干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 831-845.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0831
近30 a塔克拉玛干沙漠地面气象要素变化的经向对比分析
张冠峰1( ), 廖七妹2,3(
), 廖七妹2,3( ), 何清2, 张祖莲2, 张海亮2, 孟露2, 顾军明4, 巩庆1, 郑伟1
), 何清2, 张祖莲2, 张海亮2, 孟露2, 顾军明4, 巩庆1, 郑伟1
1.新疆维吾尔自治区且末县塔中气象站 新疆 且末 841900 2.中国气象局乌鲁木齐沙漠气象研究所 ,新疆塔克拉玛干沙漠气象国家野外科学观测研究站,中国气象局塔克拉玛干沙漠气象野外科学试验基地,新疆沙漠气象与沙尘暴重点实验室 新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002 3.新疆师范大学地理科学与旅游学院 新疆 乌鲁木齐 830054 4.新疆维吾尔自治区巴音郭楞蒙古自治州气象局 新疆 库尔勒 841000
-
收稿日期:2025-08-04修回日期:2025-11-04出版日期:2025-12-31发布日期:2026-01-16 -
通讯作者:廖七妹(2000—),女,贵州铜仁人,硕士,主要研究方向为沙漠气象。E-mail: 2084734239@qq.com。
-
作者简介:张冠峰(1972—),男,河南长葛人,主要从事气象综合观测、大气边界层研究。E-mail: 2465808371@qq.com。 -
基金资助:新疆维吾尔自治区自然科学基金面上项目(2024D01A151);国家自然科学基金项目(42030612)
Meridional contrast analysis of surface meteorological variables in the Taklamakan Desert over the past 30 years
ZHANG Guanfeng1( ), LIAO Qimei2,3(
), LIAO Qimei2,3( ), HE Qing2, ZHANG Zulian2, ZHANG Hailiang2, MENG Lu2, GU Junming4, GONG Qing1, ZHENG Wei1
), HE Qing2, ZHANG Zulian2, ZHANG Hailiang2, MENG Lu2, GU Junming4, GONG Qing1, ZHENG Wei1
1. Tazhong Meteorological Station ,Qiemo County, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Qiemo 841900, Xinjiang, China 2. Urumqi Institute of Desert Meteorology ,China Meteorological Administration, National Field Scientific Observatory for Meteorology in the Taklamakan Desert, Xinjiang, Taklamakan Desert Meteorological Field Scientific Experiment Base, China Meteorological Administration, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Desert Meteorology and Sandstorms Urumqi 830002, China 3. College of Geographic Science and Tourism ,Xinjiang Normal University Urumqi 830054, China 4. Bayingolin Mongolian Autonomous Prefecture Meteorological Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Korla 841000, Xinjiang, China
-
Received:2025-08-04Revised:2025-11-04Online:2025-12-31Published:2026-01-16
摘要:
为揭示塔克拉玛干沙漠不同下垫面对气候变化的响应特征,基于塔克拉玛干沙漠北缘(轮台)、腹地(塔中)与南缘(民丰)3个站点1997—2024年的气象观测数据,采用线性趋势、M-K检验及相关性分析,对比分析近30 a该区域地面气象要素的经向变化特征。结果表明:(1)各要素年际变化区域差异显著,轮台与塔中气温先降后升,民丰持续升温,其中塔中增温最快;轮台降水显著减少,塔中微弱增加,民丰先增后减;轮台风速显著上升,塔中与民丰存在阶段性转折;日照时数仅在民丰显著下降,其余两站微升;相对湿度在轮台与塔中小幅度上升,民丰小幅度下降。(2)各要素季节变化区域特征明显,轮台秋季增温明显、风速四季显著上升、春季相对湿度上升;塔中夏季增温明显、春夏季风速波动大、夏秋季相对湿度上升;民丰春季增温明显、四季日照时数显著减少、秋冬季相对湿度下降。3站降水均集中于夏季,塔中夏季降水占比最高(约64%)。(3)各要素相关性同样呈现出区域差异,3站气温与相对湿度均呈负相关,相对湿度与降水呈正相关;气温与降水在轮台、民丰站呈正相关,在塔中则为负相关(-0.33);气温与风速在轮台为负相关,在塔中为正相关,而在民丰几乎为不相关;气温与日照时数在轮台为正相关,而在塔中、民丰站均为负相关。这些差异凸显了干旱区不同下垫面气候变化的复杂性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张冠峰, 廖七妹, 何清, 张祖莲, 张海亮, 孟露, 顾军明, 巩庆, 郑伟. 近30 a塔克拉玛干沙漠地面气象要素变化的经向对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(6): 831-845.
