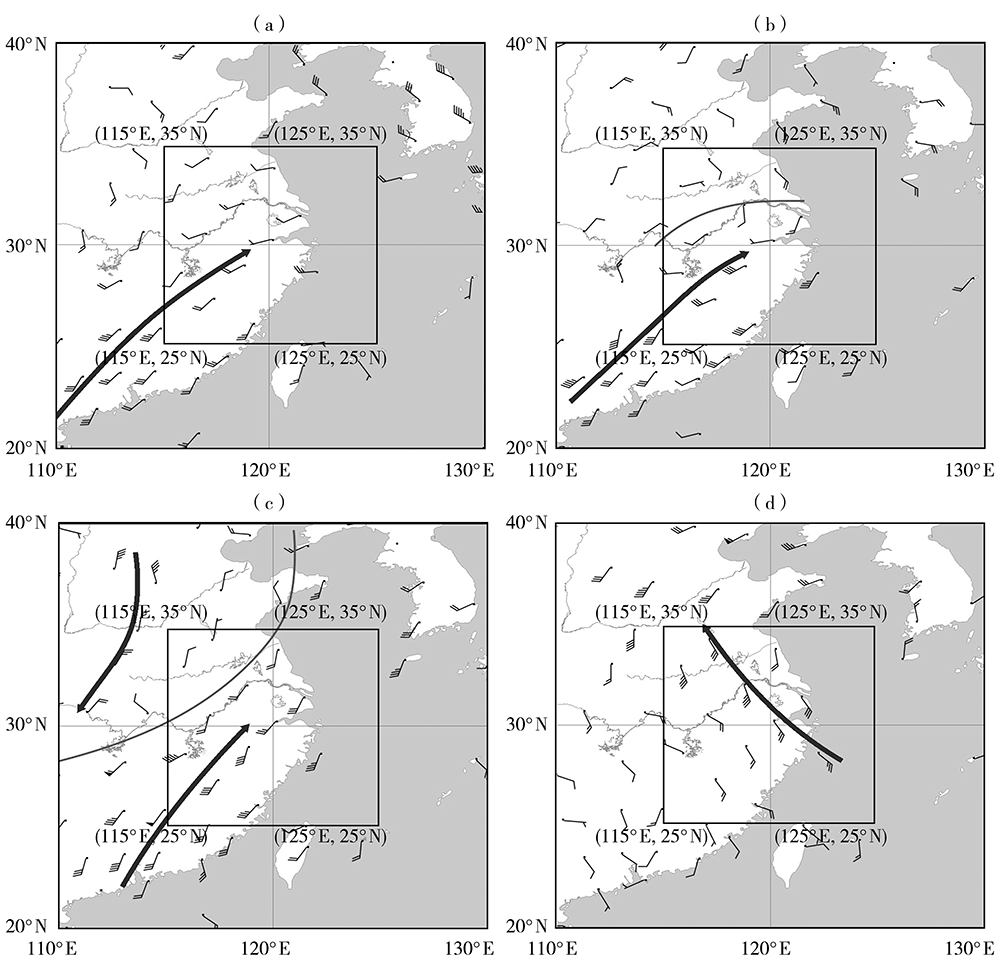
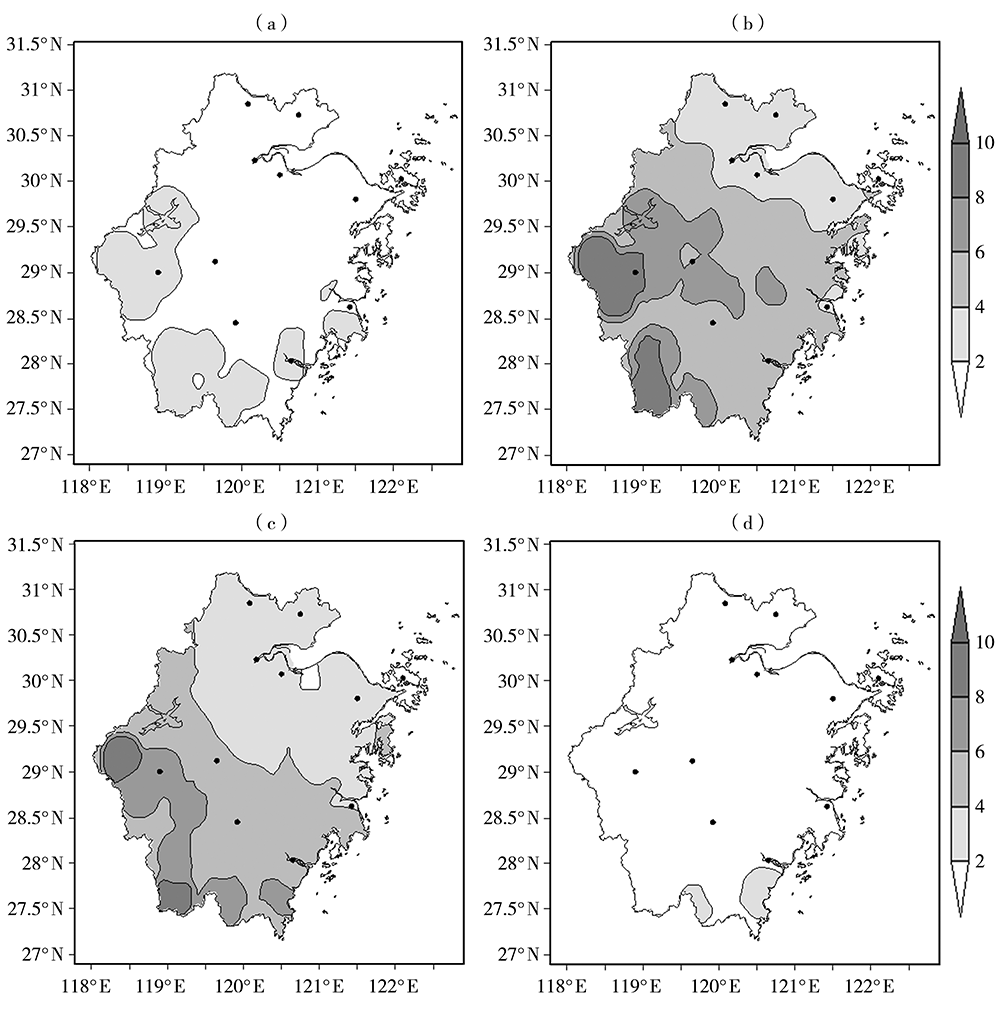
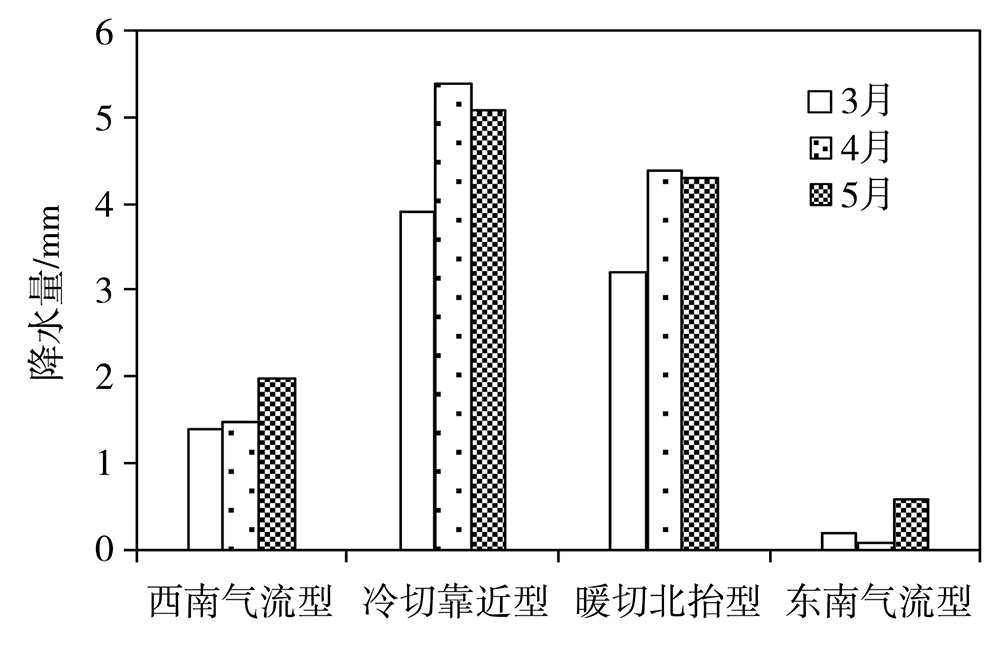
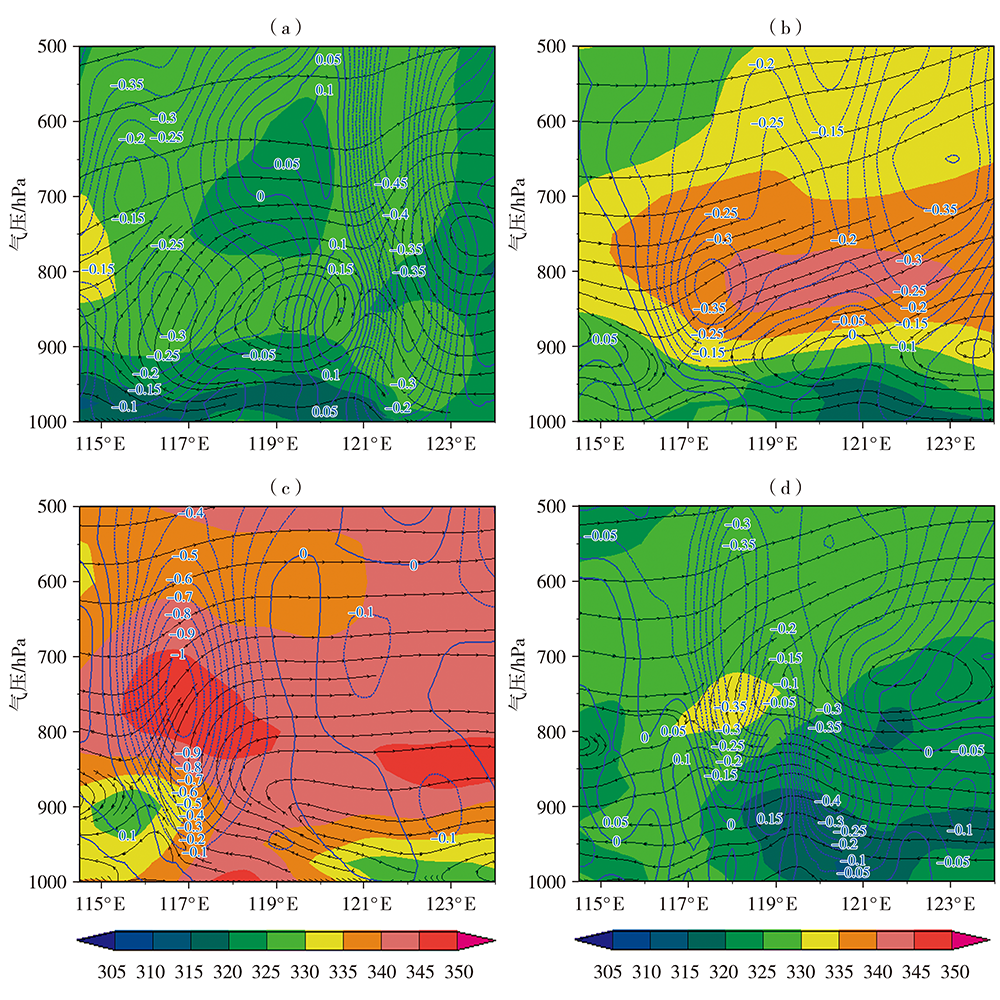
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 766-774.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-05-0766
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rainfall Characteristics of Warm Sector Weathers with Different Patterns in Spring in Zhejiang
WENG Zhimei( ),ZHOU Xuejun,GAN Jingjing,WANG Kai
),ZHOU Xuejun,GAN Jingjing,WANG Kai
- Taizhou Meteorological Bureau of Zhejiang Province, Taizhou 318000, Zhejiang, China
浙江省春季不同类型暖区天气降水特征
- 浙江省台州市气象局,浙江 台州 318000