干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 922-933.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0922
东南沿海一次近云区湍流事件的数值模拟与产生机制研究
- 中国民航大学空中交通管理学院航空气象系,天津 300300
-
收稿日期:2024-07-11修回日期:2024-08-16出版日期:2024-12-31发布日期:2025-01-15 -
通讯作者:吴迪(1991—),男,副教授,主要从事中尺度灾害性天气研究。E-mail:d_wu@cauc.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:何沛霖(2000—),男,硕士生,主要从事航空危险天气研究。E-mail:2022031024@cauc.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金-中国民用航空局联合研究基金重点项目(U2033207);国家自然科学基金项目(42005004);中央高校基本科研业务费中国民航大学专项(3122019137)
Numerical simulation and generation mechanism of a near-cloud turbulence encounter in southeast coast of China
HE Peilin( ), WU Di(
), WU Di( ), WANG Kehua, LI Kenan
), WANG Kehua, LI Kenan
- Department of Aviation Meteorology, College of Air Traffic Management, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China
-
Received:2024-07-11Revised:2024-08-16Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
摘要:
研究近云区湍流对于提高飞机颠簸预报能力,保障航空运输安全具有重要意义。利用WRF(Weather Research and Forecasting)V4.3.1模式对我国福建省上空一次中等强度近云区湍流事件开展高分辨率数值模拟,对天气尺度背景和颠簸指数进行检验,分析此次湍流事件的形成原因;借助不考虑湿过程的敏感试验,研究云系演变对湍流产生的影响机制。结果表明:此次湍流事件主要受东南沿海地区冷高压外围低层云区影响,高层南支急流逐渐向东移至湍流区上方,垂直风切变较强,伴有对流层顶折叠现象。高分辨率模拟能够合理再现湍流期间环流背景。颠簸指数(Ri数和NCSU1)对本次湍流事件的强度和位置有较好的指示作用。湍流区附近的惯性不稳定与湍流耗散动能(Turbulent Kinetic Energy,TKE)大值区均分布在云区周围,受云区影响,湍流区内纬向风增量自南向北逐渐增强,经向风增量自西向东减弱,贡献了负绝对涡度,云顶高度附近的上升气流影响了上方湍流区局地风场;下沉气流经云顶与饱和湿空气混合稀释,引起惯性不稳定,最终导致湍流事件发生。而无云时湍流区TKE消失,垂直风切变减弱,两种颠簸指数也未能诊断出湍流事件。
中图分类号:
引用本文
何沛霖, 吴迪, 王柯化, 李克南. 东南沿海一次近云区湍流事件的数值模拟与产生机制研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 922-933.
