干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 180-186.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0180
基于NDVI-LST模型的四川攀西地区近20 a干旱演变特征
刘兴忠1,2( ), 胡春1,2(
), 胡春1,2( ), 何超1,2, 何国平3, 马骁4, 姜绪彬5
), 何超1,2, 何国平3, 马骁4, 姜绪彬5
- 1.四川省气象探测数据中心,四川 成都 610072
2.高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
3.四川省攀枝花市气象局,四川 攀枝花 617000
4.四川省凉山州气象局,四川 凉山州 615000
5.黑龙江省气象数据中心,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150000
Evolution characteristics of drought in the Panzhihua and Liangshan regions of Sichuan Province based on NDVI-LST model in the past 20 years
LIU Xingzhong1,2( ), HU Chun1,2(
), HU Chun1,2( ), HE Chao1,2, HE Guoping3, MA Xiao4, JIANG Xubin5
), HE Chao1,2, HE Guoping3, MA Xiao4, JIANG Xubin5
- 1. Sichuan Meteorological Observation and Data Centre, Chengdu 610072, China
2. Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateau and Basin Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province chengdu 610072, China
3. Panzhihua Meteorological Office, Panzhihua 617000, Sichuan, China
4. Liangshan Meteorological Office, Liangshan 615000, Sichuan , China
5. Heilongjiang Meteorological Observation and Data Centre, Harbin 150000, China
摘要:
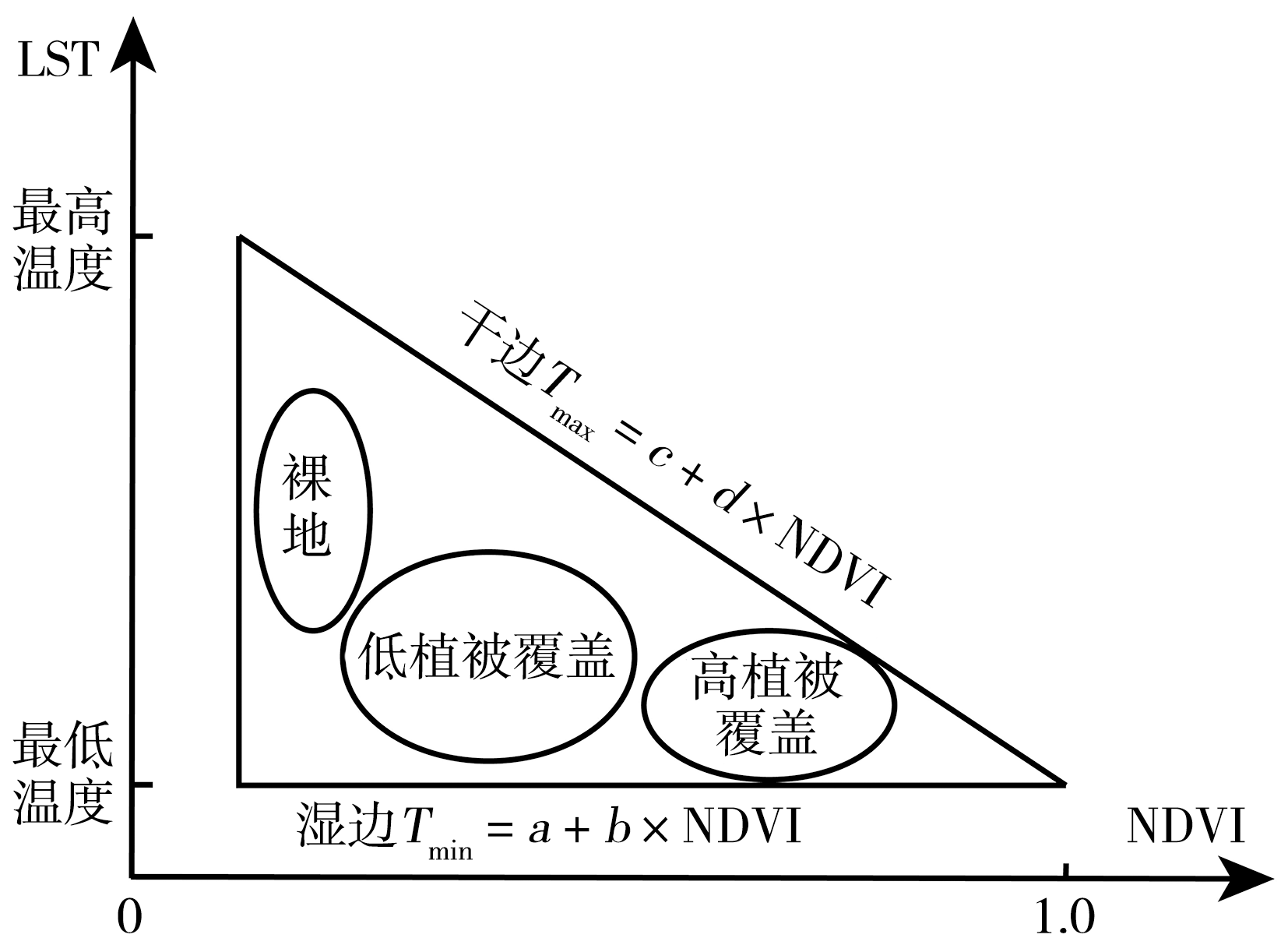
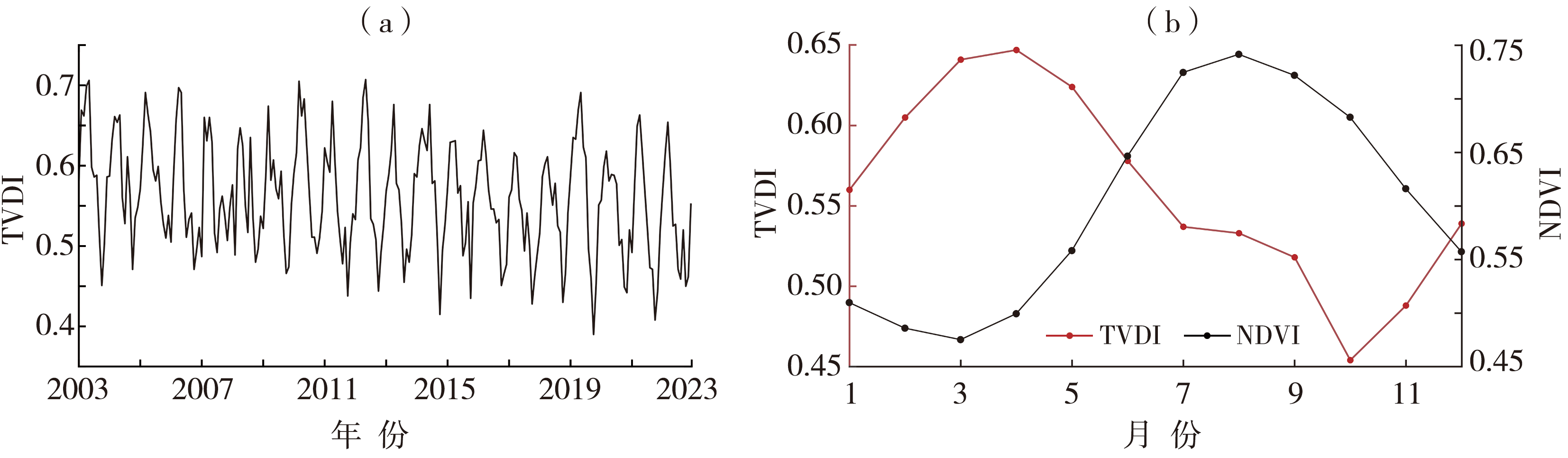
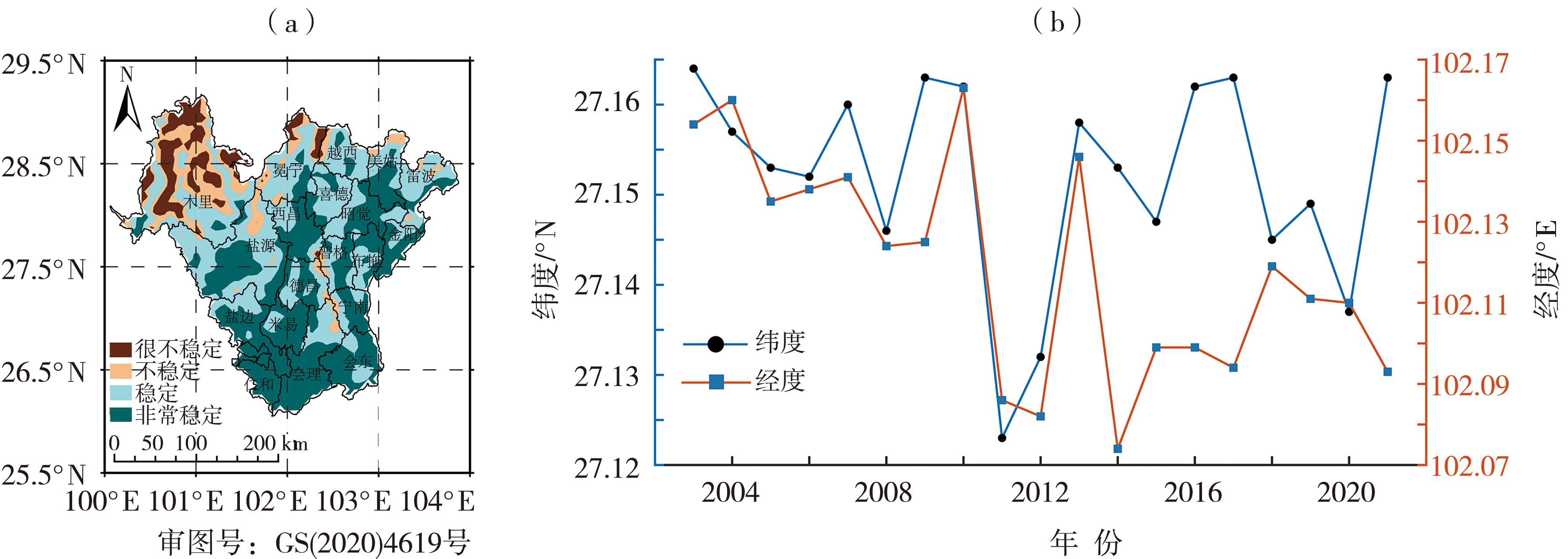