ZHANG Guanfeng, LIAO Qimei, HE Qing, ZHANG Zulian, ZHANG Hailiang, MENG Lu, GU Junming, GONG Qing, ZHENG Wei. Meridional contrast analysis of surface meteorological variables in the Taklamakan Desert over the past 30 years[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(6): 831-845.

图2 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站不同气象要素的相关性
Fig.2 The correlations of different meteorological elements at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024

图3 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节气温的年际变化
Fig.3 The inter-annual variations of annual and seasonal air temperatures at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [℃·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2016 | -0.34 | -1.200 4 | 不显著 | 下降 |
| 2017—2024 | 1.26 | 1.360 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.06 | 0.375 4 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.02 | 0.414 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2016 | -0.30 | -1.135 5 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 1.94 | 1.113 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.46 | -1.718 8 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2016 | -1.02 | -3.796 0 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 2017—2024 | 1.65 | 1.360 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2016 | -0.64 | -2.044 0 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 0.53 | 0.123 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2016 | -0.62 | -2.692 9 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 2.82 | 1.855 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2016 | -1.34 | -3.406 6 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 2.21 | 1.608 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.88 | -3.062 3 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 0.20 | 1.521 3 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.32 | 1.323 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.21 | 1.126 1 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 0.15 | 0.849 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.09 | 0.177 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
表1 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节气温的变化趋势检验结果
Tab.1 The test results of variation trends of annual and seasonal air temperatures at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [℃·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2016 | -0.34 | -1.200 4 | 不显著 | 下降 |
| 2017—2024 | 1.26 | 1.360 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.06 | 0.375 4 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.02 | 0.414 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2016 | -0.30 | -1.135 5 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 1.94 | 1.113 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.46 | -1.718 8 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2016 | -1.02 | -3.796 0 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 2017—2024 | 1.65 | 1.360 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2016 | -0.64 | -2.044 0 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 0.53 | 0.123 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2016 | -0.62 | -2.692 9 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 2.82 | 1.855 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2016 | -1.34 | -3.406 6 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 2.21 | 1.608 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.88 | -3.062 3 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 0.20 | 1.521 3 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.32 | 1.323 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.21 | 1.126 1 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 0.15 | 0.849 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.09 | 0.177 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |

图4 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节降水量的年际变化