HE Peilin, WU Di, WANG Kehua, LI Kenan. Numerical simulation and generation mechanism of a near-cloud turbulence encounter in southeast coast of China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 922-933.

图1 WRF模式模拟区域(a)及D04嵌套区域(b)地形分布(单位:m) (图a中黑色圆圈和图b中黑色虚线表示飞机所在航路)
Fig.1 The distribution of topography (Unit: m) of the WRF model simulation area (a) and D04 nested area (b) (The black circle in the fig. a and the black dotted line in the fig. b indicate the route of the aircraft)
| 模式方案 | 具体参数 |
|---|---|
| 云微物理方案 | Thompson (Thompson et al., |
| 积云对流方案 | KF (Kain, |
| 行星边界层方案 | Mellor-Yamada-Janjic (Janjic, |
| 地表表层方案 | Monin-Obukhov (Janjic, |
| 陆面过程方案 | Unified Noah (Tewari et al., |
| 长波辐射方案 | RRTMG (Iacono et al., |
| 短波辐射方案 | RRTMG (Iacono et al., |
表1 模式物理参数配置
Tab.1 Configuration and parameterizations conducted in the simulation
| 模式方案 | 具体参数 |
|---|---|
| 云微物理方案 | Thompson (Thompson et al., |
| 积云对流方案 | KF (Kain, |
| 行星边界层方案 | Mellor-Yamada-Janjic (Janjic, |
| 地表表层方案 | Monin-Obukhov (Janjic, |
| 陆面过程方案 | Unified Noah (Tewari et al., |
| 长波辐射方案 | RRTMG (Iacono et al., |
| 短波辐射方案 | RRTMG (Iacono et al., |

图2 2017年2月24日06:00 500 hPa位势高度场(黑色实线,单位:gpm)及水平风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(a),日本葵花8号卫星相当黑体温度TBB(灰色填色,单位:°C)及平均海平面气压场(黑色实线,单位:hPa)(b) (图a中黑色圆圈和图b中符号“△”分别表示飞机遭遇湍流报告区域和航路点位置,图b中字母“H”表示闭合高压中心)
Fig.2 The geopotential height field (black solid lines, Unit: gpm) and horizontal wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) at 500 hPa (a), temperature of black body (TBB) from the Japanese Himawari 8 satellite (the gray shaded, Unit: °C) and mean sea level pressure (black solid lines, Unit: hPa) (b) at 06:00 on 24 February 2017 (The black circle in fig. a and the mark “△” in fig. b represent the location of the turbulence and the waypoints on the flight route, respectively, and the letter “H” in fig. b denotes the center of closed high-pressure)