随着全球变暖不断加剧,区域性干旱事件频发,我国近些年采取了诸多措施来应对干旱事件,为分析相关措施成效,以四川攀枝花、凉山州地区(简称“攀西地区”)为例,研究该区域近20 a干旱演变特征,以服务当地生产和发展。利用中分辨率成像光谱仪(Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer,MODIS)的归一化植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI)和地表温度(Land Surface Temperature,LST)数据计算了2003—2022年攀西地区的温度植被干旱指数(Temperature Vegetation Dryness Index,TVDI),分析TVDI在不同时间尺度上的变化及该区域过去20 a来干旱的演变特征。研究表明:(1)攀西地区干旱多发生在春季的3—5月,10月前后TVDI值最低,也是最不易发生干旱的时段。(2)攀西地区干旱逐年缓解,由TVDI监测的无旱和重旱区域所占面积变化不大;轻旱面积有所增加,2013年后比之前平均增加5.30%;而中旱面积有所减少,2013年后比之前平均减少5.67%。(3)昭觉、布拖和越西等地干旱缓解明显,而木里、米易、会理等地区干旱有加重趋势。(4)攀西地区旱情大部分区域较稳定,其面积约占总面积的82.59%,干旱重心南北方向上变化较小,但有向西迁移的趋势。
中图分类号: