干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 844-853.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0844
基于最优概率分布函数的成都市近63 a干旱特征分析
- 1.成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,四川 成都 610225
2.四川省邛崃市气象局,四川 邛崃 611530
3.四川省气候中心,四川 成都 610031
4.四川省眉山市气象局,四川 眉山 620060
-
收稿日期:2024-07-01修回日期:2024-08-24出版日期:2024-12-31发布日期:2025-01-15 -
通讯作者:倪长健(1970—),男,教授,主要从事大气物理学与大气环境相关研究。E-mail:ncj1970@163.com。 -
作者简介:任至涵(1997—),女,工程师,主要从事短临天气预报、大气环境等研究。E-mail:rzh970301@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFC3709301);四川省科技教育联合基金项目(2024NSFSC1983)
Analysis of drought characteristics in Chengdu over the past 63 years based on the optimal probability distribution function
REN Zhihan1,2( ), NI Changjian1(
), NI Changjian1( ), SHI Qiaoyu3, CHEN Ning4
), SHI Qiaoyu3, CHEN Ning4
- 1. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
2. Qionglai Meteorological Bureau of Sichuan Province, Qionglai 611530, Sichuan, China
3. Sichuan Provincial Climate Center, Chengdu 610031, China
4. Meishan Meteorological Bureau of Sichuan Province, Meishan 620060, Sichuan, China
-
Received:2024-07-01Revised:2024-08-24Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
摘要:
研究成都市不同尺度干旱时空分布特征对该地区农业、经济发展及干旱防灾减灾等具有重要意义。利用成都市14个国家气象站1960—2022年逐月降水数据,选择标准降水指数(Standardized Precipitation Index,SPI),首先通过对SciPy库概率分布函数的优选,确定成都市14个国家气象站年及季降水序列的最优概率分布函数;其次,基于最优概率分布函数分别计算得到年尺度和季节尺度的SPI(分别简称“SPI12、SPI3”);最后,基于SPI12和SPI3分析成都市年、季尺度干旱的时空分布特征。结果表明:不同尺度降水序列最优分布函数均通过K-S检验(显著性水平α=0.05),最优概率分布函数均能很好地表征成都市不同尺度降水序列的分布特征。成都市年及四季干旱站次比、干旱强度均呈弱增强趋势。年及四季干旱频率为25.40%~36.51%,不同尺度干旱频率的空间分布存在较大差异,相比秋旱和冬旱,春旱和夏旱发生频率略高。成都市14个区(市、县)不同等级年旱、春旱、夏旱、秋旱和冬旱的空间分布具有较大差异,但均以轻旱和中旱发生频率较高。
中图分类号:
引用本文
任至涵, 倪长健, 石荞语, 陈宁. 基于最优概率分布函数的成都市近63 a干旱特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 844-853.
REN Zhihan, NI Changjian, SHI Qiaoyu, CHEN Ning. Analysis of drought characteristics in Chengdu over the past 63 years based on the optimal probability distribution function[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 844-853.
| 干旱强度 | 类型 | 标准降水指数(SPI) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 无旱 | -0.5<SP1 |
| 1 | 轻旱 | -1.0<SPI≤-0.5 |
| 2 | 中旱 | -1.5<SPI≤-1.0 |
| 3 | 重旱 | -2.0<SPI≤-1.5 |
| 4 | 特旱 | SPI≤-2.0 |
表1 基于标准降水指数的干旱等级划分标准
Tab.1 The classification standard of drought grades based on SPI
| 干旱强度 | 类型 | 标准降水指数(SPI) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 无旱 | -0.5<SP1 |
| 1 | 轻旱 | -1.0<SPI≤-0.5 |
| 2 | 中旱 | -1.5<SPI≤-1.0 |
| 3 | 重旱 | -2.0<SPI≤-1.5 |
| 4 | 特旱 | SPI≤-2.0 |
| 站名 | 时间尺度 | 函数 | RMSE | AIC | BIC | D | D(0.05, n) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温江 | 年 | PearsonⅢ | 0.022 0 | -472.08 | -465.65 | 0.069 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.924 7 |
| 春季 | Johnson SU | 0.024 9 | -453.28 | -444.71 | 0.059 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.980 4 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.017 2 | -503.19 | -496.76 | 0.049 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.997 9 | |
| 秋季 | exponnorm | 0.022 7 | -467.84 | -461.41 | 0.061 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.970 7 | |
| 冬季 | skewnorm | 0.022 8 | -467.60 | -461.18 | 0.052 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.995 3 | |
| 崇州 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.018 5 | -493.43 | -487.00 | 0.060 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.962 3 |
| 春季 | gamma | 0.033 6 | -418.50 | -412.07 | 0.089 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.661 8 | |
| 夏季 | burr | 0.021 6 | -471.32 | -462.75 | 0.065 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.935 1 | |
| 秋季 | foldnorm | 0.018 2 | -495.45 | -489.02 | 0.044 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.999 2 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SB | 0.016 1 | -508.19 | -499.62 | 0.045 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.998 9 | |
| 大邑 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.020 1 | -482.97 | -476.54 | 0.063 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.949 0 |
| 春季 | exponnorm | 0.020 5 | -480.58 | -474.15 | 0.055 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.983 8 | |
| 夏季 | t | 0.021 5 | -474.54 | -468.11 | 0.067 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.914 8 | |
| 秋季 | Johnson SB | 0.026 2 | -446.86 | -438.29 | 0.072 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.869 8 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.030 3 | -428.50 | -419.92 | 0.072 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.871 0 | |
