干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 265-276.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-02-0265
云南省一次罕见飑线过程发生机制分析
杨芳园1,3( ), 杨素雨2,3, 甄廷忠1(
), 杨素雨2,3, 甄廷忠1( ), 杨竹云2,3, 李晓鹏1, 胡勇华4, 石宝灵1
), 杨竹云2,3, 李晓鹏1, 胡勇华4, 石宝灵1
- 1.云南省昆明市气象局,云南 昆明 650034
2.云南省气象台,云南 昆明 650034
3.中国气象局横断山区(低纬高原)灾害性天气研究中心,云南 昆明 650034
4.云南省玉溪市红塔区气象局,云南 玉溪 653100
-
收稿日期:2024-03-21修回日期:2024-09-14出版日期:2025-04-30发布日期:2025-05-13 -
通讯作者:甄廷忠(1986—),男,重庆人,高级工程师,主要从事雷达探测及资料应用。E-mail: 584381750@qq.com。 -
作者简介:杨芳园(1987—),女,云南玉溪人,高级工程师,主要从事强对流天气机理及气候效应研究。E-mail: yfy_zh@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局水文气象重点开放实验室开放研究课题项目(23SWQXZ009);中国气象局2025年度复盘总结专项(FPZJ2025-123);云南省气象局基层台站计划项目(STIAP202201);云南省气象局青年科技创新团队项目(2022QN04)
Mechanism analysis of a rare squall line process in Yunnan Province
YANG Fangyuan1,3( ), YANG Suyu2,3, ZHEN Tingzhong1(
), YANG Suyu2,3, ZHEN Tingzhong1( ), YANG Zhuyun2,3, LI Xiaopeng1, HU Yonghua4, SHI Baoling1
), YANG Zhuyun2,3, LI Xiaopeng1, HU Yonghua4, SHI Baoling1
- 1. Kunming Meteorological Bureau of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650034, China
2. Meteorological Observatory of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650034, China
3. Research Center for Disasrous Weather over Hengduan Mountains & Low-Latitude Plateau, CMA, Kunming 650034, China
4. Hongta District Meteorological Bureau of Yunnan Province, Yuxi 653100, Yunnan, China
-
Received:2024-03-21Revised:2024-09-14Online:2025-04-30Published:2025-05-13
摘要: 基于地面自动站、多波段天气雷达、实况探空及欧洲中期天气预报中心(European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting,ECMWF)第5代再分析资料ERA5,对2022年7月7日云南省一次罕见飑线天气过程的环境条件、中尺度特征及维持机制进行了分析。结果表明,此次飑线过程发生在大陆高压与副热带高压辐合区内,环境场具有较强对流不稳定能量、中等强度垂直风切变及明显的高层干冷空气入侵特征。C波段雷达反射率和径向速度的变化与地面大风、冰雹的发生有很好的对应关系,飑线特征明显,近地层入流急流明显,伴随速度模糊和阵风锋特征;降雹单体具有三体散射、中层辐合和风暴顶辐散特征;X波段双偏振相控阵雷达的高时空分辨率观测显示,成熟冰雹云的强反射率因子超过55 dBZ,强上升气流附近存在明显的差分反射率(ZDR)柱,垂直伸展至高于湿球温度0 ℃层的高度;双偏振参数还表明,冰雹降落过程中伴有降水。分析认为,地面辐合线的持续维持、风暴内部上升气流与倾斜下沉气流共存,以及低层辐合与高层辐散配合,是此次飑线得以维持的主要机制。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨芳园, 杨素雨, 甄廷忠, 杨竹云, 李晓鹏, 胡勇华, 石宝灵. 云南省一次罕见飑线过程发生机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(2): 265-276.
YANG Fangyuan, YANG Suyu, ZHEN Tingzhong, YANG Zhuyun, LI Xiaopeng, HU Yonghua, SHI Baoling. Mechanism analysis of a rare squall line process in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 265-276.

图1 云南省2022年7月7日14:00—23:00强对流天气时空演变注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图[审图号:GS(2019)1783号]制作,底图边界无修改,下同。
Fig.1 Temporal and spatial evolution of strong convective weather from 14:00 to 23:00 on 7 July in Yunnan Province

图2 2022年7月7日08:00(a、c)、20:00(b、d)500 hPa(a、b)风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)、位势高度场(黑色等值线,单位:dagpm)和温度场(红色虚线,单位:℃),700 hPa(c、d)切变线(棕色实线)和水汽通量(箭矢,单位:g·cm-2·hPa-1·s-1)、水汽通量散度(填色,单位:10-5 g·cm-2·hPa-1·s-1) (红色粗实线范围为云南省,黑色粗实线为辐合区,字母D为低压中心)
Fig.2 The wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1), geopotential height field (black contours, Unit: dagpm) and temperature field (red dashed lines, Unit: ℃) at 500 hPa (a, b), and shear lines (brown lines), water vapor flux (arrow vectors, Unit: g·cm-2·hPa-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence (the color shaded, Unit: 10-5 g·cm-2·hPa-1·s-1) at 700 hPa (c, d) at 08:00 (a, c) and 20:00 (b, d) on 7 July 2022 (The red thick solid line rang is Yunnan Province, the black thick line is convergence zone, the letter D is the low pressure center)
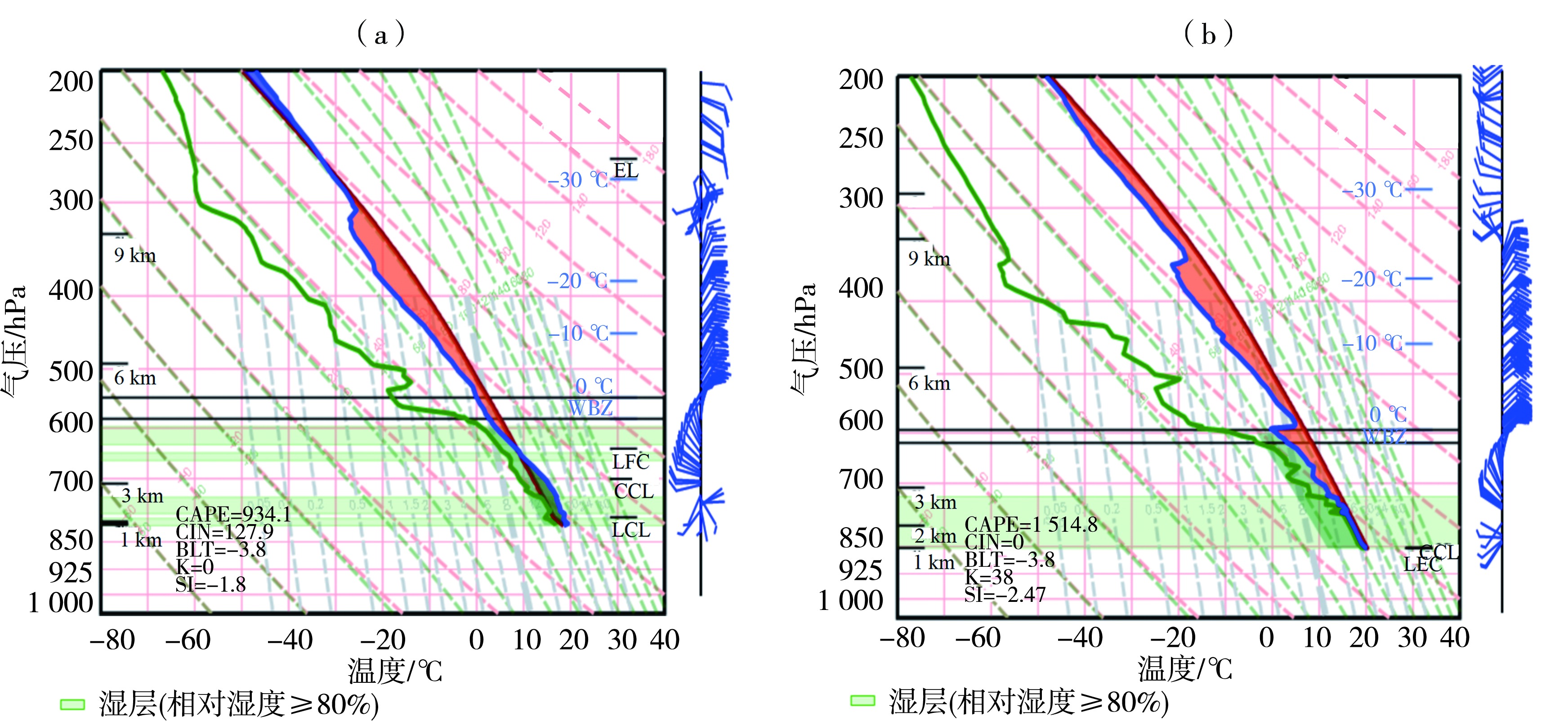
图3 2022年7月7日08:00云南昆明(a)、普洱(b)探空站T-ln P图 (蓝色实线为温度层结曲线,绿色实线为露点温度曲线,红色实线为状态曲线)
Fig.3 T-ln P diagram of Kunming (a), Pu'er (b) souding stations at 08:00 on 7 July 2022 (The blue line represents stratification curve, the green line represents dew point temperature and the red line represents state curve)