Fig.4 The inter-annual variations of annual and seasonal precipitation at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [mm·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | -9.81 | -1.837 4 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | -3.05 | -0.276 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -5.43 | -1.442 2 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2008 | 18.90 | 2.262 9 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 2009—2024 | -10.03 | -1.215 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -1.07 | -0.572 9 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 1.92 | 0.592 7 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2016 | -1.55 | -0.843 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 16.45 | 1.237 2 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2016 | 2.53 | 0.908 4 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2017—2024 | -30.33 | -0.866 0 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 1.44 | 1.501 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.13 | 0.829 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2015 | 22.81 | 1.889 2 | 显著 | 上升 |
| 2016—2024 | -50.82 | -1.146 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 2.86 | 1.323 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2015 | 10.75 | 0.419 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2016—2024 | -35.45 | -0.729 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2015 | 5.47 | 0.384 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2016—2024 | -29.87 | -1.668 1 | 显著 | 下降 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.05 | 0.125 4 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
表2 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节降水量的变化趋势检验结果
Tab.2 The test results of variation trends of annual and seasonal precipitation at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [mm·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | -9.81 | -1.837 4 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | -3.05 | -0.276 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -5.43 | -1.442 2 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2008 | 18.90 | 2.262 9 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 2009—2024 | -10.03 | -1.215 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -1.07 | -0.572 9 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 1.92 | 0.592 7 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2016 | -1.55 | -0.843 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 2017—2024 | 16.45 | 1.237 2 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2016 | 2.53 | 0.908 4 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2017—2024 | -30.33 | -0.866 0 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 1.44 | 1.501 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.13 | 0.829 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2015 | 22.81 | 1.889 2 | 显著 | 上升 |
| 2016—2024 | -50.82 | -1.146 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 2.86 | 1.323 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2015 | 10.75 | 0.419 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2016—2024 | -35.45 | -0.729 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2015 | 5.47 | 0.384 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2016—2024 | -29.87 | -1.668 1 | 显著 | 下降 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.05 | 0.125 4 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
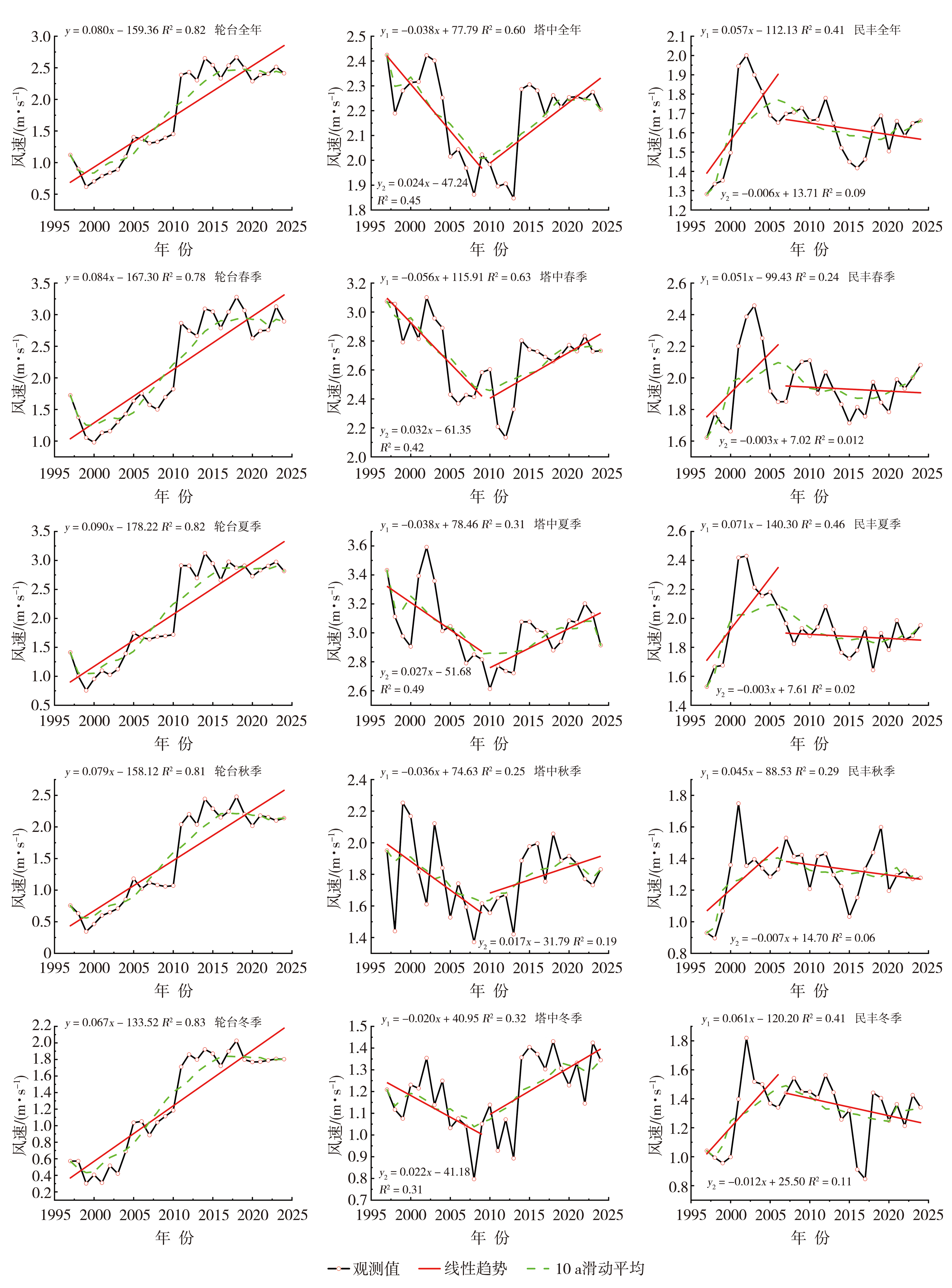
图5 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节风速的年际变化
Fig.5 The inter-annual variations of annual and seasonal wind speed at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [m·s⁻¹·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 0.80 | 4.919 4 | 显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.84 | 4.879 9 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.90 | 4.800 8 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 0.79 | 4.603 3 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.67 | 5.057 7 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2000 | -0.38 | -2.379 3 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 2010—2024 | 0.24 | 0.890 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2000 | -0.56 | -2.501 4 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.32 | 2.177 4 | 显著 | 上升 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2000 | -0.38 | -2.379 3 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.27 | 2.226 9 | 显著 | 上升 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2000 | -0.36 | -1.769 3 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.17 | 1.039 2 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2000 | -0.20 | -1.708 2 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.22 | 1.484 6 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2006 | 0.57 | 1.431 1 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 2007—2024 | -0.06 | -1.590 9 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2006 | 0.51 | 1.431 1 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.03 | -0.303 0 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2006 | 0.71 | 1.610 0 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.03 | -0.378 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2006 | 0.45 | 0.715 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.07 | -1.060 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2006 | 0.61 | 1.073 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.12 | -2.310 5 | 显著 | 下降 | ||
表3 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节风速的变化趋势检验结果
Tab.3 The test results of variation trends of annual and seasonal wind speed at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [m·s⁻¹·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 0.80 | 4.919 4 | 显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.84 | 4.879 9 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.90 | 4.800 8 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 0.79 | 4.603 3 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 0.67 | 5.057 7 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2000 | -0.38 | -2.379 3 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 2010—2024 | 0.24 | 0.890 8 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2000 | -0.56 | -2.501 4 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.32 | 2.177 4 | 显著 | 上升 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2000 | -0.38 | -2.379 3 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.27 | 2.226 9 | 显著 | 上升 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2000 | -0.36 | -1.769 3 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.17 | 1.039 2 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2000 | -0.20 | -1.708 2 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2010—2024 | 0.22 | 1.484 6 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2006 | 0.57 | 1.431 1 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 2007—2024 | -0.06 | -1.590 9 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 春季 | 1997—2006 | 0.51 | 1.431 1 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.03 | -0.303 0 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 夏季 | 1997—2006 | 0.71 | 1.610 0 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.03 | -0.378 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2006 | 0.45 | 0.715 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.07 | -1.060 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | ||
| 冬季 | 1997—2006 | 0.61 | 1.073 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 2007—2024 | -0.12 | -2.310 5 | 显著 | 下降 | ||

图6 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节日照时数的年际变化
Fig.6 The inter-annual variations of annual and seasonal sunshine duration at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [h·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 55.49 | 0.829 8 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 24.54 | 1.205 1 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.09 | 0.059 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 6.07 | 0.572 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 24.78 | 1.224 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 51.98 | 1.086 6 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 18.45 | 0.790 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -10.26 | -0.553 2 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 14.38 | 1.027 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 29.41 | 2.449 8 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | -180.30 | -3.299 3 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | -38.73 | -2.469 6 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -78.50 | -3.556 2 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | -33.63 | -2.647 4 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -29.44 | -2.311 5 | 显著 | 下降 | |
