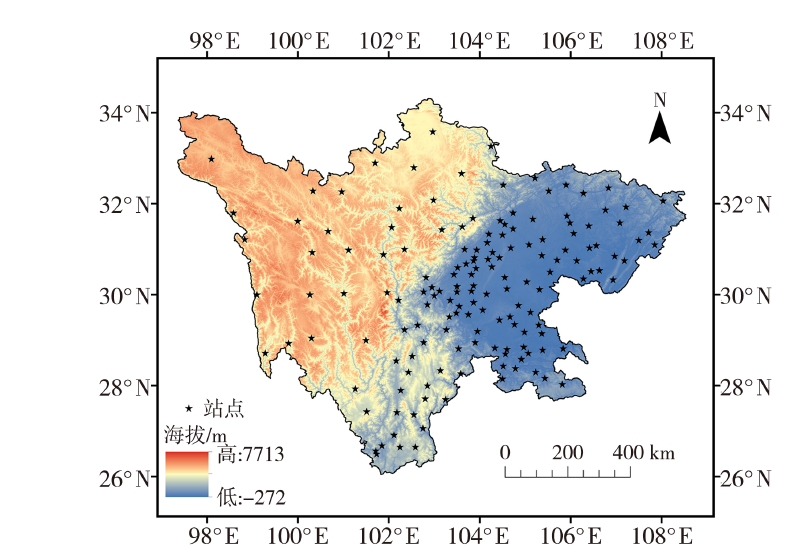
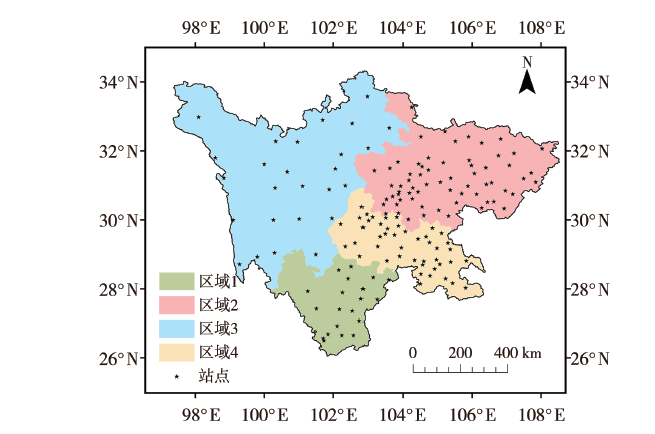
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 897-907.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0897
• Technical Reports • Previous Articles
Comparative study on spatial interpolation methods of summer precipitation in Sichuan
LI Xiang1,2( ), LI Guoping1(
), LI Guoping1( )
)
- 1. School of Atmospheric Science, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
2. Collaborative Innovation Center for Meteorological Disaster Forecasting, Early Warning and Assessment, Co-constructed by the Ministry of Finance, Nangjing 210044, China
-
Received:2021-08-05Revised:2022-04-27Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-10 -
Contact:LI Guoping
四川夏季降水量空间插值方法的比较
- 1.成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,四川 成都 610225
2.气象灾害预报预警与评估省部共建协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210044
-
通讯作者:李国平 -
作者简介:李想(1998—),女,四川内江人,硕士生,主要从事天气动力学研究.E-mail:343537657@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42175002);国家自然科学基金(42075013);国家自然科学基金(91937301);国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFC1507200)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Xiang, LI Guoping. Comparative study on spatial interpolation methods of summer precipitation in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 897-907.