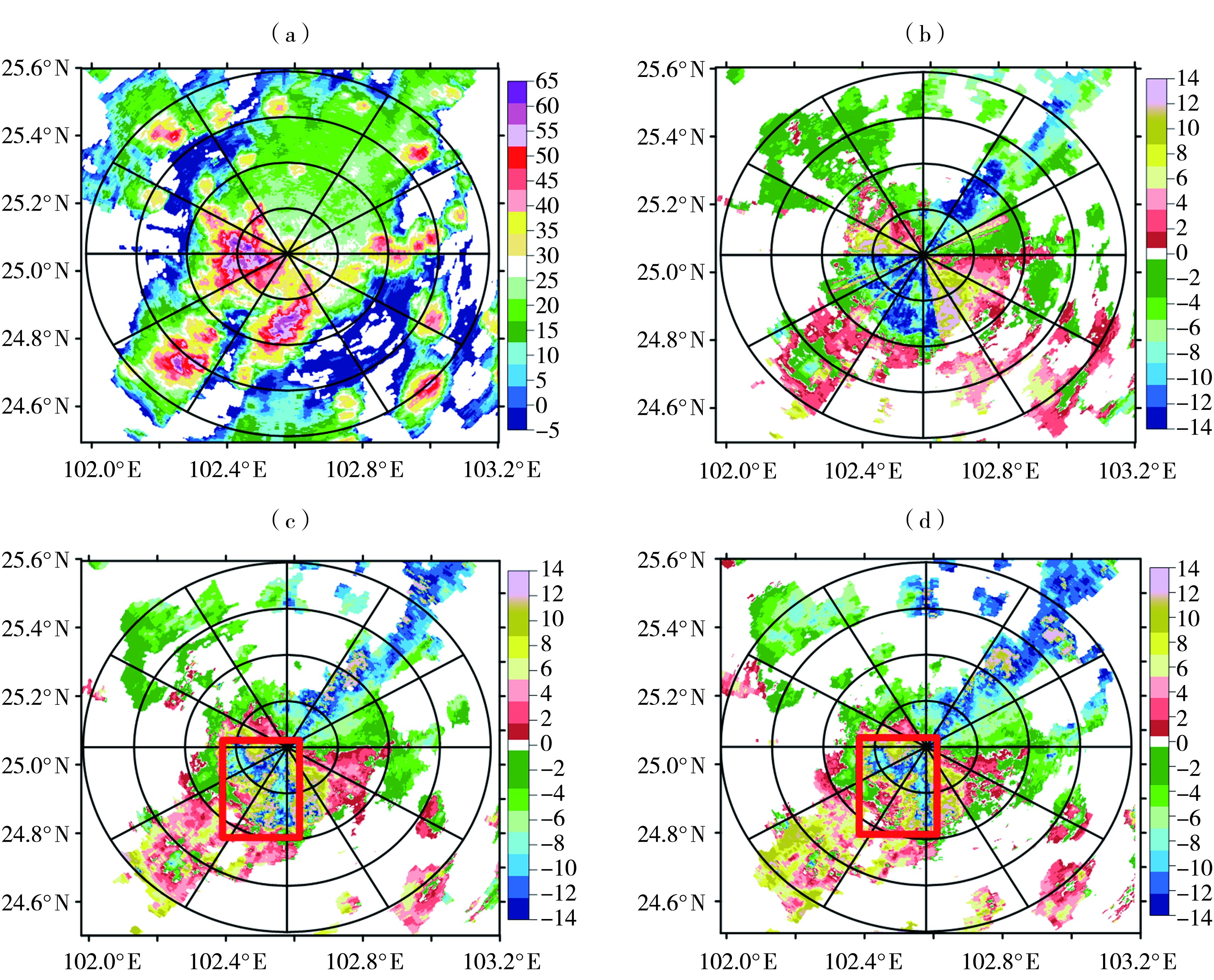
图4 2022年7月7日昆明雷达14:58组合反射率因子(a,单位:dBZ)及0.5°(b)、1.5°(c)、2.4°(d)仰角径向速度(单位:m·s-1) (红色框线范围为速度模糊区域,下同)
Fig.4 The composition reflectivity factors (a, Unit: dBZ) and radial velocity on the elevation of 0.5° (a), 1.5° (b), 2.4° (c) (Unit: m·s-1) at 14:58 of Kunming radar on 7 July 2022 (The red box indicates velocity ambiguity area, the same as below)

图5 2022年7月7日19:25(a、c)和20:01(b、d)普洱雷达站0.5°仰角反射率因子(a、b)(单位:dBZ)和径向速度(c、d)(单位:m·s-1) (红色椭圆为阵风锋位置)
Fig.5 Reflectivity factors (a, b) (Unit: dBZ) and radial velocity (c, d) (Unit: m·s-1) on 0.5° elevation at 19:25 (a, c) and 20:01 (b, d) of Pu'er radar on July 7, 2022 (The red ellipse indicates the position of gust front)
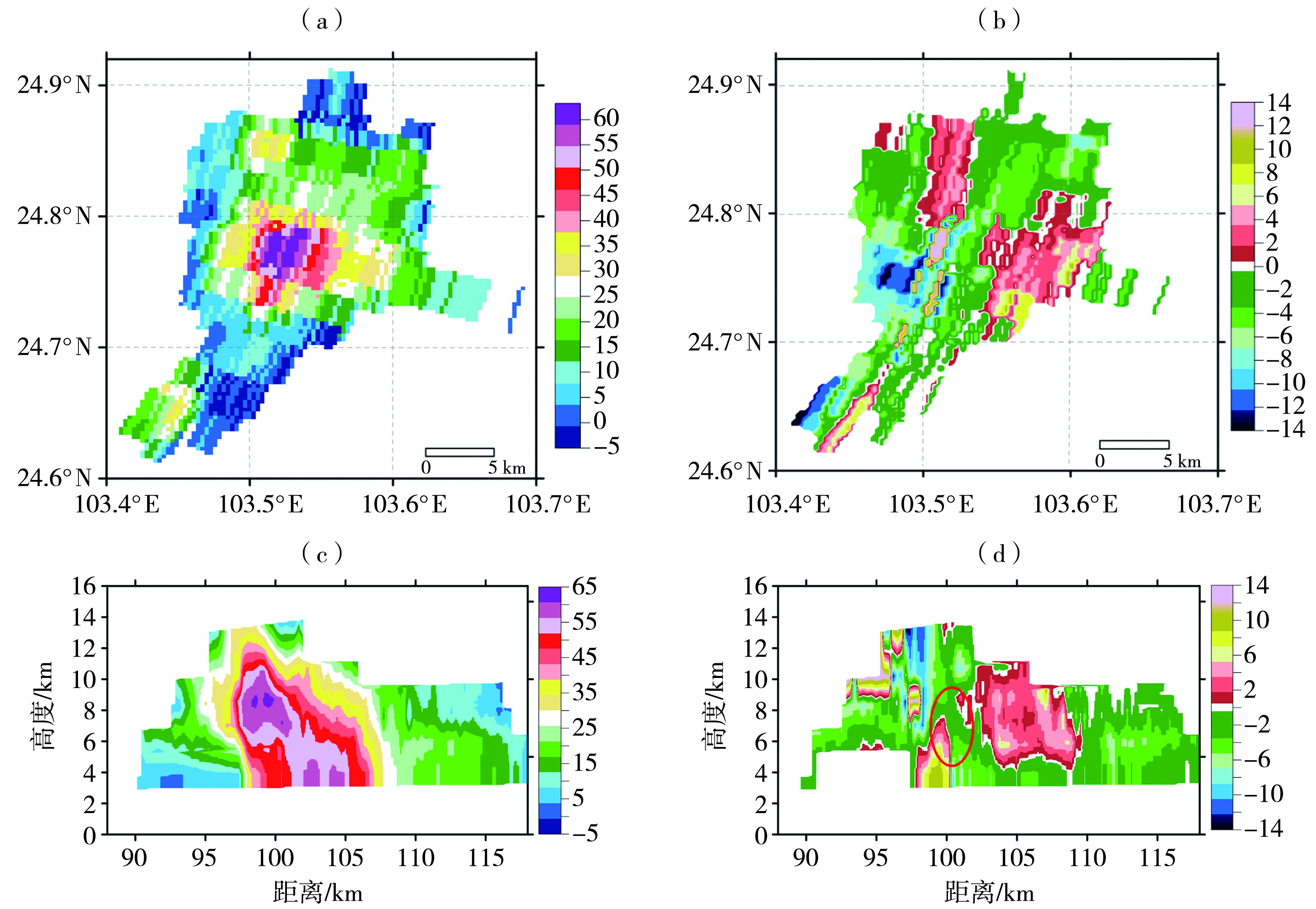
图6 2022年7月7日13:45昆明雷达3.3°仰角反射率因子(a,单位:dBZ)、径向速度(b,单位:m·s-1)及反射率因子(c,单位:dBZ)和径向速度(d,单位:m·s-1)剖面 (红色椭圆为中层径向辐合区域)
Fig.6 Reflectivity factor (a, Unit: dBZ) and radial velocity (b, Unit: m·s-1) on 3.3° elevation, and the radar vertical section of reflectivity factor (c, Unit: dBZ) and radial velocity (d, Unit: m·s-1) of Kunming radar on 7 July 2022 (The red ellipse indicates the mid-altitude radial convergence area)
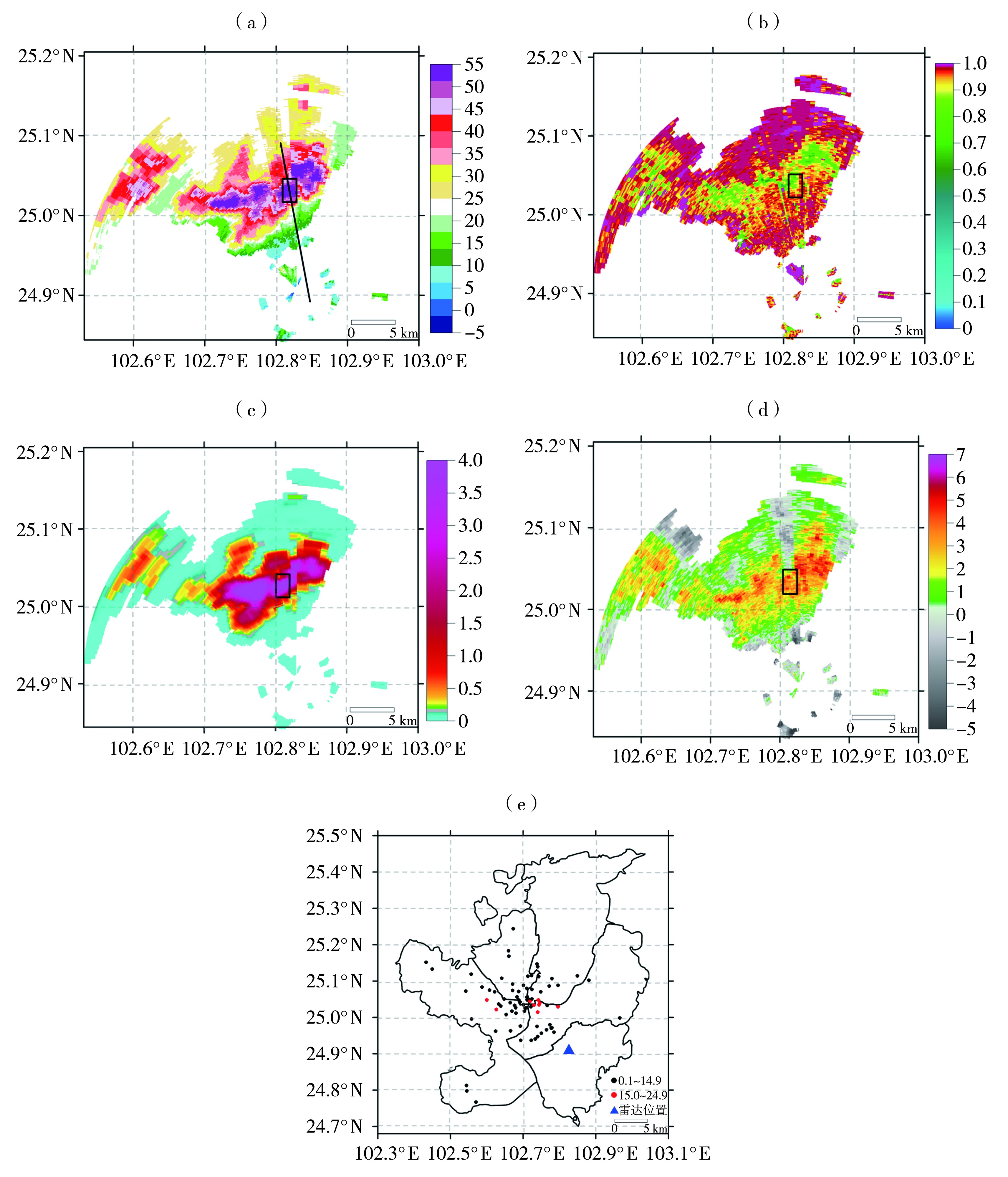
图7 2022年7月7日14:19昆明X波段雷达1.5°仰角ZH(a,单位:dBZ)、CC(b)、KDP(c,单位:°·km-1)、ZDR(d,单位:dB)及14:00—15:00主城区降雨量(e,单位:mm) (黑色框线范围为研究区域,黑线为双偏振量提取所沿路径)