| 都江堰 | 年 | skewnorm | 0.027 0 | -446.00 | -439.58 | 0.062 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.950 8 |
| 春季 | skewnorm | 0.033 4 | -419.35 | -412.92 | 0.078 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.804 3 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.016 4 | -508.55 | -502.12 | 0.044 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.999 1 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.021 4 | -475.17 | -468.74 | 0.057 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.979 0 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SB | 0.027 6 | -440.19 | -431.62 | 0.066 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.924 2 | |
| 简阳 | 年 | Johnson SB | 0.019 5 | -483.89 | -475.32 | 0.064 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.941 9 |
| 春季 | genextreme | 0.025 6 | -452.52 | -446.09 | 0.066 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.922 7 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.020 9 | -478.34 | -471.91 | 0.055 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.983 1 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.021 4 | -475.52 | -469.09 | 0.058 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.975 3 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SB | 0.019 8 | -482.26 | -473.69 | 0.048 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.997 2 | |
| 金堂 | 年 | t | 0.028 3 | -440.15 | -433.72 | 0.083 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.743 8 |
| 春季 | Gamma | 0.022 1 | -471.13 | -464.70 | 0.071 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.877 0 | |
| 夏季 | Johnson SU | 0.027 2 | -442.27 | -433.70 | 0.072 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.876 0 | |
| 秋季 | genextreme | 0.028 4 | -439.69 | -433.26 | 0.073 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.863 0 | |
| 冬季 | exponnorm | 0.031 7 | -425.66 | -419.23 | 0.093 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.614 0 | |
| 彭州 | 年 | Johnson SU | 0.020 4 | -478.41 | -469.84 | 0.057 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.977 6 |
| 春季 | skewnorm | 0.023 8 | -461.74 | -455.31 | 0.056 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.980 9 | |
| 夏季 | gamma | 0.018 4 | -494.12 | -487.69 | 0.051 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.994 0 | |
| 秋季 | exponnorm | 0.022 9 | -466.82 | -460.39 | 0.075 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.844 5 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.016 5 | -504.93 | -496.36 | 0.045 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.998 8 | |
| 郫都 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.025 7 | -452.18 | -445.75 | 0.080 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.777 0 |
| 春季 | skewnorm | 0.023 1 | -465.59 | -459.16 | 0.062 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.952 2 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.024 4 | -458.80 | -452.37 | 0.059 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.970 2 | |
| 秋季 | gengamma | 0.025 6 | -449.70 | -441.12 | 0.072 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.869 9 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.023 8 | -459.07 | -450.49 | 0.062 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.951 1 | |
| 蒲江 | 年 | Johnson SB | 0.028 6 | -435.67 | -427.09 | 0.085 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.715 1 |
| 春季 | burr | 0.022 0 | -468.89 | -460.32 | 0.062 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.953 4 | |
| 夏季 | Johnson SB | 0.026 1 | -447.44 | -438.87 | 0.075 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.837 9 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.022 4 | -469.78 | -463.35 | 0.055 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.984 9 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SU | 0.025 2 | -451.67 | -443.10 | 0.054 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.987 1 | |
| 邛崃 | 年 | invgamma | 0.022 2 | -470.51 | -464.08 | 0.058 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.975 7 |
| 春季 | burr | 0.023 8 | -458.86 | -450.28 | 0.062 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.955 1 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.024 5 | -458.53 | -452.10 | 0.062 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.954 4 | |