李想, 李国平. 四川夏季降水量空间插值方法的比较[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 897-907.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0897
| 经度 | 纬度 | 海拔 | NDVI | 坡度 | 坡向 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全区 | -0.183* | 0.227** | -0.461** | 0.027 | -0.302** | 0.049 |
| 区域1 | 0.477* | 0.156 | 0.338 | 0.227 | -0.432 | -0.015 |
| 区域2 | 0.062 | -0.069 | -0.393** | 0.103 | -0.456** | 0.049 |
| 区域3 | -0.392* | -0.112 | 0.252 | 0.542** | 0.175 | 0.062 |
| 区域4 | 0.448** | 0.443** | 0.132 | 0.217 | 0.008 | 0.185 |
Tab.1 The correlation coefficients between multi-year average summer precipitation in Sichuan and various factors in the whole region and each district
| 经度 | 纬度 | 海拔 | NDVI | 坡度 | 坡向 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全区 | -0.183* | 0.227** | -0.461** | 0.027 | -0.302** | 0.049 |
| 区域1 | 0.477* | 0.156 | 0.338 | 0.227 | -0.432 | -0.015 |
| 区域2 | 0.062 | -0.069 | -0.393** | 0.103 | -0.456** | 0.049 |
| 区域3 | -0.392* | -0.112 | 0.252 | 0.542** | 0.175 | 0.062 |
| 区域4 | 0.448** | 0.443** | 0.132 | 0.217 | 0.008 | 0.185 |
| 组合方式 | 全区 | 区域1 | 区域2 | 区域3 | 区域4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoLaAl | 0.262 | 0.254 | 0.397* | 0.375 | 0.243* |
| LoLaNd | 0.121 | 0.319 | 0.014 | 0.417 | 0.267* |
| LoLaSl | 0.146 | 0.465* | 0.371* | 0.192 | 0.256* |
| LoAlNd | 0.257 | 0.356 | 0.292 | 0.625* | 0.203 |
| LoAlSl | 0.245 | 0.44* | 0.325 | 0.417 | 0.209 |
| LoNdSl | 0.136 | 0.556* | 0.389* | 0.422 | 0.204 |
| LaAlNd | 0.276* | 0.253 | 0.247 | 0.428* | 0.219 |
| LaAlSl | 0.277* | 0.417 | 0.248 | 0.128 | 0.219 |
| LaNdSl | 0.172 | 0.402 | 0.287 | 0.375 | 0.224 |
| AlNdSl | 0.293* | 0.355 | 0.303 | 0.429* | 0.073 |