Fig.7 The ZH (a, Unit: dBZ), CC (b), KDP (c, Unit: °·km-1), ZDR (d, Unit: dB) on 1.5° elevation of Kunming X-band radar at 14:19, and rainfall in the main city from 14:00 to 15:00 (e, Unit: mm) on 7 July 2022 (The black box indicates the research area, the black line indicates the path along which dual-polarization variables are extracted for vertical cross-section analysis)

图8 2022年7月7日13:57、14:09、14:45昆明X波段雷达ZH(单位:dBZ)、CC、KDP(单位:°·km-1)以及ZDR(单位:dB)沿图7中黑色直线的垂直剖面 (数字1、2表示对流单体)
Fig.8 The vertical profile of ZH (Unit: dBZ), CC, KDP (Unit: °·km-1), and ZDR (Unit: dB) along the black line in fig.7 of Kunming X-band radar on July 7, 2022 at 13:57, 14:09 and 14:45 (The number 1 and 2 represent convective cells)

图9 2022年7月7日13:00(a)、15:00(b)、17:00(c)、19:00(d)云南地面温度(填色,单位:℃)、逐小时前2 min平均风场(流线)及瞬时大风(红色风羽)(单位:m·s-1)
Fig.9 The surface temperature (the color shaded, Unit: ℃), hourly average wind field (streamlines) in the first 2 minutes and instantaneous maximum wind speed (red bars) (Unit: m·s-1) of Yunnan at 13:00 (a), 15:00 (b), 17:00 (c) and 19:00 (d) on 7 July 2022
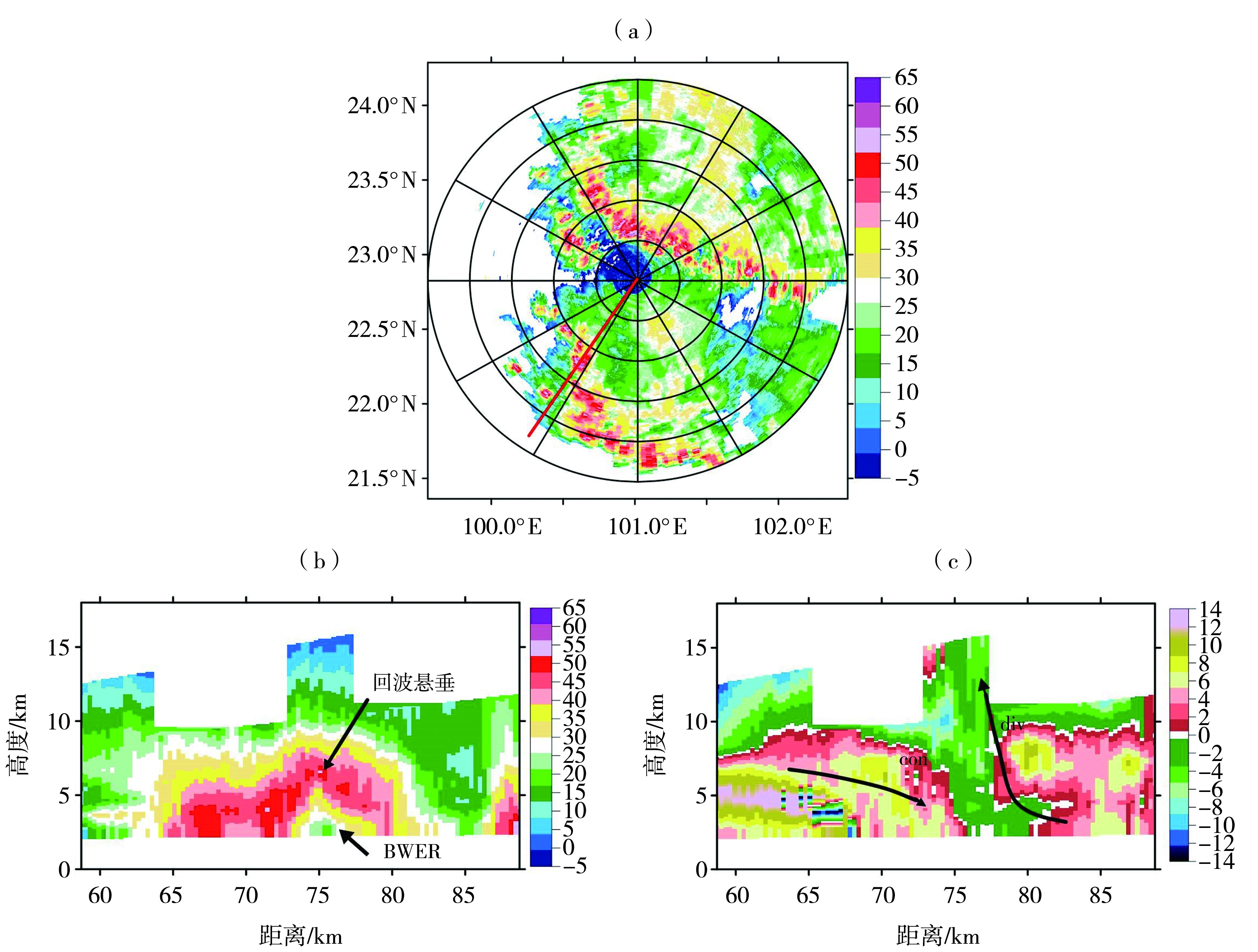
图10 2022年7月7日20:01普洱雷达组合反射率因子(a,单位:dBZ)及反射率因子(b)、径向速度(c,单位:m·s-1)剖面 (红色实线为沿飑线移动方向做剖面的位置,c图中的黑色箭头为气流运动方向)
Fig.10 The composition reflectivity factors (a, Unit: dBZ) and the radar vertical section of reflectivity factor (b) and radial velocity (c, Unit: m·s-1) of Pu'er radar at 20:01 on 7 July 2022 (The red line indicates the position of the profile along the moving direction of the squall line, the black arrows indicate the direction of air flow in fig. c)