| 秋季 | gamma | 0.015 3 | -517.59 | -511.16 | 0.056 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.982 3 | |
| 冬季 | gennorm | 0.027 9 | -441.97 | -435.54 | 0.057 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.977 6 | |
| 双流 | 年 | genextreme | 0.018 9 | -483.33 | -476.95 | 0.051 5 | 0.172 7 | 0.993 8 |
| 春季 | exponnorm | 0.021 8 | -465.58 | -459.20 | 0.060 4 | 0.172 7 | 0.967 0 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.034 6 | -408.21 | -401.83 | 0.084 8 | 0.172 7 | 0.732 4 | |
| 秋季 | genextreme | 0.022 4 | -461.83 | -455.45 | 0.057 4 | 0.172 7 | 0.979 6 | |
| 冬季 | burr | 0.017 7 | -488.42 | -479.91 | 0.048 0 | 0.172 7 | 0.997 5 | |
| 新都 | 年 | Skewnorm | 0.019 9 | -484.49 | -478.06 | 0.063 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.946 1 |
| 春季 | gamma | 0.025 5 | -453.36 | -446.93 | 0.067 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.921 0 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.022 4 | -469.66 | -463.23 | 0.073 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.864 9 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.021 1 | -477.04 | -470.61 | 0.056 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.980 7 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.025 9 | -448.03 | -439.46 | 0.079 8 | 0.171 3 | 0.787 8 | |
| 新津 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.022 6 | -468.52 | -462.09 | 0.055 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.984 3 |
| 春季 | exponnorm | 0.022 9 | -466.67 | -460.24 | 0.065 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.935 6 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.027 9 | -442.02 | -435.59 | 0.080 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.777 8 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.025 6 | -452.62 | -446.19 | 0.070 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.895 0 | |
| 冬季 | skewnorm | 0.021 1 | -477.39 | -470.96 | 0.067 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.918 4 | |
| 龙泉驿 | 年 | Skewnorm | 0.025 7 | -305.88 | -300.60 | 0.064 8 | 0.207 4 | 0.988 3 |
| 春季 | gennorm | 0.023 7 | -312.55 | -307.27 | 0.069 2 | 0.207 4 | 0.977 1 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.022 6 | -316.63 | -311.35 | 0.064 2 | 0.207 4 | 0.989 5 | |
| 秋季 | gamma | 0.033 0 | -284.25 | -278.97 | 0.087 6 | 0.207 4 | 0.867 5 | |
| 冬季 | foldnorm | 0.029 8 | -292.99 | -287.71 | 0.079 1 | 0.207 4 | 0.931 0 |
表2 成都市14个国家气象站年及四季降水序列最优概率分布函数及其检验结果
Tab.2 The optimal probability distribution functions and test results of annual and seasonal precipitation series of 14 national meteorological stations in Chengdu
| 站名 | 时间尺度 | 函数 | RMSE | AIC | BIC | D | D(0.05, n) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温江 | 年 | PearsonⅢ | 0.022 0 | -472.08 | -465.65 | 0.069 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.924 7 |
| 春季 | Johnson SU | 0.024 9 | -453.28 | -444.71 | 0.059 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.980 4 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.017 2 | -503.19 | -496.76 | 0.049 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.997 9 | |
| 秋季 | exponnorm | 0.022 7 | -467.84 | -461.41 | 0.061 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.970 7 | |
| 冬季 | skewnorm | 0.022 8 | -467.60 | -461.18 | 0.052 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.995 3 | |
| 崇州 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.018 5 | -493.43 | -487.00 | 0.060 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.962 3 |
| 春季 | gamma | 0.033 6 | -418.50 | -412.07 | 0.089 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.661 8 | |
| 夏季 | burr | 0.021 6 | -471.32 | -462.75 | 0.065 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.935 1 | |
| 秋季 | foldnorm | 0.018 2 | -495.45 | -489.02 | 0.044 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.999 2 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SB | 0.016 1 | -508.19 | -499.62 | 0.045 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.998 9 | |
| 大邑 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.020 1 | -482.97 | -476.54 | 0.063 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.949 0 |
| 春季 | exponnorm | 0.020 5 | -480.58 | -474.15 | 0.055 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.983 8 | |
| 夏季 | t | 0.021 5 | -474.54 | -468.11 | 0.067 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.914 8 | |