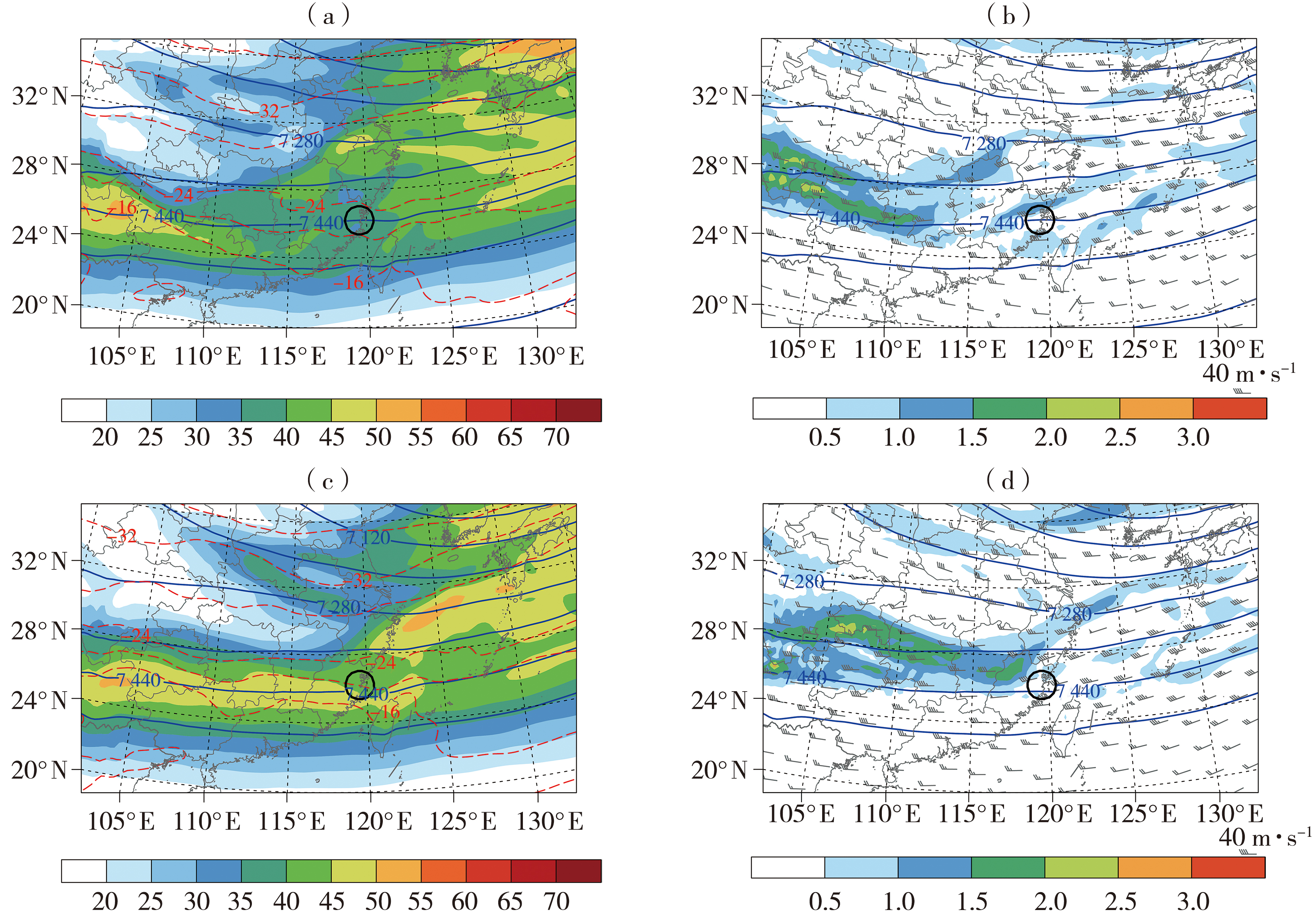
图3 2017年2月24日00:00(a、b)、06:00(c、d)400 hPa水平风速(填色,单位:m·s-1)、位势高度场(蓝色实线,单位:gpm)、温度场(红色虚线,单位:°C)(a、c)及对应的位涡场(填色,单位:PVU,1 PVU=10-6 K·kg-1·m2·s-1)、位势高度场(蓝色实线,单位:gpm)、水平风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(b,d) (黑色圆圈表示湍流报告区域,下同)
Fig.3 The horizontal wind speed (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-1), geopotential height field (blue solid lines, Unit: gpm) and temperature field (red dashed lines, Unit: °C) at 400 hPa (a, c), and the corresponding distribution of potential vorticity field (the color shaded, Unit: PVU, 1 PVU=10-6 K·kg-1·m2·s-1), geopotential height field (blue solid lines, Unit: gpm) and horizontal wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (b, d) at 00:00 (a, b), 06:00 (c, d) on 24 February 2017 (The black circles indicate the location where aircraft turbulence occurred, the same as below)
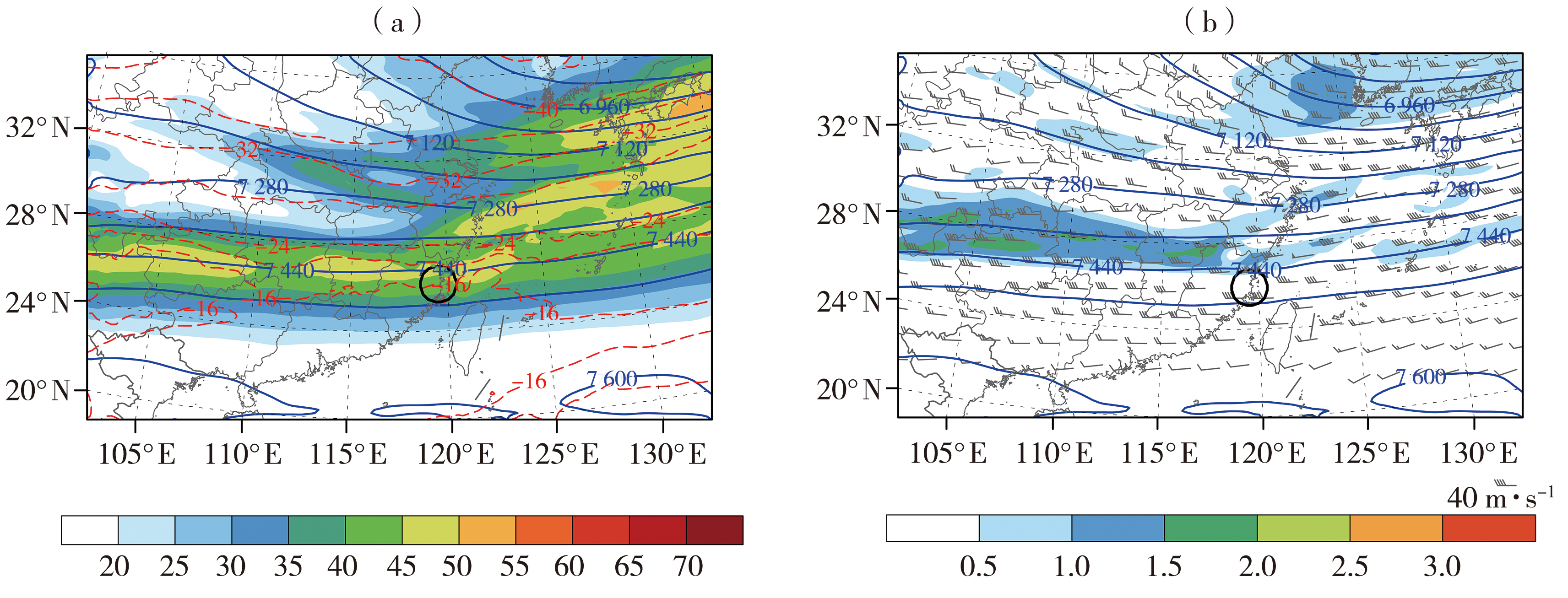
图4 2017年2月24日06:00 WRF模式模拟的400 hPa水平风速(填色,单位:m·s-1)、位势高度场(蓝色实线,单位:gpm)、温度场(红色虚线,单位:°C)(a)及对应的位涡场(填色,单位:PVU,1 PVU=10-6 K·kg-1·m2·s-1)、位势高度场(蓝色实线,单位:gpm)、水平风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(b)
Fig.4 The horizontal wind speed (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-1), geopotential height field (blue solid lines, Unit: gpm) and temperature field (red dashed lines, Unit: °C) at 400 hPa (a), and the corresponding potential vorticity field (the color shaded, Unit: PVU, 1 PVU=10-6 K·kg-1·m2·s-1), geopotential height field (blue solid lines, Unit: gpm) and horizontal wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (b) at 06:00 simulated by WRF model on 24 February 2017