| [1] | 刁秀广, 杨晓霞, 朱君鉴, 等, 2008. 一次长寿命风暴的CINRAD/SA雷达反射率及中气旋产品特征与流场结构分析[J]. 高原气象, 27(3):657-667. |
| [2] | 段鹤, 严华生, 王晓君, 2012. 滇南飑线的发生环境及其多普勒雷达回波特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 28(1):68-76. |
| [3] | 段玮, 张腾飞, 段鹤, 等, 2018. 云南省人工防雹作业条件预报技术研究与应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [4] | 方翀, 俞小鼎, 朱文剑, 等, 2015. 2013年3月20日湖南和广东雷暴大风过程的特征分析[J]. 气象, 41(11):1305-1 314. |
| [5] | 黄秀韶, 李芳, 刁秀广, 2022. 一次强降水超级单体风暴双偏振参量特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 50(6):830-841. |
| [6] | 李玉婷, 周祥华, 李晓勇, 等, 2022. 泸州X波段双偏振雷达在冰雹识别中的对比应用[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(增刊1):114-118. |
| [7] | 林文, 张深寿, 罗昌荣, 等, 2020. 不同强度强对流云系S波段双偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象, 46(1):63-72. |
| [8] | 刘黎平, 吴翀, 汪旭东, 等, 2015. X波段一维扫描有源相控阵天气雷达测试定标方法[J]. 应用气象学报, 26(2):129-140. |
| [9] | 刘艳, 张涛, 2021. 一次早春冰雹天气过程的双偏振相控阵雷达回波特征分析[J]. 地球科学前沿:汉斯, 11(9):1188-1 194. |
| [10] | 钱卓蕾, 严佩文, 李锋, 等, 2024. 基于多波段雷达观测的浙江一次飑线演变结构特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 52 (5):681-691. |
| [11] |
钱卓蕾, 赵驰宇, 朱哲君, 等, 2023. 浙江连续两次暖区飑线发展机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5):764-773.
DOI |
| [12] | 苏爱芳, 张宁, 袁小超, 等, 2016. 河南“7·14”强降水和“8·02”雷暴大风过程β中尺度对流系统对比分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 35(2):126-137. |
| [13] | 苏永彦, 刘黎平, 2022. S波段双偏振雷达和X波段相控阵天气雷达中气旋识别结果对比[J]. 气象, 48(2):229-244. |