| 秋季 | Johnson SB | 0.026 2 | -446.86 | -438.29 | 0.072 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.869 8 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.030 3 | -428.50 | -419.92 | 0.072 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.871 0 | |
| 都江堰 | 年 | skewnorm | 0.027 0 | -446.00 | -439.58 | 0.062 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.950 8 |
| 春季 | skewnorm | 0.033 4 | -419.35 | -412.92 | 0.078 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.804 3 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.016 4 | -508.55 | -502.12 | 0.044 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.999 1 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.021 4 | -475.17 | -468.74 | 0.057 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.979 0 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SB | 0.027 6 | -440.19 | -431.62 | 0.066 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.924 2 | |
| 简阳 | 年 | Johnson SB | 0.019 5 | -483.89 | -475.32 | 0.064 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.941 9 |
| 春季 | genextreme | 0.025 6 | -452.52 | -446.09 | 0.066 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.922 7 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.020 9 | -478.34 | -471.91 | 0.055 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.983 1 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.021 4 | -475.52 | -469.09 | 0.058 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.975 3 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SB | 0.019 8 | -482.26 | -473.69 | 0.048 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.997 2 | |
| 金堂 | 年 | t | 0.028 3 | -440.15 | -433.72 | 0.083 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.743 8 |
| 春季 | Gamma | 0.022 1 | -471.13 | -464.70 | 0.071 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.877 0 | |
| 夏季 | Johnson SU | 0.027 2 | -442.27 | -433.70 | 0.072 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.876 0 | |
| 秋季 | genextreme | 0.028 4 | -439.69 | -433.26 | 0.073 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.863 0 | |
| 冬季 | exponnorm | 0.031 7 | -425.66 | -419.23 | 0.093 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.614 0 | |
| 彭州 | 年 | Johnson SU | 0.020 4 | -478.41 | -469.84 | 0.057 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.977 6 |
| 春季 | skewnorm | 0.023 8 | -461.74 | -455.31 | 0.056 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.980 9 | |
| 夏季 | gamma | 0.018 4 | -494.12 | -487.69 | 0.051 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.994 0 | |
| 秋季 | exponnorm | 0.022 9 | -466.82 | -460.39 | 0.075 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.844 5 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.016 5 | -504.93 | -496.36 | 0.045 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.998 8 | |
| 郫都 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.025 7 | -452.18 | -445.75 | 0.080 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.777 0 |
| 春季 | skewnorm | 0.023 1 | -465.59 | -459.16 | 0.062 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.952 2 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.024 4 | -458.80 | -452.37 | 0.059 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.970 2 | |
| 秋季 | gengamma | 0.025 6 | -449.70 | -441.12 | 0.072 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.869 9 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.023 8 | -459.07 | -450.49 | 0.062 9 | 0.171 3 | 0.951 1 | |
| 蒲江 | 年 | Johnson SB | 0.028 6 | -435.67 | -427.09 | 0.085 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.715 1 |
| 春季 | burr | 0.022 0 | -468.89 | -460.32 | 0.062 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.953 4 | |
| 夏季 | Johnson SB | 0.026 1 | -447.44 | -438.87 | 0.075 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.837 9 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.022 4 | -469.78 | -463.35 | 0.055 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.984 9 | |
| 冬季 | Johnson SU | 0.025 2 | -451.67 | -443.10 | 0.054 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.987 1 | |
| 邛崃 | 年 | invgamma | 0.022 2 | -470.51 | -464.08 | 0.058 0 | 0.171 3 | 0.975 7 |
| 春季 | burr | 0.023 8 | -458.86 | -450.28 | 0.062 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.955 1 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.024 5 | -458.53 | -452.10 | 0.062 3 | 0.171 3 | 0.954 4 | |