Tab.2 The correlation R2 between the combination factors and the multi-year average summer precipitation in each area and the whole area
| 组合方式 | 全区 | 区域1 | 区域2 | 区域3 | 区域4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoLaAl | 0.262 | 0.254 | 0.397* | 0.375 | 0.243* |
| LoLaNd | 0.121 | 0.319 | 0.014 | 0.417 | 0.267* |
| LoLaSl | 0.146 | 0.465* | 0.371* | 0.192 | 0.256* |
| LoAlNd | 0.257 | 0.356 | 0.292 | 0.625* | 0.203 |
| LoAlSl | 0.245 | 0.44* | 0.325 | 0.417 | 0.209 |
| LoNdSl | 0.136 | 0.556* | 0.389* | 0.422 | 0.204 |
| LaAlNd | 0.276* | 0.253 | 0.247 | 0.428* | 0.219 |
| LaAlSl | 0.277* | 0.417 | 0.248 | 0.128 | 0.219 |
| LaNdSl | 0.172 | 0.402 | 0.287 | 0.375 | 0.224 |
| AlNdSl | 0.293* | 0.355 | 0.303 | 0.429* | 0.073 |

Fig.3 Comparison of interpolated results of multi-year average summer precipitation in the whole region (Unit:mm) (a) OK, (b) IDW, (c) RBF, (d) AlNdSl CoKriging interpolation, (e) LaAlSl CoKriging interpolation, (f) LaAlNd CoKriging interpolation, (g) LPI, (h) EBK
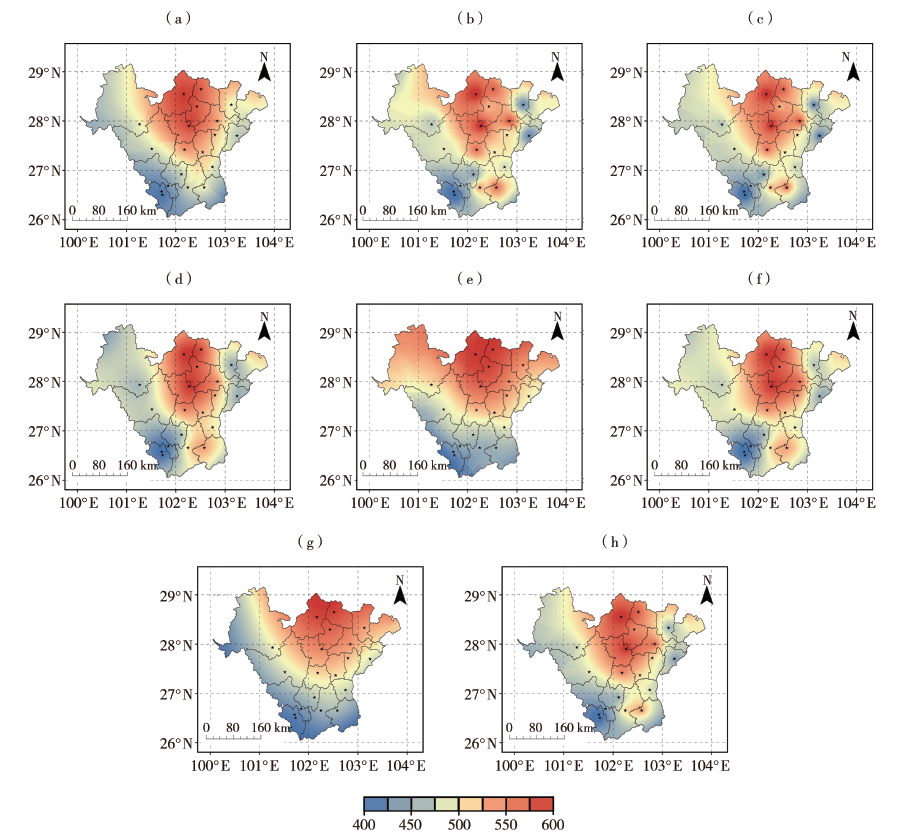
Fig.4 Comparison of interpolated results of multi-year average summer precipitation in District 1 (Unit:mm) (a) OK, (b) IDW, (c) RBF, (d) LoNdSl CoKriging g interpolation, (e) LoLaSl CoKriging interpolation, (f) LoAlSl CoKriging interpolation, (g) LPI, (h) EBK
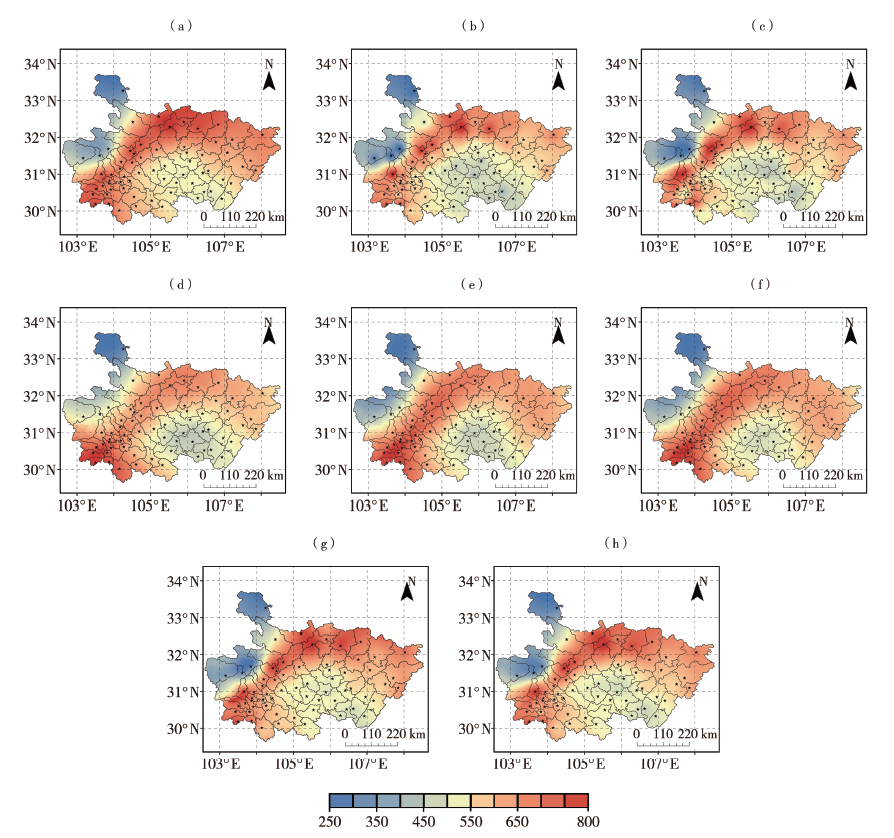
Fig.5 Comparison of interpolated results of multi-year average summer precipitation in District 2 (Unit:mm) (a) OK, (b) IDW, (c) RBF, (d) LoLaAl CoKriging interpolation, (e) LoNdSl CoKriging interpolation, (f) LoLaSl CoKriging interpolation, (g) LPI, (h) EBK

Fig.6 Comparison of interpolated results of multi-year average summer precipitation in District 3(Unit:mm) (a) OK, (b) IDW, (c) RBF, (d) LoAlNd CoKriging interpolation, (e) AlNdSl CoKriging interpolation, (f) LaAlNd CoKriging interpolation, (g) LPI, (h) EBK
