Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 759-765.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-05-0759
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
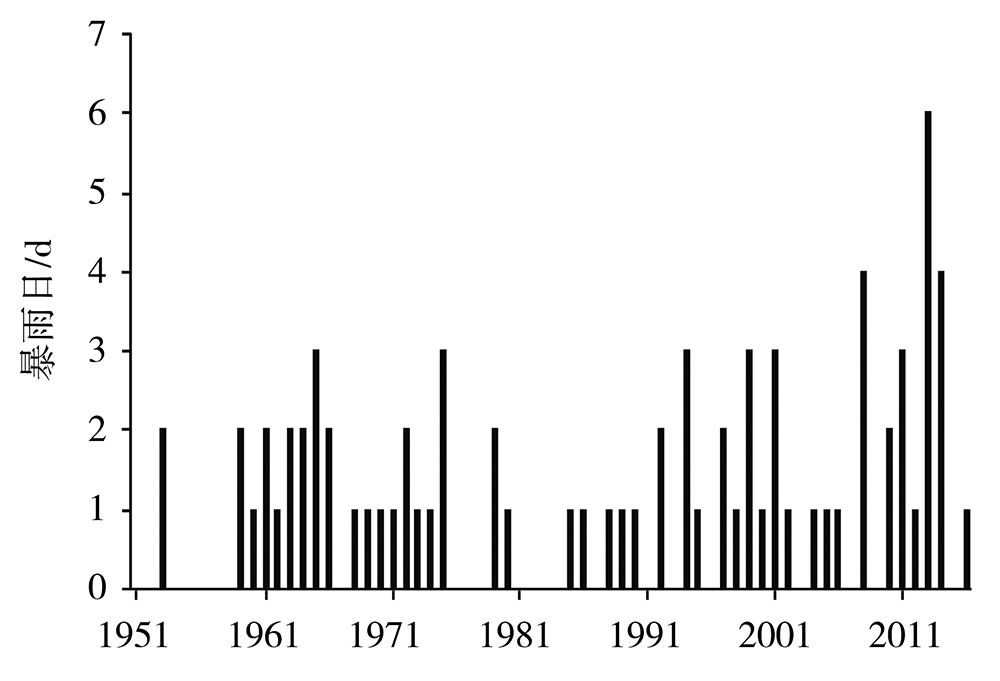
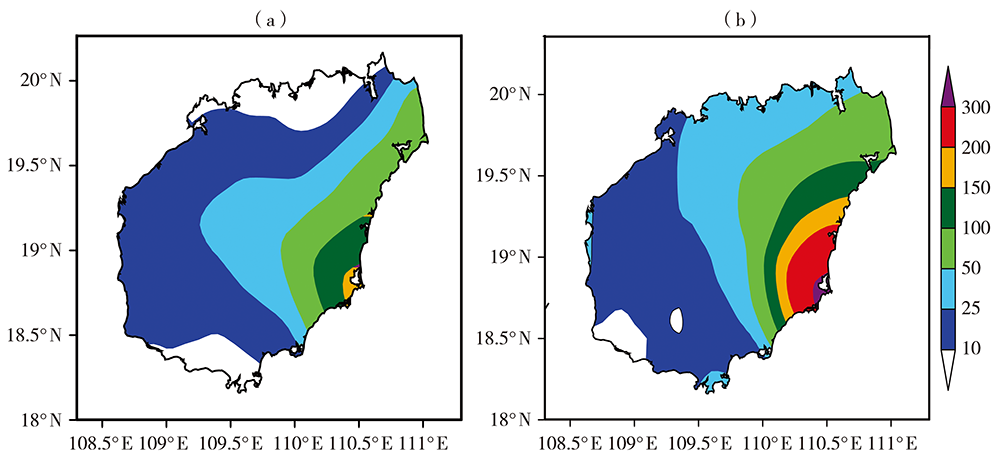
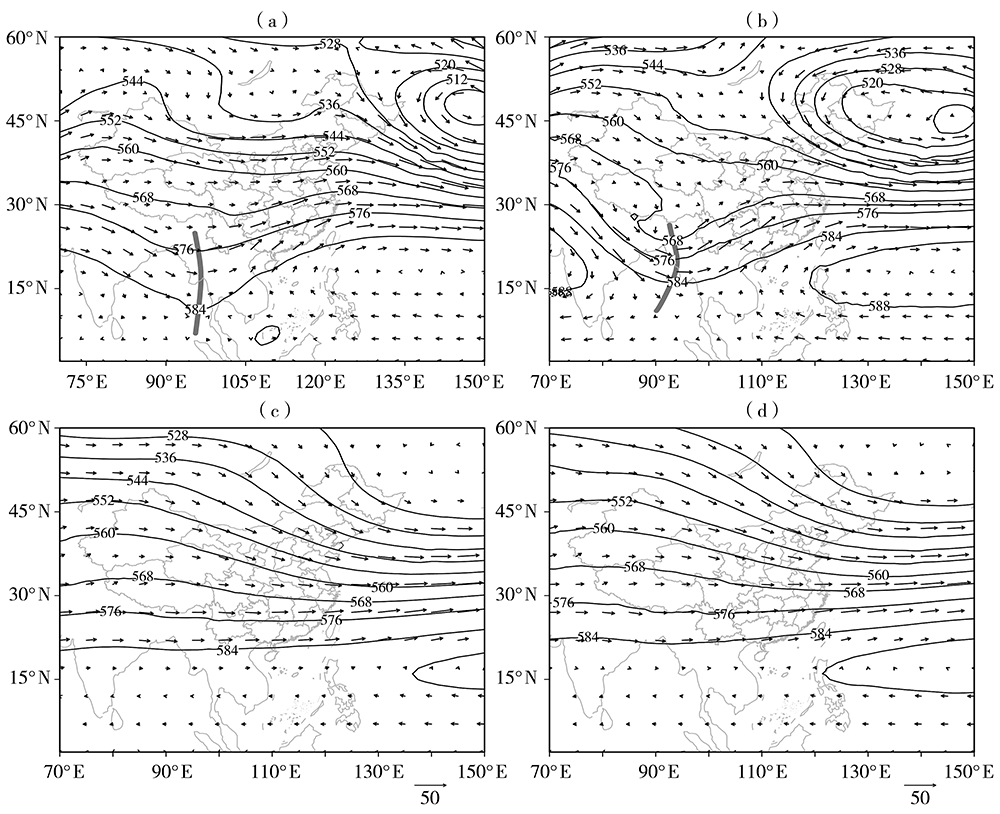
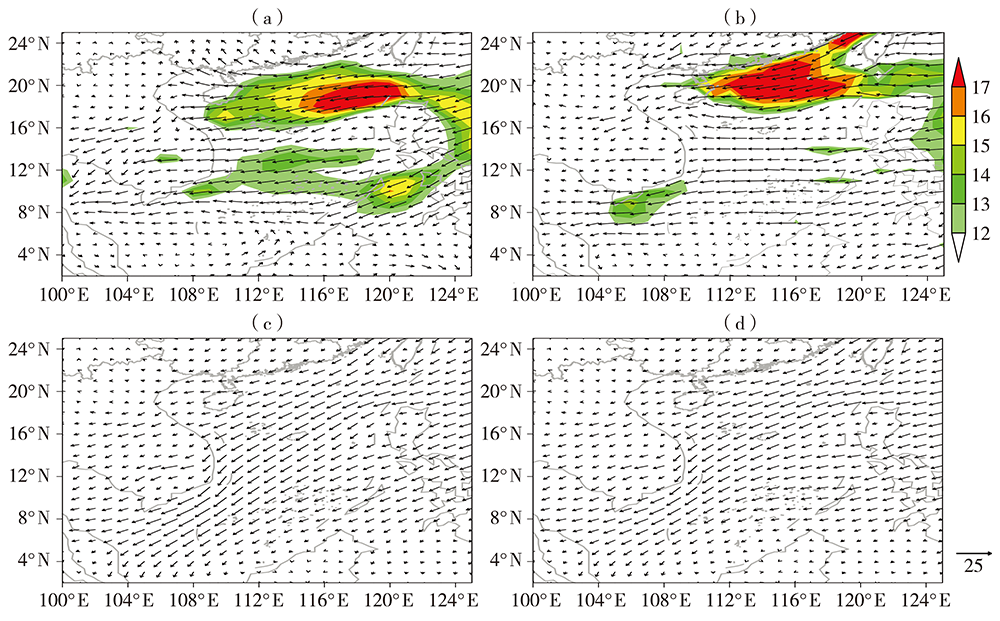