| 秋季 | gamma | 0.015 3 | -517.59 | -511.16 | 0.056 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.982 3 | |
| 冬季 | gennorm | 0.027 9 | -441.97 | -435.54 | 0.057 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.977 6 | |
| 双流 | 年 | genextreme | 0.018 9 | -483.33 | -476.95 | 0.051 5 | 0.172 7 | 0.993 8 |
| 春季 | exponnorm | 0.021 8 | -465.58 | -459.20 | 0.060 4 | 0.172 7 | 0.967 0 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.034 6 | -408.21 | -401.83 | 0.084 8 | 0.172 7 | 0.732 4 | |
| 秋季 | genextreme | 0.022 4 | -461.83 | -455.45 | 0.057 4 | 0.172 7 | 0.979 6 | |
| 冬季 | burr | 0.017 7 | -488.42 | -479.91 | 0.048 0 | 0.172 7 | 0.997 5 | |
| 新都 | 年 | Skewnorm | 0.019 9 | -484.49 | -478.06 | 0.063 7 | 0.171 3 | 0.946 1 |
| 春季 | gamma | 0.025 5 | -453.36 | -446.93 | 0.067 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.921 0 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.022 4 | -469.66 | -463.23 | 0.073 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.864 9 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.021 1 | -477.04 | -470.61 | 0.056 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.980 7 | |
| 冬季 | beta | 0.025 9 | -448.03 | -439.46 | 0.079 8 | 0.171 3 | 0.787 8 | |
| 新津 | 年 | exponnorm | 0.022 6 | -468.52 | -462.09 | 0.055 5 | 0.171 3 | 0.984 3 |
| 春季 | exponnorm | 0.022 9 | -466.67 | -460.24 | 0.065 2 | 0.171 3 | 0.935 6 | |
| 夏季 | skewnorm | 0.027 9 | -442.02 | -435.59 | 0.080 6 | 0.171 3 | 0.777 8 | |
| 秋季 | skewnorm | 0.025 6 | -452.62 | -446.19 | 0.070 1 | 0.171 3 | 0.895 0 | |
| 冬季 | skewnorm | 0.021 1 | -477.39 | -470.96 | 0.067 4 | 0.171 3 | 0.918 4 | |
| 龙泉驿 | 年 | Skewnorm | 0.025 7 | -305.88 | -300.60 | 0.064 8 | 0.207 4 | 0.988 3 |
| 春季 | gennorm | 0.023 7 | -312.55 | -307.27 | 0.069 2 | 0.207 4 | 0.977 1 | |
| 夏季 | exponnorm | 0.022 6 | -316.63 | -311.35 | 0.064 2 | 0.207 4 | 0.989 5 | |
| 秋季 | gamma | 0.033 0 | -284.25 | -278.97 | 0.087 6 | 0.207 4 | 0.867 5 | |
| 冬季 | foldnorm | 0.029 8 | -292.99 | -287.71 | 0.079 1 | 0.207 4 | 0.931 0 |

图1 1960—2022年成都市年及四季干旱站次比年际变化 (a)全年,(b)春季,(c)夏季,(d)秋季,(e)冬季
Fig.1 The inter-annual variation of drought station ratio with annual and seasonal scales in Chengdu city from 1960 to 2022 (a) annual, (b) spring, (c ) summer, (d) autumn, (e) winter

图2 1960—2022年成都市年及四季干旱强度的年际变化 (a)全年,(b)春季,(c)夏季,(d)秋季,(e)冬季
Fig.2 The inter-annual variation of drought intensity with annual and seasonal scales in Chengdu city from 1960 to 2022 (a) annual, (b) spring, (c) summer, (d) autumn, (e) winter
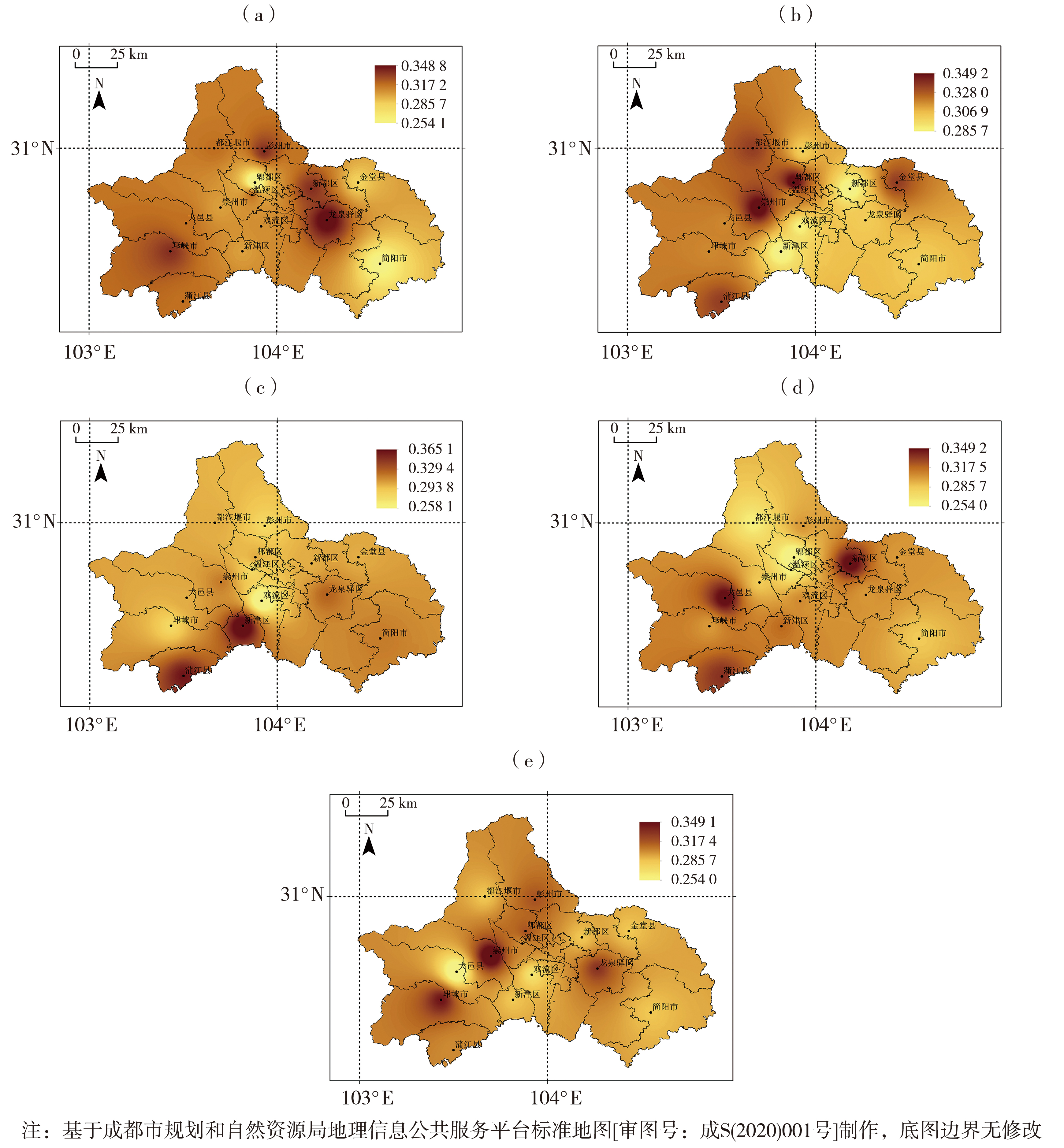
图3 1960—2022年成都市年及四季干旱频率的空间分布 (a)全年,(b)春季,(c)夏季,(d)秋季,(e)冬季
Fig.3 The inter-annual variation of drought frequency with annual and seasonal scales in Chengdu city from 1960 to 2022 (a) annual, (b) spring, (c) summer, (d) autumn, (e) winter
| 时间尺度 | 区(市、县) | 轻旱 | 中旱 | 重旱 | 特旱 | 时间尺度 | 区(市、县) | 轻旱 | 中旱 | 重旱 | 特旱 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全年 | 温江区 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 春季 | 温江区 | 15.87 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 |
| 崇州市 | 14.29 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 4.76 | 崇州市 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 大邑县 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 大邑县 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 3.17 | 4.76 | ||
| 都江堰市 | 19.05 | 6.35 | 3.17 | 3.17 | 都江堰市 | 19.05 | 4.76 | 9.52 | 0.00 | ||
| 简阳市 | 9.52 | 11.11 | 1.59 | 4.76 | 简阳市 | 12.70 | 7.94 | 9.52 | 0.00 | ||
| 金堂县 | 12.70 | 11.11 | 3.17 | 1.59 | 金堂县 | 22.22 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 4.76 | ||
| 彭州市 | 22.22 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 3.17 | 彭州市 | 15.87 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 3.17 | ||
| 郫都区 | 9.52 | 7.94 | 6.35 | 1.59 | 郫都区 | 20.63 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 3.17 | ||
| 蒲江县 | 17.46 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 蒲江县 | 12.70 | 14.29 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 邛崃市 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 1.59 | 邛崃市 | 17.46 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 1.59 | ||
| 双流区 | 14.52 | 6.45 | 8.06 | 1.61 | 双流区 | 12.90 | 11.29 | 1.61 | 3.23 | ||
| 新都区 | 17.46 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 3.17 | 新都区 | 12.70 | 11.11 | 3.17 | 1.59 | ||