| [14] | 孙继松, 戴建华, 何立富, 等, 2014. 强对流天气预报的基本原理与技术方法:中国强对流天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [15] | 王民栋, 徐萍, 陶然, 等, 2016. 滇西南中尺度对流飑线的移动路径和雷达回波特征[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 38(1):81-89. |
| [16] | 王秀明, 俞小鼎, 周小刚, 等, 2012. “6·3”区域致灾雷暴大风形成及维持原因分析[J]. 高原气象, 31(2):504-514. |
| [17] | 伍志方, 庞古乾, 贺汉青, 等, 2014. 2012年4月广东左移和飑线内超级单体的环境条件和结构对比分析[J]. 气象, 40(6):655-667. |
| [18] | 武冰路, 赵京波, 纪策, 等, 2023. 多源观测资料在冰雹监测预警中的应用[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(5):79-85. |
| [19] | 邢峰华, 黄彦彬, 李光伟, 等, 2023. 海南岛一次强飑线系统演变的双偏振特征分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 39(5):742-750. |
| [20] | 许敏, 沈芳, 刘璇, 等, 2022. 京津冀“7·5”强对流天气形成的环境条件及中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6):993-1 002. |
| [21] | 杨芳园, 沈茜, 周稀, 等, 2018. 云南省一次飑线大风天气过程的中尺度特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 37(1):48-56. |
| [22] | 于明慧, 刘黎平, 吴翀, 等, 2019. 利用相控阵及双偏振雷达对2016年6月3日华南一次强对流过程的分析[J]. 气象, 45(3):330-344. |
| [23] | 俞小鼎, 2014. 关于冰雹的融化层高度[J]. 气象, 40(6):649-654. |
| [24] | 俞小鼎, 王秀明, 李万莉, 等, 2020. 雷暴与强对流临近预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [25] | 俞小鼎, 姚秀萍, 熊廷南, 等, 2006. 多普勒天气雷达原理与业务应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [26] | 俞小鼎, 周小刚, 王秀明, 2012. 雷暴与强对流临近天气预报技术进展[J]. 气象学报, 70(3):311-337. |
| [27] | 袁春梅, 周筠珺, 2024. 我国西南地区春季典型雹暴观测与数值模拟研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(2):19-31. |
| [28] | 张宁, 苏爱芳, 史一丛, 2017. 2014年一次飑线的发展维持原因分析[J]. 气象, 43(11):1383-1 392. |