表4 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节日照时数的变化趋势检验结果
Tab.4 The test results of variation trends of annual and seasonal sunshine duration at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [h·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 55.49 | 0.829 8 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 24.54 | 1.205 1 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 0.09 | 0.059 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 6.07 | 0.572 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 24.78 | 1.224 9 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 51.98 | 1.086 6 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 18.45 | 0.790 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -10.26 | -0.553 2 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 14.38 | 1.027 3 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | 29.41 | 2.449 8 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | -180.30 | -3.299 3 | 显著 | 下降 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | -38.73 | -2.469 6 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -78.50 | -3.556 2 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | -33.63 | -2.647 4 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -29.44 | -2.311 5 | 显著 | 下降 | |

图7 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节相对湿度的年际变化
Fig.7 The inter-annual variations of annual and seasonal relative humidity at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [%·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 0.42 | 1.126 1 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.17 | 0.371 2 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2010 | -9.93 | -3.832 1 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2011—2024 | 0.64 | 0.109 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | -0.02 | -0.059 3 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.30 | -0.454 4 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 1.29 | 1.639 8 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 1.03 | 1.402 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 2.28 | 2.785 7 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 2.27 | 2.489 3 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.54 | -0.256 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | -0.98 | -1.639 8 | 不显著 | 下降 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | -0.60 | -0.750 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -0.82 | -0.928 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | -1.51 | -1.955 9 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -1.09 | -0.928 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
表5 1997—2024年塔克拉玛干沙漠轮台、塔中和民丰站全年和不同季节相对湿度的变化趋势检验结果
Tab.5 The test results of variation trends of annual and seasonal relative humidity at Luntai, Tazhong and Minfeng stations in the Taklamakan Desert during 1997-2024
| 站点 | 时段 | 趋势斜率/ [%·(10 a)-1] | Mann-Kendall检验 | 变化特征 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | 显著性 | |||||
| 轮台 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 0.42 | 1.126 1 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 0.17 | 0.371 2 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2010 | -9.93 | -3.832 1 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 2011—2024 | 0.64 | 0.109 5 | 不显著 | 上升 | ||
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | -0.02 | -0.059 3 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.30 | -0.454 4 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 塔中 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | 1.29 | 1.639 8 | 不显著 | 上升 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | 1.03 | 1.402 7 | 不显著 | 上升 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | 2.28 | 2.785 7 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | 2.27 | 2.489 3 | 显著 | 上升 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -0.54 | -0.256 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 民丰 | 全年 | 1997—2024 | -0.98 | -1.639 8 | 不显著 | 下降 |