| 新津区 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 8.06 | 0.00 | 新津区 | 9.52 | 12.70 | 3.17 | 3.17 | ||
| 龙泉驿区 | 16.28 | 16.28 | 0.00 | 2.33 | 龙泉驿区 | 16.28 | 11.63 | 2.33 | 0.00 | ||
| 夏季 | 温江区 | 4.29 | 3.17 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 秋季 | 温江区 | 9.52 | 9.52 | 6.35 | 1.59 |
| 崇州市 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 崇州市 | 14.29 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 3.17 | ||
| 大邑县 | 14.29 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 0.00 | 大邑县 | 17.46 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 都江堰市 | 12.70 | 12.70 | 1.59 | 3.17 | 都江堰市 | 11.11 | 9.52 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 简阳市 | 19.05 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 简阳市 | 11.11 | 7.94 | 7.94 | 1.59 | ||
| 金堂县 | 17.46 | 1.59 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 金堂县 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 7.94 | 0.00 | ||
| 彭州市 | 12.70 | 7.94 | 6.35 | 1.59 | 彭州市 | 15.87 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 1.59 | ||
| 郫都区 | 9.52 | 17.46 | 1.59 | 1.59 | 郫都区 | 7.94 | 6.35 | 9.52 | 1.59 | ||
| 蒲江县 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 蒲江县 | 20.63 | 6.35 | 1.59 | 4.76 | ||
| 邛崃市 | 7.94 | 14.29 | 3.17 | 3.17 | 邛崃市 | 15.87 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 3.17 | ||
| 双流区 | 9.68 | 6.45 | 8.06 | 1.61 | 双流区 | 14.52 | 6.45 | 9.68 | 0.00 | ||
| 新都区 | 14.29 | 11.11 | 1.59 | 3.17 | 新都区 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 | ||
| 新津区 | 19.05 | 14.29 | 1.59 | 1.59 | 新津区 | 19.05 | 3.17 | 9.52 | 0.00 | ||
| 龙泉驿区 | 18.60 | 6.98 | 2.33 | 4.65 | 龙泉驿区 | 13.95 | 6.98 | 6.98 | 2.33 | ||
| 冬季 | 温江区 | 12.70 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||||||
| 崇州市 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 | |||||||
| 大邑县 | 12.70 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 都江堰市 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 简阳市 | 12.70 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 | |||||||
| 金堂县 | 4.76 | 19.05 | 4.76 | 0.00 | |||||||
| 彭州市 | 14.29 | 12.70 | 3.17 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 郫都区 | 11.11 | 14.29 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 蒲江县 | 12.70 | 9.52 | 6.35 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 邛崃市 | 15.87 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 双流区 | 12.90 | 8.06 | 4.84 | 1.61 | |||||||
| 新都区 | 11.11 | 12.70 | 3.17 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 新津区 | 14.29 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 3.17 | |||||||
| 龙泉驿区 | 13.95 | 13.95 | 2.33 | 2.33 |
表3 1960—2022年成都市全年及不同季节不同地区不同等级干旱频率
Tab.3 The frequency of different grades of drought in different regions in Chengdu city in the whole year and different seasons from 1960 to 2022 单位:%
| 时间尺度 | 区(市、县) | 轻旱 | 中旱 | 重旱 | 特旱 | 时间尺度 | 区(市、县) | 轻旱 | 中旱 | 重旱 | 特旱 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全年 | 温江区 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 春季 | 温江区 | 15.87 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 |
| 崇州市 | 14.29 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 4.76 | 崇州市 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 大邑县 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 大邑县 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 3.17 | 4.76 | ||
| 都江堰市 | 19.05 | 6.35 | 3.17 | 3.17 | 都江堰市 | 19.05 | 4.76 | 9.52 | 0.00 | ||
| 简阳市 | 9.52 | 11.11 | 1.59 | 4.76 | 简阳市 | 12.70 | 7.94 | 9.52 | 0.00 | ||
| 金堂县 | 12.70 | 11.11 | 3.17 | 1.59 | 金堂县 | 22.22 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 4.76 | ||
| 彭州市 | 22.22 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 3.17 | 彭州市 | 15.87 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 3.17 | ||
| 郫都区 | 9.52 | 7.94 | 6.35 | 1.59 | 郫都区 | 20.63 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 3.17 | ||
| 蒲江县 | 17.46 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 蒲江县 | 12.70 | 14.29 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 邛崃市 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 1.59 | 邛崃市 | 17.46 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 1.59 | ||
| 双流区 | 14.52 | 6.45 | 8.06 | 1.61 | 双流区 | 12.90 | 11.29 | 1.61 | 3.23 | ||
| 新都区 | 17.46 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 3.17 | 新都区 | 12.70 | 11.11 | 3.17 | 1.59 | ||
| 新津区 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 8.06 | 0.00 | 新津区 | 9.52 | 12.70 | 3.17 | 3.17 | ||