| [29] | 张腾飞, 张杰, 尹丽云, 等, 2016. 滇南春季一次强对流风暴系统特征及成因[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 38(2):245-255. |
| [30] | 张勇, 刘德, 张亚萍, 等, 2013. 渝西一次强对流风暴过程的中尺度特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(4):338-345. |
| [31] | 章国材, 2011. 强对流天气分析与预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [32] |
周聪, 张涛, 夏昕, 等, 2024. 基于S波段双偏振雷达的成都初春冰雹特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(1):95-106.
DOI |
| [33] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等, 2000. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [34] |
竹利, 卢德全, 廖文超, 等, 2021. 连续两次飑线大风成因对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(5):796-806.
DOI |
| [35] | BRINGI V N, CHANDRASEKAR V, 2010. 偏振多普勒天气雷达原理和应用[M]. 李忱, 张越, 译. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [36] | RYZHKOV A V, ZHURAVLYOV V B, RYBAKOVA N A, 1994. Preliminary results of X-band polarization radar studies of clouds and precipitation[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 11(1): 132-139. |
| [37] | RYZHKOV A V, ZRNIC D S, 2019. Radar polarimetry for weather observations[M]. Switzerland: Springer Cham. |
| [1] | 梁军, 贾旭轩, 张胜军, 冯呈呈, 李婷婷, 程航, 刘晓初. 辽东半岛一次大暴雨过程触发和维持机制分析 [J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 435-449. |
| [2] | 胡嘉缨, 赵桂香, 闫慧, 徐逸雯, 操俊伟. 复杂地形下一次飑线的组织化过程及成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(2): 289-299. |
| [3] | 徐莎莎, 朱欢, 蒋启进, 殷俊, 张渊. 一次飑线初始阶段的极端大风成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 228-237. |