| 春季 | 1997—2024 | -0.60 | -0.750 8 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 夏季 | 1997—2024 | -0.82 | -0.928 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| 秋季 | 1997—2024 | -1.51 | -1.955 9 | 显著 | 下降 | |
| 冬季 | 1997—2024 | -1.09 | -0.928 6 | 不显著 | 下降 | |
| [1] | 爱沙江·艾力, 瓦尔斯江·阿布力孜, 艾尼瓦尔·居马, 2001. 新疆轮台县县域经济可持续发展研究[J]. 新疆经济管理干部学院学报(1): 9-12. |
| [2] | 顾军明, 霍文, 艾力·买买提明, 等, 2014. 塔克拉玛干沙漠北缘近地层气象要素变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 32(2): 239-247. |
| [3] | 黄俊利, 魏文寿, 杨青, 等, 2012. 塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘极端降水变化趋势与突变特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 6(2):30-34. |
| [4] | 江远安, 陈鹏翔, 邵伟玲, 等, 2015. 近50 a塔克拉玛干沙漠和古尔班通古特沙漠及其周边地区气候变化特征的对比分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 9(3):14-23. |
| [5] | 姜婷婷, 谷海斌, 盛建东, 2014. 基于GIS技术的耕地地力评价研究: 以新疆轮台县为例[J]. 新疆农业科学, 51(2): 375-383. |
| [6] | 李玲萍, 胡丽莉, 刘维成, 等, 2017. 河西走廊东部夏季沙尘暴气象要素变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 35(3): 427-432. |
| [7] | 李智宽, 谭成好, 杨婕, 等, 2024. 21世纪以来新疆地区沙尘暴时空变化及其关键气象影响因子[J]. 环境科学学报, 44(10): 1-9. |
| [8] | 刘树华, 胡予, 胡非, 等, 2005. 沙漠-绿洲陆-气相互作用和绿洲效应的数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(5): 1 019-1 027. |
| [9] | 刘一玮, 王彦, 王庆元, 2021. 降水与相对湿度协同算法研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(5):49-54. |
| [10] | 罗凤敏, 高君亮, 辛智鸣, 等, 2020. 乌兰布和沙漠东北部不同下垫面的小气候变化特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 36(10):124-133. |
| [11] | 齐斐斐, 买买提艾力·买买提依明, 霍文, 等, 2020. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地地表辐射和能量平衡及小气候特征[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1):32-39. |
| [12] | 孙蕾, 伏晓慧, 张金柱, 2014. 迁站和仪器更换对阿拉山口风速资料的影响分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 8(2):65-69. |
| [13] | 唐舰, 何秉宇, 姜红, 2006. 近50年塔里木盆地南缘孤立绿洲气候变化分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 20(5): 95-98. |
| [14] | 吴丽萍, 杨余辉, 杨景燕, 等, 2022. 新疆北部地区不同下垫面区域气候变化差异分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 61(11):19-26. |
| [15] | 杨莲梅, 2003. 塔克拉玛干地区气候变化对全球变暖的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 23(5): 21-26. |
| [16] | 伊尔夏提·艾力, 2012. 塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘民丰地区气候与沙尘气溶胶观测分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. |
| [17] | 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌, 2025. 古气候暖期对预估2300年全球变暖的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 21(5):729-732. |
| [18] | 周波涛, 钱进, 2021. IPCC AR6报告解读:极端天气气候事件变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6): 713-718. |
| [19] | 周成龙, 杨兴华, 钟昕洁, 等, 2017. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地沙尘天气特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 34(2): 324-329. |
| [20] | 周雪英, 贾健, 刘国强, 等, 2019. 1997—2017年塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地降水特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 39(1):187-194. |
| [21] | AZORIN-MOLINA C, ALI SAFAEI PIROOZ A, BEDOYA-VALESTT S, et al, 2023. Biases in wind speed measurements due to anemometer changes[J]. Atmospheric Research, 289: 106771. DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2023.106771. |
| [22] | DING Y H, WANG H J, 2016. Newly acquired knowledge on the scientific issues related to climate change over the recent 100 years in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61(10): 1 029-1 041. |
| [23] | DONG W H, MING Y, DENG Y, et al, 2024. Recent wetting trend over Taklamakan and Gobi Desert dominated by internal variability[J]. Nature Communications, 15: 4 379. DOI:10.1038/s41467-024-48743-x. |
| [24] | JIANG Q D, YANG X P, 2019. Sedimentological and geochemical composition of aeolian sediments in the taklamakan desert: Implications for provenance and sediment supply mechanisms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 124(5): 1 217-1 237. |
| [25] | KENDALL M G, 1970. Rank correlation methods 4th edition[M]. London: Charles Griffin. |
| [26] | KOTHAWALE D R, RUPA KUMAR K, 2005. On the recent changes in surface temperature trends over India[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(18): 2005GL023528. DOI:10.1029/2005GL023528. |