| 龙泉驿区 | 16.28 | 16.28 | 0.00 | 2.33 | 龙泉驿区 | 16.28 | 11.63 | 2.33 | 0.00 | ||
| 夏季 | 温江区 | 4.29 | 3.17 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 秋季 | 温江区 | 9.52 | 9.52 | 6.35 | 1.59 |
| 崇州市 | 15.87 | 7.94 | 4.76 | 3.17 | 崇州市 | 14.29 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 3.17 | ||
| 大邑县 | 14.29 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 0.00 | 大邑县 | 17.46 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 都江堰市 | 12.70 | 12.70 | 1.59 | 3.17 | 都江堰市 | 11.11 | 9.52 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||
| 简阳市 | 19.05 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 简阳市 | 11.11 | 7.94 | 7.94 | 1.59 | ||
| 金堂县 | 17.46 | 1.59 | 9.52 | 1.59 | 金堂县 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 7.94 | 0.00 | ||
| 彭州市 | 12.70 | 7.94 | 6.35 | 1.59 | 彭州市 | 15.87 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 1.59 | ||
| 郫都区 | 9.52 | 17.46 | 1.59 | 1.59 | 郫都区 | 7.94 | 6.35 | 9.52 | 1.59 | ||
| 蒲江县 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 4.76 | 1.59 | 蒲江县 | 20.63 | 6.35 | 1.59 | 4.76 | ||
| 邛崃市 | 7.94 | 14.29 | 3.17 | 3.17 | 邛崃市 | 15.87 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 3.17 | ||
| 双流区 | 9.68 | 6.45 | 8.06 | 1.61 | 双流区 | 14.52 | 6.45 | 9.68 | 0.00 | ||
| 新都区 | 14.29 | 11.11 | 1.59 | 3.17 | 新都区 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 | ||
| 新津区 | 19.05 | 14.29 | 1.59 | 1.59 | 新津区 | 19.05 | 3.17 | 9.52 | 0.00 | ||
| 龙泉驿区 | 18.60 | 6.98 | 2.33 | 4.65 | 龙泉驿区 | 13.95 | 6.98 | 6.98 | 2.33 | ||
| 冬季 | 温江区 | 12.70 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | ||||||
| 崇州市 | 19.05 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 | |||||||
| 大邑县 | 12.70 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 都江堰市 | 11.11 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 简阳市 | 12.70 | 9.52 | 3.17 | 3.17 | |||||||
| 金堂县 | 4.76 | 19.05 | 4.76 | 0.00 | |||||||
| 彭州市 | 14.29 | 12.70 | 3.17 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 郫都区 | 11.11 | 14.29 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 蒲江县 | 12.70 | 9.52 | 6.35 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 邛崃市 | 15.87 | 11.11 | 4.76 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 双流区 | 12.90 | 8.06 | 4.84 | 1.61 | |||||||
| 新都区 | 11.11 | 12.70 | 3.17 | 1.59 | |||||||
| 新津区 | 14.29 | 6.35 | 4.76 | 3.17 | |||||||
| 龙泉驿区 | 13.95 | 13.95 | 2.33 | 2.33 |
| [1] | 阿帕尔·肉孜, 阿吉古丽·沙依提, 叶尔克江·霍依哈孜, 等, 2024. 基于SPI的1961—2020年昌吉地区作物生长季气象干旱时空特征研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(2): 163-168. |
| [2] |
蔡怡亨, 李帅, 张强, 等, 2023. 1997—2021年四川省干旱时空变化特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 241-250.
DOI |
| [3] | 高婧, 井立红, 李海燕, 等, 2024. 近60 a新疆塔城地区降水及气象干旱变化特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(1): 134-142. |
| [4] | 郭冬, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 吴秀兰, 等, 2022. 四种气象干旱指数在新疆区域适用性研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(3): 90-101. |
| [5] | 郭嘉豪, 王会肖, 赵茹欣, 等, 2020. 基于最优拟合函数的SPI指数的松嫩平原干旱特征分析[J]. 北京师范大学学报:自然科学版, 56(2): 240-249. |
| [6] | 国家气候中心, 中国气象局预报与网络司, 中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 2017. 气象干旱等级: GB/T20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [7] | 贺晋云, 张明军, 王鹏, 等, 2011. 近50年西南地区极端干旱气候变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 66(9): 1 179-1 190 |
| [8] | 洪兴骏, 郭生练, 周妍来, 2013. 标准化降水指数SPI分布函数的适用性研究[J]. 水资源研究, 2: 33-41. |
| [9] | 胡国华, 李滔, 盛丰, 等, 2020. 基于降水量距平百分率的湘江流域干旱时空特征研究[J]. 长沙理工大学学报:自然科学版, 17(1): 74-82. |
| [10] | 黄瑶, 何军, 甘薇薇, 等, 2023. 基于SPI的金沙江下游气象干旱时空分布特征及预测方法[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(2): 81-89. |
| [11] | 李雪纯, 赵君, 徐进超, 2018. 基于降水距平百分率的安徽省近50a干旱时空分布特征分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电(9): 133-136. |
| [12] | 芦佳玉, 延军平, 李英杰, 2018. 基于SPEI及游程理论的云贵地区1960—2014年干旱时空变化特征[J]. 浙江大学学报: 理学版, 45(3): 363-372. |
| [13] | 潘妮, 卫仁娟, 詹存, 等, 2017. 干旱指数在四川省的适用性分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 15(4): 71-78. |
| [14] | 任至涵, 倪长健, 陈云强, 等, 2022. 基于Copula函数的成都夏季O3污染潜势模型[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(9): 4 009-4 017 |
| [15] | 商守卫, 王银堂, 崔婷婷, 等, 2022. 基于标准化降水指数的成都市气象干旱演变特征[J]. 水电能源科学, 40(12): 26-29. |
| [16] | 粟晓玲, 褚江东, 张特, 等, 2022. 西北地区地下水干旱时空演变趋势及对气象干旱的动态响应[J]. 水资源保护, 38(1): 34-42. |
| [17] |
孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等, 2022. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 764-770.