| [4] | 桑明慧, 竹利, 沈晓玲, 张春艳, 左骏. 一次导致大风的暖区飑线后侧入流分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 84-94. |
| [5] | 吴古会, 彭芳, 齐大鹏, 杜小玲, 杨秀庄. 贵州一次辐合线锋生极端暴雨过程的中尺度特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 753-763. |
| [6] | 钱卓蕾, 赵驰宇, 朱哲君, 沈哲文. 浙江连续两次暖区飑线发展机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 764-773. |
| [7] | 韦惠红, 吴翠红, 魏凡, 鲁易, 孔海妹, 赵欢. 湖北雷暴阵风锋特征及其对流触发作用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(1): 73-81. |
| [8] | 许敏, 沈芳, 刘璇, 刘艳杰, 张湘涵. 京津冀“7·5”强对流天气形成的环境条件及中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 993-1002. |
| [9] | 张海耀, 黄玉霞, 吴辉彦, 李霞, 穆腊梅, 杨蕙宁. 黄土高原复杂地形区两次冰雹天气过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 646-655. |
| [10] | 曹倩, 雷桂莲, 易艳红, 章毅之, 刘良玉, 彭王敏子. 不同雷达观测资料同化对一次罕见飑线天气模拟的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 469-484. |
| [11] | 冯晋勤, 卢芸芸, 赖巧珍, 蔡菁. 福建西部山区一次中尺度对流系统触发机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 62-72. |
| [12] | 竹利,卢德全,廖文超,郑淋淋. 连续两次飑线大风成因对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 796-806. |
| [13] | 聂云, 周继先, 李习瑾, 冉阳, 陈超. 贵州一次暖区飑线过程的环境条件和结构特征#br#[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 782-793. |
| [14] | 官晓军, 覃靖. 福建省一次强飑线过程的强度和移动特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(5): 799-808. |
| [15] | 王君 . 豫北两次特大暴雨事件的物理量极端性和中尺度特征王君[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3): 419-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