图5 2017年2月24日01:00(a、b、c)、07:00(d、e、f)控制试验模拟的7.2 km高度Ri数(a、d),垂直风切变(b、e,单位:10-2 s-1)和大气稳定度N2(c、f,单位:10-4 s-2)空间分布 [黑色实线为湍流中心所在经度(119.45°E)]
Fig.5 The spatial distribution of the Richardson number (Ri) (a, d), vertical wind shear (b, e, Unit: 10-2 s-1), and atmospheric stability N2 (c, f, Unit: 10-4 s-2) at 7.2 km height at 01:00 (a, b, c) and 07:00 (d, e, f) on 24 February 2017 simulated by the control experiment (the black solid line is the longitude (119.45°E) of the turbulence center)

图6 2017年2月24日07:00控制试验模拟的Ri数(a)及NCSU1指数(b,单位:10-12 s-3)沿119.45°E的纬度-高度剖面 (黑色实线表示等位温线,单位:K;底部黑点区域表示地形,黑色矩形表示湍流报告区域)
Fig.6 The latitude-height sections of the Richardson number (Ri) (a) and NCSU1 index (Unit: 10-12 s-3) (b) along 119.45°E at 07:00 on 24 February 2017 simulated by the control experiment (The black solid lines are the equipotential temperature lines, Unit: K; the black spots area at the bottom represent the terrain, and the black rectangles indicate the location where aircraft turbulence occurred)

图7 2017年2月24日01:00(a、b)和07:00(c、d)控制试验模拟的7.2 km高度水平风速(填色,单位:m·s-1)、气压场(蓝色实线,单位:hPa)和温度场(红色虚线,单位:°C)(a、c),水平风场(填色,单位:m·s-1)、等位温线(黑色实线,单位:K)及1.5 PVU等位涡线(蓝色实线)沿119.45°E的纬度-高度剖面(b、d) (黑色矩形表示湍流报告区域,灰色填色表示地形,下同)
Fig.7 The horizontal wind speed (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-1), pressure field (blue solid lines, Unit: hPa), temperature field (red dashed lines, Unit: °C) (a, c) at 7.2 km height, the latitude-height sections of horizontal wind speed (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-1), equipotential temperature lines (black solid lines, Unit: K) and 1.5 PVU equipotential vorticity lines (blue solid lines) (b, d) along 119.45°E at 01:00 (a, b) and 07:00 (c, d) on 24 February 2017 simulated by the control experiment (The black circles indicate the location where aircraft turbulence occurred, the gray shaded area represents the terrain, the same as below)
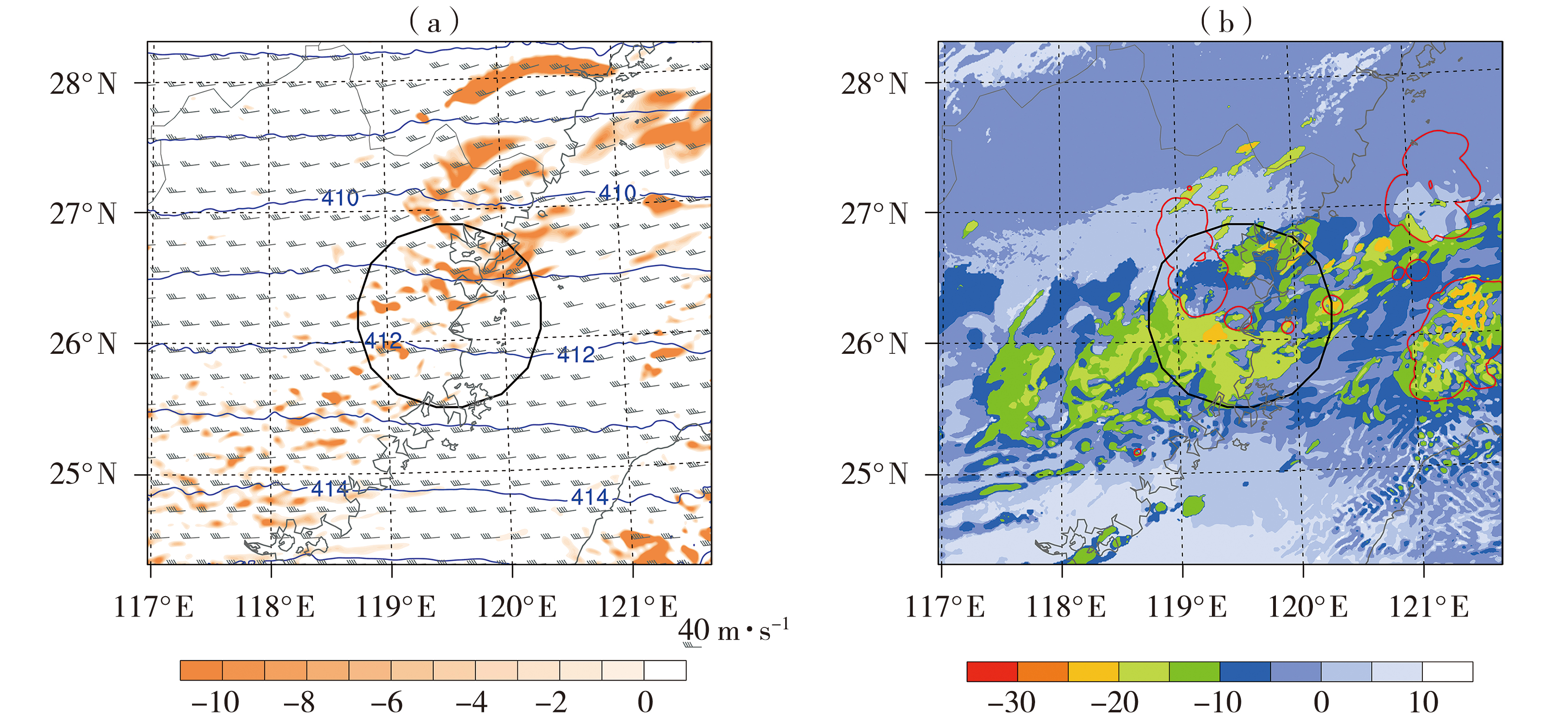
图8 2017年2月24日07:00控制试验模拟的D04区域7.2 km高度绝对涡度(填色,单位:10-5 s-1)、气压场(蓝色实线,单位:hPa)、水平风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)(a)及TBB(填色,单位:°C)、湍流耗散动能(TKE)等值线(红色实线,仅显示>0.1 m2·s-2数值)(b)
Fig.8 The absolute vorticity (the color shaded, Unit: 10-5 s-1), pressure field (blue solid lines, Unit: hPa) and horizontal wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (a), the TBB (the color shaded, Unit: °C) and turbulence kinetic energy (red solid lines, only showing the values greater than 0.1 m2·s-2) (b) at 7.2 km height at 07:00 on 24 February 2017 in D04 region simulated by the control experiment

图9 2017年2月24日07:00敏感试验模拟的Ri数(a)、NCSU1指数(b,单位:10-12 s-3)、垂直风切变(c,单位:10-2 s-1)、大气稳定度N2(d,单位:10-4 s-2)沿119.45°E的纬度-高度剖面 (黑色实线为等位温线,单位:K;蓝色实线为1.5 PVU等位涡线)
Fig.9 The latitude-height sections of the Richardson number (Ri) (a), NCSU1 index (b, Unit: 10-12 s-3), vertical wind shear (c, Unit: 10-2 s-1), atmospheric stability N2 (d, Unit: 10-4 s-2) along 119.45°E at 07:00 on 24 February 2017 simulated by the sensitivity experiment (The black solid lines are the equipotential temperature lines, Unit: K; the blue solid lines are 1.5 PVU equipotential vorticity lines)

图10 2017年2月24日07:00控制与敏感试验模拟的D04区域7.2 km高度水平风速(填色,单位:m·s-1)、风矢量(风矢,单位:m·s-1)差值场(a),水平风速差值场(填色,单位:m·s-1)、敏感试验模拟的等位温线(黑色实线,单位:K)及1.5 PVU等位涡线(蓝色实线)沿119.45°E的纬度-高度剖面(b)