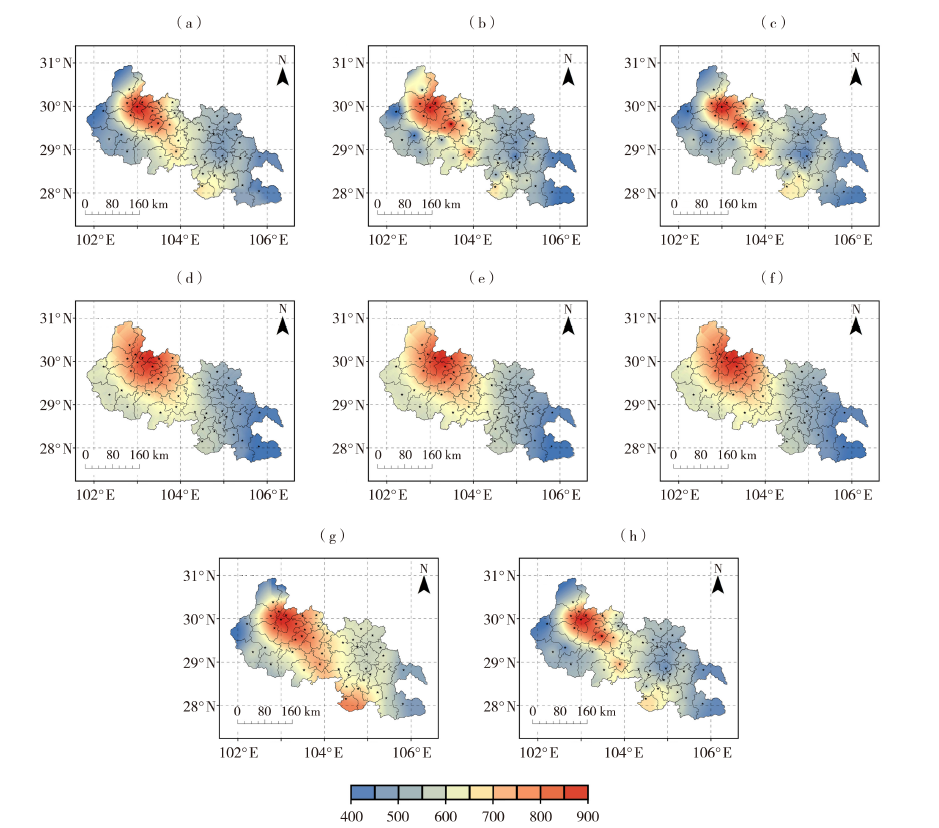
Fig.7 Comparison of interpolated results of multi-year average summer precipitation in District 3 (Unit:mm) (a) OK, (b) IDW, (c) RBF, (d) LoLaNd CoKriging interpolation, (e) LoLaSl CoKriging interpolation, (f) LoLaAl CoKriging interpolation, (g) LPI, (h) EBK (Unit: mm)
| 区域 | 插值方法 | 平均误差/mm | 平均绝对误差/mm | 标准均方根误差/mm | 综合相对误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全区 | OK | 9.61 | 49.63 | 64.51 | 9.91 |
| IDW | 9.97 | 51.62 | 69.58 | 10.48 | |
| RBF | 3.92 | 47.00 | 60.87 | 9.17 | |
| EBK | 2.61 | 46.80 | 61.08 | 9.11 | |
| AlNdSl组合CoK | 4.27 | 56.60 | 74.67 | 11.11 | |
| LaAlSl组合CoK | 2.36 | 64.07 | 85.02 | 12.51 | |
| LaAlNd组合CoK | 3.61 | 62.72 | 83.04 | 12.33 | |
| 区域1 | OK | -1.97 | 41.92 | 48.94 | 7.77 |
| IDW | -0.07 | 41.88 | 49.45 | 7.84 | |
| RBF | -0.09 | 41.29 | 48.85 | 7.69 | |
| EBK | 1.07 | 41.79 | 47.80 | 7.82 | |
| LoNdSl组合CoK | 2.57 | 39.20 | 46.58 | 7.46 | |
| LoLaSl组合CoK | 2.50 | 40.39 | 48.62 | 7.70 | |
| LoAlSl组合CoK | -1.97 | 41.92 | 48.94 | 7.77 | |
| 区域2 | OK | 2.89 | 51.95 | 73.06 | 10.60 |
| IDW | 7.05 | 52.47 | 78.70 | 11.25 | |
| RBF | 2.98 | 48.78 | 67.77 | 9.84 | |
| EBK | 2.88 | 46.52 | 64.58 | 9.26 | |
| LoLaAl组合CoK | 1.11 | 63.93 | 97.06 | 13.70 | |
| LoNdSl组合CoK | 3.19 | 58.10 | 85.58 | 12.33 | |
| LoLaSl组合CoK | 3.21 | 63.41 | 93.74 | 13.64 | |
| 区域3 | OK | 0.44 | 37.84 | 48.65 | 9.30 |
| IDW | 1.62 | 37.65 | 47.99 | 9.29 | |
| RBF | 4.68 | 32.86 | 43.66 | 8.13 | |
| EBK | 2.39 | 33.17 | 41.90 | 8.20 | |
| LoAlNd组合CoK | 0.41 | 34.87 | 43.91 | 8.60 | |
| AlNdSl组合CoK | 0.24 | 30.15 | 39.96 | 7.40 | |
| LaAlNd组合CoK | 1.12 | 37.64 | 48.57 | 9.27 | |