DOI |
| [18] | 王劲松, 李耀辉, 王润元, 等, 2012. 我国气象干旱研究进展评述[J]. 干旱气象, 30(4): 497-508. |
| [19] | 王理萍, 王树仿, 王新华, 等, 2017. 五种干旱指数在云南省的适用性分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 36(7): 117-124. |
| [20] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [21] | 吴绍飞, 张翔, 王俊钗, 等, 2016. 基于站点降雨量最优拟合函数的SPI指数计算[J]. 干旱区地理, 39(3): 555-564. |
| [22] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [23] | 杨睿, 耿广坡, 周洪奎, 等, 2021. 基于SPEI_PM指数的渭河流域气象干旱时空演变特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 42(11): 962-974. |
| [24] | 余兴湛, 蒲义良, 康伯乾, 2022. 基于SPEI的广东省近50 a干旱时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 051-1 058 |
| [25] | 张更喜, 粟晓玲, 刘文斐, 2021. 考虑CO2浓度影响的中国未来干旱趋势变化[J]. 农业工程学报, 37(1): 84-91. |
| [26] |
张金丹, 刘明春, 李兴宇, 等, 2023. 石羊河流域干湿气候变化特征及对NDVI的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5): 697-704.
DOI |
| [27] | 张强, 潘学标, 马柱国, 等, 2009. 干旱[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [28] | 张玮煊, 刁鹏, 巴音才次克, 等, 2023. 基于SPEI的开都河流域干旱时空演变特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(6): 102-110. |
| [29] | JI Z H, LIU X Q, 2019. Comparative analysis of PM2.5 pollution risk in China using three-dimensional Archimedean copula method[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 10(1): 2 368-2 386 |
| [30] | WU H, SVOBODA M D, HAYES M J, et al, 2007. Appropriate application of the standardized precipitation index in arid locations and dry seasons[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 27(1): 65-79. |
| [1] | 张玉翠, 谭江红, 闫彩霞. 湖北省区域性高温、干旱及其复合事件变化特征及危险性评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 825-835. |
| [2] | 杨晓玲, 孙旭映, 杨金虎, 吴雯, 赵慧华, 陈静. 石羊河流域复合高温干旱事件的识别及其演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 836-843. |
| [3] | 谢子扬, 李长顺, 蔡嘉仪, 王珊珊. 1988—2023年气候变化与土壤墒情关系研究的文献计量分析与可视化[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 953-964. |
| [4] | 王雅君, 罗菊英, 程烈海, 李伟. 基于机器学习的湖北省夏季干旱预测模型构建与检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 661-670. |
| [5] | 王玥彤, 何东坡, 李忠燕, 王烁, 陈早阳. 贵州省两次气象干旱对比分析及基于机器学习的干旱预测模型建立[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 671-682. |
| [6] | 苏宏梅, 张楠, 冉新民, 康超. 干旱半干旱区中小流域洪水机器学习预警模型及其应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 683-693. |
| [7] | 陈逸骁, 岳思妤, 夏雯雯. 中国干旱灾害的时空变化及其与直接经济损失的关联性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 485-497. |
| [8] | 穆佳, 吴迪, 刘洋, 王冬妮, 任景全. 吉林省玉米干旱风险对产量的影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 498-506. |
| [9] | 颜鹏程, 李忆平, 曾鼎文, 王丽娟, 张金玉, 陆晓娟, 岳平, 靳洁. 2024年4—6月我国区域性高温干旱特征及其影响因子[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 507-518. |
| [10] | 李春华, 朱飙, 杨金虎, 黄鹏程. 我国干旱半干旱区近60 a气象干旱气候特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 519-526. |
| [11] | 李源源, 赵霞, 岳靓, 邱阳. 干旱胁迫下植物根系分泌物与根际微生物相互作用的研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 325-337. |
| [12] | 田国珍, 任玉欢, 杨茜, 黄小燕, 赵斯楠, 左小瑞, 李智才. 三种遥感干旱监测指数在黄土高原东部的适用性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 338-346. |
| [13] | 朱占云, 张露萱, 李福刚, 张珏, 张玮玮, 李强. 新安江流域气象干旱和水文干旱特征及两者之间的关系研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 157-165. |
| [14] | 刘兴忠, 胡春, 何超, 何国平, 马骁, 姜绪彬. 基于NDVI-LST模型的四川攀西地区近20 a干旱演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 180-186. |
| [15] | 刘文英, 孙素琴, 朱星球, 欧阳欣欣. 江西省区域性高温和干旱过程分析与评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 187-196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