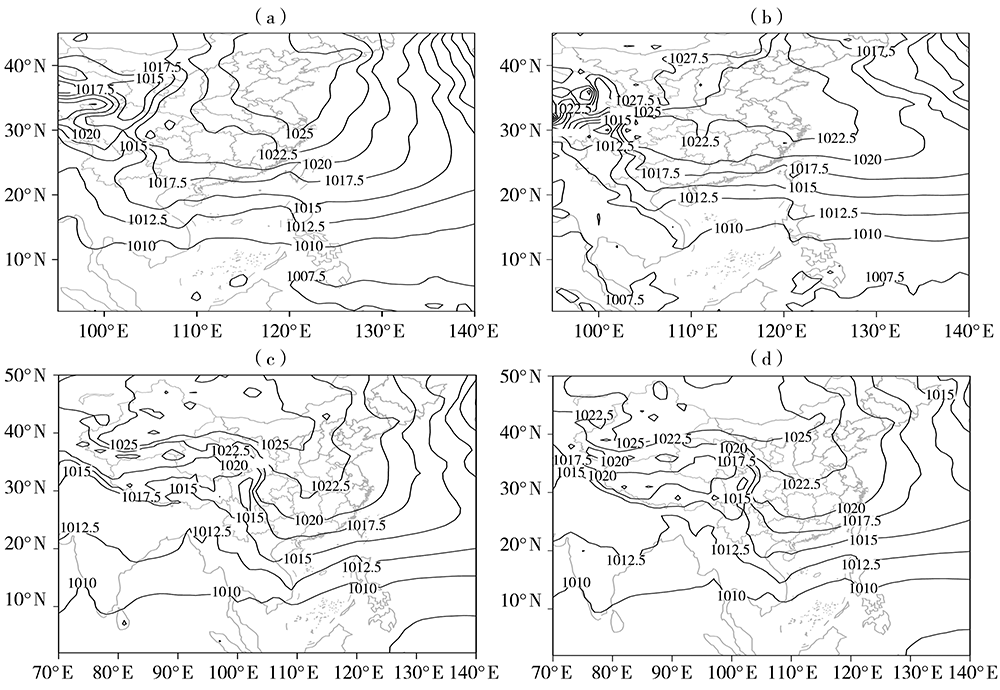
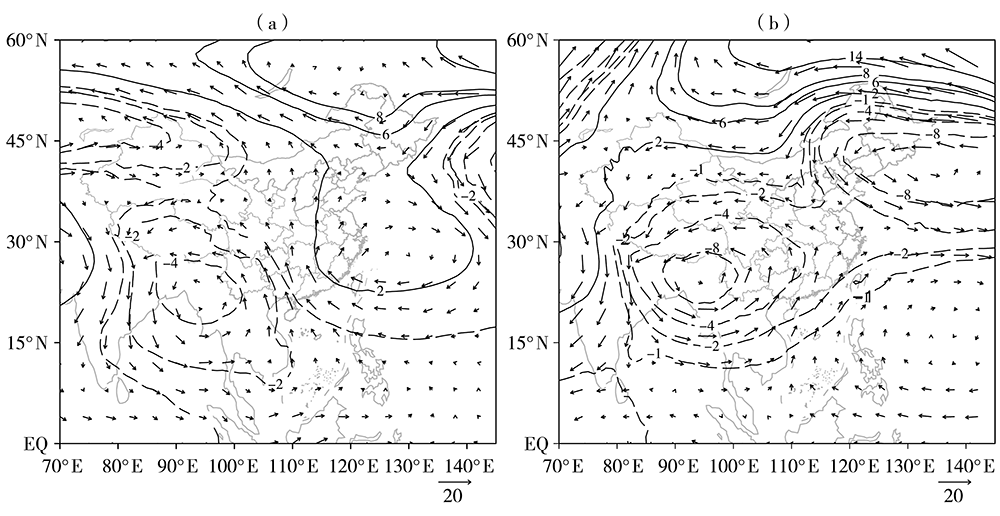
Temporal and Spatial Distribution and Anomalous Circulation Characteristics of Winter Rainstorms in Hainan Province
YANG Wei1,2( ),FENG Wen1,2,ZENG Li3,CHEN Youlong1,2(
),FENG Wen1,2,ZENG Li3,CHEN Youlong1,2( )
)
- 1. Hainan Provincial Meteorological Observatory, Haikou 570203, China
2. Key Laboratory of South China Sea Meteorological Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Hainan Province, Haikou 570203, China
3. China Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, Jiuquan 732750, Gansu, China
海南省冬季暴雨时空分布及环流异常特征
- 1.海南省气象台,海南 海口 570203
2.海南省南海气象防灾减灾重点实验室,海南 海口 570203
3.中国酒泉卫星发射中心,甘肃 酒泉 732750