| 区域4 | OK | 12.23 | 75.36 | 90.80 | 13.01 |
| IDW | 18.09 | 65.22 | 85.21 | 11.46 | |
| RBF | 8.70 | 60.64 | 74.30 | 10.53 | |
| EBK | 6.30 | 61.42 | 75.53 | 10.62 | |
| LoLaNd组合CoK | 5.27 | 71.37 | 91.25 | 12.07 | |
| LoLaSl组合CoK | 5.02 | 70.93 | 90.96 | 12.00 | |
| LoLaAl组合CoK | 3.66 | 71.02 | 91.07 | 12.01 |
Tab.3 Cross-check results of multi-year average summer precipitation in the whole region and each district
| 区域 | 插值方法 | 平均误差/mm | 平均绝对误差/mm | 标准均方根误差/mm | 综合相对误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全区 | OK | 9.61 | 49.63 | 64.51 | 9.91 |
| IDW | 9.97 | 51.62 | 69.58 | 10.48 | |
| RBF | 3.92 | 47.00 | 60.87 | 9.17 | |
| EBK | 2.61 | 46.80 | 61.08 | 9.11 | |
| AlNdSl组合CoK | 4.27 | 56.60 | 74.67 | 11.11 | |
| LaAlSl组合CoK | 2.36 | 64.07 | 85.02 | 12.51 | |
| LaAlNd组合CoK | 3.61 | 62.72 | 83.04 | 12.33 | |
| 区域1 | OK | -1.97 | 41.92 | 48.94 | 7.77 |
| IDW | -0.07 | 41.88 | 49.45 | 7.84 | |
| RBF | -0.09 | 41.29 | 48.85 | 7.69 | |
| EBK | 1.07 | 41.79 | 47.80 | 7.82 | |
| LoNdSl组合CoK | 2.57 | 39.20 | 46.58 | 7.46 | |
| LoLaSl组合CoK | 2.50 | 40.39 | 48.62 | 7.70 | |
| LoAlSl组合CoK | -1.97 | 41.92 | 48.94 | 7.77 | |
| 区域2 | OK | 2.89 | 51.95 | 73.06 | 10.60 |
| IDW | 7.05 | 52.47 | 78.70 | 11.25 | |
| RBF | 2.98 | 48.78 | 67.77 | 9.84 | |
| EBK | 2.88 | 46.52 | 64.58 | 9.26 | |
| LoLaAl组合CoK | 1.11 | 63.93 | 97.06 | 13.70 | |
| LoNdSl组合CoK | 3.19 | 58.10 | 85.58 | 12.33 | |
| LoLaSl组合CoK | 3.21 | 63.41 | 93.74 | 13.64 | |
| 区域3 | OK | 0.44 | 37.84 | 48.65 | 9.30 |
| IDW | 1.62 | 37.65 | 47.99 | 9.29 | |
| RBF | 4.68 | 32.86 | 43.66 | 8.13 | |
| EBK | 2.39 | 33.17 | 41.90 | 8.20 | |
| LoAlNd组合CoK | 0.41 | 34.87 | 43.91 | 8.60 | |
| AlNdSl组合CoK | 0.24 | 30.15 | 39.96 | 7.40 | |
| LaAlNd组合CoK | 1.12 | 37.64 | 48.57 | 9.27 | |