Fig.10 The difference field of the horizontal wind speed (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-1), wind vector (vectors, Unit: m·s-1) between control and sensitivity experiments (a), the latitude-height sections of horizontal wind speed difference between control and sensitivity experiments (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-1), equipotential temperature lines (black solid lines, Unit: K) and 1.5 PVU equipotential vorticity lines (blue solid lines) along 119.45°E simulated by sensitivity experiment (b) at 7.2 km height at 07:00 on 24 February 2017
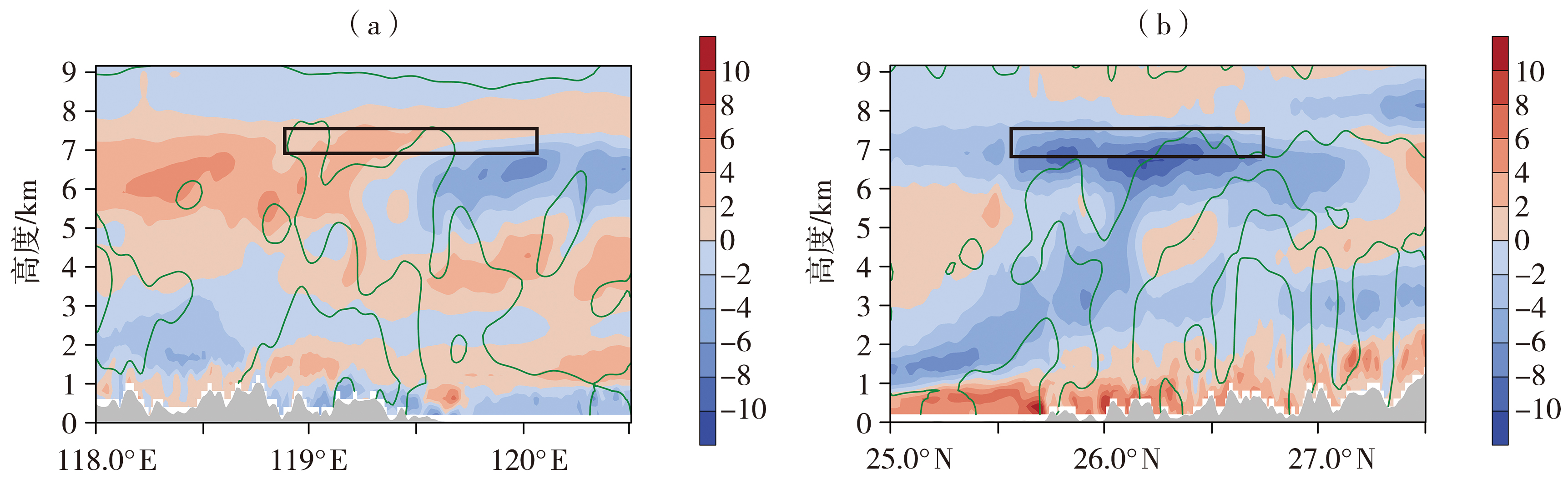
图11 2017年2月24日07:00控制试验与敏感试验模拟的经向风(a)、纬向风(b)差值场 (绿色实线表示控制试验模拟的绝对涡度零值线,单位:10-5 s-1)
Fig.11 The difference field of meridional wind (a) and zonal wind (b) between the control experiment and the sensitivity experiment at 07: 00 on February 24, 2017 (The green solid line represents the absolute vorticity zero line simulated by the control experiment, Unit: 10-5 s-1)

图12 2017年2月24日07:00控制试验模拟的总水成物混合比含量(填色,单位:g·kg-1)、瞬时风场(箭矢,单位:m·s-1)及温度场(黑色虚线,单位:°C)沿26.25°N(a)、119.45°E(b)的垂直剖面
Fig.12 The vertical sections of the total hydrometeor mixing ratio content (the color shaded, Unit: g·kg-1), instantaneous wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and temperature field (black dashed line, Unit: °C) at 07:00 on 24 February 2017 simulated by control experiment along 26.25°N (a) and 119.45°E (b)
| [1] | 高松, 陈贵川, 吴钲, 等, 2019. 一次西南低涡影响下的川渝地区暴雨个例分析[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4): 597-612. |
| [2] |
马思敏, 穆建华, 舒志亮, 等, 2022. 六盘山区一次典型暴雨过程的地形敏感性模拟试验[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 457-468.