| [27] | LI M Y, YAO J Q, 2023. Precipitation extremes observed over and around the Taklimakan Desert, China[J]. PeerJ, 11: e15256. DOI:10.7717/peerj.15256. |
| [28] | LIUZZO L, BONO E, SAMMARTANO V, et al, 2016. Analysis of spatial and temporal rainfall trends in Sicily during the 1921-2012 period[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 126(1): 113-129. |
| [29] | MANN H B, 1945. Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometric, 13(3): 245-259. |
| [30] | ONGOMA V, CHEN H S, 2017. Temporal and spatial variability of temperature and precipitation over East Africa from 1951 to 2010[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 129(2): 131-144. |
| [31] | PEARSON K, 1916. On some novel properties of partial and multiple correlation coefficients in a universe of manifold characteristics[J]. Biometrika, 11(3): 231-238. |
| [32] | REVESZ R L, HOWARD P H, ARROW K, et al, 2014. Global warming: Improve economic models of climate change[J]. Nature, 508(7495): 173-175. |
| [33] | SU Y N, WANG X, LUO X J, et al, 2025. Warming-induced increase in flooding in the Taklimakan Desert[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 36(3): 1 351-1 354. |
| [34] | TANG S J, ZHOU T J, ZHANG L X, et al, 2024. Moisture sources for the unprecedented precipitation event in the heart of Taklimakan desert[J]. Weather and Climate Extremes, 46: 100739. DOI:10.1016/j.wace.2024.100739. |
| [35] | WHEELER T, VON BRAUN J, 2013. Climate change impacts on global food security[J]. Science, 341(6145): 508-513. |
| [36] | YANG F, HE Q, HUANG J P, et al, 2020. Desert environment and climate observation network over the Taklimakan Desert[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 102(6): E1 172-E1 191. |
| [37] | ZHANG W T, YE G L, LEUNG J C, et al, 2025. Microphysical characteristics of summer precipitation over the taklamakan desert based on GPM-DPR data from 2014 to 2023[J]. Atmosphere, 16(4): 354. DOI: 10.3390/atmos16040354. |
| [38] | ZHOU B T, QIAN J, 2021. Changes of weather and climate extremes in the IPCC AR6[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 17(6): 713-718. |
| [1] | 刘宗瑞, 万紫悦, 赵宇瀚, 刘卫平, 王若安, 马玉霞. 基于机器学习的环流分型与甘肃大气污染机制研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 563-575. |
| [2] | 沈姣姣, 郝苏娟, 金丽娜, 张雅斌, 樊丹丹, 郭琦. 近60 a西安城市化对气候环境的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 403-412. |
| [3] | 陈敏, 陈豫英, 陈荣, 陈宇曦, 杨苑媛. 贺兰山东麓暴雨天气分型及气象要素演变特征研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 413-423. |
| [4] | 王敏, 孙树峻, 张健, 李天方, 陈锐, 杨星, 肖雅文. 甘孜州植被覆盖度演变特征及其与气候因子的相关性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 944-952. |
| [5] | 董元柱, 王天河, 谭睿琦, 王思晨, 焦英姿, 唐靖宜. 西北干旱区荒漠戈壁两次极端沙尘事件的对比研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 197-208. |
| [6] | 王孝慈, 王继竹, 孟英杰, 李双君. 2016—2020年长江沿线雾的特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 734-743. |
| [7] | 潘留杰, 梁绵, 祁春娟, 李培荣, 朱庆亮. “十四运”关键场馆气象要素特征及客观预报检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 491-502. |
| [8] | 陈荣, 王建英, 杨文军, 陈敏, 王谦, 李琨. 银川市大气边界层逆温影响因素及其与冬季PM2.5的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 123-131. |
| [9] | 李正鹏, 闭建荣, 左大鹏, 张琳焓, 杨帆. 2019年8和9月西北干旱区塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地云的宏观参量特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 567-576. |
| [10] | 张亚春, 马耀明, 马伟强, 王宾宾, 王玉阳, . 青藏高原不同下垫面蒸散量及其与气象因子的相关性[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 366-373. |
| [11] | 杨婧, 朱海斌, 刘建军, 严晓瑜, 纳丽, 刘玉兰. 气象条件对银川市区近地面臭氧质量浓度的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 302-308. |
| [12] | 龚静, 朱世珍, 张鹏亮, 王启花, 王丽霞, 郭三刚, 张博越. 青海省东部地区云特征参量与降水相关性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(06): 948-956. |
| [13] | 黄开龙, 林锦春, 马盼, 黄文静, 陆俊翔, 唐小新, 王式功. 气象条件对深圳市罗湖区上呼吸道感染就诊人数的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(06): 995-1005. |
| [14] | 曹寰琦, 何清, , 金莉莉, 李振杰, 赵佳伟, 杨兴华, . 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地地表能量平衡闭合特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6): 955-964. |
| [15] | 李汉林, 何清, 金莉莉. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地和北缘典型天气近地层风速廓线特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6): 965-978. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