| 区域4 | OK | 12.23 | 75.36 | 90.80 | 13.01 |
| IDW | 18.09 | 65.22 | 85.21 | 11.46 | |
| RBF | 8.70 | 60.64 | 74.30 | 10.53 | |
| EBK | 6.30 | 61.42 | 75.53 | 10.62 | |
| LoLaNd组合CoK | 5.27 | 71.37 | 91.25 | 12.07 | |
| LoLaSl组合CoK | 5.02 | 70.93 | 90.96 | 12.00 | |
| LoLaAl组合CoK | 3.66 | 71.02 | 91.07 | 12.01 |
| [1] | 陆林. 我国公共气象服务能力建设研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2013. |
| [2] | 刘红年, 徐玉貌, 张宁, 等. 大气科学概论[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 2019. |
| [3] | 黄成荣, 贾丽红, 汤浩, 等. 不同插值算法对GRAPES模式在乌鲁木齐地区的降水分级检验比较[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2011, 5(2):23-27. |
| [4] | 李颖, 张俊东, 陈庆涛. GPS大气可降水量空间插值方法对比研究[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2013, 36(1):1-6. |
| [5] | 程柏涵. 山区降水空间分布的影响因素及插值方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. |
| [6] | 李月, 齐实, 程伯涵, 等. 哀牢山山区降水时空分布的影响因素及插值方法比较[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(6):600-611. |
| [7] | 张连成, 胡列群, 李帅, 等. 基于GIS的新疆地区两种气温插值方法对比研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(2):330-336. |
| [8] | 武鹏飞, 张钧泳, 谭娇. 基于DEM修订的新疆区域气温空间插值精度优化研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2019, 13(2):108-114. |
| [9] | 朱会义, 贾绍凤. 降雨信息空间插值的不确定性分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2004, 23(2):34-42. |
| [10] | 鲁振宇, 杨太保, 郭万钦. 降水空间插值方法应用研究——以黄河源区为例[J]. 兰州大学学报, 2006, 42(4):11-14. |
| [11] | 王江, 乐章燕, 廖荣伟, 等. 中国区域温度和降水不同空间插值方法精度对比[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2016, 32(06):85-93. |
| [12] | 仲嘉亮. 基于GIS的新疆多年平均降水量空间插值精度比较研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2010, 4(4):51-54. |
| [13] |
ESTIVILL-CASTRO V, LEE I. Multi-level clustering and its visualization for exploratory spatial analysis[J]. GeoInformatica, 2002, 6(2):123-152.