DOI |
| [3] | 聂云, 周继先, 李习瑾, 等, 2020. 贵州一次暖区飑线过程的环境条件和结构特征[J]. 干旱气象, 38(5): 782-793. |
| [4] |
孙明燕, 张述文, 2023. 边界层湍流垂直混合强度对局地热对流模拟影响的个例研究[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 290-300.
DOI |
| [5] | 谢婷, 马育军, 张午朝, 2021. 青海湖北岸大气向下长波辐射特征及云的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 288-295. |
| [6] |
殷青青, 任璐, 田文寿, 等, 2022. 华北地区一次对流激发重力波的卫星观测和数值模拟研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 444-456.
DOI |
| [7] | ARAKAWA A, JUNG J H, 2011. Multiscale modeling of the moist-convective atmosphere: A review[J]. Atmospheric Research, 102(3): 263-285. |
| [8] | HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al, 2020. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 146(730): 1 999-2 049 |
| [9] | IACONO M J, DELAMERE J S, MLAWER E J, et al, 2008. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 113(D13), e2008jd009944. DOI: 10.1029/2008JD009944. |
| [10] | JANJIC Z I, 1994. The step-mountain eta coordinate model: Further developments of the convection, viscous sublayer, and turbulence closure schemes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 122(5): 927-945. |
| [11] | KAIN J S, 2004. The kain-fritsch convective parameterization: An update[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 43(1): 170-181. |
| [12] | KAPLAN M L, HUFFMAN A W, LUX K M, et al, 2005. Characterizing the severe turbulence environments associated with commercial aviation accidents. Part 2: Hydrostatic mesoscale numerical simulations of supergradient wind flow and streamwise ageostrophic frontogenesis[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 88(3): 153-173. |
| [13] | KIM J H, CHUN H Y, 2012. A numerical simulation of convectively induced turbulence above deep convection[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 51(6): 1 180-1 200 |
| [14] | KIM J, CHUN H, 2010. A numerical study of clear-air turbulence (CAT) encounters over South Korea on 2 April 2007[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 49(12): 2 381-2 403 |
| [15] | KNOX J A, 1997. Possible mechanisms of clear-air turbulence in strongly anticyclonic flows[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 125(6): 1 251-1 259 |
| [16] | LANE T P, SHARMAN R D, CLARK T L, et al, 2003. An investigation of turbulence generation mechanisms above deep convection[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 60(10): 1 297-1 321 |
| [17] | LANE T P, SHARMAN R D, TRIER S B, et al, 2012. Recent advances in the understanding of near-cloud turbulence[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93(4): 499-515. |
| [18] | LEE D B, CHUN H Y, 2018. A numerical study of aviation turbulence encountered on 13 February 2013 over the Yellow Sea between China and the Korean peninsula[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 57(4): 1 043-1 060 |
| [19] | MILES J W, HOWARD L N, 1964. Note on a heterogeneous shear flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 20(2): 331-336. |
| [20] | SHARMAN R D, TRIER S B, 2019. Influences of gravity waves on convectively induced turbulence (CIT): A review[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 176(5): 1 923-1 958 |
| [21] | SHARMAN R D, TRIER S B, LANE T P, et al, 2012. Sources and dynamics of turbulence in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere: A review[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(12), L12803. DOI: 10.1029/2012GL051996. |
| [22] | SHARMAN R, LANE T, 2016. Aviation Turbulence:Processes, Detection, Prediction[M]. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG Switzerland. |
| [23] | SHARMAN R, TEBALDI C, WIENER G, et al, 2006. An integrated approach to mid-and upper-level turbulence forecasting[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 21(3): 268-287. |
| [24] | SQUIRES P, 1958. Penetrative downdraughts in cumuli[J]. Tellus, 10(3): 381-389. |
| [25] | STRAUSS L, SERAFIN S, HAIMOV S, et al, 2015. Turbulence in breaking mountain waves and atmospheric rotors estimated from airborne in situ and Doppler radar measurements[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 141(693): 3 207-3 225 |
| [26] | TEWARI M, CHEN F, WANG W, et al, 2004. Implementation and verification of the unified NOAH land surface model in the WRF model[C]// 20th conference on weather analysis and forecasting/16th conference on numerical weather prediction, Seattle, US. |
| [27] | THOMPSON G, FIELD P R, RASMUSSEN R M, et al, 2008. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 136(12): 5 095-5 115 |
| [28] | TRIER S B, SHARMAN R D, 2009. Convection-permitting simulations of the environment supporting widespread turbulence within the upper-level outflow of a mesoscale convective system[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 137(6): 1 972-1 990 |
| [29] | TRIER S B, SHARMAN R D, LANE T P, 2012. Influences of moist convection on a cold-season outbreak of clear-air turbulence (CAT)[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 140(8): 2 477-2 496 |
| [30] | WILLIAMS P D, JOSHI M M, 2013. Intensification of winter transatlantic aviation turbulence in response to climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 3: 644-648. |
| [1] | 桑明慧, 竹利, 沈晓玲, 张春艳, 左骏. 一次导致大风的暖区飑线后侧入流分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 84-94. |
| [2] | 钱卓蕾, 赵驰宇, 朱哲君, 沈哲文. 浙江连续两次暖区飑线发展机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 764-773. |
| [3] | 褚颖佳, 郭飞燕, 高帆, 胡鹏, 郑丽娜, 刘奕辰, 鲁亓. 冷涡影响下两次不同类型强对流过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 279-289. |
| [4] | 孙明燕, 张述文. 边界层湍流垂直混合强度对局地热对流模拟影响的个例研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 290-300. |
| [5] | 马思敏, 穆建华, 舒志亮, 孙艳桥, 邓佩云, 周楠. 六盘山区一次典型暴雨过程的地形敏感性模拟试验[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 457-468. |
| [6] | 李涛, 陈杰, 汪方, 韩锐. 一种基于神经网络的中国区域夏季降水预测订正算法[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 308-316. |
| [7] | 吴斌, 钱业, 王瑞芳, 赵鑫, 金磊. 全球气候模式对影响西北太平洋台风强度的大尺度环境因子的模拟评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 466-479. |
| [8] | 王溪雯, 张飞民, 王芝兰, 杨凯, 王澄海. 青藏高原西部一次高原涡生成的数值模拟研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 54-64. |
| [9] | 董 甫, 张 玲, 张海鹏, 李 佳, 宋柳贤. 基于WRF模式的强天气过程集合预报综述[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 699-708. |
| [10] | 郑婧, 陈娟, 徐星生, 许彬. 一次低空急流加强下的暴雨过程成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(03): 411-422. |
| [11] | 官晓军, 覃靖. 福建省一次强飑线过程的强度和移动特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(5): 799-808. |
| [12] | 吴琼, 徐卫民. 湖陆山地复杂地形下近地层风速预报研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3): 384-. |
| [13] | 沈晓燕1,2,颜玉倩1,2,肖宏斌1,2,权晨1,2. WRF模式不同参数化方案组合对青海气温、降水及风速模拟的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(3): 423-. |
| [14] | 高晓梅1,孙雪峰2,秦瑜蓬1,王世杰1,王文波1. 山东一次强对流天气的环境条件和对流风暴特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(3): 447-. |
| [15] | 陈军,李小兰,喻义军,方标,滕林,胡萍. 贵州铜仁一次大范围高架雷暴降雹天气过程分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(4): 649-656. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