DOI URL |
| [14] | HAN J, KAMBER M. Data Mining: concepts and techniques[J]. Data Mining Concepts Models Methods & Algorithms Second Edition, 2001, 5(4):1-18. |
| [15] | 赵冰雪, 王雷, 程东亚. 安徽省气象数据空间插值方法比较与分布特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(03):141-145. |
| [16] | 阳宽达, 谢红霞, 隋兵, 等. 基于GIS的降雨空间插值研究——以湖南省为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(03):134-138+145. |
| [17] | 马诺, 唐冶, 常存, 等. 基于DEM的气温空间插值方法比较[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(3):465-471. |
| [18] | 张玮玮, 张眉, 吴杨, 等. 复杂地形下浙江夏季气候要素空间插值方法评价[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4):674-682. |
| [19] | 汤国安, 杨昕. ArcGIS地理信息系统空间分析实验教程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. |
| [20] | 颜慧敏. 空间插值技术的开发与实现[D]. 成都: 西南石油学院, 2005. |
| [21] | 魏义坤, 杨威, 刘静. 关于径向基函数插值方法及其应用[J]. 沈阳大学学报, 2008(1):7-9. |
| [22] | 易湘生, 李国胜, 尹衍雨, 等. 土壤厚度的空间插值方法比较——以青海三江源地区为例[J]. 地理研究, 2012, 31(10):1793-1805. |
| [23] | 王艳妮, 谢金梅, 郭祥. ArcGIS中的地统计克里格插值法及其应用[J]. 软件导刊, 2008, 7(12):36-38. |
| [24] | 张崎. 基于Kriging方法的结构可靠性分析及优化设计[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2005. |
| [25] | 李志斌. 基于地统计学方法和Scorpan模型的土壤有机质空间模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2010. |
| [26] | 张锦明. DEM插值算法适应性研究[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2012. |
| [27] | 袁艳艳. 汉江流域降水量的空间插值研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2013. |
| [28] | 范永东. 模型选择中的交叉验证方法综述[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2013. |
| [29] | 田宏伟, 李树岩. 河南省夏玉米干旱综合风险精细化区划[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(5):852-859. |
| [30] | 李豪, 刘涛, 徐精文. 基于混合地理加权回归与克里格的区域降水量空间插值方法[J]. 中国农业气象, 2018, 39(10):674-684. |
| [1] | WEN Xiaopei, WU Wei, LI Changyi, LI Ji, XiAO Mingjing, LIU Shijun, ZHU Wengang. Influences of updated land-use datasets on WRF simulations for high-temperature weather in Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 868-878. |
| [2] | LI Tao, CHEN Jie, WANG Fang, HAN Rui. A correction algorithm of summer precipitation prediction based on neural network in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 308-316. |
| [3] | ZHOU Bin,WANG Chunxue,ZHANG Shunqian. Quasi-biennial Period Characteristics of Extreme Summer Drought Days and Its Possible Causes in Sichuan Basin During 1961-2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 727-733. |
| [4] | YU Jing,WANG Ying,GAO Yamin,QI Jiahui,FU Ming. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Surface Evapotranspiration in the Korqin Grassland Based on MOD16 Products [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 831-837. |
| [5] | ZHANG Wulong, KANG Lan, ZHOU Wei, YIN Hang, . Extreme Short-time Heavy Precipitation Forecast Based on GRAPES-MESO Model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 507-513. |
| [6] | WANG Lingling, HE Wei, LUO Mina, QIU Yue, XIAO Pei. Monitoring and analysis of summer drought based on scaled drought condition index in grassland region of the western Sichuan plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 884-893. |
| [7] | LI Yuan, LI Ruifen, ZHANG Xi. Influence of El Niño Events with Different Patterns on the Following Summer Precipitation in Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 762-770. |
| [8] | LUO Liansheng, XU Min, HE Dongyan. Interdecadal Characteristics of Summer Precipitation over Huaihe River Basinand the Associated Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies Since 2000 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 540-549. |
| [9] | ZENG Yelong1, TAN Wei1, WANG Chao2, CHEN Zhongchao1. Spatial Downscaling of TRMM 3B43 Precipitation Data Based on GWR Model in Karst Mountainous Area of Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 405-. |
| [10] | WANG Weijia, GUO Xueliang, LI Hongyu, DONG Xiaobo. Aerosols Characteristics Beneath the Clouds Based on Airborne Observation in Early Summer over Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(2): 167-175. |
| [11] | QI Dongmei1, LI Yueqing1, WANG Ying2, DENG Mengyu1, REN Qian1. Temporal-spatial Abnormity Characteristics of Drought in Sichuan Province Based on Z Index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(5): 734-744. |
| [12] | SHANG Lin, GU Weizong, TANG Zidong, MENG Xiangxin, LUO Jiali, CUI Qiang. Decadal Variation of the Relationship Between Summer Precipitation in Shandong Province and Previous Winter SST over the Equatorial Central and Eastern Pacific [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 552-558. |
| [13] | GU Shuhong1,2, HU Jiamin1,2, GU Kun2,3, ZHANG Bo1,2,GU Xiaoping1,2, CHEN Zhongyun1,2, XU Yongling1,2. Research on Drought Monitoring of Dryland Agriculture Based on Soil Water Content Simulation in Guizhou Mountainous Area [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 29-35. |
| [14] | TENG Huachao. Shandong Climate Center, Ji’nan 250031, China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(5): 789-795. |
| [15] | YUAN Shujie, LI Yuchun, XIANG Le, ZHANG Yiwei. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Direct Solar Radiation over Rugged Terrains in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 20-25. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||